Important Points
To make a professional calculation of the level of illumination and the number of required lumens, it is imperative to take into account the following points:
- lamp type;
- the height at which the lighting device will be placed;
- lamp type;
- its location in the room relative to the vertical plane. Here it is necessary to evaluate the efficiency of the lighting device;
- reflective characteristics of the material used for the interior decoration of the room: walls, floor and ceiling.
When determining the reflectivity of walls, ceilings and floors, it must be remembered that the brighter the room is, the higher the amount of light reflection will be:
- if the ceiling and walls are made in light colors, then the light reflection coefficient will be approximately 0.7;
- when decorating a room with light, beige and light gray facade paints, this coefficient will be approximately 0.5-0.6;
- for dark colors - 0.3;
- when decorating a room with black granite or marbles, the reflection coefficient will be approximately 0.1.
To calculate the optical characteristics of the room, the efficiency parameter and special unified tables are used.
They will be able to quickly make the necessary calculations, eliminating possible errors or errors.
Correction depending on the mode of the heating system
Manufacturers in the passport data indicate the maximum power of radiators: in high-temperature mode of use - the temperature of the coolant in the supply is 90 ° C, in the return - 70 ° C (indicated by 90/70) in the room, it should be 20 ° C. But in this mode, modern systems heating rarely works. Typically, a medium power mode of 75/65/20 or even a low temperature mode with parameters of 55/45/20 is used. It is clear that the calculation needs to be corrected.
To take into account the mode of operation of the system, it is necessary to determine the temperature difference of the system. The temperature difference is the difference between the temperature of the air and the heaters. In this case, the temperature of the heating devices is considered as the arithmetic mean between the supply and return values.
It is necessary to take into account the features of the premises and climate in order to correctly calculate the number of radiator sections
To make it clearer, we will calculate cast-iron heating radiators for two modes: high-temperature and low-temperature, sections of a standard size (50cm). The room is the same: 16m 2. One cast-iron section in the high-temperature mode 90/70/20 heats 1.5m 2. Therefore, we need 16m 2 / 1.5m 2 \u003d 10.6 pieces. Rounding - 11 pcs. The system is planned to use low-temperature mode 55/45/20. Now we find the temperature difference for each of the systems:
- high temperature 90/70/20- (90+70)/2-20=60 o C;
- low-temperature 55/45/20 - (55 + 45) / 2-20 \u003d 30 ° C.
That is, if the low-temperature mode of operation is used, twice as many sections will be needed to provide the room with heat. For our example, a room of 16m 2 requires 22 sections of cast iron radiators. The battery is big. This, by the way, is one of the reasons why this type of heating device is not recommended for use in networks with low temperatures.
In this calculation, the desired air temperature can also be taken into account. If you want the room to be not 20 ° C but, for example, 25 ° C, simply calculate the heat head for this case and find the desired coefficient
Let's do the calculation for the same cast-iron radiators: the parameters will be 90/70/25. We consider the temperature difference for this case (90 + 70) / 2-25 \u003d 55 ° C. Now we find the ratio 60 ° C / 55 ° C \u003d 1.1. To ensure a temperature of 25 ° C, you need 11pcs * 1.1 \u003d 12.1pcs.
How much light is needed to illuminate the apartment
Light plays a huge role in our life, it makes it possible not only to see, but also to evaluate the colors and shapes of surrounding objects. The efficiency of work, as well as our psychological state, depends on the correct illumination of the room. Poor lighting leads to the fact that the eyes begin to tire quickly.
For human eyes, natural light is most comfortable, but at night you have to make do with artificial light sources.
How much light is needed to illuminate a room? Every time we start repairs in an apartment, we all face the question “How to calculate the number of light bulbs needed to create comfortable lighting?” Experts have long studied this issue and developed appropriate standards for various types of premises. All of them are summarized in a document called DBN "Natural and piece lighting" (in Ukraine) and SNiP "Natural and artificial lighting" (in Russia). Building codes determine the comfortable level of illumination for a person, and for different rooms these values \u200b\u200bwill differ.
To determine the illumination of a room, units such as lux and lumens are used, but for the most part, people are used to distinguishing lamps by their power, which is measured in watts.
But it must be taken into account that with the same power, the luminous fluxes from lamps of different types will differ.
However, we will not dive deep into science, since specialists should be involved in the calculation of illumination, but consider a simplified method that ordinary buyers can use when choosing a lighting device. Using the table below, you can estimate how many watts you need per square meter of an apartment with a height ceiling up to 3 meters.
See also: types of LED lamps
|
Application |
Lamp type |
Pressure per square meter (W/m2) |
|
Admission, de vicoration is dimmed light (100-150 lux). Application example - Bedroom. |
roasting lamp |
10-12 |
|
Halogen lamp |
6-8 |
|
|
Fluorescent lamp |
2,5-3 |
|
|
Light one lamp |
1,5-2 |
|
|
Placement with an average level of illumination (150-200 lux). Application example - Sanvuzol, corridor, kitchen. |
roasting lamp |
15-18 |
|
Halogen lamp |
10-12 |
|
|
Fluorescent lamp |
3,5-4,5 |
|
|
Light one lamp |
2-3 |
|
|
Application with bright lighting (200-250 lux). The butt of the application is Vitalnya, a working office, a child of the room. |
roasting lamp |
20 |
|
Halogen lamp |
13 |
|
|
Fluorescent lamp |
5-5,7 |
|
|
Light one lamp |
2,5-3,5 |
To get an idea of how many lamps are needed to illuminate a room, it is necessary to multiply the area of the room (in square meters) by the power value (W / m2) from the line of the table. Calculation example:
It is necessary to light a children's room with an area of 30 square meters and a ceiling height of 2.8 meters.
The first thing you need to calculate is to decide on the light source that we will use. Suppose you decide to use fluorescent lamps (which are also popularly called "housekeepers"). Then we take the total illumination per square meter from the table as 5.2 W / m2, and multiply this value by the area of \u200b\u200bthe room: 30x5.2 \u003d 156 W. It turns out that the total illumination should be approximately the same as that provided by lamps that consume a total of 156 watts.
That is, you need to buy a lamp (or several lamps) in which 10 fluorescent lamps with a power of 15 W are installed, or 7-8 lamps of 20 W each.
In the same way, you can calculate the required number of halogen or LED lamps.
If the ceiling height in the room is more than 3 meters, the total number of required W / m2 must be multiplied by at least 1.5. And if the walls of the apartment are dark in color, it is also recommended to take the number of lamps with a margin.
It should be noted that the table shows the illumination standards for the room as a whole. In some cases, it is required to calculate special local lighting, for example, "working area", etc.
Rooms with standard ceiling heights
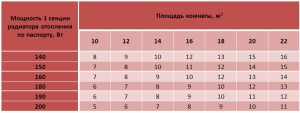
The calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators for a typical house is based on the area of the rooms.The area of a room in a typical building is calculated by multiplying the length of the room by its width. To heat 1 square meter, 100 watts of heater power is required, and to calculate the total power, you need to multiply the resulting area by 100 watts. The value obtained means the total power of the heater. The documentation for the radiator usually indicates the thermal power of one section. To determine the number of sections, you need to divide the total capacity by this value and round the result up.
A room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with the usual height of the ceilings. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. Find the number of sections.
- We determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe room by multiplying its length by its width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the total power of heating devices 14 100 \u003d 1400 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1400/160 = 8.75. Round up to a higher value and get 9 sections.
You can also use the table:
Table for calculating the number of radiators per M2
For rooms located at the end of the building, the estimated number of radiators must be increased by 20%.
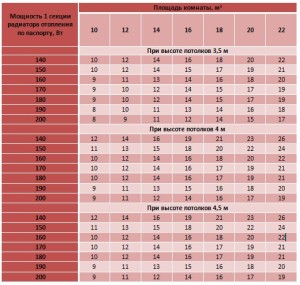
Rooms with a ceiling height of more than 3 meters
The calculation of the number of sections of heaters for rooms with a ceiling height of more than three meters is based on the volume of the room. Volume is the area multiplied by the height of the ceilings. To heat 1 cubic meter of a room, 40 watts of heat output of the heater is required, and its total power is calculated by multiplying the volume of the room by 40 watts. To determine the number of sections, this value must be divided by the power of one section according to the passport.
A room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with a ceiling height of 3.5 m. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. It is necessary to find the number of sections of heating radiators.
- We find the area of the room by multiplying its length by the width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the volume of the room by multiplying the area by the height of the ceilings: 14 3.5 \u003d 49 m 3.
- We find the total power of the heating radiator: 49 40 \u003d 1960 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1960/160 = 12.25. Round up and get 13 sections.
You can also use the table:
As in the previous case, for a corner room, this figure must be multiplied by 1.2. It is also necessary to increase the number of sections if the room has one of the following factors:
- Located in a panel or poorly insulated house;
- Located on the first or last floor;
- Has more than one window;
- Located next to unheated premises.
In this case, the resulting value must be multiplied by a factor of 1.1 for each of the factors.
Corner room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with a ceiling height of 3.5 m. Located in a panel house, on the ground floor, has two windows. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. It is necessary to find the number of sections of heating radiators.
- We find the area of the room by multiplying its length by the width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the volume of the room by multiplying the area by the height of the ceilings: 14 3.5 \u003d 49 m 3.
- We find the total power of the heating radiator: 49 40 \u003d 1960 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1960/160 = 12.25. Round up and get 13 sections.
- We multiply the resulting amount by the coefficients:
Corner room - coefficient 1.2;
Panel house - coefficient 1.1;
Two windows - coefficient 1.1;
First floor - coefficient 1.1.
Thus, we get: 13 1.2 1.1 1.1 1.1 = 20.76 sections. We round them up to a larger integer - 21 sections of heating radiators.
When calculating, it should be borne in mind that different types of heating radiators have different thermal output. When choosing the number of heating radiator sections, it is necessary to use exactly those values that correspond to the selected type of batteries.
In order for the heat transfer from the radiators to be maximum, it is necessary to install them in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations, observing all the distances specified in the passport. This contributes to a better distribution of convective currents and reduces heat loss.
- Consumption of diesel heating boiler
- Bimetal heating radiators
- How to calculate heat for home heating
- Calculation of reinforcement for the foundation
Convert watts to lumens
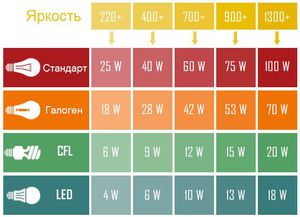
Incandescent lamps have taught consumers that the more watts, the better the lamp shines. But not everyone knows that there are more reliable and economical light sources that give the same illumination as an incandescent lamp. The table shows the approximate figures needed when calculating how many watts per square meter of lighting are needed:
The table clearly shows the difference in energy consumption between different types of lamps. However, you should not assume that the parameters given in it are very accurate. Here are only approximate characteristics of lighting fixtures that can be used when calculating how many lumens per square meter are needed.
The norms adopted in Russia were adopted quite a long time ago, and the calculation made according to them does not satisfy the modern quality of life. Many people complain that their apartments and houses are not well lit. For such consumers, when calculating how many lumens are needed per square meter, it is recommended to increase all indicators by 1.5 times.
There is also a need to install several switches in the same room that activate different lighting fixtures. A person, having such a system, can adjust the level of illumination from soft and relaxing to bright working.
Creating favorable conditions for normal rest in the house requires taking into account all possible parameters and nuances. Particular attention should be paid to the level of illumination. After all, it is on this parameter that the general health of a person, his emotional and psychological comfort depends.
Therefore, it is very important to calculate how many lumens of lighting per square meter are needed? You will learn about this and about what level of illumination you need to create from our article.
Recommendations for stretch ceiling lighting
Features of the material impose certain restrictions on the devices used. PVC film melts when the temperature rises to 60-70°C, fabric - about 80°C.
Therefore, incandescent lamps with a stretch ceiling are poorly combined. You can take only low-power - up to 40 watts. And for halogen, the restrictions are even stricter - no higher than 35 watts.
With stretch fabrics, it is recommended to use LED or energy-saving lamps that do not heat up during operation. Of these, the first type is preferable, they are more durable and consume less electricity. Energy-saving lamps are effective only when they are constantly on, they consume a lot of electricity during switching on and do not immediately flare up to full power.
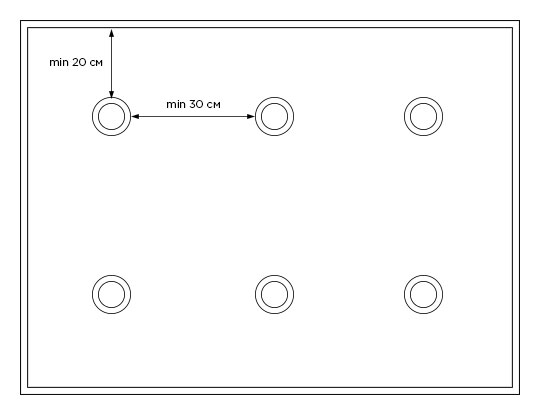
Ceiling lights are distributed over the surface evenly or in groups, highlighting certain areas. When drawing up the layout, take into account the minimum distances:
- from the edge of the canvas should be at least 20 cm;
- from the seam (if the film is soldered) - 15 cm;
- between adjacent devices - 30 cm.
The luminaires are not attached to a thin canvas, but to the ceiling through embedded platforms that are mounted in advance. Therefore, it is necessary to choose models, calculate the number of devices and develop a diagram of their location before installing a stretch ceiling.
Accounting for the reflection coefficient of surfaces
Finishing materials absorb light differently, the degree of reflection depends on the color and texture of the surface.This property affects the overall level of illumination of the room, therefore, after calculations, adjustments are made.
Surfaces have a certain reflectance, which is roughly divided into five groups:
- 70% is white.
- 50% - other light colors.
- 30% - gray.
- 10% - dark colors.
- 0% - black.
Usually, finishing materials of different colors are chosen (flooring, wallpaper, stretch fabric). To simplify the calculations, first find the average reflection coefficient. To do this, add up the numbers that characterize the walls, floor and ceiling, and then divide by 3.
For example, in the room there is a white stretch fabric, pale wallpaper on the walls and parquet of medium darkness. We calculate:
70% + 50% + 30% = 150%
150% / 3 = 50%, or 0.5.
In further calculations, the value of the luminous flux for the light bulb is multiplied by 0.5. For example, if you choose LED-devices with a nominal indicator of 560 lumens, you need to substitute 280 Lm into the formula.

Calculation of illumination of premises - norms, examples. Electrosteam
- Lamps
- LED lamp
- with socket E27
- with socket E14
- with GU5.3 base
- T8 with G13 base
- with GU10 base
- with G4 base
- with G9 base
- with plinth s14s / s14d
- with plinth GX53
- with GU4 base
- with base G53
- with plinth G24d/G24q
- Fluorescent lamps
- T8 linear fluorescent lamps with G13 base
- T5 with G5 base
- T4 with G5 base
- Ring
- T2 linear lamps with W4.3 x 8.5d base
- T12 Linear Fluorescent Lamps
- Energy-saving lamps
- with socket E27
- with socket E14
- with base E40
- with plinth GX53
- with GU5.3 base
- with GU10 base
- with base R7S
- Halogen lamps
- with base GU5.3 (MR16)
- with base G9/GY4
- with plinth GU10/GZ10
- with base R7s/Fa4
- with base G4/ GY6.35
- with base E14, E27
- with socket GU4 (MR11) 12V
- with socket G53
- with plinth B15d/BA15d
- with base G8.5
- Incandescent lamps
- Incandescent lamps with socket E27
- Glow lamp candle E14/E27
- Incandescent ball
- Reflector lamps
- Retro incandescent lamps
- Linear incandescent lamp
- Light bulbs for refrigerators, ovens, cooker hoods
- Special Lamps
- For plants
- UV lamps
- germicidal lamps
- infrared
- For aquariums
- Insect lamps
- For food
- Metal halide lamps
- with socket E27
- with E40 base
- with Rx7s base
- with base G8.5
- with base GX8.5
- with plinth GX10
- with base G12
- with base Fc2
- with PGj5 base
- with plinth K12S
- with GU6.5 base
- HPS sodium lamps
- with socket E27
- LED lamp
Heat transfer coefficient for different materials
Heat transfer in materials with a high heat transfer coefficient occurs more intensively than in materials with a low coefficient. The value of the coefficient depends on the properties of the material, its temperature, the area that transfers heat, and other conditions.
A window air conditioner is a good example of a device that has very efficient heat exchangers installed. When cooled, they use the process of changing the state of aggregation of matter. When the liquid turns into a gas, it consumes a large amount of heat and draws that heat from the room, thus cooling it.
The heat transfer coefficient also depends on the amount of deposits, deposits and sedimentary materials on the surface - usually outside and inside the heat exchanger tubes. This can either be just contamination, in the case of plaque, or fouling - in case of biological fouling of the object by microorganisms or mollusks. Plaque is usually formed due to corrosion, or when a deposit dissolved in the liquid settles on the surface of the heat exchangers. Sometimes these impurities in the liquid are due to its contamination, and sometimes they are part of the liquid, for example, they can be salts dissolved in water.
The parts of the heat exchanger, which are supposed to conduct heat well or, conversely, poorly, are made of materials that are usually selected for their thermal conductivity. In some cases, thermal conductivity is not the most important criterion by which these materials are selected. Sometimes the price and ease of manufacturing parts from a particular material play a big role in the choice.So, for example, despite the fact that aluminum has a lower thermal conductivity than copper, radiators in cars are now mainly made of aluminum, due to its low price. This was not always the case - earlier radiators were made of copper, and now such radiators can still be ordered from some manufacturers.
Condensing heat exchanger of a window air conditioner. The condenser is cooled by a fan, while the gaseous refrigerant inside condenses and turns into a liquid. In this case, heat exchange occurs with the environment, into which heat is released from the room.
In addition to the price, the inconvenience in using copper is also that products made from it are heavier than products made from aluminum. This is important, for example, for racing cars. When deciding what to make a radiator from, it is worth weighing all the advantages of aluminum and copper, and not based only on their thermal conductivity.
Calculation of sections of aluminum radiators per square meter
As a rule, manufacturers pre-calculated the power standards of aluminum batteries. which depend on parameters such as ceiling height and room area. So it is believed that in order to heat 1 m2 of a room with a ceiling up to 3 m in height, a thermal power of 100 watts will be required.
These figures are approximate, since the calculation of aluminum heating radiators by area in this case does not provide for possible heat loss in the room or higher or lower ceilings. These are generally accepted building codes that manufacturers indicate in the data sheet of their products.
Of considerable importance is the parameter of the thermal power of one radiator fin. For an aluminum heater, it is 180-190 W
The media temperature must also be taken into account. It can be found in the thermal management, if the heating is centralized, or measured independently in an autonomous system. For aluminum batteries, the indicator is 100-130 degrees. Dividing the temperature by the heat output of the radiator, it turns out that 0.55 sections are required to heat 1 m2.
In the event that the height of the ceilings has "outgrown" the classical standards, then a special coefficient must be applied: if the ceiling is 3 m, then the parameters are multiplied by 1.05; at a height of 3.5 m, it is 1.1; with an indicator of 4 m - this is 1.15; wall height 4.5 m - the coefficient is 1.2. You can use the table that manufacturers provide for their products.
How many aluminum radiator sections do you need?
The calculation of the number of sections of an aluminum radiator is made in a form suitable for heaters of any type:
- S is the area of the room where the installation of the battery is required;
- k - correction factor of the indicator 100 W / m2, depending on the height of the ceiling;
- P is the power of one radiator element.
When calculating the number of sections of aluminum heating radiators, it turns out that in a room of 20 m2 with a ceiling height of 2.7 m, an aluminum radiator with a power of one section of 0.138 kW will require 14 sections.
Q = 20 x 100 / 0.138 = 14.49
In this example, the coefficient is not applied, since the ceiling height is less than 3 m
But even such sections of aluminum heating radiators will not be correct, since possible heat losses of the room are not taken into account. It should be borne in mind that depending on how many windows there are in the room, whether it is a corner room and whether it has a balcony: all this indicates the number of sources of heat loss
When calculating aluminum radiators by the area of the room, the percentage of heat loss should be taken into account in the formula, depending on where they will be installed:
- if they are fixed under the windowsill, then the losses will be up to 4%;
- installation in a niche instantly increases this figure to 7%;
- if an aluminum radiator is covered for beauty on one side with a screen, then the losses will be up to 7-8%;
- completely closed by the screen, it will lose up to 25%, which makes it, in principle, unprofitable.
These are not all indicators that should be considered when installing aluminum batteries.
Norms of illumination of residential premises
It is important to maintain an optimal level of illumination. In a dark room, you have to strain your eyes a lot, which is unpleasant and harmful to your eyesight.
But too bright light bulbs are also not comfortable and not useful.
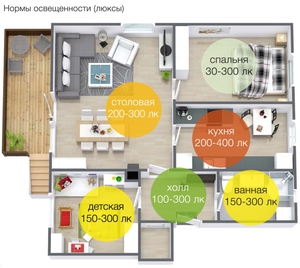
The level of illumination in a room can be measured and evaluated. The standard unit for this is lux (Lx). State standards for illumination have been developed for various zones and premises, including residential ones. According to SP 52.13330.2011 and SNiP 23-05-95 for apartments and private houses, the standards are as follows (in Lux per 1 sq m):
- The highest rates are in offices and utility rooms - 300.
- Children should also have light, but the level is reduced to 200.
- In the rest of the living rooms, in the kitchen, in the living room and in the bedroom, an average level of 150 is required.
- In dressing rooms, dimmer light is enough - 75.
- In corridors, hallways, toilets and bathrooms - 50.

Thermal power of 1 section
As a rule, manufacturers indicate average heat transfer rates in the technical characteristics of heaters. So for heaters made of aluminum, it is 1.9-2.0 m2. To calculate how many sections you need, you need to divide the area of \u200b\u200bthe room by this coefficient.
For example, for the same room of 16 m2, 8 sections will be required, since 16 / 2 = 8.
These calculations are approximate and it is impossible to use them without taking into account heat losses and real conditions for placing the battery, since you can get a cold room after installing the structure.
To get the most accurate figures, you will have to calculate the amount of heat that is needed to heat a particular living area. To do this, many correction factors will have to be taken into account. This approach is especially important when it is required to calculate aluminum heating radiators for a private house.
The formula needed for this is as follows:
KT = 100W/m2 x S x K1 x K2 x K3 x K4 x K5 x K6 x K7
- CT is the amount of heat that a given room requires.
- S is the area.
- K1 - coefficient designation for a glazed window. For standard double glazing it is 1.27, for double glazing it is 1.0, and for triple glazing it is 0.85.
- K2 is the coefficient of the level of wall insulation. For an uninsulated panel, it = 1.27, for a brick wall with one layer of masonry = 1.0, and for two bricks = 0.85.
-
K3 is the ratio of the area occupied by the window and the floor. When between them:
- 50% - the coefficient is 1.2;
- 40% — 1.1;
- 30% — 1.0;
- 20% — 0.9;
- 10% — 0.8.
-
K4 is a coefficient that takes into account the air temperature according to SNiP on the coldest days of the year:
- +35 = 1.5;
- +25 = 1.2;
- +20 = 1.1;
- +15 = 0.9;
- +10 = 0.7.
-
K5 indicates an adjustment in the presence of external walls. For example:
- when it is alone, the indicator is 1.1;
- two outer walls - 1.2;
- 3 walls - 1.3;
- all four walls - 1.4.
-
K6 takes into account the presence of a room above the room for which calculations are made. If available:
- unheated attic - coefficient 1.0;
- heated attic - 0.9;
- living room - 0.8.
-
K7 is a coefficient that indicates the height of the ceiling in the room:
- 2.5 m = 1.0;
- 3.0 m = 1.05;
- 3.5 m = 1.1;
- 4.0 m = 1.15;
- 4.5 m = 1.2.
If you apply this formula, then you can foresee and take into account almost all the nuances that can affect the heating of living space. Having made a calculation on it, you can be sure that the result obtained indicates the optimal number of aluminum radiator sections for a particular room.
If you decide to install aluminum heating radiators, it is important to know the following:
Whatever principle of calculation is undertaken, it is important to do it as a whole, since properly selected batteries allow not only to enjoy the heat, but also significantly save on energy costs. The latter is especially important in the face of ever-increasing tariffs.
Lighting in residential areas
In the corridor (hallway), the layout in most cases does not provide for natural light - there are no windows. Therefore, one has to limit oneself to artificial light. To create a comfortable environment, lamps with a wide angle of dispersion of the light flux are used.
The kitchen is a workplace. In it, in addition to general, spot lighting is used for the convenience of cooking - above the sink and cutting tables.
The living room in all houses combines many functions: they relax here, meet guests, work, play sports, eat, etc. Therefore, the use of all possible types of lamps to create full-fledged lighting in the room becomes an important aspect.
Self-calculation
You can determine the required number of lumens using the following example. It is necessary to calculate the amount of light for the workplace. The norm set by the state says that the level of illumination should be 300 lumens per square.
With an approximate area of the room of 30 squares, the total number of lumens will be 9000 (the SanPiN norm multiplied by the area of \u200b\u200bthe room). Approximate illumination value found. But then you should take into account such a value as the coefficient of the height of the room. The greater the distance from the floor to the ceiling, the greater this parameter:
- at 2.7−3 m - 1.2;
- at 3.1−3.4 m - 1.5;
- at 3.5−4.5 m - 2.
Innovative Devices
Increasingly, people are changing their choice from traditional incandescent lamps in favor of LED. They, some time ago, were considered unacceptable light sources that could be used in an apartment or house. With the growth of production capacity and science, they began to represent significant competition for standard lighting devices.
Their ability to compete is explained by the following factors:
- lamp life is much longer than conventional;
- LED lamp consumes less energy than halogen and incandescent lamps;
- The LED lamp does not heat up when used for a long time, which allows you to use it better and more creatively in interior design.

An important role is also played by the fact that LED lamps are more environmentally friendly
than their predecessors. They do not create fluctuations in the light flux, and they do not emit ultraviolet radiation.
Many experts advise using LED lamps when planning a room. However, it is necessary to take into account the fact that it is possible to purchase low-quality products.
When buying a product, it is recommended to pay attention to the manufacturer's brand. As a rule, the more famous it is, the better products it produces.
What you should know
When determining how many light bulbs or fixtures you need, the first step is always to calculate the number of lumens per square meter for a particular room.
In this case, you need to know what levels of illumination are set for each specific residential or non-residential premises. All these norms are given in special documentation - SNiP.
Norms for SNiP
You can create the desired level of illumination using various light sources:
- incandescent lamps;
- fluorescent and LED bulbs;
- halogen and metal halide lamps;
- LED strips;
- neon lamps, etc.
Each of the above light sources has different technical indicators of illumination.
The most important parameter in assessing the level of illumination is the luminous flux emitted by the light source.
The power values of lighting devices indicated in the table are given for incandescent lamps, since these basic regulatory documents were developed even before the era of the advent of modern energy-saving technologies. Today, ordinary incandescent lamps are almost never found in the house. They were replaced by LED (led), fluorescent and halogen light sources. At the same time, LED bulbs are the most popular, as they are very economical in terms of electricity consumption, have better technical performance and a longer service life than other energy-saving light sources.
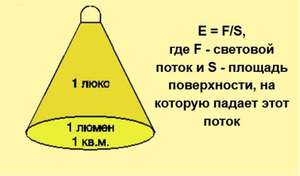
Light output is measured in lumens. The value of the luminous flux can be found on the packaging of light bulbs. At the same time, it is not always correct to raise the question of how many lumens are needed to illuminate one square meter. This is due to the fact that the luminous flux in this case reflects only the specific capabilities of a particular light source. In this case, the remoteness from the selected lighting object for the room is not taken into account. Therefore, it is rational to introduce such a parameter as lighting. It is measured in lux.
Based on this, equality was established between lux and lumens. Thus, for one meter of the square area of the room there is a luminous flux of one lumen and it is equal to one lux.
This rule applies to all premises, both residential and non-residential.