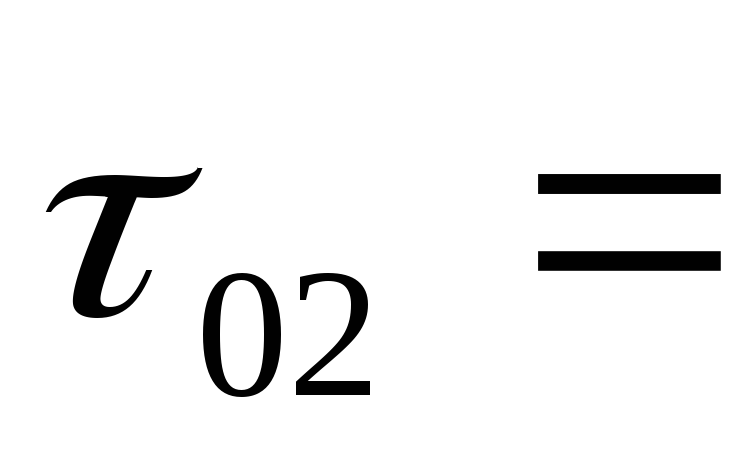Answer
The calculation of displacement in the heating system is a very important event on which further heating calculations depend
Here is some data:
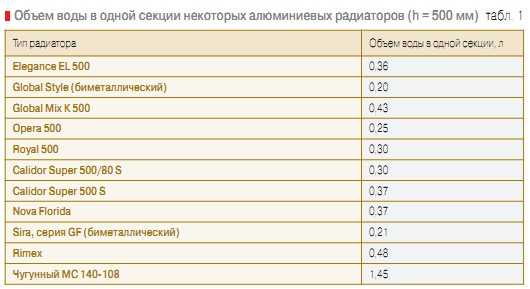
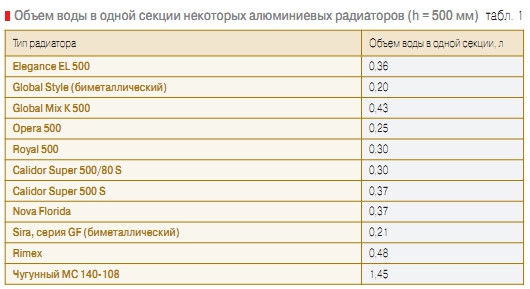
The volume of coolant in the radiator:
aluminum radiator - 1 section - 0.450 liters
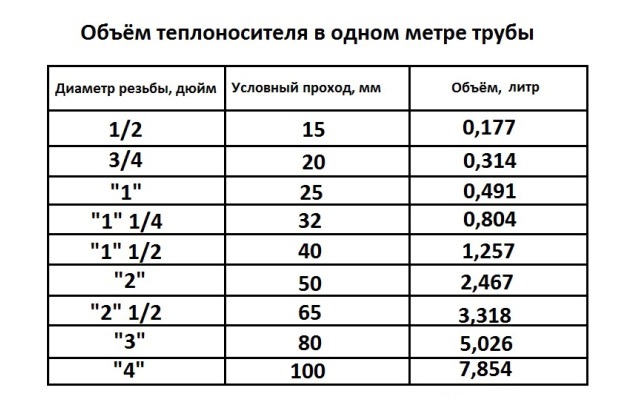
ø15 (G ½") - 0.177 liters
ø20 (G ¾") - 0.310 liters
ø25 (G 1.0″) - 0.490 liters
ø32 (G 1¼") - 0.800 liters
ø40 (G 1½") - 1.250 liters
ø50 (G 2.0″) - 1.960 liters
The volume of coolant in the system is calculated by the formula:
V=V(radiators)+V(pipes)+V(boiler)+V(expansion tank)
An approximate calculation of the maximum volume of the coolant in the system is necessary so that the thermal power of the boiler is enough to heat the coolant. In case of exceeding the volume of the coolant, as well as exceeding the maximum volume of the heated room (we will conditionally take the norm of 100 W per square meter of heated power), the heating boiler may not reach the boundary temperature of the carrier, which will lead to its continuous operation and increased wear and significant fuel consumption .
It is possible to estimate the maximum volume of coolant in the system for heating boilers of the AOGV system by multiplying its thermal power (kW) by a factor numerically equal to 13.5 (liter / kW).
Vmax=Qmax*13.5 (l)
So, for standard boilers of the AOGV type, the maximum volume of coolant in the system is:
AOGV 7 - 7 * 13.5 = up to 100 l
AOGV 10 -10 * 13.5 \u003d up to 140 l
AOGV 12 - 12 * 13.2 \u003d up to 160 liters, etc.
An example of transferring thermal power
1 Cal/Hour = 0.864 * 1 W/Hour
The most widely used heating systems with the use of a liquid coolant. These complex systems include a range of equipment: pumping stations, boilers, heat exchangers, etc. The stable operation of the equipment depends not only on its technical condition, but also on the type and quality of the coolant itself.
In most cases, for heating country houses, summer cottages, garages and other objects, the heating system was filled with water. In addition to the undeniable benefits, this brought a number of inconveniences, in addition, significant shortcomings were revealed over time. A small volume of coolant in the heating system of boiler houses made it possible to find a worthy alternative to it.
How to correctly determine the type of heating boiler and calculate its power
In the heating system, the boiler plays the role of a heat generator
When choosing between boilers - gas, electric, liquid or solid fuel, they pay attention to the efficiency of its heat transfer, ease of operation, take into account what type of fuel prevails in the place of residence
The efficient operation of the system and the comfortable temperature in the room directly depend on the power of the boiler. If the power is low, the room will be cold, and if it is too high, fuel will be uneconomical. Therefore, it is necessary to choose a boiler with optimal power, which can be calculated quite accurately.
When calculating it, it is necessary to take into account
:
- heated area (S);
- specific power of the boiler per ten cubic meters of the room. It is set with an adjustment that takes into account the climatic conditions of the region of residence (W sp.).
There are established values of specific power (Wsp) for certain climatic zones, which are for:
- Southern regions - from 0.7 to 0.9 kW;
- Central regions - from 1.2 to 1.5 kW;
- Northern regions - from 1.5 to 2.0 kW.
Boiler power (Wkot) is calculated by the formula:
W cat. \u003d S * W beats. / 10
Therefore, it is customary to choose the power of the boiler, at the rate of 1 kW per 10 kv. m of heated space.
Not only power, but also the type of water heating will depend on the area of \u200b\u200bthe house. A heating design with natural water movement will not be able to efficiently heat a house with an area of more than 100 square meters. m (due to low inertia).For a room with a large area, a heating system with circular pumps will be required, which will push and accelerate the flow of coolant through the pipes.
Since the pumps operate in non-stop mode, certain requirements are imposed on them - noiselessness, low energy consumption, durability and reliability. On modern gas boiler models, the pumps are already built directly into the body.
Features of the selection of a circulation pump
The pump is selected according to two criteria:
- The amount of liquid pumped, expressed in cubic meters per hour (m³/h).
- Head expressed in meters (m).
With pressure, everything is more or less clear - this is the height to which the liquid must be raised and is measured from the lowest to the highest point or to the next pump, if the project provides for more than one.
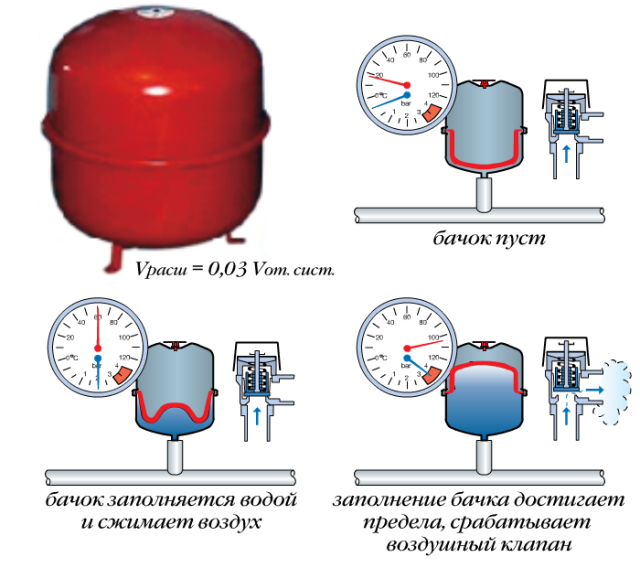
Expansion tank volume
Everyone knows that a liquid tends to increase in volume when heated. So that the heating system does not look like a bomb and does not flow at all seams, there is an expansion tank into which the displaced water from the system is collected.
What volume should be purchased or made a tank?
It's simple, knowing the physical characteristics of water.
The calculated volume of coolant in the system is multiplied by 0.08. For example, for a coolant of 100 liters, the expansion tank will have a volume of 8 liters.
Let's talk about the amount of pumped fluid in more detail.
The water consumption in the heating system is calculated according to the formula:
G = Q / (c * (t2 - t1)), where:
- G - water consumption in the heating system, kg / s;
- Q is the amount of heat that compensates for heat loss, W;
- c is the specific heat capacity of water, this value is known and is equal to 4200 J / kg * ᵒС (note that any other heat carriers have worse performance compared to water);
- t2 is the temperature of the coolant entering the system, ᵒС;
- t1 is the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the system, ᵒС;
Recommendation! For a comfortable stay, the temperature delta of the heat carrier at the inlet should be 7-15 degrees. The floor temperature in the "warm floor" system should not be more than 29ᵒ
C. Therefore, you will have to figure out for yourself what type of heating will be installed in the house: will there be batteries, a “warm floor” or a combination of several types.
The result of this formula will give the coolant flow rate per second of time to replenish heat losses, then this indicator is converted into hours.
Advice! Most likely, the temperature during operation will vary depending on the circumstances and the season, so it is better to immediately add 30% of the reserve to this indicator.
Consider the indicator of the estimated amount of heat required to compensate for heat losses.
Perhaps this is the most complex and important criterion that requires engineering knowledge, which must be approached responsibly.
If this is a private house, then the indicator can vary from 10-15 W / m² (such indicators are typical for "passive houses") to 200 W / m² or more (if it is a thin wall with no or insufficient insulation).
In practice, construction and trade organizations take as a basis the heat loss indicator - 100 W / m².
Recommendation: Calculate this indicator for a particular house in which a heating system will be installed or reconstructed. To do this, heat loss calculators are used, while losses for walls, roofs, windows, and floors are separately calculated. These data will make it possible to find out how much heat is physically given off by the house to the environment in a particular region with its own climatic regimes.
We multiply the calculated loss figure by the area of \u200b\u200bthe house and then substitute it into the water consumption formula.
Now you should deal with such a question as water consumption in the heating system of an apartment building.
The water volume of the heat carrier in the pipe and radiator how the calculation is carried out
The water volume or heat carrier in a wide variety of pipelines, for example, low-pressure polymer ethylene (HDPE pipe), polypropylene pipes, metal-plastic pipes, profile pipes, is important to know when choosing some kind of equipment, especially an expansion tank. For example, in a metal-plastic pipe with a diameter of 16 in a meter of pipe 0.115 gr
heat carrier
For example, in a metal-plastic pipe, a diameter of 16 in a meter of pipe is 0.115 gr. heat carrier.
Did you know? The fastest is not. Yes, and you actually need to know this until you are faced with a choice, such as an expansion tank. Knowing the volume of heat carrier in the heating system is necessary not only for choosing an expansion tank, but also for purchasing antifreeze. Antifreeze is sold undiluted to -65 degrees and diluted to -30 degrees. Having learned the volume of the heat carrier in the heating system, you will be able to purchase an even amount of antifreeze. For example, undiluted antifreeze needs to be diluted 50 * 50 (water * antifreeze), which means that with heat carrier volumes equal to 50 liters, you will need to purchase only 25 liters of antifreeze.
We recommend for you a form for calculating the volume of water (heat carrier) in the water supply and heating radiators. Enter the length of a pipe of a specific diameter and instantly find out how much heat carrier is in this section.
Water volume in pipes of different diameters: calculation
Once you have calculated the volume of the heat carrier in the water metering unit, however, to create a complete picture, and specifically to find out the entire volume of the heat carrier in the system, you will also need to calculate the volume of the heat carrier in the heating radiators.
Volumetric calculation of water in pipes
Volumetric calculation of water in a heating radiator
Water volume in certain metal batteries
Now it will definitely not be difficult for you to calculate the volume of heat carrier in the heating system.
Volumetric calculation of the heat carrier in heating radiators
In order to calculate the entire volume of the heat carrier in the heating system, we also need to add the water volume in the boiler. You can find it in the boiler passport or take approximate numbers:
floor boiler - 40 liters of water;
mounted boiler - 3 liters of water.
A brief guide to using the calculator "Volume calculation of water in a wide variety of pipelines":
- in the first list, select the pipe material and its diameter (it can be plastic, polypropylene, metal-plastic, steel and diameters from 15 - ...)
- in another list we write the footage of the selected pipe from the first list.
- Click "Calculate".
"Calculate the amount of water in heating radiators"
- in the first list, select the center distance and what materials the heater is made of.
- enter the number of sections.
- Click "Calculate".
Heating ‘target=”_blank”>’)
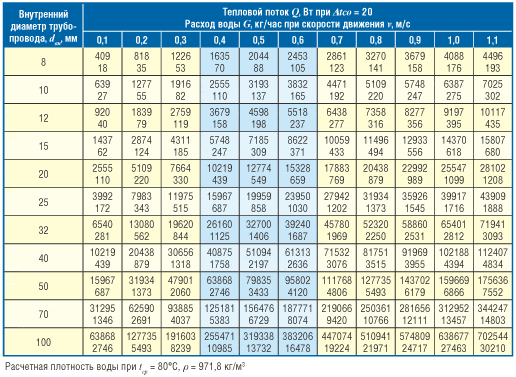
Coolant flow in the heating system
The flow rate in the heat carrier system means the mass amount of heat carrier (kg / s) intended to supply the required amount of heat to the heated room. Calculation of the coolant in the heating system is defined as the quotient of the calculated heat demand (W) of the room (rooms) divided by the heat output of 1 kg of coolant for heating (J / kg).
Some tips for filling the heating system with coolant in the video:
The coolant flow in the system during the heating season in vertical central heating systems changes as they are regulated (this is especially true for the gravitational circulation of the coolant - in more detail: "Calculation of the gravitational heating system of a private house - scheme"). In practice, in calculations, the flow rate of the coolant is usually measured in kg / h.
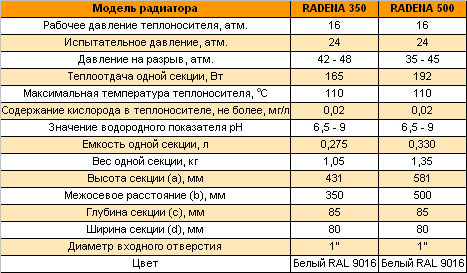
Technical aspects of aluminum batteries
To equip an autonomous heating system, it is necessary not only to perform installation work in accordance with current regulations, but also to choose the right aluminum radiators.This can be done only after a thorough study and analysis of their properties, design features, technical characteristics.
Classification and design features
Manufacturers of modern heating equipment make sections of aluminum radiators not from pure aluminum, but from its alloy with silicon additives. This allows the products to give corrosion resistance, greater strength and extend their service life.
Today, the distribution network offers a wide range of aluminum radiators that differ in their appearance, which are represented by such products as:
- panel;
- tubular.
According to the constructive solution of a single section, which are:
- Solid or cast.
- Extruded or made up of three separate elements, internally bolted together with foam or silicone gaskets.
Batteries are also distinguished by size.
Standard sizes with a width within 40 cm and a height equal to 58 cm.
Low, up to 15 cm high, which makes it possible to install them in very limited spaces. Recently, manufacturers have been producing aluminum radiators of this series of "plinth" design with a height of 2 to 4 cm.
tall or vertical. With a small width, such radiators can reach a height of two or three meters. Such a working arrangement in height helps to efficiently heat large volumes of air in the room. In addition, such an original design of radiators performs an additional decorative function.
The service life of modern aluminum radiators is determined by the quality of the source material and does not depend on the number of its constituent elements, their dimensions and internal volume.
. The manufacturer guarantees their stable operation with proper operation up to 20 years.
Main performance characteristics
Comparative characteristics
Technical characteristics and design solutions of aluminum radiators are developed to provide them with convenient and reliable space heating. The main components that characterize their technical properties and operational capabilities are such factors.
Operating pressure. Modern aluminum radiators are designed for pressure indicators from 6 to 25 atmospheres. To guarantee these indicators in the factory, each battery is tested at a pressure of 30 atmospheres. This fact makes it possible to install this heating equipment in any heating system, where the possibility of water hammer formation is excluded.
Power. This indicator characterizes the thermodynamic process of heat transfer from the surface of the heating battery to the environment. It indicates how much heat in watts the device can produce per unit of time.
By the way, it happens by the method of convection and thermal radiation in the ratio of 50 to 50. The numerical value of the heat transfer parameter of each section is indicated in the device passport.
When calculating the number of batteries required for installation, their power plays a primary role. The maximum heat transfer of one section of the heating aluminum radiator is quite large and reaches 230 watts. Such an impressive figure is due to the high ability of aluminum to heat transfer.
This means that less energy is needed to heat it than for a cast-iron counterpart.
The temperature range of heating the coolant in aluminum batteries exceeds 100 degrees.
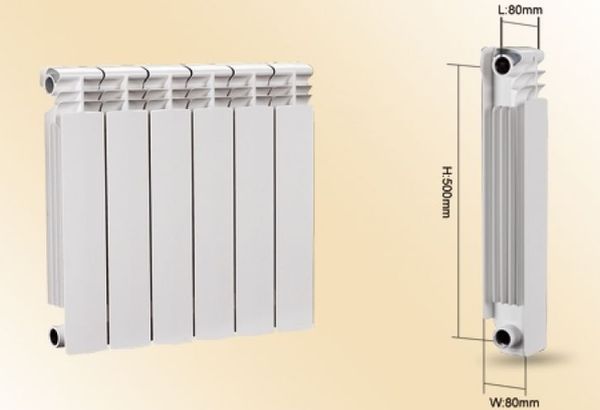
For reference, a standard section of an aluminum radiator 350–1000 mm high, 110–140 mm deep, with a wall thickness of 2 to 3 mm, has a coolant volume of 0.35–0.5 liters, and is capable of heating an area of 0.4– 0.6 square meters.
Antifreeze parameters and types of coolants
The basis for the production of antifreeze is ethylene glycol or propylene glycol.In their pure form, these substances are very aggressive environments, but additional additives make antifreeze suitable for use in heating systems. The degree of anti-corrosion, the service life and, accordingly, the final cost depend on the additives introduced.
The main task of additives is to protect against corrosion. Having a low thermal conductivity, the rust layer becomes a heat insulator. Its particles contribute to clogging of channels, disable circulation pumps, lead to leaks and damage in the heating system.
Moreover, the narrowing of the inner diameter of the pipeline entails hydrodynamic resistance, due to which the coolant velocity decreases, and energy costs increase.
Antifreeze has a wide temperature range (from -70°C to +110°C), but by changing the proportions of water and concentrate, you can get a liquid with a different freezing point. This allows you to use intermittent heating mode and turn on space heating only when needed. As a rule, antifreeze is offered in two types: with a freezing point of no more than -30 ° C and no more than -65 ° C.
In industrial refrigeration and air conditioning systems, as well as in technical systems with no special environmental requirements, antifreeze based on ethylene glycol with anti-corrosion additives is used. This is due to the toxicity of the solutions. For their use, expansion tanks of a closed type are required; use in double-circuit boilers is not allowed.
Other possibilities of application were received by a solution based on propylene glycol. This is an environmentally friendly and safe composition, which is used in the food, perfume industry and residential buildings. Wherever it is required to prevent the possibility of toxic substances entering the soil and groundwater.
The next type is triethylene glycol, which is used at high temperatures (up to 180 ° C), but its parameters have not been widely used.
Types of radiators
The most popular among the total number of convectors are three types:
- Aluminum radiator;
- Cast iron battery;
- Bimetal radiator.
If you know which convector is installed in your home and are able to count the number of sections, then it will not be difficult to make simple calculations. Next, calculate volume of water in the radiator
, table
and all the necessary data are presented below. They will help to accurately calculate the amount of coolant in the entire system.
|
Convector type |
Average volume of water liter/section |
|
Aluminum |
|
|
Old cast iron |
|
|
New cast iron |
Bimetallic
Aluminum
Although in some cases the internal heating system of each battery may differ, there are generally accepted parameters that allow you to determine the amount of liquid that fits into it. With a possible error of 5%, you will know that one section of an aluminum radiator can contain up to 450 ml of water
It is worth paying attention to the fact that for other coolants the volumes can be increased
cast iron
Calculating the amount of liquid that fits in a cast-iron radiator is a little more difficult. An important factor will be the novelty of the convector. In new imported radiators, there are much fewer voids, and due to the improved structure, they heat no worse than the old ones.
The new cast iron convector holds about 1 liter of liquid, the old one will fit 700 ml more.
Bimetallic
These types of radiators are quite economical and productive. The reason why filling volumes can change lies only in the features of a particular model and pressure spread. On average, such a convector is filled with 250 ml of water.
Possible changes
Each battery manufacturer sets its own minimum / maximum allowable standards, but the volume of coolant in the inner tubes of each model may change based on pressure increases.Usually, in private houses and new buildings, an expansion tank is installed on the basement floor, which allows you to stabilize the pressure of the liquid even when it expands when heated.
The parameters are also changing on outdated radiators. Often, even on non-ferrous metal tubes, growths form due to internal corrosion. The problem can be impurities in the water.
Due to such growths in the tubes, the amount of water in the system must be gradually reduced. Considering all the features of your convector and the general data from the table, you can easily calculate the required amount of water for the heating radiator and the entire system.
The circulation pump is selected according to two main characteristics:
G* - flow rate, expressed in m 3 / hour;
H - head, expressed in m.
*To record the coolant flow, manufacturers of pumping equipment use the letter Q. Manufacturers of valves, for example, Danfoss, use the letter G to calculate the flow. This letter is also used in domestic practice. Therefore, as part of the explanations of this article, we will also use the letter G, but in other articles, going directly to the analysis of the pump operation schedule, we will still use the letter Q for flow.
3.1 General information
Need
in heat at heat-using consumers
varies depending on meteorological
conditions, the number of hot
water in domestic hot water systems
water supply, system modes
air conditioning and ventilation
for heating installations. For systems
heating, ventilation and air conditioning
air is the main factor influencing
heat consumption, is the temperature
outside air. heat consumption,
coming to cover loads
hot water supply and technological
consumption, on the outside temperature
air is independent.
Methodology
changes in the amount of heat supplied
consumers in accordance with schedules
their heat consumption is called the system
heat supply control.
Distinguish
central, group and local
regulation of heat supply.
One
of the most important tasks of system regulation
heat supply is to calculate
regime charts with various methods
load regulation.
Regulation
heat load possible by several
methods: temperature change
coolant - a qualitative method;
periodic shutdown of systems -
intermittent regulation; the change
heat exchanger surface.
V
thermal networks, as a rule, is accepted
central quality regulation
according to the main heat load, which
usually is the heating load
small and public buildings.
Central
quality regulation of the release
heat is limited to the smallest
water temperatures in the supply pipeline,
required for heating water
entering the hot water systems
consumer water supply:
for
closed heating systems
less than 70°C;
for
open heating systems - not
less than 60°С.
On the
based on the data obtained, a
network temperature chart
water depending on the temperature
outside air. temperature graph
it is advisable to perform on a sheet
millimeter paper A4 or with
using Microsoft
office
Excel.
On the graph are determined by temperature
break point adjustment ranges
and their description is performed.

.Central
quality regulation of heating
load
Central quality regulation
according to the heating load
in case the thermal load on
housing and communal needs is
less than 65% of the total load of the area
and with respect .
.
With this kind of regulation,
dependent connection schemes for elevators
heating systems water temperature in
server
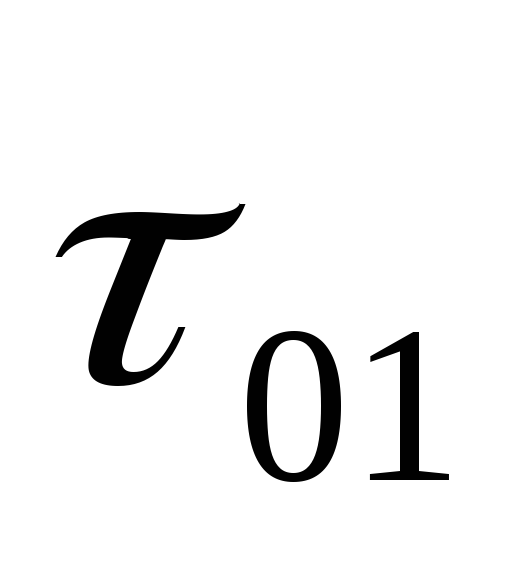
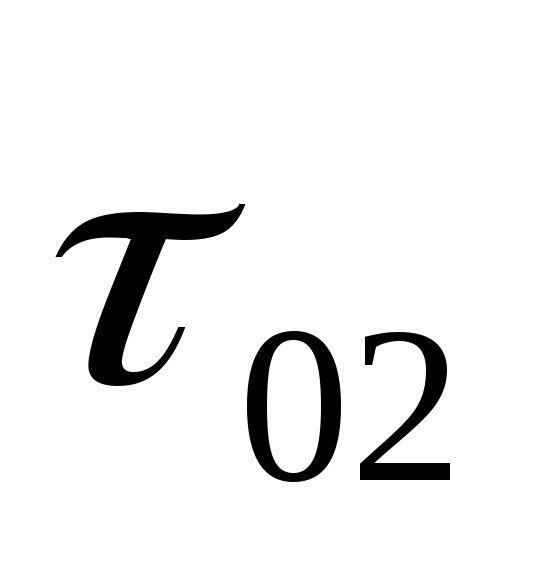

determined by the following expressions:
 (2)
(2)
Payment
produced for value #1. For all
the rest were calculated according to the above
the proposed formula, the results
listed in table 3.
 (3)
(3)
Payment
produced for value #1. For all
the rest were calculated according to the above
the proposed formula, the results
listed in table 3.
where t
- settlement
temperature difference of the heating
instrument, 0 C, determined by
formula:
 ,
,
(4)

here
3 and
2 - calculated
water temperature respectively after
elevator and in the return line
heating network defined at
3 =
95 0 С;
2 =
70 0 С);
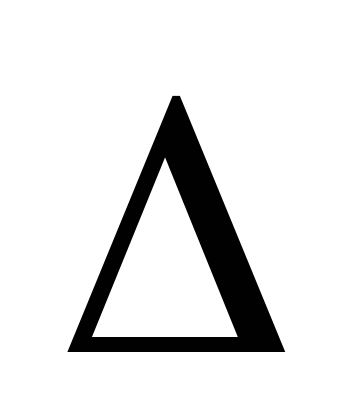
— calculated network temperature difference
water in the heating network
=
1 —
2
(5)
=110-70=40
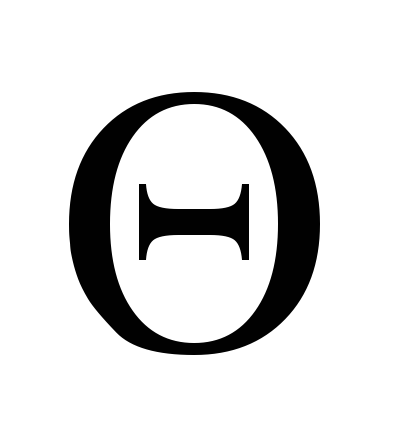
estimated network temperature difference
water in the local heating system,
 (6)
(6)


different temperatures
outside airt
n (usuallyt
n = +8; 0; -10;t
NR v ;t
nro) determine
01;
02 ;
03 and build a heating temperature graph
water. To meet the load
hot water temperature
water in the supply line
01 cannot be lower than 70 0 C in closed
heating systems. For this
the heating schedule is straightened to
the level of these temperatures and becomes
heating and domestic (see example solution).
outdoor temperature,
corresponding to the break point of the graphs
water temperature t
n ",
divides the heating period into ranges
with different control modes:
v
range I with temperature range
outdoor air from +8 0 C tot
n » carried out by group or local
regulation, whose task is
preventing "overheating" of systems
heating and useless heat losses;
v
ranges II and III with temperature range
outdoor air from t
n 'tot
NRO is carried out
central quality regulation.
Table 3 - Temperature chart
|
Temperature |
Temperature |
|||
Correct calculation of the coolant in the heating system
By the combination of features, the undisputed leader among heat carriers is ordinary water. It is best to use distilled water, although boiled or chemically treated water is also suitable - to precipitate salts and oxygen dissolved in water.
However, if there is a possibility that the temperature in the room with the heating system will drop below zero for some time, then water will not be suitable as a heat carrier. If it freezes, then with an increase in volume, there is a high probability of irreversible damage to the heating system. In such cases, an antifreeze-based coolant is used.
General calculations
It is necessary to determine the total heating capacity so that the power of the heating boiler is sufficient for high-quality heating of all rooms. Exceeding the permissible volume can lead to increased wear of the heater, as well as significant energy consumption.
The required amount of heating medium is calculated according to the following formula: Total volume = V boiler + V radiators + V pipes + V expansion tank
Boiler
The calculation of the power of the heating unit allows you to determine the boiler capacity indicator. To do this, it is enough to take as a basis the ratio at which 1 kW of thermal energy is sufficient to efficiently heat 10 m2 of living space. This ratio is valid in the presence of ceilings, the height of which is not more than 3 meters.
As soon as the boiler power indicator becomes known, it is enough to find a suitable unit in a specialized store. Each manufacturer indicates the volume of equipment in the passport data.
Therefore, if the correct power calculation is performed, there will be no problems with determining the required volume.
To determine the sufficient volume of water in the pipes, it is necessary to calculate the cross section of the pipeline according to the formula - S = π × R2, where:
- S - cross section;
- π is a constant constant equal to 3.14;
- R is the inner radius of the pipes.
Having calculated the value of the cross-sectional area of \u200b\u200bthe pipes, it is enough to multiply it by the total length of the entire pipeline in the heating system.
Expansion tank
It is possible to determine what capacity the expansion tank should have, having data on the coefficient of thermal expansion of the coolant. For water, this indicator is 0.034 when heated to 85 °C.
When performing the calculation, it is enough to use the formula: V-tank \u003d (V syst × K) / D, where:
- V-tank - the required volume of the expansion tank;
- V-syst - the total volume of liquid in the remaining elements of the heating system;
- K is the expansion coefficient;
- D - the efficiency of the expansion tank (indicated in the technical documentation).
Currently, there is a wide variety of individual types of radiators for heating systems. In addition to functional differences, they all have different heights.
To calculate the volume of working fluid in radiators, you must first calculate their number. Then multiply this amount by the volume of one section.
You can find out the volume of one radiator using the data from the technical data sheet of the product. In the absence of such information, you can navigate according to the average parameters:
- cast iron - 1.5 liters per section;
- bimetallic - 0.2-0.3 l per section;
- aluminum - 0.4 l per section.
The following example will help you understand how to correctly calculate the value. Let's say there are 5 radiators made of aluminum. Each heating element contains 6 sections. We make the calculation: 5 × 6 × 0.4 \u003d 12 liters.
As you can see, the calculation of the heating capacity comes down to calculating the total value of the four above elements.
Not everyone can determine the required capacity of the working fluid in the system with mathematical accuracy. Therefore, not wanting to perform the calculation, some users act as follows. To begin with, the system is filled by about 90%, after which the performance is checked. Then bleed the accumulated air and continue filling.
During the operation of the heating system, a natural decrease in the level of the coolant occurs as a result of convection processes. In this case, there is a loss of power and productivity of the boiler. This implies the need for a reserve tank with a working fluid, from where it will be possible to monitor the loss of coolant and, if necessary, replenish it.
The amount of coolant in the heating system
The coolant is needed after the installation of a new heating system, after its repair or reconstruction.
Before filling the heating system, it is required to determine the exact amount of coolant in order to buy or prepare the required volume in advance. It is necessary to collect information about the passport volume of all heating appliances and pipelines (in more detail: "Calculation of the volume of the heating system, including radiators"). Usually such data is contained on the packaging or in the reference literature. The volume of pipes is easily calculated from their length and known cross section. For the most common elements of heating networks, the volumes of the coolant are as follows:
- Section of a modern radiator (aluminum, steel or bimetallic) - 0.45 liters
- Radiator section of the old type (cast iron, MS 140-500, GOST 8690-94) - 1.45 liters
- Linear meter of pipe (15 millimeters inner diameter) - 0.177 liters
- Linear meter of pipe (32 millimeters inner diameter) - 0.8 liters
It is not enough for us to calculate the flow rate of the coolant - the formula for calculating the volume of the expansion tank is also absolutely necessary. It is not enough just to sum up the volumes of the components of the heating network (radiators, boiler and pipelines). The fact is that in the process of heating the initial volume of the liquid changes significantly, and therefore the pressure increases. In order to compensate for it, so-called expansion tanks are used.
Their volume is calculated using the following indicators and coefficients:
E - the so-called expansion coefficient of the liquid (calculated as a percentage). It is different for different coolants. For water, it is 4%, for antifreeze based on ethylene glycol - 4.4%.
d is the expansion tank efficiency factor VS is the calculated coolant flow rate (the summed volume of all components of the heat supply system) V is the result of the calculation. Expansion tank volume.
Formula for calculation - V = (VS x E) / d
The calculation of the coolant in the heating system is completed - it's time to fill it!
There are two options for filling the system, depending on its design:
- Self-filling - at the highest point of the system, a funnel is inserted into the hole, through which the coolant is gradually poured. It is necessary not to forget to open the tap at the lowest point of the system and substitute some kind of container.
- Forced pumping with a pump. Almost any low power electric pump will do. During the filling process, the readings of the pressure gauge should be monitored so as not to overdo it with pressure. It is highly advisable not to forget to open the air valves on the batteries.
Section volume and coolant flow
Today, not all autonomous heating systems are filled with water.
. This is due to two factors.
Section size
- A situation arises when the owners need to leave the house without heating for a long time, since due to a long absence there is no need for space heating.
- Water tends to freeze even at zero temperature. When water freezes, it expands and turns into ice, that is, it passes from one physical state to another. During this process, the intermolecular bonds of water are released and changed, as a result, a huge force develops that breaks radiators and pipes made of any metal.
To avoid such situations, to fill the heating system, instead of water, another coolant is used, devoid of the freezing problem. It can be such household antifreezes as:
- ethylene glycol;
- saline solution;
- glycerin composition;
- food alcohol;
- petroleum oil.
Thanks to special additives that are introduced into these components, the coolant compositions retain their aggregate state in liquid form even at low temperatures.
Coolant calculation
Determining the amount of heat carrier flow required for an autonomous heating system requires an accurate calculation. For an easy way to find out how much antifreeze is needed to fill the heating system, there are various calculation tables.
Volume of water in one section
For basic calculations, you can use the information that is presented in thematic reference books:
- A standard section of an aluminum battery contains 0.45 liters of coolant.
- A running meter of a 15 mm pipe contains 0.177 liters, and a pipe with a diameter of 32 mm contains 0.8 liters of coolant.
Information about the characteristics of the make-up pump and expansion tank can be taken from the passport data of this equipment.
The total volume of the heating system will be equal to the total volume of all heating devices:
- radiators;
- pipelines;
- boiler heat exchanger;
- expansion tank.
The refined formula of the main calculation is adjusted taking into account the coefficient of expansion of the coolant. For water it is 4%, for ethylene glycol ─ 4.4%.
Conclusion
When designing an autonomous heating system, many people have a question, how many liters of coolant can one section of an aluminum battery hold.This is necessary in order to calculate the consumption of gas, electricity and determine how much antifreeze you need to purchase if the system does not use water.
During the construction or reconstruction of a private house, the question always arises - what equipment to choose for heating the room, because comfortable living in it in the winter directly depends on this. Therefore, it is necessary to make the right choice of heating.
A heating system is a complex consisting of pumps, appliances, automation equipment, pipelines and other devices designed to deliver heat from a generator to residential premises. The efficient and well-coordinated operation of this system depends on its correct installation, accurate calculation of the number of sections, the selected wiring diagram and other factors.