Weaknesses of electric boiler plants
- It is necessary to check at the electrical substation the possibility of providing the power necessary for the operation of the mini-boiler room and install a separate line for connecting the boiler.
- It is necessary to provide for the possibility of stopping the mini-boiler house due to interruptions in the supply of electricity, both in the event of an accident and during maintenance work on the line.
You may also be interested
Individual heating is being introduced everywhere, and every year it becomes more and more popular. No wonder: an autonomous boiler room makes users independent of state heating mains, allows you to turn the heating on and off at will, as well as control its power. In addition, in the long run, individual heating saves quite an impressive amount of money.
Wood-fired boilers make sense primarily for facilities located at a distance from gas mains, or for forestry and timber processing industries, for which it is simply not advisable to use liquid or gaseous fuels, and it is also necessary to resolve the issue of waste disposal. At the same time, wood-fired boilers are suitable for servicing residential, domestic, industrial, social and administrative buildings: in other words, they are completely universal.
wall boiler
How meaningful is such an opportunity as an application for the home? What food do they need? How to connect them correctly? What safety precautions must be observed during installation and operation? As you can see, there are many questions, and that's not all. At present, ordinary consumers are trying to live well in terms of coziness and comfort, which means that the attitude to heating boilers is becoming the most demanding. No one wants to mess around with maintenance anymore - everyone wants to install, connect and forget.
Block-modular solid fuel boilers
For the convenience of consumers and simplifying installation, fully equipped and ready-to-work boiler rooms are assembled at the factory.
There are two types of modules:
- Container block-modular solid fuel boiler house. It is assembled in insulated metal containers installed using loading equipment. The advantage of the design is the possibility of freely completing and increasing the productivity of the station at the request of the customer. The disadvantage is the high installation requirements and the high installation time.
- Mobile block-modular boiler rooms based on solid fuel boilers. The stations are mounted on a car frame with wheels. By design, they resemble a car trailer. The station is easy to mount and connect, but has limitations regarding performance and configuration.
Regardless of the type chosen, BMCs are equipped with the following:
- Heating equipment - BMK are equipped with models of world manufacturers of boilers. Optionally, you can choose German Buderus or domestic ZOTA, etc.
- Automation - a control panel is installed in the boiler room. The operation of the boiler is monitored by one operator who controls the process of heating the coolant. Automation fully regulates the working process: the supply of fuel and air.
- Water treatment and security system.
Fuel consumption in BMK is 20-30% less than in industrial boilers purchased separately. Thanks to the factory settings and equipment, it is possible to achieve maximum efficiency and economy.
Requirements for BMK on solid fuel
During the assembly of the module, all installed equipment is registered with state supervision bodies, in particular Rostekhnadzor. After the assembly, the manufacturer invites a representative of the supervisory authorities and carries out the launch and commissioning of the station.
The consumer receives a fully finished boiler room. All devices and equipment are set up and ready for operation. To get started, you will need to connect the power supply and the heating system to the outlets specially designed for this. After that, you can start the BMC.
The technical characteristics of the BMC on solid fuel fully comply with those declared by the manufacturer and do not change during operation. Installation and connection of the boiler room is carried out by a representative of the manufacturer. If necessary, independent connection is allowed.
The climatic company "Termomir" offers high power hot water boilers in assortment.
A heating boiler is a device that, by means of fuel combustion (or with the help of electricity), heats the coolant. Further, the coolant circulates through the heating system, giving off the received thermal energy through radiators, underfloor heating, etc. devices and space heating.
The main characteristics of heating boilers are: power in kW, the number of heating circuits, the type of fuel, the type of combustion chamber and the method of installation, additional equipment includes, for example, a pump, as well as boiler control, etc.
You can select the required power of the heating boiler for a private house or apartment using the formula - 1 kW for heating 10 m 2 insulated premises with a ceiling height of up to 3 m. If heating of the basement, glazed rooms with high ceilings, etc., as well as hot water is required, the boiler power must be increased.
The heating boiler can have 1 (only for heating) or 2 circuits (heating and hot water supply (DHW)). An indirect heating boiler can be connected to a single-circuit hot water boiler or a model with an already built-in boiler can be purchased. Heating boilers can be floor and wall (mounted). Wall-mounted boilers most often have low power and dimensions, and high-power industrial boilers are floor-mounted, have large sizes and are installed in separate boiler rooms.
How to choose the best boiler and how to choose according to the area can be found in the articles: How to choose a heating boiler and How to choose a gas boiler. From the highest quality boiler manufacturers, we recommend European brands Buderus, Bosch, Vaillant, Ariston, Baxi and Protherm.
Need help choosing or haven't found the right model? Call!
Characteristics edit edit code
Hot water boilers are small (4-65 kW), medium (70-1800 kW) and large (from 1.8 MW) power.
- Nominal inlet water temperature - the water temperature that must be provided at the inlet to the boiler at rated heating output, taking into account allowable deviations. It is 60-110 °C for different models.
- The minimum inlet water temperature is the inlet water temperature that provides an acceptable level of low-temperature corrosion of pipes of heating surfaces (under the action of condensate falling out of gases). Depends on the humidity and sulfur content of the fuel; usually for gas boilers is 60 ° C, for rare models a little lower.
- The maximum outlet water temperature is the temperature of the water at the outlet of the boiler, at which the nominal value of water subcooling to boiling at operating pressure is ensured. The main parameter for classifying boilers as dangerous objects, in the CIS, regulations clearly distinguish between boilers up to 115 °C inclusive and above this value. The nominal outlet temperature can be from 70°C to 150°C and above.
- The temperature gradient of water in a hot water boiler is the difference in water temperatures at the outlet of the boiler and at the inlet to the boiler. Cast iron boilers have more stringent restrictions in this parameter compared to steel ones.
STEAMRATOR
BEREG Group of Companies is the official dealer of the Finnish manufacturer of steam boilers and mobile block-modular steam boilers STEAMRATOR 
Mobile and stationary block-modular STEAMRATOR steam generators are widely used in public utilities, at construction sites, in the maintenance or repair of underground utilities, in oil production and in other areas of industry and the national economy.
Due to their relatively compact dimensions and well-thought-out design, STEAMRATOR modular steam generators are often used as a source of steam for process needs.
STEAMRATOR mobile steam generators are certified by the State Standard of the Russian Federation and have permission from Rostekhnadzor for use in Russia.
| The lineup: | MH 700 | MHC 700N | MHT 700 | STEAM800 | SteamMate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (own / equipped), kg | 440 / 440 | 1515 / 3540 | 1500 / 2460 | 3800 / 5700 | 40 / 40 |
| Length, mm | 2 000 | 2 135 | 4 300 | 3 600 | 550 |
| Width, mm | 910 | 1 720 | 2 100 | 2 240 | 530 |
| Height, mm | 1 365 | 1 780 | 2 100 | 2 210 | 850 |
| Productivity, kg/h | 350 | 350 | 350 | 800 | up to 60 |
| Thermal power, kW | 200 | 200 | 200 | 530 | 40 |
| Water volume of the coil, l | 30 | 30 | 30 | 45 | 10 |
| Heat transfer area, m 2 | 6,85 | 6,85 | 6,85 | 10,4 | 1,04 |
| Operating pressure range, bar | up to 13 | up to 13 1) | up to 13 | 1-10 | up to 9 |
| Design pressure, bar | 15 | 15 2) | 15 | 15 | 10 |
| Number of steam outlets | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Maximum electricity consumption during steam generation, kW | 0,85 | 0,85 | 0,85 | 4,5 | — |
| Power supply voltage, V | 230 | 230 | 230 | 380 | — |
| Water pump | piston | piston | piston | piston | manual 3) |
| Burner | Oilon KP 26 | Oilon KP 26 | Oilon KP 26 | Oilon KP 50H | injection gas |
| Type of fuel | diesel | diesel | diesel | diesel | liquefied gas |
| Fuel consumption (at 100% power) | 20 l/hour | 20 l/hour | 20 l/hour | 55 l/h | 5 kg/hour |
| Efficiency, % | 80 — 90 | 80 — 90 | 80 — 90 | 80 — 90 | 70 — 80 |
| Fuel tank volume, l | — | 167 | 118 | 700 | — |
| Water tank volume, l | — | 1880 | 760 | 1 500 | — |
| Service life of a steam generator equipped at the same time, hour | — 4) | until 6 | up to 2 | ~ 2 | — 4) |
| Water level indicator | — | X | X | X | — |
| Fuel gauge | — | X | X | X | — |
| Power of heating elements during idle time of the steam generator, kW | 0,75 | 1,5 | — | 1,5 | — |
| Gasoline generator power, kW | — | — 2) | 2.2 | — | — |
| Gasoline generator fuel consumption, l/h | — | — | 0,23 | — | — |
| Steam hose, m | — 5) | 10 5) | 15 5) | 30 5) | — 6) |
| Nozzle set 7) | — 3) | X | X | — 3) | — |
1) - possible 1 - 56 bar (power supply voltage 380 V) 2) - possible 60 bar (power supply voltage 380 V) 3) - optional equipment 4) - service life depends on the volume of fuel and water tanks used 5) - additional equipment possible delivery of steam hoses 10, 15, 20 or 30 m long 6) — additional delivery of steam hoses is possible: rubber hose 10 m long Teflon 10, 15 or 20 m long 7) — the set of nozzles includes: rubberized handle scraper nozzle nozzle nozzle nozzle for steaming pipes
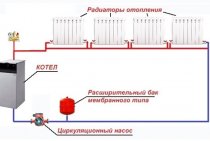
Advantages of electric boilers
It may not necessarily work on electric energy. There are other types of fuel as well. For example, coal or firewood, fuel oil or oil, gas. But with all this diversity electric boiler room
has its own advantages. I must say that electric is cheaper due to the cost of equipment. Therefore, when buying and installing this unit, you will not need large financial investments.
Electricity is the second low cost fuel after gas. Therefore, in the absence of centralized gas pipelines near your home, you can connect equipment such as, for example, electrical. Additional monetary savings will be even more significant if you remember that electric boilers do not require maintenance services.
How to connect the unit correctly
If we consider an electric heating boiler from the point of view of fire safety, then it meets all standards and requirements. Such a unit simply cannot catch fire. The only thing that can lead to a fire is improperly selected wiring in terms of insufficient cross-section of the wire itself. If the cross section is small, then there is a high probability of heating and ignition. In order to choose the right wire, or rather, its cross section, it is necessary to apply the rule known to all electricians - eight amperes of current should fall on one square millimeter of the cross section.
Range of modern equipment
The best solution for using an electric boiler is to connect it to the "warm floor" system. This is due to the fact that among all known heat sources, electric ones are the most expensive.A warm floor does not require high temperatures, so here you can save a lot. In such situations, wall-mounted electrical units are most often used. They are not only compact, but also a kind of mini-boiler rooms, the design of which already includes a circulation pump and an expansion tank, if necessary.
In general, with a pump today in its category is an effective model. Efficiency is due to the uniform distribution of the coolant over the heating devices. And this allows not only to evenly distribute heat throughout the rooms, but also save on electricity by lowering the temperature of the coolant itself.
Oil-fired diesel boilers
Liquid fuel boilers are very close (according to the principle of fuel combustion) to gas boilers. Modern liquid fuel burners provide a very high degree of fuel atomization, so the combustion of liquid fuel is really as close as possible to the combustion of gas.
Diesel fuel (or "fuel oil") is widely used around the world as either a primary or backup fuel. However, the cost of diesel fuel has been very high in recent years. Dual-fuel boilers (gas/oil, gas/diesel) that run on solid fuel and with interchangeable burners can run on gas or diesel fuel.
Large capacity boilers must be equipped with an economizer, which is an additional heat exchanger that utilizes the heat of the flue gases. Thus, depending on the type of economizer, it is possible to increase the efficiency of the boiler from 4 to 12%.
For steam boilers and hot water boilers, mainly steel ferrous metal tubular economizers are used. The task of these units is to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases without condensation of water vapor. For hot water low-temperature boilers, stainless steel condensing heat exchangers are used, mainly of a lamellar design.
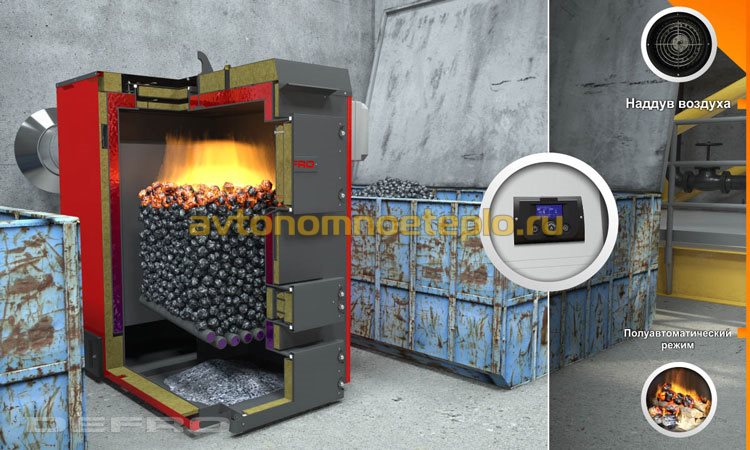
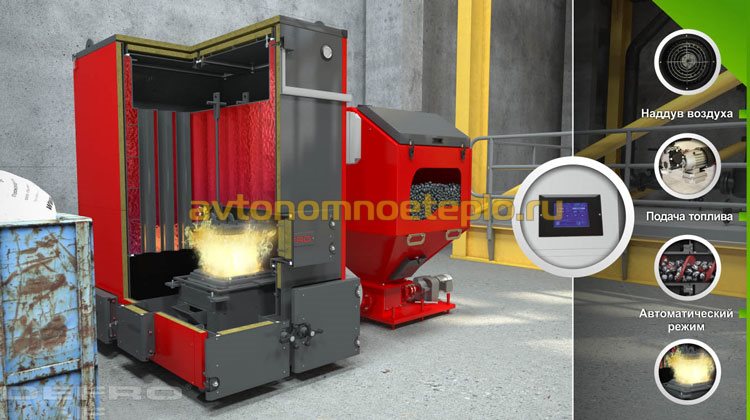
Types of industrial solid fuel boilers
- According to the principle of operation - classic units are practically not used anymore. Instead of them, industrial pyrolysis boilers are increasingly being installed on long-burning solid fuels. The principle of operation of gas-generating equipment is based on the afterburning of carbon dioxide produced during fuel combustion. Industrial pyrolysis boiler is the most economical model. Payback of equipment is achieved in 2-3 heating seasons.
According to the degree of automation - industrial solid fuel hot water heating boilers are offered with mechanical and manual fuel supply. The operation of automatic models is fully controlled by a microprocessor controller. Automation regulates the supply of fuel, the injection of air into the furnace and the removal of combustion products. Modern models are equipped with automatic soot removal. The use of the controller increases the cost-effectiveness of devices, compared with classical models, by 30-40%. Additional savings from automation is achieved due to the absence of the need for the constant presence of maintenance personnel in the boiler room.
Additional functions - in addition to heating, boilers work to produce hot water and steam.
The principle of operation of an industrial solid fuel boiler is not much different from conventional household equipment. The main difference is greater productivity and, accordingly, increased fuel consumption.
Steam boilers of high power
Industrial steam boilers of high power on solid fuels, simultaneously work to heat the coolant and produce steam. The principle of operation is as follows:
- The water entering the heat exchanger is preheated by the air heated during the combustion of the fuel.
- Fuel combustion occurs at high temperatures. Water is brought to the boiling point and evaporated.
- Wet steam enters a special collector, where moisture particles are removed.After that, the steam is additionally heated to the required temperature.
Steam industrial boilers are divided into two categories, according to the heat exchanger inside the device. There are fire tube and water tube units.
Hot water industrial boilers
The device of industrial hot water boilers does not provide for the production of steam, as in the previous model of heating equipment. Boilers for industrial use are distinguished by the following characteristics:
- Versatility - almost all solid fuel units are designed to be able to work on any type of solid fuel: firewood and wood waste, coal, sawdust, peat and briquettes. The efficiency of the models is somewhat lower than that of household equipment, which is offset by the unpretentiousness of the equipment to fuel quality.
- High performance - hot water industrial boilers have a capacity of up to several MW. Simultaneously with the heating of the coolant, water is heated for hot water supply. Industrial equipment is capable of heating large premises or a whole cottage village.
Industrial long-burning pyrolysis boilers have a design that allows you to pre-prepare fuel for the gas generation process. The gas generation process requires that the moisture content of the feedstock be no higher than 30%. Air is forced into the combustion chamber, which preheats and dries the fuel.
METHODS FOR DETERMINING QUALITY INDICATORS
Table 4
|
Quality indicator name |
Quality indicator designation |
Method for determining the quality indicator |
Document confirming the value of the indicator |
|
1. Purpose indicators |
|||
|
1.1. Functional and technical indicators |
|||
|
1.1.1. Rated steam capacity (GOST 23172), |
Dnom |
Measurement. Tests according to the established methodology |
Working design of the boiler, test reports, report on them and |
|
1.1.2. Nominal steam parameters (GOST 23172): |
|||
|
pressure, MPa |
p |
Also |
Also |
|
temperature, °C |
t |
||
|
1.1.3. Rated intermediate steam temperature |
tp.p. |
||
|
1.1.4. Characteristics of the main (warranty) |
|||
|
1.1.4.1. Net calorific value |
registration |
Working project of the boiler |
|
|
1.1.4.2. Maximum ballast, ash abrasiveness and |
— |
Also |
|
|
1.1.5. Exhaust gas temperature at normal |
Vyx |
Measurement. Tests according to the established methodology |
Boiler design. Report or acts on tests and |
|
1.1.6. Loss of pressure in the path of the intermediate |
DRprom |
Also |
Also |
|
1.2. Structural indicators |
|||
|
1.2.1. Specific gravity of pressure boiler metal |
— |
Estimated |
Working project of the boiler |
|
1.2.2. Boiler specific gravity, t/(t h-1) |
— |
Also |
|
|
1.3. Agility indicators |
|||
|
1.3.1. Permissible estimated number of starts per term |
N |
Estimated, according to the established methodology |
Working project of the boiler |
|
1.3.2. Permissible rate of load change in |
— |
Also |
Also |
|
1.3.3. Lower range limits |
Measurement. Tests according to the established methodology |
Detailed design of the boiler, report or acts on tests and |
|
|
2. Reliability indicators |
|||
|
2.1. MTBF, h |
TO |
Statistical |
Operational statistics |
|
2.2. Availability factor |
KG |
Also |
|
|
2.3. Established service life between major |
Tsl.o.c.r |
||
|
2.4. Estimated boiler service life, years |
Tsl.r.p |
||
|
2.5. Estimated life of those working under pressure |
TR |
Estimated, according to the established methodology |
Working project of the boiler |
|
2.6. Estimated service life (resource) before replacement |
Tr.z |
Statistical |
Operational statistics |
|
2.7. Specific total labor intensity of repairs per 1 |
— |
According to repair organizations and data |
|
|
3. Indicators of economical use of fuel |
|||
|
3.1. Gross efficiency at nominal steam output |
h |
Measurement. Tests according to the established methodology |
Working design of the boiler, test reports or report on |
|
4. Manufacturability indicators |
|||
|
4.1. Deliverable blockiness factor (see p. |
TOp.b. |
Estimated |
Working project of the boiler |
|
4.2. Maintainability factor (see appendix |
— |
Technical (working) design of the boiler, section on |
|
|
5. Ergonomic indicators |
|||
|
5.1. Equivalent sound level in zones |
— |
Measurement. Measurements during tests according to GOST |
Test report or certificates and operating data |
|
6. Environmental performance |
|||
|
6.1. Specific emission of nitrogen oxides during combustion |
— |
Measurement. Tests according to the established methodology |
Also |
|
7. Qualitative characteristics |
|||
|
7.1. Possibility of operation of the boiler on sliding pressure |
— |
Measurement. Tests according to the established methodology |
Working design of the boiler, report or test reports |
(Changed edition, Rev. No.
1).
INFORMATION DATA
1. DESIGNED
AND INTRODUCED by the Ministry of Heavy, Energy and Transport Engineering
the USSR
2. APPROVED AND
INTRODUCED BY Decree of the USSR State Committee for Management
product quality and standards dated 27.09.89 No. 2941
3. INTRODUCED
FOR THE FIRST TIME
4. REFERENCE REGULATIONS AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS
|
The designation of the NTD to which the link is given |
Item number |
|
, |
|
|
GOST 12.1.050-86 |
Appendix |
|
, |
|
|
GOST 3619-89 |
, |
|
, |
|
|
Appendix |
|
|
GOST 24569-81 |
|
|
Sanitary norms SN-245 |
2.1 |
5.
The limitation of the period of validity was lifted according to the protocol No. 5-94 of the Interstate Council
for standardization, metrology and certification (IUS 11-12-94)
6. EDITION
(November 2005) with Amendment No. 1 approved in November 1990 (IUS 2-91)
Construct difference
By design features, boilers are divided into:
- fire-tube;
- water pipe.
Fire-tube boiler (gas-tube, smoke-fire and smoke-fire-tube) is a steam or water-heating boiler, in which the heating surface consists of tubes of small diameter, inside which hot products of fuel combustion move. Heat exchange occurs by heating the coolant (water), which is located outside the tubes (in a water jacket).
Fire-tube boilers are widely used in Ukraine and European countries. They have a simple and reliable design, a large water volume, which serves as a natural damper, which evens out thermal stresses inside the boiler body, thus ensuring a long service life and consistently high efficiency.
The maximum performance of fire tube boilers is 35 MW in terms of power and 25 bar in terms of overpressure. This limitation is due to the fact that the fire-tube boiler is an all-welded structure, which is manufactured at the factory and delivered assembled to the installation site. The limiting capacity of a fire-tube boiler is dictated by the size of the boiler, which can be transported to the site by road, rail or sea.
A water-tube boiler is a steam or water-heating boiler, in which the heating surface (screen) consists of tubes inside which the coolant (water) moves. Heat exchange occurs by heating the tubes with hot products of the burning fuel. Distinguish direct-flow and drum water-tube boilers.
Water tube steam boilers are much more complex in design than fire tube boilers. Water-tube boilers have a relatively smaller water volume compared to fire-tube boilers.These boilers respond faster to changing loads, they are easy to transport (they can be delivered in parts), they can be assembled on site. This explains why water-tube boilers are used for high heat loads and high steam pressure.
The disadvantage of water-tube boilers is that there are many units and assemblies in their design, the connections of which become unusable over time, which is dangerous at high pressures and temperatures. However, despite this, the heat exchanger of a water-tube boiler is easier to repair than the body of a fire-tube boiler.