Gravity heating
A modern country house is not inferior to a city apartment in terms of comfort. The development of building technologies has made it possible to build independent life support systems at small facilities. If desired, you can equip almost any autonomous engineering system in the house, for example heating.
Home heating systems on the water
Gravity heating
The most popular in our country is liquid heatingcharacterized by simplicity and efficiency. The principle of operation is based on the ability of water to accumulate and transfer a large amount of thermal energy. Technology water heating installations widespread and known to almost every specialist in heating systems.
Atmospheric circulation – naturally and reliably
According to the method of transporting the coolant through pipes, there are two types heating:
With forced circulation
with gravitational (natural) circulation.
In systems with forced circulation, a pump is installed to ensure the flow of water through the pipes. This scheme requires uninterrupted power supply for the pump. Otherwise, the efficiency of the heating system of this type is sharply reduced.Gravity heating is a non-volatile system, since it does not have a motor. The movement of the coolant occurs due to the difference in the volumetric weight of cold and hot liquids. The water heated in the boiler rises through the riser and is distributed to the heating devices. Cooling down, the coolant decreases in volume and tends to go down, so the return line is laid at floor level.
Advantage gravity heating lies in the high reliability of the system. As long as gravity is in effect, and objects have weight, a working system with atmospheric circulation of the coolant will function.
Connection diagrams for heating devices
Water heating installation performed according to one of the schemes:
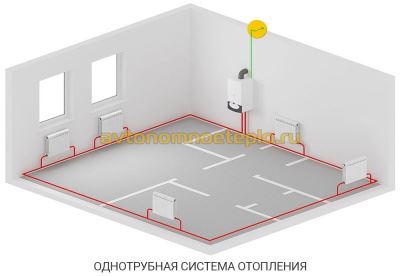
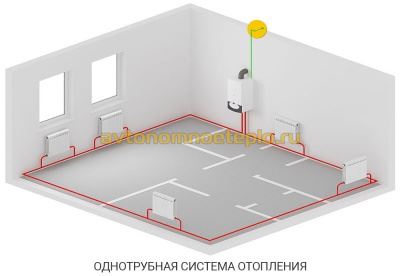
One-pipe wiring
heat main in two pipes;
Collector (beam) wiring.
Installing the heating circuit in one pipe allows you to save on pipes, but this scheme is untenable in large houses. As the coolant moves along the series-connected radiators, the temperature of the working medium drops, and the last heaters receive the cooled coolant.
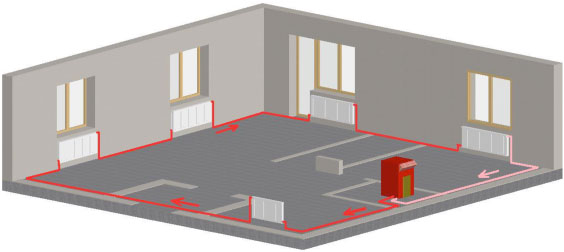
Two-pipe wiring diagram gravity heating allows you to connect radiators in parallel, which ensures more uniform heating of all rooms. In addition, it becomes possible to more accurately adjust the temperature in each heater.
The collector circuit is considered the most progressive. The advantages of radial connection of radiators are obvious: precise temperature control of each heater, speed and ease of installation, maintainability.
Our offer
The company "Design Prestige" employs real professionals who are able to competently conduct water heating installation in a short time. When fulfilling an order, we apply the latest technologies and use professional-class equipment, which is a guarantee of the quality of the work performed.
Advantages.
- The equipment used in this system has a fairly simple design, so that the installation process is not particularly difficult. The same quality determines the ease of operation of the system in question.
- This equipment is absolutely independent of the intensity of the energy supply of the building.Therefore, the presence or absence of electric current does not affect the microclimate of the heated room.
- The system does not require the use of special pumps that ensure uninterrupted circulation of the liquid. This circumstance completely eliminates vibration, and also ensures a silent operation of the equipment.
- This system has a high level of reliability, and also has a long operating period. It can function for about forty years.
- Gravity heating equipment is able to regulate its work in automatic mode.
It is important to note that the reliability of this system directly depends on quantitative spmoregulation. This means that, as the temperature of the heating fluid changes, some metamorphoses are also undergone by the flow rate of the coolant.
Due to the change in the density of the mentioned element, the level of heat transfer increases or decreases. Therefore, the intensity of the latter is affected by the quantitative content of water.
In addition, the heat loss of the room itself, relative to which this system operates, is of great importance. The higher the heat transfer rate, the more intense the heat transfer process.
If we consider a two-pipe system, then in it the circulation circle is determined by one device, which leads to a slightly different way of self-regulation. In this case, said circle is shorter. Due to this circumstance, heat transfer is significantly improved.
As for the single-pipe, here the heating circle includes several units. In connection with this feature, uneven distribution of heat is noted. This often provokes the need to use a special circulation pump, but such a system is not relevant to the species in question.
Flaws.
Like everything man-made, the gravitational heating system has its drawbacks, which are expressed in the following:
- The system has a sufficiently low circulation pressure, due to which its radius of action is reduced to thirty meters horizontally.
- The same factor, along with the high heat capacity of water, determines the low start-up speed of the equipment.
- Often, an expansion water tank is installed in an unheated room, which can cause this liquid to freeze in winter. This is fraught with undesirable consequences, manifested in the destruction of pipes.
Advantages and disadvantages of gravity systems
The main advantage of this heating system is its reliability and durability. Under normal operating conditions, such a system can function without repairs for several decades. The gravitational heating system works, based on the laws of physics, without the use of expensive volatile equipment. (See also: Heating Fluid)
However, these systems have significant drawbacks.
- Gravity heating has a short range. On a horizontal plane - less than 30 meters.
- Slow heating of heating equipment due to low pressure and significant heat capacity of water.
- The probability of freezing of the coolant in the expansion tank, if it is located in an unheated room. (See also: Specifics of a water heating system)
Schematic diagram of the gravity system
Such a heating system includes a boiler, two pipelines - supply and return, heating devices and an expansion tank.
Water is heated in the heat generator and flows through a direct pipeline to the heating devices. Having given up part of the heat, the coolant returns to the source of thermal energy through the return pipeline.
All horizontal pipes during installation are placed with a pre-calculated slope.Thus, hot light water is squeezed upwards along the main riser, from where it is distributed along the horizontal branches to the heating devices. From them, the chilled water returns to the boiler by gravity. There it displaces the heated water, heats up itself, and the cycle repeats. (See also: Solid fuel boilers)
Slopes help get rid of air bubbles. Air is lighter than water, so it freely enters the expansion tank, being removed from the system.
The rise of water along the riser occurs due to the heating of the coolant, its expansion and the appearance of gravitational pressure. The movement of a liquid along a closed circuit is carried out due to the difference in the densities of liquids with different heating temperatures. Gravitational pressure is used to move fluid and overcome resistance in pipes. The higher the resistance, the greater the gravitational pressure required to overcome them. To reduce friction, increase the diameter of the pipes, which leads to an increase in costs. The circulation pressure depends on the temperature difference between the heated and cooled liquids and on the difference between the heights to the center of the boiler and the heater. The higher the device, the easier the circulation of the coolant.
Single Pipe Heating Gravity System
Such a heating system can only be installed with the upper distribution of the supply pipe. There are no reverse risers in such a system. (See also: Forced circulation heating system)
Such systems can be mounted according to two schemes: flow-through and with trailing sections.
With a flow circuit, there is no supply riser, and radiators located one above the other are connected in series. Hot coolant passes from top to bottom through all radiators. A perfectly cooled liquid enters the lower appliances, which leads to good heating of the radiators on the upper floors and completely cold radiators on the lower ones.
Bypasses are included in the system with closing radiators. This allows part of the water from the riser to be supplied to the lower radiators, bypassing the upper ones. In this system, water at almost the same temperature enters the upper and lower radiators.
Gravity heating types of heating somatic schemes
Heating schemes with natural circulation are of two types: one-pipe and two-pipe. Old houses had only one pipe in their heating system. But at present, a two-pipe heating system with lower or upper dilution is most often used. What are the main differences between the schemes? Single-pipe gravity heating is considered the simplest. The pipeline is placed under the ceiling of the premises, and the return circuit is under the floor. Of the positive aspects, a small number of components necessary for the functioning of the system can be noted. It also features easy installation. As advantages, we can note the possibility of its operation when installing the boiler and radiators at the same level. Typically, in a two-story house, such a scheme is rarely used, because it does not allow the house to be heated evenly. However, this can be corrected by installing volumetric pipes and radiators on the ground floor. When installing a single-pipe circuit, control valves are not provided, which means that it will not be possible to regulate the temperature.
A two-pipe heating system is more difficult both in operation and in the device, because it involves several heating circuits. One of them is intended for the flow of hot coolant, the other for cold. In this case, you will need many more components. The dead-end heating system of a two-story house will necessarily require insulation of the main riser to avoid heat loss. For a two-pipe system, it is necessary to use pipes of large diameter, at least 32 mm, otherwise hydraulic resistance will prevent gravity circulation.
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of the coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case it is required to perform a hydraulic calculation of the system, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the pipe diameter, etc. You may need the help of a professional when doing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
In the EU countries, closed systems are the most popular among other solutions. In the Russian Federation, the scheme has not yet been widely used. The principles of operation of a closed-type water heating system with pumpless circulation are as follows:
- When heated, the coolant expands, water is displaced from the heating circuit.
- Under pressure, the liquid enters a closed membrane expansion tank. The design of the container is a cavity divided by a membrane into two parts. One half of the tank is filled with gas (most models use nitrogen). The second part remains empty for filling with coolant.
- When the liquid is heated, pressure is created sufficient to push through the membrane and compress the nitrogen. After cooling, the reverse process occurs, and the gas squeezes the water out of the tank.
Otherwise, closed-type systems work like other natural circulation heating schemes. As disadvantages, one can single out the dependence on the volume of the expansion tank. For rooms with a large heated area, you will need to install a capacious container, which is not always advisable.
Open system with gravity circulation
The open type heating system differs from the previous type only in the design of the expansion tank. This scheme was most often used in old buildings. The advantages of an open system is the possibility of self-manufacturing containers from improvised materials. The tank usually has modest dimensions and is installed on the roof or under the ceiling of the living room.
The main disadvantage of open structures is the ingress of air into pipes and heating radiators, which leads to increased corrosion and rapid failure of heating elements. Airing the system is also a frequent "guest" in open circuits. Therefore, radiators are installed at an angle, Mayevsky cranes are required to bleed air.
Single pipe system with self-circulation
This solution has several advantages:
- There is no paired pipeline under the ceiling and above the floor level.
- Save money on system installation.
The disadvantages of such a solution are obvious. The heat transfer of heating radiators and the intensity of their heating decreases with distance from the boiler. As practice shows, a single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation, even if all slopes are observed and the correct pipe diameter is selected, is often redone (by installing pumping equipment).
Two-pipe system with self-circulation
The two-pipe heating system in a private house with natural circulation has the following design features:
- Supply and return flow through separate pipes.
- The supply pipeline is connected to each radiator via an inlet.
- The battery is connected to the return line with the second eyeliner.
As a result, a two-pipe radiator type system provides the following advantages:
- Uniform distribution of heat.
- No need to add radiator sections for better warm-up.
- Easier to adjust the system.
- The diameter of the water circuit is at least one size smaller than in single-pipe schemes.
- Lack of strict rules for installing a two-pipe system. Small deviations regarding slopes are allowed.
The main advantage of a two-pipe heating system with lower and upper wiring is the simplicity and at the same time the efficiency of the design, which allows you to level errors made in the calculations or during installation work.
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of the coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case it is required to perform a hydraulic calculation of the system, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the pipe diameter, etc. You may need the help of a professional when doing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
In the EU countries, closed systems are the most popular among other solutions. In the Russian Federation, the scheme has not yet been widely used. The principles of operation of a closed-type water heating system with pumpless circulation are as follows:
- When heated, the coolant expands, water is displaced from the heating circuit.
- Under pressure, the liquid enters a closed membrane expansion tank. The design of the container is a cavity divided by a membrane into two parts. One half of the tank is filled with gas (most models use nitrogen). The second part remains empty for filling with coolant.
- When the liquid is heated, pressure is created sufficient to push through the membrane and compress the nitrogen. After cooling, the reverse process occurs, and the gas squeezes the water out of the tank.
Otherwise, closed-type systems work like other natural circulation heating schemes. As disadvantages, one can single out the dependence on the volume of the expansion tank. For rooms with a large heated area, you will need to install a capacious container, which is not always advisable.
Open system with gravity circulation
The open type heating system differs from the previous type only in the design of the expansion tank. This scheme was most often used in old buildings. The advantages of an open system is the possibility of self-manufacturing containers from improvised materials. The tank usually has modest dimensions and is installed on the roof or under the ceiling of the living room.
The main disadvantage of open structures is the ingress of air into pipes and heating radiators, which leads to increased corrosion and rapid failure of heating elements. Airing the system is also a frequent "guest" in open circuits. Therefore, radiators are installed at an angle, Mayevsky cranes are required to bleed air.
Single pipe system with self-circulation
This solution has several advantages:
- There is no paired pipeline under the ceiling and above the floor level.
- Save money on system installation.
The disadvantages of such a solution are obvious. The heat transfer of heating radiators and the intensity of their heating decreases with distance from the boiler.As practice shows, a single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation, even if all slopes are observed and the correct pipe diameter is selected, is often redone (by installing pumping equipment).
Two-pipe system with self-circulation
The two-pipe heating system in a private house with natural circulation has the following design features:
- Supply and return flow through separate pipes.
- The supply pipeline is connected to each radiator via an inlet.
- The battery is connected to the return line with the second eyeliner.
As a result, a two-pipe radiator type system provides the following advantages:
- Uniform distribution of heat.
- No need to add radiator sections for better warm-up.
- Easier to adjust the system.
- The diameter of the water circuit is at least one size smaller than in single-pipe schemes.
- Lack of strict rules for installing a two-pipe system. Small deviations regarding slopes are allowed.
The main advantage of a two-pipe heating system with lower and upper wiring is the simplicity and at the same time the efficiency of the design, which allows you to level errors made in the calculations or during installation work.
Types of gravity heating system
There are two types of gravity heating system:
The two-pipe system is more complex and involves the presence of two circuits. Inside one circuit, the coolant (water) moves from the boiler to the batteries, and along the second, the water returns to the boiler. Remember that this kind of system requires more careful design. The installation process will also not be the easiest, consider it in stages:
- installation of a riser, it will play the main role, it passes from the tank to the boiler;
- main riser with wiring, connected at the level of 1/3 of the total height of the room from the floor level;
- the overflow pipe is attached to the expansion tank, through it the excess liquid goes into the sewer;
- in order for the water to go back to the boiler, the return pipes cut into the lower part of the batteries.
In a single-circuit system, the desired number of radiators plays a fundamental role. The volume of the expansion tank depends on this. Usually, it is filled to three-quarters of the total volume.
It is worth constantly monitoring the water level in the tank, it should not be lower than the level of the pipe through which the water is distributed to the radiators. This threatens to stop the circulation of the coolant.
Although the single-pipe system is simple, it only seems so at first glance. A project not done correctly will entail a lot of problems and consequences, entrust this matter to professionals.
When designing a natural system, the main attention should be paid to the uniform distribution of pressure in a closed circuit and the correct circulation of the coolant.