Thermal power calculation
The documentation provided for each heating device specifies the heat flow at a standard temperature delta between the room air and the coolant (usually 70 degrees). If there are no documents, then it is worth focusing on the value of 180 watts per section for any device in which the center distance of the connections is 500 millimeters.
The easiest way to calculate the heat output of a heating system is to divide the area of the house by 10. The result obtained is the required heat output in kilowatts. If the house is located in the southern region, then for every 10 "squares" of area there should be 0.7-0.9 kW of power, and in the north - 2 kW. But this calculation is approximate. A more accurate calculation of the thermal power can be as follows. For every meter of volume of the house should be 40 watts. In addition, additional coefficients are used (the same as in the previous case, depending on the region). If the house is private, then the resulting value must be multiplied by 1.5. The corner flat requires multiplying the result by 1.2. To this result, you need to add 200 kW for each door and 100 kW for each window.
In case of severe frosts, which are not typical for this area, it is recommended to increase the heat output by 20%. It also does not hurt to install a throttle in front of the heaters to control the patency of the coolant supply or a thermostatic head.
Electricity and heating
Electric heater
Electricity is one of the best achievements of technological progress. Its transmission through electric networks occurs at any distance and with minimal losses, and its use at the place of consumption is environmentally friendly.
Modern electric heating systems and appliances are simple, economical, safe to operate, and also characterized by compactness and compatibility with automatic indoor climate control systems.
A necessary and sufficient condition for the arrangement and use of heating using electric energy is the availability of a source of this type of energy and reliable power supply networks that can withstand the load of the relevant devices.
The installation of new and reconstruction of existing electrical networks in individual houses requires much lower costs than the implementation of new or repair and reconstruction of existing water heating systems connected to boilers that burn solid or liquid fuels. A comparison of water and electric heating shows that the cost of installing water from scratch is at least three times more expensive. The operating costs, fuel costs, and low efficiency of traditional liquid heating make electric home heating even more preferable.
Planning and design
Before choosing a heating system built on the principles of using electric current, you should find out the total required power consumption for the future system. This power is determined from the following factors:
- House area.
- Seasonality of home heating.
Based on the power required for heating, it is necessary to make sure that the transformer substation from which the house is powered has sufficient power. If the power of the substation is less than necessary, then it will be necessary to take the necessary measures to change the connection station or increase the power of the existing substation. If it is impossible to implement these measures, in order to obtain the required power, in order to avoid emergency situations, electricity heating will have to be completely abandoned, or it will be used as auxiliary or main heating with the main or additional, respectively, heating of another type.
The choice of heating devices is different depending on whether the house is used for living all year round or as a summer cottage for the period from spring to autumn. But the most important thing for a house is thermal insulation, because. any perfect, powerful system will not warm if the thermal insulation is in a deplorable state.In addition, significant heat losses will lead to high energy costs.
From the point of view of safety for consumers, heating with electricity is the best among other types.
But when planning it, one should take into account the condition and power of the electrical wiring at home, and in the case of a large heated area and, as a result, a large total power consumption of heating appliances, a three-phase power supply may be required
In a house under construction, heating with electricity is provided in the main design of the building in order to avoid repairs or reconstructions of the building itself during the installation of electric heating equipment. And installation and carrying out related work will require the involvement of qualified specialists.
Advantages
In general, heating a house with electricity has a number of advantages, including:
- High efficiency.
- Convenience, ease of use of the system.
- Efficient management, regulation of heat transfer.
- Relatively small dimensions of heating devices that are unpretentious or do not need maintenance.
- Electric heating is highly hygienic and environmentally friendly in operation.
- Quiet heating system.
- Combined heat supply, with the use of electrical heating devices, is versatile and reduces costs.
Gas heating
A double-circuit boiler is a very convenient device.
Gas heating is by far one of the best. Natural gas is an economical, efficient, safe, environmentally friendly fuel.
Gas and electric heating are close in their efficiency, safety and a number of other advantages. But a closer look reveals its specific shortcomings.
Comparison with electric boilers reveals the following. Electric boilers are more expensive than gas boilers, but in some cases their performance is higher, management is more convenient and easier, and their use is safer. The electric boiler only needs to be connected to the power supply, and the gas analogues additionally require the purchase of a mounted burner, regular cleaning of soot and soot. Electric boilers are easy to install, which is another advantage.
Gas heating requires permission for its installation, preparation of a place for its installation, wiring of the system for it, connection and installation of all necessary equipment, which in total is quite expensive. But the monthly payment for heating will be lower than for electricity, although it also depends on the efficiency of the purchased gas system. And the rest of the gas inherent disadvantages of the water system within the intra-house space, as a system that uses a coolant.
When comparing gas heating with heating with direct electric heaters, the advantages of electric heating are the lack of an installation permit, much lower capital investment, ease of installation and maintenance. The disadvantage is a more expensive source of energy - electric.
Which heating battery to choose for an apartment
In city apartments, radiators are in plain sight, so they should look aesthetically pleasing so as not to spoil the interior of the room. Despite the fact that the appearance of heating batteries is of great importance, you should not focus only on this indicator. If necessary, the radiator can be hidden with a decorative screen or box, but this will reduce the heating efficiency.
Features of a centralized heating system is that the pressure in it can reach high values. If during the testing of the heating main the house valve remains open, then the pressure in the system will increase to 12 atmospheres. As a result of the rapid opening of the valve or water hammer when the valve valve is torn off, the pressure can reach as much as 20 atmospheres.
Not all radiators are able to withstand such pressure and remain intact.For this reason, it is necessary to choose durable batteries for city apartments. If the pressure in the system is greater than the maximum allowable value, then the radiator will begin to leak.
So you should not save, the choice of a heating battery should be thoughtful. Removing the consequences of flooding will cost more than buying several durable and high-quality radiators.
Types and technical data of heating devices
Initial data for design
The main source material for calculating the surface of heating devices is a detailed axonometric diagram of the heating system of the building, developed and calculated in terms of hydraulics (the diameters of each of the sections are determined).
The calculated axonometric diagram should indicate the calculated load (heat fluxes) of each heating device of the system, Qnp in W or kJ/h. Heat fluxes of heating devices Qnp calculated on the basis of the table of calculated heat losses of the premises, taking into account the installation of devices near external fences, see. The diagram also indicates the calculated thermal and hydraulic loads of the risers of the system, respectively Qst and Gst, calculated with a certain margin, taken into account by the coefficient β4, cm. .
The diameters of each of the floor nodes of the system (the floor node of the room includes the actual heating devices and openly laid horizontal and vertical pipelines) are determined based on the results of the hydraulic calculation and must be plotted on the diagram.
For each room, the calculated indoor air temperature is known, tvin °C.
The technical data of most modern appliances are given in chapter 2. It should be noted that the information on this subject in the heating literature is mostly outdated.
Types and technical data of heating devices
One of the main elements of water heating systems - a heating device - is designed to transfer heat from the coolant (water) to the room.
Devices for heating systems are made with a smooth and ribbed outer surface of five main types: sectional radiators, panel radiators, convectors, ribbed tubes, smooth-tube devices.
For heating devices, in addition to sanitary-hygienic, economic, architectural, construction, production and installation requirements, a thermal engineering requirement is added - the device must have an increased value of the heat transfer coefficient, which leads to a decrease in metal consumption. In radiator water heating systems, for example, metal consumption for appliances reaches 60-80% of the total metal cost for installation.
The task of design is to choose the most optimal type and standard size from the entire range of devices manufactured by the industry, taking into account the requirements listed above and specific design conditions.
Below is a brief description of modern devices that are most widely used.
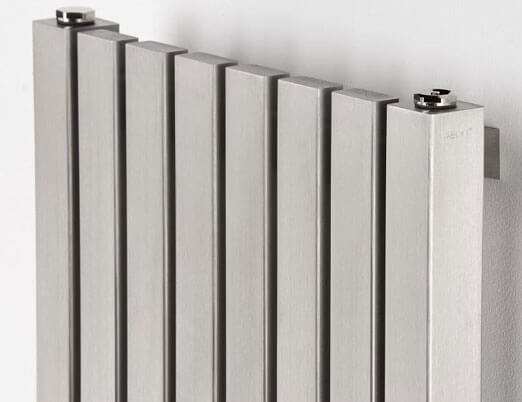
2.2. Steel panel radiators
Steel panel radiators are one of the most commonly used in individual heating systems (usually in country houses). They have a small thermal inertia, which means that it is easier to control the temperature in the room with their help. The working pressure for most models of steel panel radiators lies within 9 atm. Thanks to the widest range of models, you can choose the steel panel radiator that is optimal in terms of parameters for almost any room. The standard height of steel panel radiators is: 300, 350, 400, 500, 600 and 900 mm (there are also lower ones - 250 mm), width - from 400 to 3000 mm, depth from 46 to 165 mm. The range of steel panel radiators of each of the leading manufacturers consists of several hundred models of different depths, widths and heights.Obviously, only large suppliers can afford to work with this type of heating devices and keep such a wide range in stock.
The name of this type of heating devices gives a fairly accurate idea of their appearance - it is, indeed, a rectangular panel, in the vast majority of cases, white. The design of a steel panel radiator is, roughly speaking, two steel sheets welded together (usually 1.25 mm thick) with vertical channels, in the cavity of which the coolant circulates. To increase the heated surface, and, as a result, heat transfer, steel U-shaped ribs are welded to the back side of the panel.
Technical characteristics of radiators are presented in table. 1 and table. 2
Table 1 - Technical data of kermi radiators.
Bimetallic batteries
These radiators are constructed with a steel core inside and aluminum fins on the outside. The high strength of the batteries is achieved by the presence of steel inside. Most of the models are tested under pressure of 60 and even 150 atmospheres. They also have good chemical stability.
The high heat transfer of bimetallic radiators is due to aluminum fins with a large surface area. Due to the small cross section of the channels inside the sections, a high speed of the coolant movement is ensured and there is no need for frequent flushing. The main disadvantage of bimetallic radiators is their high cost. So, a ten-section bimetallic battery will cost several times more than other options.
Panel heating radiators
In the post-Soviet space, panel steel radiators are not very common. More willingly they are used in the countries of the USA and Europe. The advantages of these radiators include: a high degree of heat transfer, reliability and durability. With a large area of \u200b\u200bsuch radiators, a low temperature of the coolant is sufficient to quickly heat the room.
Panel steel heaters are characterized by the lowest convection. The air is heated evenly, which is comfortable and very healthy. Only a warm floor can enter into worthy competition with them. But unfortunately, it is better not to use such radiators in standard Russian heating systems. They do not withstand the high pressure of the coolant, which is observed in our central heating
If you have a private house, then we advise you to pay very close attention to panel heating radiators.
Panel batteries are similar to convector-type appliances, being their more advanced version.
Heating convectors or registers
A heating convector is a pipe on which thin steel plates are fixed. The design is simple and rather primitive. They were often used in Soviet-built houses. But now, having gone through some evolution, they have somewhat changed their appearance and functionality.
There is a very large selection on the market. Along with the cheap ones, quite expensive, elite models of imported production are also offered. Electric convectors are becoming very popular. They are used when installing underfloor heating. Skirting convectors, popular in Western countries, are considered a novelty.
In appearance, these rather modest, relatively cheap products have many advantages. Simplicity of a design provides convectors with good reliability. Small dimensions do not interfere with the implementation of design ideas.
Another big plus is the affordable price. A significant disadvantage is the small heat transfer with the convection method of heating. Simply put, the air is heated unevenly due to a kind of thermal draft.

Aluminum radiators
Noteworthy aluminum sectional radiators.They quickly conquered the market for heating appliances. Lightweight and easy to install, they confidently replaced the heavyweights - cast-iron radiators. Let's take a look at their obvious benefits.
Aluminum radiators have excellent heat dissipation. Therefore, in cold weather, the room heats up very quickly. The small mass of the radiator facilitates their easy transportation and installation. And one more advantage: beautiful aluminum radiators fit perfectly into any modern interior.
The most popular models of aluminum radiators: 350mm and 500mm. The power and number of sections of the heating radiator depends on the area and height of the heated room.
Basically, two types of radiators are made: extruded and cast. Depending on the purpose of the room, aluminum radiators are used with a pressure parameter of 6 or 12 atmospheres.

water system
The most commonly used and therefore have the widest range of heaters for water heating systems. This is due to their good efficiency and the optimal level of costs for the acquisition, installation and maintenance.
Structurally, the devices are not too different from each other. Inside each there are channels for the flow of hot water, the heat from which is transferred to the surface of the device, and then, with the help of convection, to the air of the room. For this reason they are called convection.
In water heating systems, the following types of radiators can be used:
- cast iron;
- steel;
- aluminum;
- bimetallic.
All these heaters have their own characteristics, due to which they are selected for each specific case, depending on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, the nuances of installation, the quality and type of coolant (which is sometimes antifreeze).
Cast iron was one of the most popular materials in domestic heating systems. His choice, as a rule, was due to the relatively low cost. Later, such devices began to be used less frequently, since they have a low heat transfer coefficient (only 40%), due to which the power of one section is approximately 130 watts. Although they can still be found in old-style systems. In a modern interior, designer models of cast-iron radiators are sometimes used.
The advantages of such devices are a large surface area that gives off heat to the room, and a long service life (up to 50 years). Although there are still more disadvantages - they include a relatively large volume of coolant used (up to 1.4 liters), and the difficulty of repair, and the inertia of heating, due to which the temperature increase of the device is relatively slow, and even the need for periodic (at least once every 3 year) cleaning. In addition, heavy sections are very difficult to install.
The use of aluminum radiators makes it possible to ensure the maximum level of heat transfer - the power of the section can reach 200 W (which is enough for heating 1.5–2 sq. M).
Their cost is quite affordable, and their light weight allows you to install yourself. True, the operation of the device is possible for only 20–25 years.
Their advantages include the presence in the design of convection panels that improve air circulation over the surface, ease of installation of devices for regulating the intensity of the coolant flow, as well as ease of installation. The radiator section, which has a power of up to 180 W, is capable of heating about 1.5 square meters. m area.
Despite the advantages that such heating devices have, there are problems in their use. So, for example, for bimetallic radiators, dilution of water with antifreezes is not recommended, which, although they do not allow the system to freeze, adversely affect the internal surfaces of heating devices.
Electrical heating devices
All electrical appliances used when it is impossible to install a water heating system have different features and characteristics - from power to the principles of heat generation. At the same time, the main disadvantages of any such equipment are the high cost of operation and the need for an electrical network capable of withstanding heavy loads (with a total power of electric heaters of more than 9–12 kW, a network with a voltage of 380 V is required). Each variety has its own advantages.
The design that electric heating devices of this type have allows you to quickly heat the room with the help of air flows moving through them.
Air gets inside the devices through the holes in the lower part, it is heated using a heating element, and the exit is provided by the presence of upper slots. To date, there are electric convectors with a power of 0.25 to 2.5 kW.
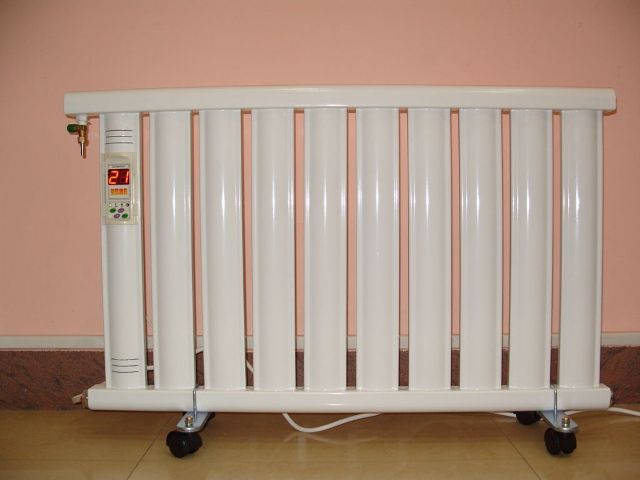
Oil devices
Oil electric heaters also use the convection method of heating. Inside the case contains a special oil, which is heated by a heating element. In this case, the heating can be regulated using a thermostat that turns off the device when the air reaches the set temperature.
The features of the heaters is their high inertia. Due to this, the heaters heat up very slowly, however, even after a power cut, their surface continues to emit heat for a long period of time.
In addition, the surface of oil equipment heats up to 110-150 degrees, which is much higher than the parameters of other devices and requires special handling - for example, installation away from objects that can ignite.
The use of such radiators makes it possible to conveniently control the intensity of heating - almost all of them have 2-4 operating modes. In addition, taking into account the performance of one section of 150–250 kW, it is quite easy to select a device for a particular room. And the range of most manufacturers includes models with a power of up to 4.5 kW.
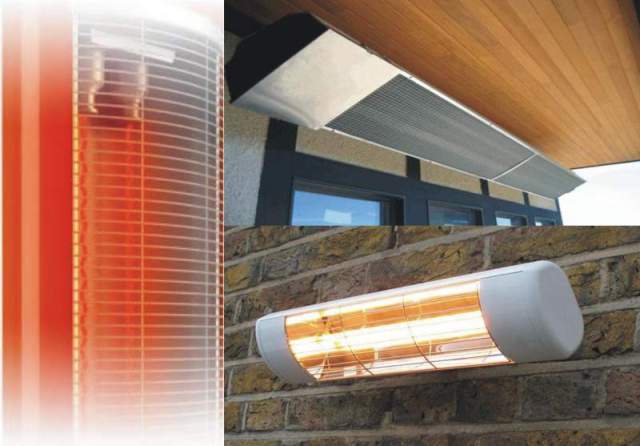
Choosing heating devices, the principle of which is based on the radiation of thermal waves in the infrared range, the owner of a private house or premises for other purposes receives the following advantages:
- a noticeable reduction in electricity consumption compared to traditional electrical equipment (within 30%);
- no decrease in the oxygen content in the air, which saves people in the room from headaches;
- very high heating rate (even a cold room warms up within a few minutes).
Kinds
The classification of devices for infrared heating is made according to the method of emitting waves. There are film devices that transmit radiation to surrounding objects from resistor conductors located on the surface of a special film. Power - within 800 W per 1 sq. m.
The second type is carbon fiber. In them, radiation comes from a spiral inside a sealed glass bulb. Household appliances of this type have a power of 0.7 to 4.0 kW.
The advantage of the former is the ability to use them as electric underfloor heating. While carbon heaters are much more powerful, although they require compliance with increased fire safety measures.
What criteria to rely on when choosing heating radiators
Undoubtedly, first of all important indicators are reliability, durability and safety. Of course, you are interested in the heating system to work properly and for a long time for many years. It is unlikely that anyone will like the options for unexpected flooding of neighbors due to damaged radiators. This possibility should be minimal.
The duration of trouble-free operation is a very important parameter that should be taken into account when buying a radiator.
Undoubtedly, the second most important criterion is the efficiency of the heating equipment. After all, radiators are installed so that, regardless of the cold weather, the room always has the optimum air temperature. Radiators with better thermal conductivity will provide the owners with the most comfortable living.
It is important to choose radiators with the perfect combination: "price - quality". It's no secret: the modern standard of living forces many to save
Therefore, the cost of heating radiators is of considerable importance. By the way. each type of radiator has both disadvantages and advantages, because the ideal equipment has not yet been invented.
In modern multi-storey buildings, water serves as a heat carrier. But passing through the pipes, such a coolant is a rather aggressive environment. Therefore, many radiators are subject to internal corrosion. Most modern heating radiators are covered with polymer protection on the inside. Please note: steel radiators corrode less than aluminum ones. But the most reliable are the cast-iron products familiar to us, as well as some bimetallic radiators.
An important parameter for the efficient operation of the radiator is the operating pressure. Therefore, in the radiator you choose, this indicator cannot be less than the minimum value, which is 7 atm. Radiators with a characteristic pressure indicator of 15 atmospheres are the most optimal and are able to withstand water hammer.
All household radiators are qualified depending on the material used, design. The modern market offers consumers steel, cast iron and the most popular aluminum and bimetallic heating radiators. Which of them is best suited in a particular case, let's try to figure it out.
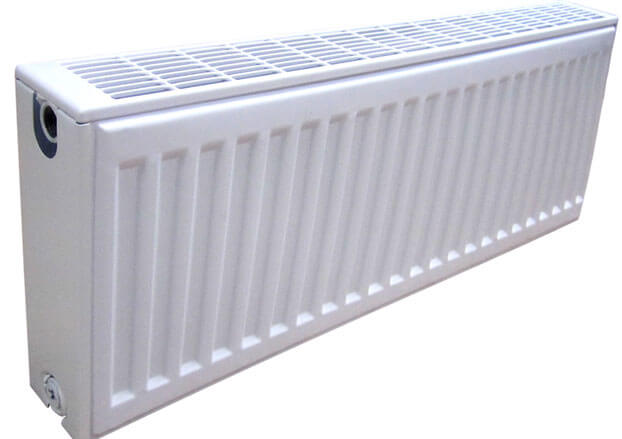
Steel tubular heating radiators
Products by design resemble cast-iron batteries. But at the same time they have a beautiful modern design. These are products of foreign manufacturers. When buying steel tubular batteries, one very important nuance must be taken into account - they operate at low pressure. In the USA and European countries, heating systems are often installed in low-rise buildings and high pressure is not created when the coolant moves.
Therefore, before buying a beautiful foreign radiator, carefully read the accompanying technical documentation.
Pay special attention to the properties and characteristics of products. Make the final purchase decision only if you are absolutely sure that this radiator will work in difficult domestic conditions.

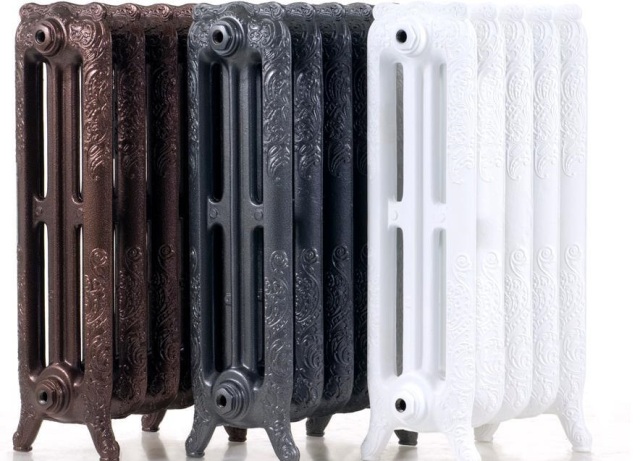
Which cast iron radiators to choose
This type of battery has been used for many years. They have good heat dissipation, but due to several features, they have recently lost their popularity. A significant drawback is the appearance - cast-iron radiators do not look the best (read: "What are the types of heating batteries - review and comparison"). In addition, due to the large internal section, the coolant inside the radiator moves slowly, which means that dirt will accumulate in it. However, regular flushing is not always required: with a lower lateral connection, the sludge was carried out by a stream of water without lingering in the heater. Another disadvantage of cast iron batteries is that they do not tolerate water hammer.
Cast iron radiators
Consider the most simple and familiar cast iron radiators. Their working pressure is 9 atmospheres, the maximum test pressure reaches 15 atmospheres.
The advantages of cast iron heaters include excellent resistance to corrosion, undemanding to the purity of the coolant. Due to this, cast-iron radiators are widely used in city houses equipped with central heating. After all, corrosion resistance is a very important parameter. In summer, water must be drained from heating systems, leaving the heater to be torn apart by corrosion. Cast iron radiator will not rust in anticipation of the new heating season.
The internal passage hole of the cast-iron radiator has a large diameter. According to the laws of physics, this leads to a small hydraulic flow resistance. In this regard, cast iron radiators are successfully used in heating systems with natural circulation.
Still, the shortcomings are obvious. The main disadvantage: cast iron is too heavy a metal. Therefore, radiators have a large mass. This leads to a complication of the installation process of such a heating system with the need to use reliable fasteners.
Cast iron radiators are characterized by high thermal inertia. Therefore, they heat up for a long time, cool down for a long time. This temperature regime is not very comfortable: for a long time the air remains cold or, conversely, too warm.
It is unlikely that cast-iron radiators decorate the interior. Bulky heating systems always want to be hidden from prying eyes. Cleaning will have to be done often and thoroughly, because the cast-iron construction in the form of sections tends to accumulate dust abundantly.

Registers for heating
For the manufacture of registers for heating, pipes are used, connected by electric or gas welding, with a diameter of 32 mm to 200 mm or more. But do not forget that the technical characteristics of heating registers are somewhat worse than those of radiators of the same size. Registers are mainly used in workshops, industrial or technical premises, garages. Although they can be found both in private houses and in apartments where an autonomous heating system is installed.
The advantages of registers for heating are as follows:
- They are able to heat large areas;
- Gives off "soft" heat. That is, even the most primitive register for heating has a significant length and, accordingly, occupies a significant area. Therefore, the heat source comes out not as a point, but rather extended. Thus, heating is performed not locally, but around the entire perimeter.
- Easy to care for. Heating registers have a flat surface, since ordinary pipes are used for their manufacture. Accordingly, there are no hard-to-reach places and roughness where dust would accumulate.
- They can withstand significant temperatures and pressure drops, provided that the manufacture of the registers is of high quality.
Register for heating. Click on the photo to enlarge.
Heating registers are produced using a smooth-walled pipe, a profile pipe. As a rule, parallel pipes (of the same type) are connected by transverse pipes through which the coolant circulates, or the device is made in the form of a coil. On the one hand, a hot coolant enters such a register for heating through a pipe, and on the other hand, an already cooled one leaves.
In the manufacture of registers for heating, you need to consider some rules:
- It is better not to use large diameter pipes, as heating will require a lot of water, and the boiler may not be able to cope with heating such a volume of coolant. The optimal section is 32 mm.
- To maximize heat transfer, it is worth maintaining a distance of 50 mm more between the pipes than their diameter.
These are almost all the main requirements that need to be taken into account when creating registers for heating, while no drawing is needed to create such devices. The main parameters are the diameter and length of the pipes.To determine these values, you need to calculate the number of devices, based on the parameters of the room and taking into account the calculation of the power of the registers. To solve this problem, you can use special online calculators.
What devices are better to choose? Give preference to registers for heating, convectors or radiators? There is no single answer, since each of them has a number of advantages and disadvantages.
When buying, pay attention to the quality of the product, consider the technical specifications. It will not be superfluous to consult a master, who will later be engaged in the installation of purchased radiators or registers for heating
Heating appliances
First of all, modern heating radiators are bimetallic and aluminum models. However, there is a stable demand for both steel and cast iron products, which is due to the new approach of manufacturers to the manufacture of outdated, it would seem, heating appliances. Let us briefly describe the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
Aluminum
The most popular in the post-Soviet space for the price / quality ratio (cheaper than bimetallic, in many respects more reliable than steel and cast iron).
Advantages:
- the best heat transfer among all analogues;
- expensive models withstand pressure up to 20 bar;
- little weight;
- the simplest installation.
Flaws:
poor corrosion resistance, especially noticeable at the junction of aluminum with other metals;
Bimetallic
Generally recognized as the best type of radiators. The name was given due to the combination of steel (inner layer) and aluminum (casing) in its design.
Advantages:
Flaws:
high price.
Steel
They are poorly suited for multi-storey buildings and a centralized heating system in general, but they show all their best properties in private houses, they fit perfectly into the heating systems of industrial premises in factories and factories. You can read more about steel heating radiators.
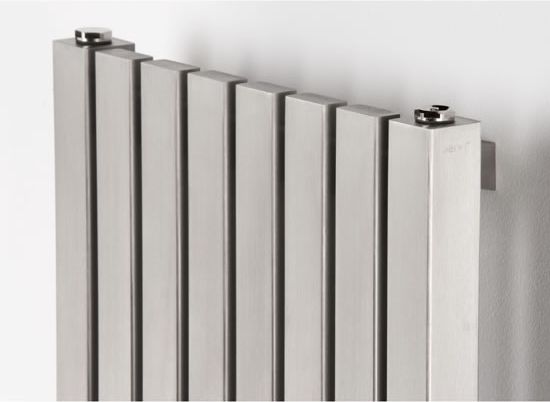

- heat transfer above average;
- rapid onset of heat transfer;
- low cost;
- aesthetic look.
Flaws:
Cast iron
It should be understood that modern cast-iron heating radiators are no longer bumpy and heavy remnants of the past, which “decorated” almost every house during the Soviet era. Modern manufacturers have significantly improved their appearance, making them almost indistinguishable from bimetallic or aluminum models. Moreover, the fashion for the so-called is expanding, the shapes and patterns of which bring the atmosphere of the beginning of the 20th century into the house.Advantages:
Flaws:
huge weight and resulting difficulties with installation (often require special support-legs).
Heating system
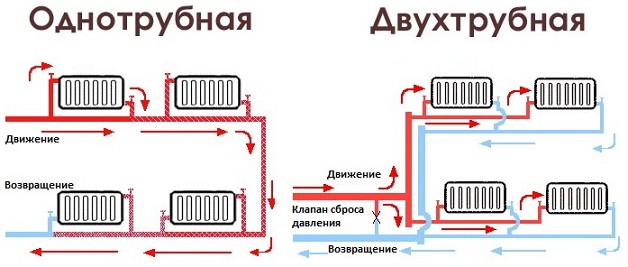
Most modern country houses use a horizontal heating system, the main difference of which from vertical wiring is the partial (less often complete) absence of vertical risers.
In Russia, such a type of horizontal system as a single-wire heating system (or one-pipe) is especially popular.
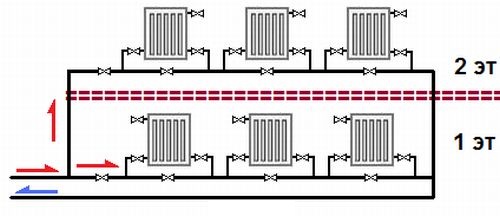
Water circulation without a pump is made possible by changing the density of hot and cold water.
A single-pipe system has several advantages over a two-pipe system:
Convectors for heating
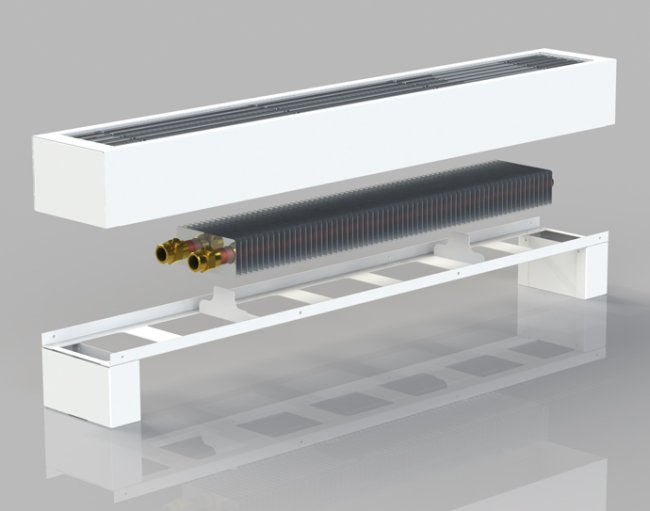
Convectors are devices in which heat transfer occurs due to convection. The simplest model is a pipe (heat exchanger) with metal plates strung on it. Nowadays, the appearance of such a unit has a lot of variations, which allows it to fit into any modern design without much difficulty. Devices are mounted differently. Can be built-in, hinged wall, floor.
The structure of the floor convector. Click on the photo to enlarge.
Convectors have a number of advantages. First of all, they are reliable, the drawing of such a unit is quite simple. These heaters are better than cast iron or steel radiators because convectors are less bulky.
And what is important - they have a relatively low cost. Disadvantages include low heat transfer coefficient
For the full operation of such a device, a high temperature and speed of water movement are necessary. In addition, during the operation of the devices, dust is also swallowed from the floor, which is then sprayed around the room.