What is forced circulation?
The natural circulation of the coolant occurs according to physical laws: heated water or antifreeze rises to the top of the system and, gradually cooling down, goes down, returning to the boiler. For successful circulation, it is necessary to strictly maintain the angle of inclination of the direct and return pipes. With a small length of the system in a one-story house, this is not difficult to do, and the height difference will be small.
For large houses, as well as multi-storey buildings. such a system is most often unsuitable - it may form air locks, disruption of circulation and, as a result, overheating of the coolant in the boiler. This situation is dangerous and may cause damage to system components.
Therefore, a circulation pump is installed in the return pipe, immediately before entering the boiler heat exchanger, which creates the necessary pressure and water circulation rate in the system. At the same time, the heated coolant is diverted to the heating devices in a timely manner, the boiler operates normally, and the microclimate in the house remains stable.
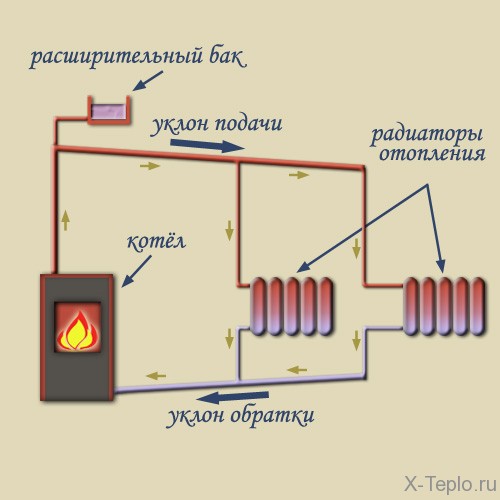
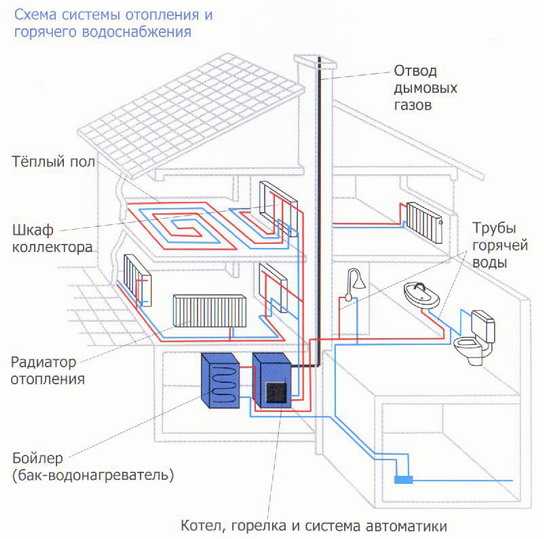
Scheme: elements of the heating system
- the system works stably in buildings of any length and number of storeys;
- it is possible to use pipes of a smaller diameter than with natural circulation, which saves the cost of their purchase;
- it is allowed to place pipes without a slope and lay them hidden in the floor;
- warm water floors can be connected to the forced heating system;
- stable temperature conditions extend the life of fittings, pipes and radiators;
- It is possible to regulate the heating for each room.
Disadvantages of a forced circulation system:
- calculation and installation of the pump is required, its connection to the mains, which makes the system volatile;
- The pump makes noise during operation.
The disadvantages are successfully solved by the correct placement of the equipment: the pump is placed in a separate boiler room next to the heating boiler and a backup power source is installed - a battery or generator.
The principle of operation of a gravity heating system
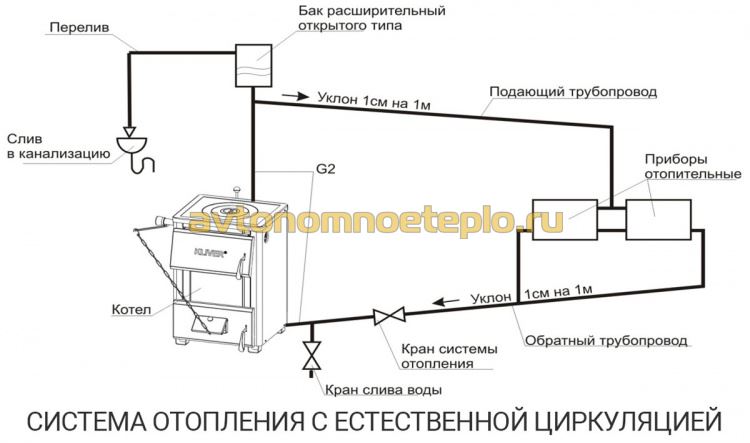
The principle of operation of heating looks simple: water moves through the pipeline, driven by hydrostatic pressure, which appeared due to the different masses of heated and cooled water. Another such design is called gravity or gravity. Circulation is the movement of cooled down in batteries and heavier liquid under the pressure of its own mass down to the heating element, and the displacement of light heated water into the supply pipe. The system functions when the natural circulation boiler is located below the radiators.
In open circuits, it communicates directly with the external environment, and excess air escapes into the atmosphere. The volume of water increased from heating is eliminated, constant pressure is normalized.
Natural circulation is also possible in a closed heating system if it is equipped with an expansion tank with a membrane. Sometimes open-type structures are converted into closed ones. Closed circuits are more stable in operation, the coolant does not evaporate in them, but they are also independent of electricity. What affects circulation pressure
The circulation of water in the boiler depends on the difference in density between the hot and cold liquids and on the magnitude of the height difference between the boiler and the lowest radiator. These parameters are calculated even before the installation of the heating circuit. Natural circulation occurs because the return temperature in the heating system is low. The coolant has time to cool down, moving through the radiators, it becomes heavier and with its mass pushes the heated liquid out of the boiler, forcing it to move through the pipes.

Scheme of water circulation in the boiler
The height of the battery level above the boiler increases the pressure, helping the water to overcome the resistance of the pipes more easily. The higher the radiators are located in relation to the boiler, the greater the height of the cooled return column and with the greater pressure it pushes the heated water up when it reaches the boiler.
The density also regulates the pressure: the more the water warms up, the less its density becomes in comparison with the return. As a result, it is pushed out with more force and the pressure increases. For this reason, gravity heating structures are considered self-regulating, because if you change the temperature of the water heating, the pressure on the coolant will also change, which means that its consumption will change.
During installation, the boiler should be placed at the very bottom, below all other elements, in order to ensure sufficient pressure of the coolant.
Pipes for systems with natural circulation
When choosing the diameter of the pipes, not only the dimensions of the system and the number of radiators play a role, but also the material from which they are made, or rather, the smoothness of the walls. For gravitational systems, this is a very important parameter. The worst situation is with ordinary metal pipes: the inner surface is rough, and after use it becomes even more uneven due to corrosion processes and accumulated deposits on the walls. Therefore, such pipes take the largest diameter.
Steel pipes in a few years may look like this
From this point of view, metal-plastic and reinforced polypropylene are preferable. But metal-plastic fittings are used that significantly narrow the clearance, which can become critical for gravity systems. Therefore, reinforced polypropylene look more preferable. But they have limitations on the temperature of the coolant: the operating temperature is 70 ° C, the peak temperature is 95 ° C. For products made of special PPS plastic, the operating temperature is 95 ° C, the peak temperature is up to 110 ° C. So, depending on the boiler and the system as a whole, it is possible use these pipes, provided that they are quality branded products, and not a fake. Read more about polypropylene pipes here.
Metal-plastic and polypropylene can also be used for the installation of heating systems
But if it is planned to install a solid fuel boiler. then no polypropylene can withstand such thermal loads. In this case, either use steel, or galvanized and stainless steel on threaded connections (do not use welding when installing stainless steel, as the seams leak very quickly)
Copper is also suitable (it is written about copper pipes here), but it also has its own characteristics and must be handled with care: it will not behave normally with all coolants, and it is better not to use it in one system with aluminum radiators (they quickly collapse )
A feature of systems with natural circulation is that they cannot be calculated due to the formation of turbulent flows that cannot be calculated. They are designed based on experience and averaged, empirically derived norms and rules. Basically the rules are:
- raise the acceleration point as high as possible;
- do not narrow the supply pipes;
- put a sufficient number of sections of radiators.
Then another one is used: from the place of the first branching and each subsequent one, they lead a pipe of a diameter smaller by a step. For example, a 2-inch pipe comes from the boiler, then 1 ¾ from the first branch, then 1 ½, etc. The waste is collected from a smaller diameter to a larger one.
There are several more features of the installation of gravity systems. First, it is desirable to make pipes at a slope of 1-5%, depending on the length of the pipeline. In principle, with a sufficient difference in temperature and height, horizontal wiring can also be made, the main thing is that there are no sections with a negative slope (tilted in the opposite direction), which, due to the formation of air pockets in them, will block the movement of water flow.
Gravity single-pipe system with vertical wiring for two wings (circuits)
The second feature is that an expansion tank and / or an air vent must be installed at the highest point of the system. The expansion tank can be open (the system will also be open) or membrane (closed).When installing an open air outlet, there is no need for it to collect at the highest point - in the tank and exit into the atmosphere. When installing a membrane-type tank, the installation of an automatic air vent is also required. With horizontal wiring, the Mayevsky taps on each of the radiators will not interfere - with their help it is easier to remove all air plugs in the branch.
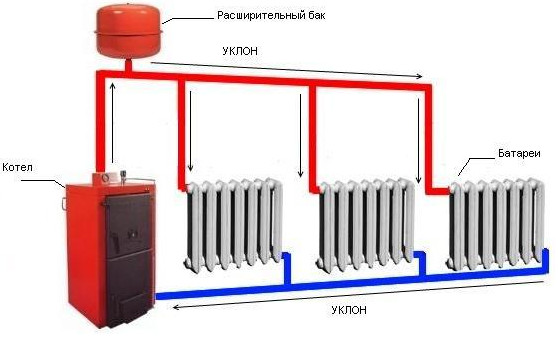
Scheme of installation of gravity heating systems
Since the circulation of water in the heating system occurs without the participation of a pump, for the unhindered flow of fluid through the lines, they must have a diameter larger than in the scheme where water circulation is forced. The gravity system functions by reducing the resistance that water has to overcome: the farther the pipe from the boiler, the wider it is.
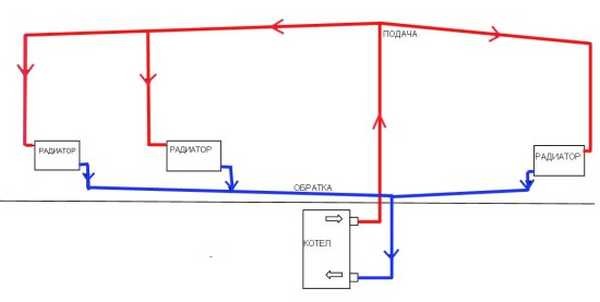
Water heating with natural circulation can have an upper or lower wiring. When the wiring is designed as two-pipe, heated water enters directly into each battery, and does not pass through them one by one, as in a single-pipe scheme.
The upper wiring, in which the coolant first rises to the ceiling, and from there descends to the batteries, is best suited to install such a design. If the wiring is planned lower. then an accelerating circuit is being built: a height difference at which water from the boiler first goes up, where it enters the expansion tank at the upper point of the pipeline, and then goes down to the heating radiators.
The higher the heating device is located, the higher the pressure inside the pipeline. Therefore, the batteries of the upper floors often warm up better than those on the lower ones. Accordingly, if you make heating with natural circulation two-pipe, the batteries placed on the same level as the boiler or below do not warm up enough.
To avoid such a situation, the boiler room is thoroughly buried, providing a sufficiently high pressure for the coolant to pass through the pipes at the required speed. The boiler is placed in the basement, approximately 3 meters below the center of the lowest heating element. Pipes with hot water, on the contrary, are raised as high as possible, placing an expansion tank at the highest point of the structure, and then the water from the supply pipe descends to the radiators.
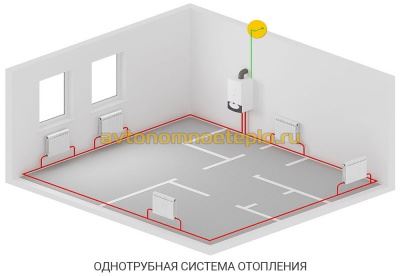
Types of single-pipe system wiring
In a single-pipe system, there is no separation between a direct and a return pipe. The radiators are connected in series, and the coolant, passing through them, gradually cools down and returns to the boiler. This feature makes the system economical and simple, but requires setting the temperature regime and correctly calculating the power of the radiators.
A simplified version of a one-pipe system is only suitable for a small one-story house. In this case, the pipe passes through all the radiators directly, without temperature control valves. As a result, the first batteries along the coolant turn out to be much hotter than the last ones.
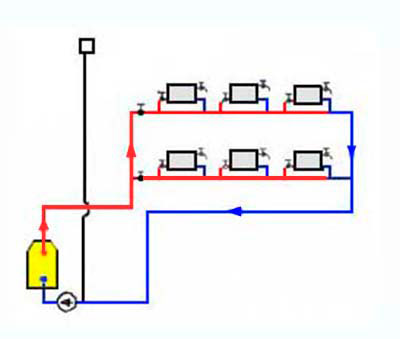
For extended systems, this wiring is not suitable. after all, the cooling of the coolant will be significant. For them, they use the Leningradka single-pipe system, in which the common pipe has adjustable outlets for each radiator. As a result, the coolant in the main pipe is more evenly distributed throughout all rooms. The layout of a single-pipe system in multi-storey buildings is divided into horizontal and vertical.
Horizontal wiring
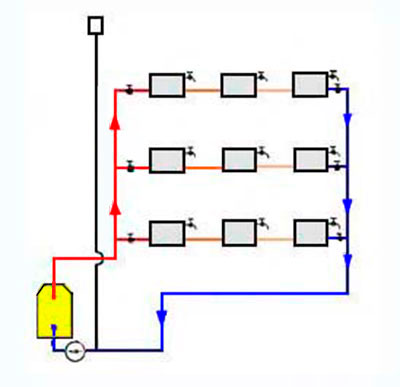
They are combined into a return line riser and fed back to the boiler or boiler. Temperature control taps are located on each floor, and Mayevsky taps are on each radiator.Horizontal wiring can be performed both by flow and by the Leningradka system.
Vertical wiring
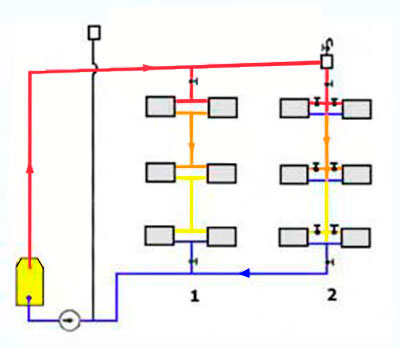
The choice of wiring system for a private house depends mainly on its layout. With a large area of \u200b\u200beach floor and a small number of storeys of the house, it is better to choose vertical wiring, so you can achieve a more even temperature in each room. If the area is small, it is better to choose horizontal wiring, as it is easier to adjust. In addition, with a horizontal type of wiring, you do not have to make extra holes in the ceilings.
Video: one-pipe heating system
The principle of operation of the system with natural circulation
The heating scheme of a private house with natural circulation is popular due to the following advantages:
- Easy installation and maintenance.
- No need to install additional equipment.
- Energy independence - no additional electricity costs are required during operation. In the event of a power outage, the heating system continues to operate.
The principle of operation of water heating, using gravity circulation, is based on physical laws. When heated, the density and weight of the liquid decrease, and when the liquid medium cools, the parameters return to their original state.
At the same time, there is practically no pressure in the heating system. In heat engineering formulas, the ratio is 1 atm. for every 10 m of water column pressure. The calculation of the heating system of a 2-storey building will show that the hydrostatic pressure does not exceed 1 atm. in one-story buildings 0.5-0.7 atm.
Since the liquid increases in volume when heated, for natural circulation, an expansion tank will be required. The water passing through the water circuit of the boiler is heated, which leads to an increase in volume. The expansion tank must be located on the coolant supply, at the very top of the heating system. The task of the buffer tank is to compensate for the increase in liquid volume.
The self-circulating heating system can be used in private houses, making the following connections possible:
- Connection to underfloor heating - requires the installation of a circulation pump, only on a water circuit laid in the floor. The rest of the system will continue to operate with natural circulation. After a power outage, the room will continue to be heated using installed radiators.
- Work with an indirect water heating boiler - connection to a system with natural circulation is possible, without the need to connect pumping equipment. To do this, the boiler is installed at the top of the system, just below the air expansion tank of a closed or open type. If this is not possible, then the pump is installed directly on the storage tank, additionally installing a check valve to avoid recirculation of the coolant.
In systems with gravitational circulation, the movement of the coolant is carried out by gravity. Due to natural expansion, the heated liquid rises up the accelerating section, and then, under a slope, “flows down” through the pipes connected to the radiators back to the boiler.
Increasing temperatures
Another factor is the difference between the density of cold and hot water. We note the following fact - heating with natural circulation is a self-regulating type. Thus, if you increase the temperature of water heating, then its flow rate changes and the circulation pressure becomes higher.
Strong heating of the liquid to a large extent contributes to faster circulation. But this only happens in a cold room: when the air temperature in them reaches a certain point, the batteries will cool down much more slowly.
The density of both the water heated in the boiler and the water already in the radiators is almost equal. The pressure will decrease, the rapid circulation of water will be replaced by a measured circulation inside the system.
As soon as the temperature of the premises of a private house drops again to a certain level, this will serve as a signal to increase the pressure. The system will attempt to equalize the temperature conditions. To do this, you will have to restart the fast circulation process. This is where the ability to self-regulate comes from.
In short, the rule is as follows - a one-time change in temperature and volume of water allows you to get the desired heat output from batteries for space heating.
As a result, comfortable temperature conditions are maintained.
Scheme of action
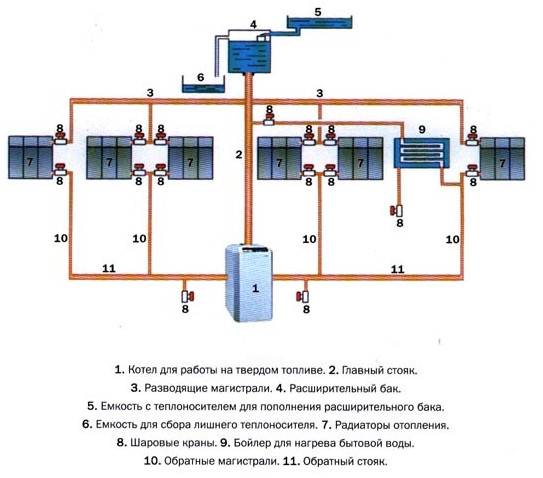
The water heating system includes a boiler (water heater), return and supply pipelines, as well as heating equipment, an expansion tank and a safety valve. The liquid is heated to the desired temperature in the boiler and rises into the supply pipeline and risers due to expansion.
From there, it passes into heating equipment - batteries and radiators, to which it gives off part of the heat. Then the return pipeline sends water to the boiler, where it is again heated to the desired temperature. The cycle repeats as long as the system is operational.
It is important to remember that horizontal pipes are mounted with a slope in relation to the movement of the working medium.
Designing heating with forced circulation
Detailed home heating scheme
The primary task for self-installation of water heating with a circulation pump is to draw up the correct scheme. To do this, you need a plan of the house, on which the location of pipes, radiators, valves and safety groups is applied.
System calculation
At the stage of drawing up the schemes, it is necessary to correctly calculate the parameters of the pump for the forced heating system of a private house. To do this, you can use special programs or do the calculations yourself. There are a number of simple formulas that will help make the calculation:
Where Rn is the rated power of the pump, kW, p is the density of the coolant, for water this indicator is 0.998 g / cm³, Q is the flow rate of the coolant, l, N is the required pressure, m.
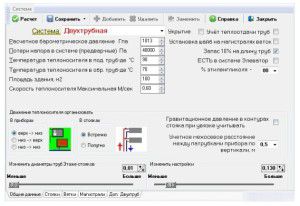
An example of a heating calculation program
To calculate the pressure indicator in the forced heating system of a house, it is necessary to know the total resistance of the pipeline and heat supply as a whole. Alas, it is almost impossible to do it yourself. To do this, you should use special software systems.
Having calculated the resistance of the pipeline in a water heating system with circulation, it is possible to calculate the required pressure indicator using the following formula:
Where H is the calculated head, m, R is the resistance of the pipeline, L is the length of the largest straight section of the pipeline, m, ZF is a coefficient, which is usually equal to 2.2.
Based on the results obtained, the optimal model of the circulation pump is selected.
If the calculated pump power indicators for a self-installed forced circulation heating system are large, it is recommended to purchase paired models.
Installation of heating with circulation
Example of concealed installation of collector heating
Based on the calculated data, pipes of the required diameter are selected, and shut-off valves are selected for them. However, the diagram does not show the method of mounting the trunk. Pipelines can be installed in a hidden or open way. The first is recommended to be used only with full confidence in the reliability of the entire heating system of a private cottage with forced circulation.
It must be remembered that the quality of the components of the system will depend on its performance and performance. In particular, this applies to the material for the manufacture of pipes and valves. In addition, for a two-pipe scheme of a forced circulation heating system, it is recommended to heed the advice of professionals:
- Installation of an emergency power supply for the circulation pump in the event of a power outage;
- When using antifreeze as a coolant, check its compatibility with the materials for the manufacture of pipes, radiators and the boiler;
- According to the house heating scheme with forced circulation, the boiler should be located at the lowest point in the system;
- In addition to the pump power, it is necessary to calculate the expansion tank.
The technology for installing circulation type heating is no different from the standard
It is important to take into account the features of the contour house - the material for making the walls, its heat loss. The latter directly affects the power of the entire system.
Analysis of the parameters of heating systems with forced circulation will help to form an objective opinion about it:
What it is
If a system with forced circulation requires a pressure drop created by a circulation pump or provided by a connection to a heating main, then the picture is different. Heating by natural circulation uses a simple physical effect - the expansion of a liquid when heated.
If we discard the technical subtleties, the basic scheme of work is as follows:
- The boiler heats a certain volume of water. So, of course, it expands and, due to its lower density, is displaced upwards by a colder mass of coolant.
- Having risen to the top point of the heating system, the water, gradually cooling down, by gravity describes a circle through the heating system and returns to the boiler. At the same time, it gives off heat to the heaters and by the time it is again at the heat exchanger, it has a greater density than at the beginning. Then the cycle repeats.
Useful: of course, nothing prevents you from including a circulation pump in the circuit. In normal mode, it will provide faster water circulation and uniform heating, and in the absence of electricity, the heating system will work with natural circulation.
The operation of the pump in a natural circulation system.
The photo shows how the problem of interaction between the pump and the natural circulation system is solved. When the pump is running, the check valve is activated, and all the water goes through the pump. It is worth turning it off - the valve opens, and water circulates through a thicker pipe due to thermal expansion.
Boiler for gravity systems
Since such schemes are mainly needed for a device that is independent of electricity, the boilers must also work without the use of electricity. It can be any non-automated units, except for pellet and electric ones.
Most often, solid fuel boilers operate in systems with natural circulation. They are good for everyone, but in many models the fuel burns out quickly. And if there are severe frosts outside the window, and the house is not sufficiently insulated, then in order to maintain an acceptable temperature at night, you have to get up and throw fuel. Especially this situation is often found where firewood is heated. The way out is to buy a long-burning boiler (non-volatile, of course). For example, in Lithuanian solid fuel boilers Stropuva, under certain conditions, firewood burns up to 30 hours, and coal (anthracite) up to several days. The specifications for Candle boilers are slightly worse: the minimum burning time for firewood is 7 hours, for coal - 34 hours. There are boilers without automation and pumps and the German company Buderus, Czech Viadrus and Polish-Ukrainian Wikchlach, as well as Russian manufacturers: Energiya, Ogonyok.
Non-volatile long-burning boiler Stropuva
There are Russian-made gas-fired non-volatile boilers, for example, Conord. which are produced in Rostov-on-Don. They can be used in systems with natural circulation. The same plant produces energy-independent universal boilers "Don", which are also suitable for operation without electricity. The floor gas boilers of the Italian company Bertta - the Novella Autonom model and some other units of European and Asian manufacturers work in systems with natural circulation.
The second way, which will help increase the time between fireboxes, is to increase the inertia of the system. For this, heat accumulators (TA) are installed. They work well with solid fuel boilers, which do not have the ability to regulate the intensity of combustion: the excess heat is removed to the heat accumulator, in which energy is accumulated and consumed as the coolant cools in the main system. The connection of such a device has its own characteristics: it must be placed on the supply pipeline at the bottom. Moreover, for efficient heat extraction and normal operation - as close as possible to the boiler. However, for gravitational systems, this solution is far from the best. They quite slowly reach the normal circulation mode, but they are self-regulating: the colder it is in the room, the more the coolant cools down, passing through the radiators. The greater the difference in temperatures, the greater the density difference and the faster the coolant moves. And the installed TA makes the heating more inertial, and much more time and fuel are required for acceleration. True, and the heat is given off longer. In general, it's up to you.
To stabilize the temperature in the system, a thermal accumulator is installed.
Approximately the same problems with stove heating with natural circulation. Here, the furnace array itself plays the role of a heat accumulator, and a lot of energy (fuel) is also required to accelerate the system. But in the case of using TA, it is usually possible to exclude it, and in the case of a furnace, this is unrealistic.
From the laws of physics
Suppose that in radiators and a boiler, the temperature of the liquid changes in jumps along the central axes: the upper parts contain hot liquid, and the lower parts contain cold liquid.
Hot water has a lower density, which reduces its weight compared to cold water. As a result, the heating system consists of two communicating vessels closed to each other, in which liquid moves from top to bottom.
A high column formed by cooled water with a large weight, upon reaching the radiators, pushes out a low column. As a result, the hot fluid is pushed and circulation occurs.
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of the coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case it is required to perform a hydraulic calculation of the system, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the pipe diameter, etc. You may need the help of a professional when doing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
In the EU countries, closed systems are the most popular among other solutions. In the Russian Federation, the scheme has not yet been widely used. The principles of operation of a closed-type water heating system with pumpless circulation are as follows:
- When heated, the coolant expands, water is displaced from the heating circuit.
- Under pressure, the liquid enters a closed membrane expansion tank. The design of the container is a cavity divided by a membrane into two parts. One half of the tank is filled with gas (most models use nitrogen).The second part remains empty for filling with coolant.
- When the liquid is heated, pressure is created sufficient to push through the membrane and compress the nitrogen. After cooling, the reverse process occurs, and the gas squeezes the water out of the tank.
Otherwise, closed-type systems work like other natural circulation heating schemes. As disadvantages, one can single out the dependence on the volume of the expansion tank. For rooms with a large heated area, you will need to install a capacious container, which is not always advisable.
Open system with gravity circulation
The open type heating system differs from the previous type only in the design of the expansion tank. This scheme was most often used in old buildings. The advantages of an open system is the possibility of self-manufacturing containers from improvised materials. The tank usually has modest dimensions and is installed on the roof or under the ceiling of the living room.
The main disadvantage of open structures is the ingress of air into pipes and heating radiators, which leads to increased corrosion and rapid failure of heating elements. Airing the system is also a frequent "guest" in open circuits. Therefore, radiators are installed at an angle, Mayevsky cranes are required to bleed air.
Single pipe system with self-circulation
This solution has several advantages:
- There is no paired pipeline under the ceiling and above the floor level.
- Save money on system installation.
The disadvantages of such a solution are obvious. The heat transfer of heating radiators and the intensity of their heating decreases with distance from the boiler. As practice shows, a single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation, even if all slopes are observed and the correct pipe diameter is selected, is often redone (by installing pumping equipment).
Two-pipe system with self-circulation
The two-pipe heating system in a private house with natural circulation has the following design features:
- Supply and return flow through separate pipes.
- The supply pipeline is connected to each radiator via an inlet.
- The battery is connected to the return line with the second eyeliner.
As a result, a two-pipe radiator type system provides the following advantages:
- Uniform distribution of heat.
- No need to add radiator sections for better warm-up.
- Easier to adjust the system.
- The diameter of the water circuit is at least one size smaller than in single-pipe schemes.
- Lack of strict rules for installing a two-pipe system. Small deviations regarding slopes are allowed.
The main advantage of a two-pipe heating system with lower and upper wiring is the simplicity and at the same time the efficiency of the design, which allows you to level errors made in the calculations or during installation work.
Power calculation
The effective heat output of the boiler is calculated in the same way as in all other cases.
By area
The simplest way is the calculation recommended by SNiP for the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. 1 kW of thermal power should fall on 10 m2 of the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. For the southern regions, a coefficient of 0.7 - 0.9 is taken, for the middle zone of the country - 1.2 - 1.3, for the regions of the Far North - 1.5-2.0.
Like any rough calculation, this method neglects many factors:
- Ceiling heights. It is far from being the standard 2.5 meters everywhere.
- Heat leaks through openings.
- The location of the room inside the house or against external walls.
All calculation methods give large errors, so the thermal power is usually included in the project with some margin.
By volume, taking into account additional factors
A more accurate picture will give another method of calculation.
- The thermal power of 40 watts per cubic meter of air volume in the room is taken as the basis.
- Regional coefficients apply in this case as well.
- Each standard size window adds 100 watts to our calculations. Each door is 200.
- The location of the room near the outer wall will give, depending on its thickness and material, a coefficient of 1.1 - 1.3.
- A private house, in which the bottom and top are not warm neighboring apartments, but the street, is calculated with a coefficient of 1.5.
However: and this calculation will be VERY approximate. Suffice it to say that in private houses built using energy-saving technologies, the project includes a heating power of 50-60 watts per square meter. Too much is determined by heat leakage through walls and ceilings.
Advantages of installing a two-pipe system
When designing water heating with forced circulation for a private house, they choose, based on the material capabilities of the owner, a one-pipe or two-pipe scheme. A single-pipe system is cheaper, easier to install, and a two-pipe system is more efficient in operation. When installing a horizontal two-pipe heating system, three pipeline laying schemes are possible: dead-end, associated and collector.
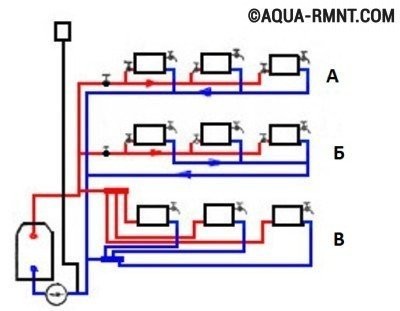
We note right away that the latter, namely the collector pipe layout, has the greatest efficiency. However, its implementation increases the consumption of materials, as well as the complexity of the installation work.