Computer Acoustic Modeling Software
To calculate all the required acoustic parameters of architectural acoustics, our engineers use two main programs for modeling halls with natural acoustics and with the use of electric sound amplification systems: ODEON 12.12 and EASE 4.3.
ODEON
The ODEON software was originally developed and used only for room simulations with natural acoustics. But recently, in this software environment, it has become possible to simulate halls with a sound amplification system, and the database of characteristics of equipment for electric sound is gradually being supplemented. ODEON has been used for calculations since 1984, its development is carried out at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU). At the same time, year after year, developers continue to improve the quality and speed of calculations. The ODEON program takes into account the geometry and acoustic properties of surfaces. This program uses the method of imaginary sources, combined with the method of ray trajectories.
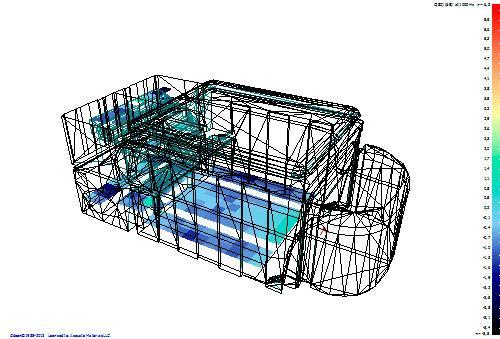
An example of calculating the distribution of the musical clarity index C80 over the audience area in the Small Hall of the Moscow State Conservatory. P.I. Tchaikovsky (ODEON 12.12)
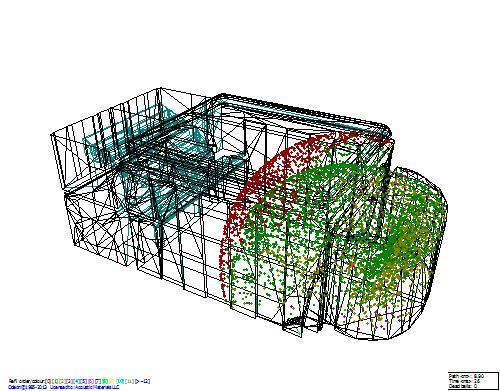
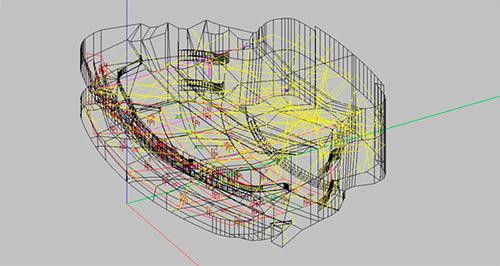
An example of calculating the sound field in the Small Hall of the Moscow State Conservatory. P.I. Tchaikovsky (ODEON 12.12). The sound field is shown at the 26th millisecond after the pulsed excitation of sound on the stage. Red dots are direct sound, green dots are singly reflected, yellow are doubly reflected.
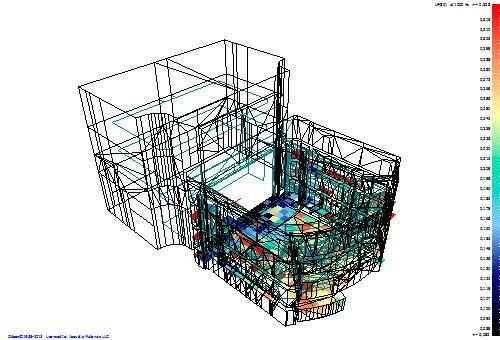
An example of calculating the distribution of the energy of early side reflections LF in the spectator zone in the Theater of Nations (ODEON 12.12)
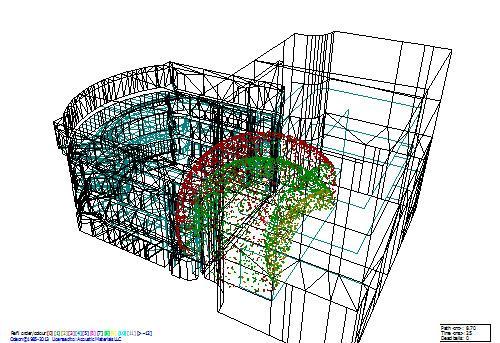
An example of sound field calculation in the Theater of Nations (ODEON 12.12). The sound field is shown at the 25th millisecond after the pulsed excitation of sound on the stage. Red dots are direct sound, green dots are singly reflected, yellow are doubly reflected.
EASE
EASE software has been one of the leaders in electro-acoustic room modeling with built-in acoustic amplification systems for over 30 years. Developed by AFMG Technologies GmbH, Germany. The EASE program, together with the additional AURA module, is designed to simulate the operation of a sound amplification system in a room and the acoustic parameters of rooms. With the help of this program, all the main acoustic parameters of the room (reverberation time RT, STI, C80, D50, LF, etc.) can be calculated. The simulation is based on the method of ray trajectories. EASE comes with a large and detailed database of loudspeaker systems from all major manufacturers for high simulation accuracy. The available software package makes it possible to simulate the acoustics of concert and opera halls, theaters, churches, mosques, open-type offices, foyers, restaurants, music studios, metro and railway stations, airport terminals, industrial premises and outdoor concert venues.
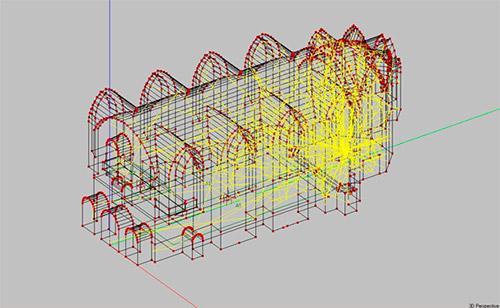
An example of building ray trajectories in the concert hall of the Church of the Holy Spirit, Minsk (EASE 4.3)
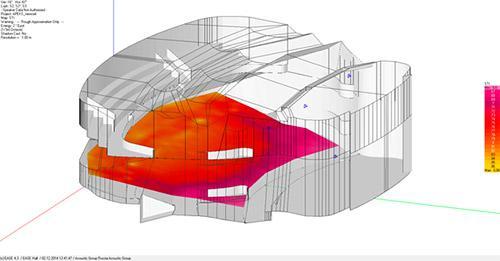
An example of calculating the distribution over the spectator zone of the energy of early lateral reflections LF in the concert hall of the Church of the Holy Spirit, Minsk (EASE 4.3)
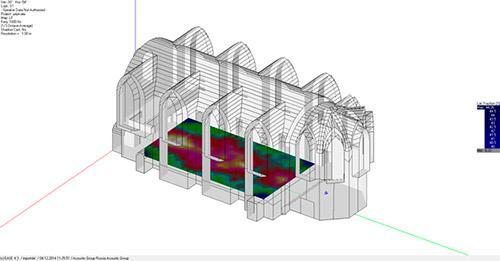
An example of calculating the distribution of the speech clarity index RaSTI d over the audience area in the Apeks cinema and concert hall, Voronezh (EASE 4.3)
An example of constructing ray trajectories in the Apeks cinema and concert hall, Voronezh (EASE 4.3)
architectural acoustics
For a number of environments, good sound and acoustic comfort are a must, just like adequate lighting or ventilation.These are commercial and home cinemas, rehearsal halls, foyers of public premises, lobbies of railway stations and airports, meeting rooms, studio premises, sports halls, open-air office premises, etc. In such rooms, in order to achieve acoustic comfort, it is necessary to simultaneously solve several, often contradictory, acoustic problems.
Useful signal - the sound of warning systems or concert sound amplifying equipment in the premises should be loud and of high quality (intelligible), and the level of noise that naturally also occurs in such premises should be low and not tiring. Separate serious requirements are imposed on the halls of the opera and ballet theaters, as well as concert halls, since it is in them that the sound of music and the human voice has that emotional impact on the audience, for which the music was written and these halls were built.
There are many examples in the history of architecture when halls that seem to be built “according to all acoustic rules” do not sound. The explanation for this is that the construction of music halls is like a fine art, when the result depends not only on a well-designed project and correctly applied materials, but also on the totality of a large number of seemingly insignificant details. To obtain the required sound, not only proportions, shape and a certain arrangement of materials along the building envelope are important. The final result is influenced even by the pitch and the force with which the screws fasten the wooden wall panels to the frame.
There are quite a lot of such nuances in architectural acoustics, and only an experienced acoustician knows the actual contribution of each “little thing” to the final result. Therefore, only the joint work of an architect, designer, technologist and acoustic engineer allows you to create a room that can later be proudly called the "Temple of Music".
An example of constructing a picture of a beam sound propagation in hall (simulation in the EASE software environment)

Distribution of the speech intelligibility index RaSTI in the spectator zone (simulation in the EASE software environment)