Threading methods
The thread is made by two main methods: using a manual fixture and a machine. Manually cut blanks in a single copy or in a small amount. In large-scale production, equipment is used - machines:

- Screw-cutting type;
- Thread-rolling with the participation of rollers and flat dies;
- Milling, where they get a big step;
- Grinding type using circles of a given profile, where fine-pitch and high-precision screws are obtained;
- Screw-cut type;
- For internal threading in nuts;
- For whirl cutting with heads with multiple cutting edges.
When threading in a vortex method, four elements fixed in the head are involved in the work. The head itself rotates from a separate drive. This whole structure is installed on a lathe - its support. The method is distinguished by an increased processing speed due to less heating of the cutting tool (alternate contact with the workpiece). Also, the helix is less rough and has a clearer profile.
Cutting a thread on a pipe is not so difficult.
Articles
To securely connect a tap to a pipe, or install a heater in a heating system, it is important to know how and with what to cut a thread on a pipe. After all, most valves are threaded, respectively, the connection of such elements by welding is impossible.
After all, most of the valves are threaded, respectively, the connection of such elements by welding is impossible.
Threaded water pipe
For example, if a new washbasin or toilet is to be installed in your apartment, and it is not possible to unwind a long-term connection on a steel water pipe, then the best option is:
- Turn off the water supply;
- Cut off a part of the pipe with a grinder at the installation site of the washbasin;
- Perform pipe threading;
- Install a ball valve or tee on the pipe;
- Connect it with a flexible hose to the washbasin faucet.
This job can easily be done by a qualified plumber. However, any owner of an apartment, having acquired a tool for threading pipes, is able to independently carry out this work.
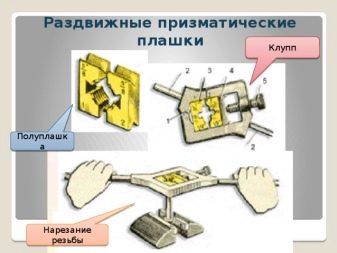
Thread-cutting dies
To date, 2 types of threading devices are used to equip a pipe with a threaded connection:
- Thread-cutting dies;
- Klupp pipe.
With their help, you can cut threads on any sewer or water pipe, which is used in engineering networks of residential buildings and private cottages.
Klupp pipe
Advice!
If you have never cut a thread, then it will be difficult to do this with a die. The slightest distortion of the tool can lead to a defect.
Therefore, it is better to use a die cutter, since it has a guide that greatly simplifies the cutting process.
Let's brush up on the theory behind the threading process.
So:
- threading on pipes is the formation of a helical surface on the outside of a pipe (plumbing or heating system);
- helical surface is a connecting element uniformly rotating around the axis of the race,
- tee or tap, with a uniformly translational movement along this axis;
- the thread pitch is the translational movement of the element being screwed relative to the thread axis, corresponding to one full turn.
In other words, in order to install stop valves, it is necessary to cut threads on the pipes, the pitch of which matches the pitch of the connecting elements. Then such a connection of sewer or water pipes will be tight and durable, and able to withstand high pressure.
What cutters are used for threading
On the turning unit, cutting operations can be carried out - both on the outer and on the inner surface. In this case, different types of cutting elements are used. They can be divided into three main groups:
- Rod;
- Prismatic;
- Round.
The first group includes the instrument of the simplest type. By design, this is a working head on a rod of various sections and shapes. The profile shape matches the head. Some models of rod cutters have carbide soldering on the working faces. This increases the resource of the latter, which are less subject to abrasion of the working surface, and, as a result, are not sharpened as often.
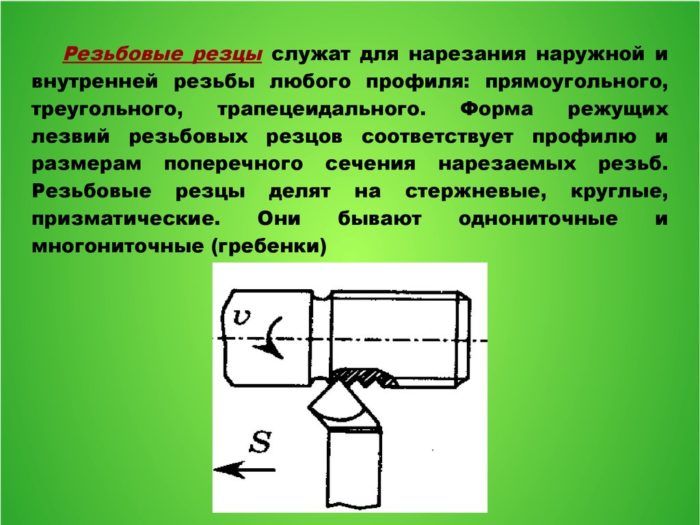
Prismatic type devices carry out processing of workpieces only from the outside. Compared to the previous group, they can cope with larger surfaces, they can be sharpened more times. In a lathe, the element is fixed with a dovetail holder.
Round cutting elements can be used to make internal and external threads. They are more convenient to work with than prismatic ones, they are more versatile - they have a wide range of applications. They lend themselves well to regrinding a large number of times. Attach the cutters in the holder to the hole in the end. Prismatic and round elements are classified as shaped tools for turning equipment.
Tools
To carry out the work, you need to prepare all the necessary tools and devices for cutting. In each case, a pipe threaded set will vary in composition, but for manual use it consists of dies, a die and a ratchet holder. The composition of the set is also additionally equipped with a pipe cutter, a gas wrench, a file, a hacksaw, a grinder, lubricants and other tools. For those who do not want to work the old fashioned way with the classic method, there is an alternative - a power tool.
The cutting itself is carried out using dies. Some are cut on one side only, others on both.
For internal threading, the kit may also include several taps with different depths of the cut. Some are designed for roughing the inner surface of the pipe, others for finishing. This equipment is presented in the form of a screw with chip grooves. It is attached to the collars with the help of the tail section.
With the help of a tap, internal cutting is performed in several approaches. Their number depends on the material with which they work. For example, for threading in titanium alloys, special sets of several taps are designed.
A die, progonka or lerka is used to carve various shapes on pipes. It is a steel nut with a cutting base inside, in which there are special holes - grooves for waste. Dies are tubular, hexagonal, round and square. Modification of their body is solid, split and sliding.
Sliding (prismatic) models are also called half-plates, they are attached to the die with screws and a special gasket - cracker. This is necessary to evenly distribute pressure on the screw. With the help of dies, cylindrical, conical, round or metric threads are cut. The component parts of the die are special wrenches and cartridges with which it is attached to the frame body.
Klupp consists of a frame in which cutting elements - dies are fixed. Each mandrel is equipped with four steel dies. Klupp is also equipped with a special ratchet handle. Only one die can be inserted into the die holder, several can be inserted into the die holder. The cutting mechanism of runs is capable of cutting two types of threads: 0.5 - 1 ¼, 1 ½ - 2 inches.
A manual die cutter, as a rule, cuts pipes of small diameter. They are equipped with a special handle - holder.They can also be used with a suitable pipe wrench. It is small in size, simple and easy to use.
A ratchet holder screw screw is a modification of the design with a gear mechanism designed to make threads with a diameter of more than one inch. The ratchet is an indispensable mechanism. Left- and right-hand ratchets make it easy to work in hard-to-reach places, such as near walls. Using the ratchet lever, the die is quickly removed from the thread by turning it in the opposite direction, providing a reciprocating method of threading.
It is called oblique klupp because the distance between the sliding dies is regulated in it. This tells the diameter of the cut. Designs of this type are the easiest to use.
Mayevsky's screw plugs of a more complex design are used for pipe threading. They contain three sets of interchangeable dies and specialize in thread diameters up to 2 inches. Designs of this type are used for threading pipes with a small diameter.
Cutting on pipes of large diameter is carried out on an industrial scale. For example, to cut a seamless pipe with a diameter of 219 mm, a special machine is needed. Casing pipes (columns) are cut only on special machines under special conditions, subject to all safety measures.
How to cut an external thread. Cutting threads on pipes and fittings. Die. Klupp
How to cut an external thread. Cutting threads on pipes and fittings. Die. Klupp. 4.46/5 (89.23%) lost 13
An external thread is cut using round or sliding dies, as well as screw boards. Thread cutting can be done both on machines and manually.
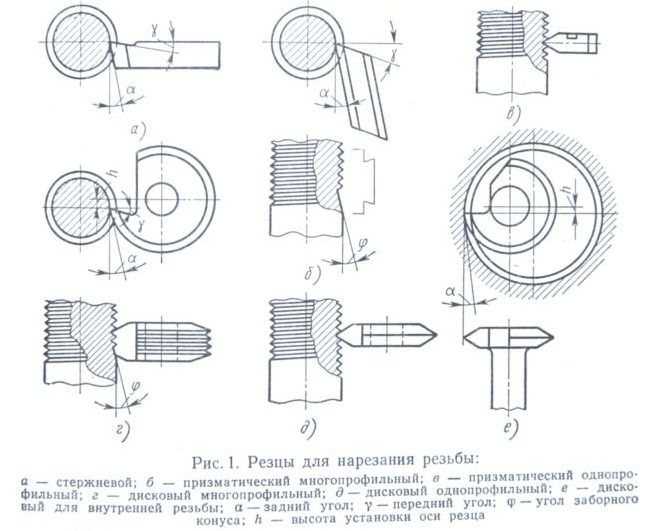
Threading with round dies (lerks).
Round dies (lehrs) are a disk with a cut hole. To remove chips and form feathers with cutting edges (Fig. 1), several chip holes are made in the die. The dies (lehrs) are inserted into the lerko holder and clamped with screws (Fig. 2).
Rice. 1. Die round cut (lerka).
Rice. 2. Lerko holder:
1 - frame; 2 - handle; 3 - clamping screw.
The diameter of the cut rod is taken slightly less than the outer diameter of the thread and sawed down cone-shaped for the lehr to enter. The choice of rods for cutting metric or inch threads is given in Table. one:
Table 1. Shaft diameters for threaded bolts.
| Metric thread | Inch thread | ||
| Outer diameter in mm | Stem diameter in mm | Outside diameter in inches | Stem diameter in mm |
| 5 | 4,89 | 1/4 | 6,19 |
| 6 | 5,86 | 5/6 | 7,7 |
| 8 | 7,83 | 3/8 | 9,3 |
| 10 | 9,8 | 7/16 | 10,8 |
| 12 | 11,7 | 1/2 | 12,4 |
| 14 | 13,7 | 5/8 | 15,6 |
| 16 | 15,7 | 3/4 | 18,7 |
| 20 | 19,6 | 7/8 | 21,8 |
| 22 | 21,6 | 1 | 25 |
| 24 | 23,6 | 1 1/4 | 31,3 |
| 27 | 26,6 | 1 1/2 | 37,6 |
| 30 | 29,5 | 1 3/4 | 43,8 |
| 36 | 35,4 | 2 | 50 |
Sliding dies (Fig. 3, a) consist of two prismatic halves with a cut hole. A groove is made in the middle part of the die hole, which forms the cutting edges.
Rice. 3. Sliding dies and crackers:
a - plate; b - cracker.
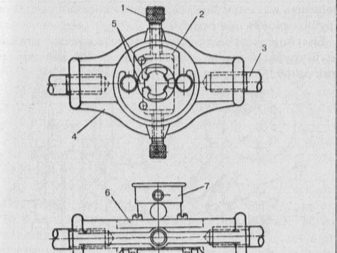
Klupp for threading.
For fastening the dies, a screw clamp with a rectangular or oblique frame is used (Fig. 4). The prismatic protrusions of the klupp enter the grooves of the dies, and from the side the dies are pressed with bolts.
Rice. 4. Klupp (oblique)
1 - frame; 2 - handle; 3 - clamping screw.
To avoid direct pressure of the bolt on the dies, a so-called cracker is installed between the dies and the bolt (see Fig. 3, b), which has the shape of a dies.
Thread cutting technology.
Cutting with prismatic dies is somewhat different from cutting with lerks. When cutting with dies, the rods are not sawn into a cone, but the dies are moved apart.
Then they are clamped on the rod, the end of which must coincide with the upper plane of the dies. By turning the die to the right and slightly to the left, threading is performed.
The position of the lerkoderzhatel and klupp is set strictly perpendicular to the cut rod, otherwise the thread will be oblique and one-sided.
Cooling and lubrication for threading.
When cutting threads with taps and dies, lubricant must be used.As a lubricant, you can use a regular emulsion, dissolving one part of the emulsion in one hundred and sixty parts of water. In addition, you can apply: for cast iron - lard and kerosene; for steel and brass, boiled and rapeseed oil and lard; for red copper - lard and turpentine; for aluminum - kerosene.
It is not recommended to use machine and mineral oils when cutting threads, since they, by increasing cutting resistance, do not give clean holes and lead to rapid wear of taps and dies.
Screw boards.
In order to cut threads on screws with diameters up to 6 mm, screw boards are used. On the screw boards there are several cut holes of different diameters with chip grooves, two for each hole.
Threading with dies is performed in the same way as tapping. The rod is firmly clamped in a vise, lubricated with oil, and then a die with dies is put on the rod, clamped with a screw and rotated a full turn in one direction and half a turn in the other. If the rod is thicker than required, it must be filed.
The thread of the bolts is measured with annular thread gauges or a thread gauge.
Cutting threads on pipes and fittings.
Pipes and fittings (connecting parts for pipes) are cut with a special tool using fixtures.
Klupp for cutting threads on pipes.
On pipes, the thread is cut with a special screw thread (Fig. 5). The die cutter for cutting pipes according to the device differs from ordinary die cutters. Four steel combs enter the slots of its holder.
By turning the top handle, they can be brought together or moved apart. Therefore, pipes of various diameters can be cut with one die. In addition, the klupp has guides that are regulated by the lower handle.
The guides ensure the correct position of the die on the pipe when cutting.
Rice. 5. Klupp for cutting pipes.
Pipes during cutting are fixed with a special pipe clamp. The clamp consists of a frame in which crackers with cutouts for pipes of various diameters are placed.
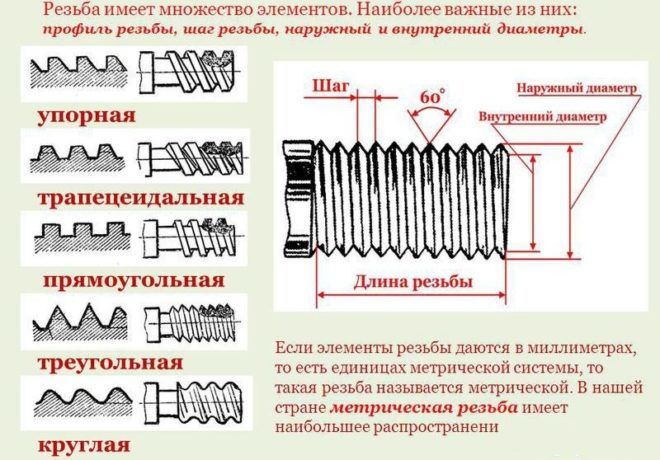
Thread profiles
Forms of blanks, depending on the type of surface, are cylindrical and conical. Threads are external (on the surface) and internal (in the hole of the blank). The type of threaded connection depends on the thread profile.
There are five types of profile:
- triangular;
- rectangular;
- trapezoidal;
- persistent;
- round.
The thread can be single-start and multi-start:
- single-threaded - formed by a single threaded thread;
- multi-start - created by two or more threads placed at the same distance from one another.
The main indicators of both types of threads are pitch and stroke. Thread pitch - the distance between the nearest turns and is measured along the center line of the workpiece being processed. The course of one thread is the gap in the middle of two peaks of one turn on the working surface of the product. The stroke is equal to the product of the thread pitch by the number of starts.
Cutting tool die
A die is a cutting turning tool made in the form of a nut. Holes drilled in it are made for chip removal. The tool consists of cutting elements located on each side and forming a cone. A die on a lathe forms a thread on bolts, studs, screws and other metal products.
The most used types of plates:
- metric;
- left;
- pipe.
You can make the task easier by making a small chamfer on the end so that its height coincides with the height of the thread profile. The size of the die must match the diameter of the part.
Then the die of the desired size is fixed in the die holder, fixed in the tailstock of the lathe. The threading speed depends on the material for the workpiece: brass products are processed at about 15 m/min., cast iron - 3 m/min., steel blanks - 4 m/min.
At this processing speed, the die wears out less.In the process of cutting, each turn of the die must be replaced by turning it back a third of the circle in order to clear the holes from chips.
Video: How to cut threads on a lathe
A selection of questions
- Mikhail, Lipetsk — What discs for metal cutting should be used?
- Ivan, Moscow — What is the GOST of metal-rolled sheet steel?
- Maksim, Tver — What are the best racks for storing rolled metal products?
- Vladimir, Novosibirsk — What does ultrasonic processing of metals mean without the use of abrasive substances?
- Valery, Moscow — How to forge a knife from a bearing with your own hands?
- Stanislav, Voronezh — What equipment is used for the production of galvanized steel air ducts?
Thread Basics
When gas pipes are connected to a water supply system, cylindrical pipe threads are rolled or cut. The end parts of the pipes are combined with special elements. The last 2 curls of a cylindrical thread are called a run. The runaway allows fixing the coupling element on the tubular product. This ensures the sealing of the connection with the seal.
To disconnect connected, for example, heating pipes without cutting, you need to use a drive. It includes a lock nut, a coupling element, a long thread. It has such a length that it is possible to easily wind the coupling part, locknut.
In order to save material, products with thin walls are used in gas supply and other complexes. They are rolled on. The thickness of the walls should be greater than when creating a thread on a water pipe.
Cutting technique on a metal part
The helical surface formed by the cutter is called a thread. It provides important tasks - with its help, elements of parts can move relative to each other, articulate or significantly seal joints in various mechanical devices.
To understand how to cut threads on a lathe, you need to follow the threading process - it is quite simple and understandable. The cutter is fixed in the support of the lathe. It moves uniformly along the axis of the rotating part. The pointed tip of the tool cuts a helical line on the surface of the part.
To properly install and guide the cutting tool, a special template is used, which is placed above the blank. The cutter is placed along the center line of the machine. According to the resulting gap, it is determined how accurately threading is carried out.
Cutting has its own characteristics:
- the process of thread formation has some features;
- the material from which the part is made sets the rake angle of the cutter;
- the value of the angle depends on the viscosity, hardness and brittleness of the metal;
- the planes of the cutter at the rear side corners should not rub against the cut grooves;
- internal threads are cut in already bored or drilled holes.
For each material being processed, certain metal-cutting tools are designed. For steel blanks, cutters are used, the plates of which are made of hard alloys T15K6, T14K8, T15K6, T30K4. For cast iron blanks, cutting tools with carbide inserts VK4, V2K, VK6M, VK3M are used.
threading with a tap how to cut threads by hand
How to cut threads with a threading device was described earlier. The threading device differs greatly from the tap device, but the principle of threading with both tools remains the same.
A tap is a metalworking and turning tool, in its shape somewhat reminiscent of a long rod. Inside this very rod there are cutting elements, with the help of which the thread is cut manually.
A tap can be used for more than just cutting new threads. With this tool, you can also restore the thread, making it as "new".
According to the principle of operation, taps are manual and machine. Machine taps are fixed on a lathe, and threading occurs in automatic mode.
How to choose the type of tap?
For manual threading, you first need to select the correct type of tap. The choice of tap for threading depends primarily on:
- thread pitch;
- profile;
- Forms of threaded connection;
- Tolerance;
In addition, the choice of a particular tap is also influenced by the material of manufacture of the parts on which the thread will be cut. The main choice of a tap, first of all, depends on the diameter of the thread being cut.
Threading with a tap by hand
Threading with a tap occurs as follows. The part to be threaded is fixed in a vise or other device. The main thing is that the part is securely fixed in the device, since when threading with a tap, you will need to apply a lot of effort.
Then, a hole is drilled into the part for threading with a tap, depending on the type of thread - blind or through. The diameter of the drilled hole should be somewhat smaller than the diameter of the cutting elements of the tap.
Be sure to chamfer the top edge of the tapping hole. After that, a tap is taken and installed in a drilled hole, which should be located in a vise with a chamfer up.
Threading with a tap is done clockwise, all the time, pressing the tap into the hole. It is necessary to press the tap smoothly, without unnecessary jerks, gradually turning it, thus, until a clean and even thread is obtained.
After making several turns with the tap clockwise, it is returned in the opposite direction, thereby getting rid of the accumulated metal chips.
During threading, it is necessary to cool the tap in time, otherwise the tool can be easily damaged. If an aluminum thread is cut, then the tap is cooled with kerosene; if a thread is cut on a copper part, then with turpentine; when cutting a steel thread, it is best to cool the tap with an emulsion.
Types and properties of cutters
The turning tool for metal consists of a holder and a working head. The quality of processing parts directly depends on these elements. The holder has a rectangular or square section. With its help, the cutter is fixed on the lathe.
The working head processes the details. It is made up of various cutting planes and edges. The angle of sharpening the head is determined by the material from which the part is made.
External and internal threads are cut with different types of thread cutters.
The most used of them:
- rod;
- prismatic;
- round.
Rod cutters consist of a rod with a working head. These types come in different profiles. The most wear-resistant are cutters, to which hard-alloy working edges are soldered. They do not need frequent turning, as they remain sharp for a long time.
Prismatic cutters are used to process only the outer side of the blank. Their advantage over rods is the ability to process large surfaces. But they should be sharpened more often.
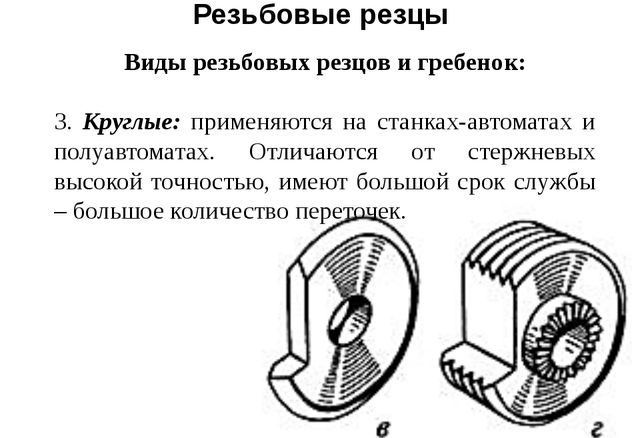
Round cutters are used in the process of cutting internal and external threads. These tools are very easy to use, their scope is quite wide. Round cutters allow multiple regrinding.
According to the design differences, metal-cutting tools are divided into several types:
- straight;
- curved;
- bent;
- drawn.
The top of any threaded tool is a rounded head or a chamfer. The thread profile is formed by a cutter of the proper configuration. With cutting tools of a bent shape, a threaded thread is cut on the surface of the blank.
Straight cutters are rarely used here.The thread inside the part is made with curved cutters, sometimes straight, fixed in a special holder.
Cutters are divided into categories:
- made of high speed alloy steel;
- with hard-alloy plates soldered to the working element;
- cutting attachments with interchangeable multi-faceted inserts fixed on the head.
In the direction of the screw thread, the tools are differentiated into right and left. When working, the first feed goes from left to right, the second - the feed goes to the left. The right ones are used more often.
We cut the thread with a die
Peculiarities
Threading was invented two centuries ago when the screw lathe first appeared in Britain. Inventor G. Maudsley discovered a method for applying precise threads and invented a device for measuring it (micrometer) with an accuracy of 0.0001 inches.
Around the same time, mechanical engineer D. Whitworth created the first screw thread profile and proposed a system of its standards. Since then, the invention bears his name - Whitworth carving. It formed the basis for various national standards.
The main feature of threading is that the tool for its implementation must be made of a material of greater hardness than the element being cut, and for the manufacture of this tool, in turn, designs with even harder elements in composition must be used.
Nowadays, there are countless options for threading a pipe.
It is only important to choose the one that is needed. A good result is guaranteed if high-quality materials and tools are used in the implementation of work, the instructions are followed, as well as cutting technology
When threading, it is best to use a quality tool, as a cheap option is unlikely to last long.
Now most piping systems are made of plastic. It is often necessary to fasten structures using connecting elements made of plastic and metal. In the domestic sphere, such fasteners are a fairly common solution, they are called combined. In modern communication systems, one of the types of plastic or metal pipes is traditionally used. However, in some cases it is expedient to use combined designs.
Pipes with a diameter of up to 40 mm are joined by a threaded method. Flanged connections are used for larger diameter pipes where it is not possible to tighten the thread.
The connection of a polypropylene pipe with a metal pipe is carried out using fittings that are specially designed for this. They are connections, one side of which has a metal thread, and the other has a plastic sleeve. Multiple combined connections are made with special complex fittings.