Conducted calculations
Depending on which of the above parameters will be subject to detailed study, an appropriate calculation is made. For example, determining the required power of a pump or a gas boiler.
In addition, very often it is necessary to calculate heating devices. In the process of this calculation, it is also necessary to calculate the heat losses of the building. This is due to the fact that, having made a calculation, for example, of the required number of radiators, one can easily make a mistake when choosing a pump. A similar situation occurs when the pump cannot cope with supplying the required amount of coolant to all radiators.
Formula for accurate calculation
There is a rather complicated formula by which you can make an accurate calculation of the power of a heating radiator:
QT = 100 W/m2 × S(room)m2 × q1 × q2 × q3 × q4 × q5 × q6 × q7, where
q1 - type of glazing: ordinary glazing - 1.27; double glazing - 1; triple - 0.85.
q2 - wall insulation: poor - 1.27; wall in 2 bricks - 1; modern - 0.85.
q3 - the ratio of the areas of window openings to the floor: 40% - 1.2; 30% - 1.1; 20% - 0.9; 10% - 0.8.
q4 - outdoor temperature (minimum): -35 ° C - 1.5; -25°C - 1.3; -20°C - 1.1; -15° C - 0.9; -10C° - 0.7.
q5 - number of outer walls: four - 1.4; three - 1.3; angular (two) - 1.2; one is 1.1.
q6 - type of room located above the calculated room: cold attic - 1; heated attic - 0.9; heated residential - 0.8.
q7 - the height of the premises: 4.5m - 1.2; 4m - 1.15; 3.5m - 1.1; 3m - 1.05; 2.5m - 1.3.
Let's calculate the heating radiators by area:
A room of 25 m 2 with two double-leaf window openings with triple glazing, 3 m high, enclosing structures of 2 bricks, a cold attic is located above the room. The minimum air temperature in winter is +20°C.
QT = 100W/m 2 × 25 m 2 × 0,85 × 1 × 0,8(12%) × 1,1 × 1,2 × 1 × 1,05
The result is 2356.20 watts. This number is divided by 150 watts. So, for our premises, 16 sections are required.
Design features
Structural radiators are divided into two groups:
- needle;
- ribbed.
The first type is mainly used for natural cooling of LEDs, the second - for forced cooling. With equal overall dimensions, a passive needle radiator is 70 percent more efficient than a ribbed one.
Needle type heatsinks for high power and smd LEDs
But this does not mean that lamellar (finned) radiators are only suitable for working in tandem with a fan. Depending on the geometric dimensions, they can also be used for passive cooling.
LED lamp with ribbed heatsink
Both types of radiators can be square, rectangular or round in cross section.
Characteristics from the Chinese
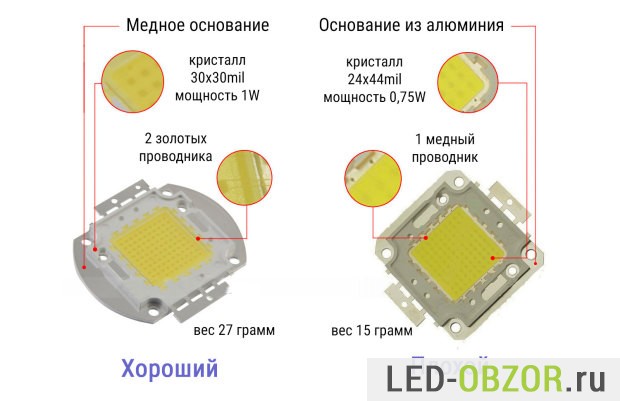
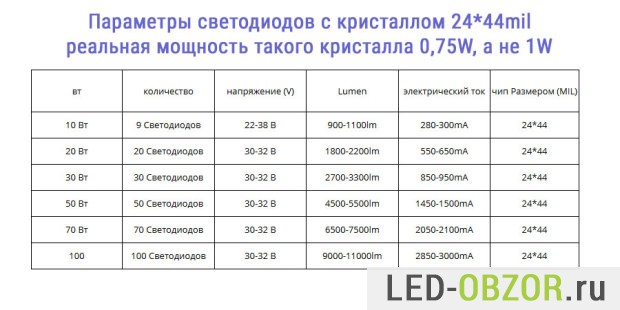
A caring seller places a table with the parameters of LED matrices on the product page. If these data are not indicated, then I do not advise buying in this place, there may be a large variation in quality.
In the table for 24*24mil, you can see that the seller indicates the standard power of 10W, 20W, 30W, 50W, 70W, 100W and the number of installed crystals. Pay close attention to voltage and current. For 100W, the number of volts is 30-32V, Ampere 2-2.1A.
We calculate the power for 24 * 24mil:
- minimum 30V*2A = 60W;
- maximum 32V * 2.1A = 67.2W;
- that is, instead of the promised 100W, it will be 60-65W.
The value of 60-65W is still too high, since 1 chip per 0.5W, then it’s really 50W there, but they sold it to us as 100W. Crystals are already the cheapest and worst, so any overclocking is contraindicated for them.
Calculate for 24*44mil:
- minimum 30V * 2.850A = 85.5W;
- maximum 32V * 3A = 96W;
- the average will be 90W.
According to the table, we got 90W, in reality there is 75W, they overestimated it by 15W.
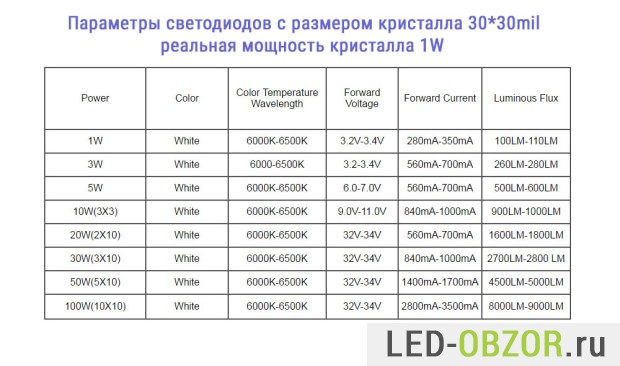
Let's calculate for 30*30mil:
- minimum 32V * 2.8A = 89.6W
- maximum 34V * 3.5A = 119W
- average 105W
The 30*30mil size provides the promised specifications. The same chips are placed in ordinary high-quality single-wool 1W with a power consumption of 10W, 20W, 30W, 50W, 70W, 100W
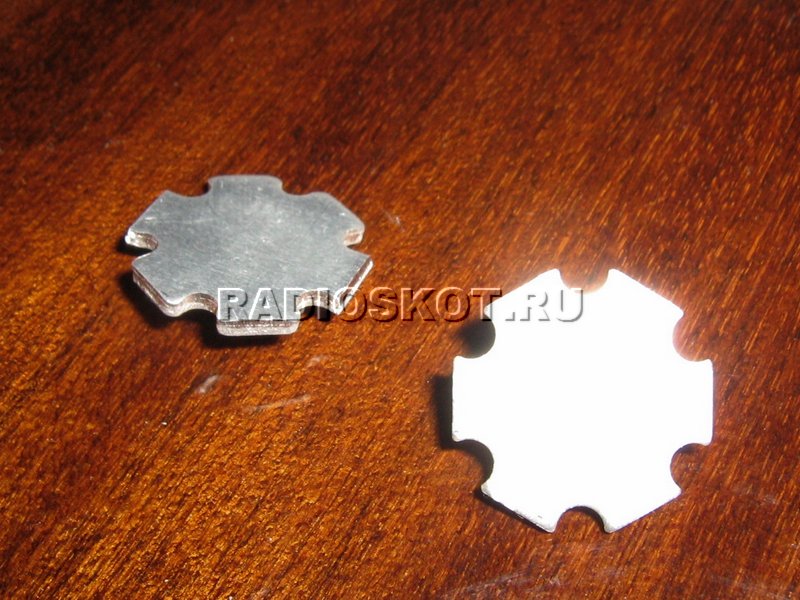
Do-it-yourself cooling
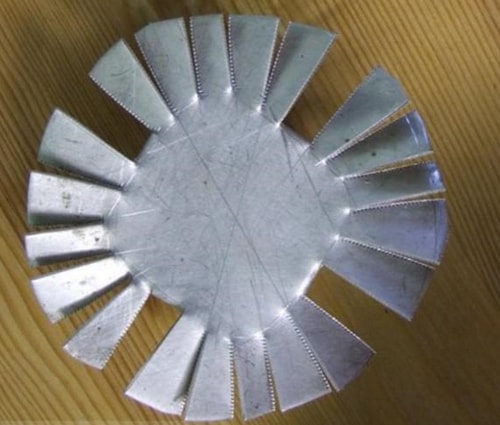

This is a banal radiator made from improvised means, it turns out to be quite thin and cannot be used for more serious lamps.

If you leave the cooler, active cooling of the LEDs will allow you to use more powerful LEDs. Such a solution will create additional noise from the fan and require additional power, plus periodic maintenance of the cooler.

Having made an assembly of the required area from such profiles, you can get good cooling, do not forget to coat all the joints with at least a thin layer of thermal paste. It is worth saying that there is a special profile for cooling, which is industrially produced in a wide variety of types.
If you do not have the opportunity to make a do-it-yourself LED cooling radiator, you can look for suitable items in old electronic equipment, even in a computer. There are several on the motherboard. They are needed to cool chipsets and power switches for power circuits. An excellent example of such a solution is shown in the photo below. Their area is usually from 20 to 60 cm2. That allows you to cool the LED with a power of 1-3 watts.
Another interesting option for making a radiator from aluminum sheets. This method will allow you to gain almost any required cooling area. Watch video:
10 W LED
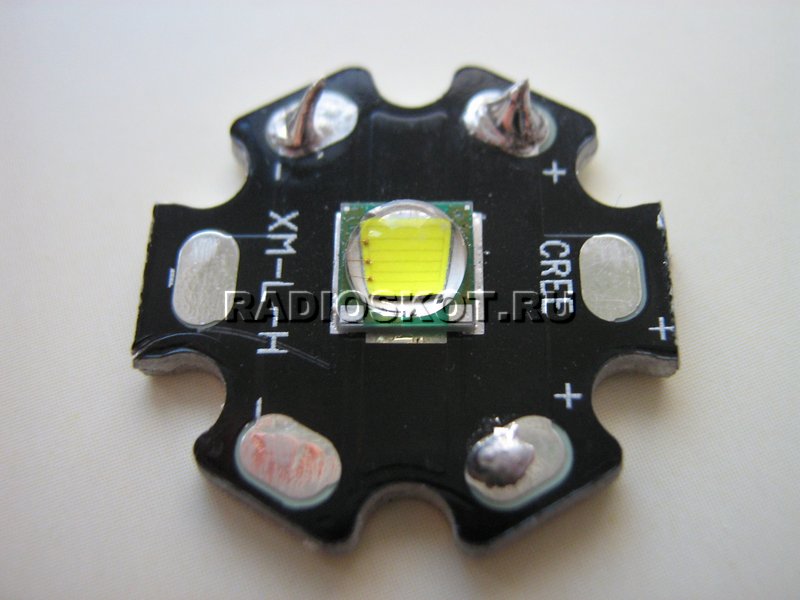
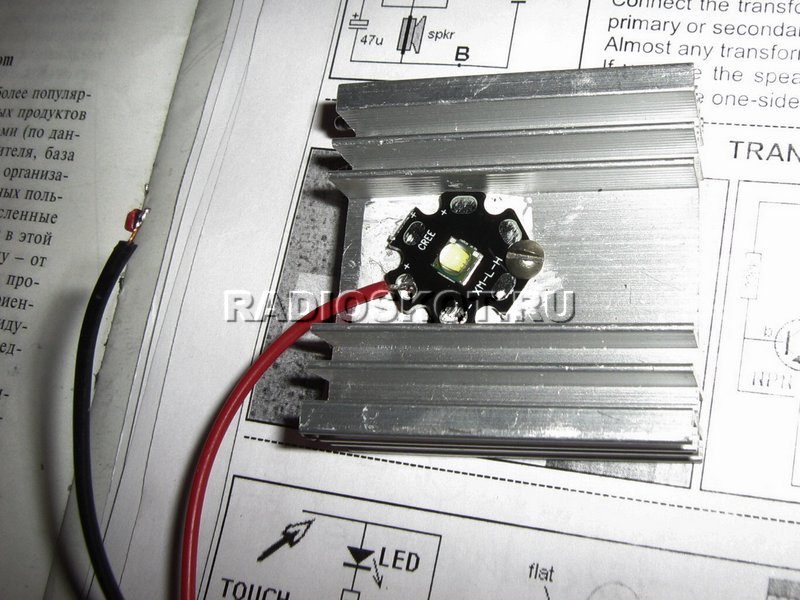
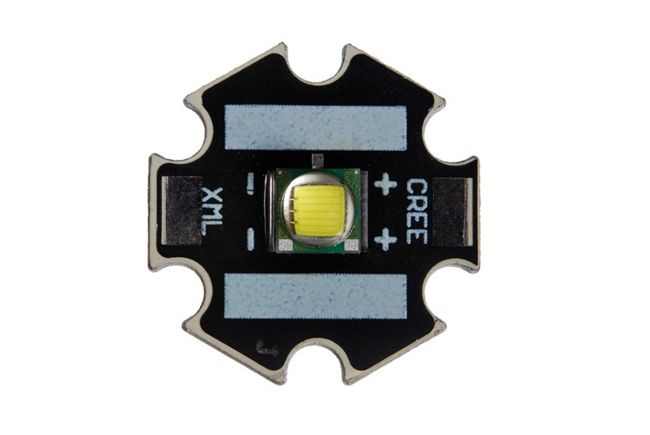
Today, a powerful ten-watt LED of the Cree XM-L-H model came to us for research and experiments. The design of the LED is a standard aluminum "star" with patches for soldering wires and cutouts for screwing the LED device to the radiator.
Naturally, you understand that the design of this LED is not designed to dissipate such a large amount of power. During the experiments, already half a watt caused a slight heating of the case.
The technical parameters of the Cree XM-L-H LED are listed on the website.
First of all, let's take the current-voltage characteristic of the indicated LED device and put the results in the table.
| LED voltage | 2,3 | 2,4 | 2,5 | 2,57 | 2,63 | 2,72 | 2,81 | 2,95 3,1 |
| LED current, mA | 1 | 10 | 50 | 100 | 250 | 500 | 1000 | 2000 3000 |
As you can see, the slope of the I–V characteristic is quite large, and a small voltage deviation within 0.1V immediately leads to a sharp change in the current consumption. And given that the operating current reaches 3 amperes, the use of a quenching resistor to stabilize the current is eliminated. Indeed, for a normal power supply of this LED at 10 watts, let's say from a 12V car battery, you would have to install a 3 Ohm resistor with a power of 35 watts!
So in this case, the use of a special converter-driver has no alternative. Moreover, its price is within 2-4.
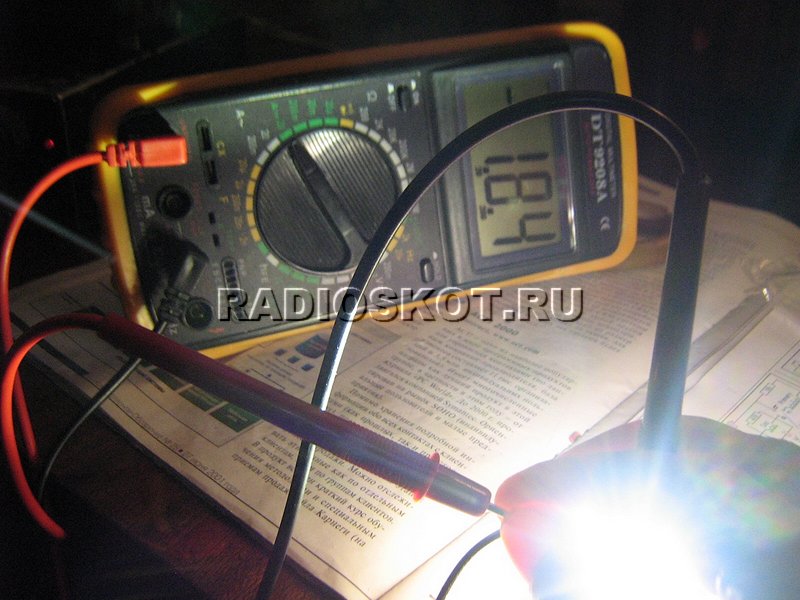
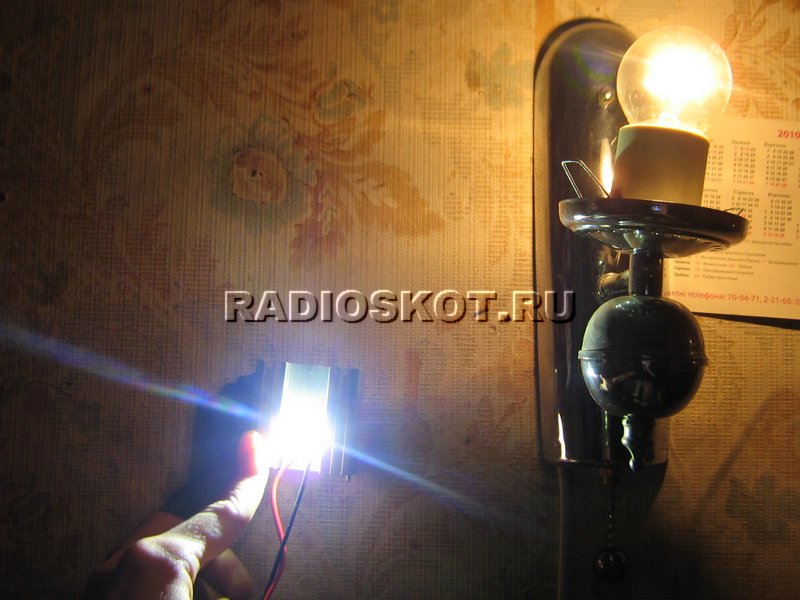
And now let's test the LED in a duel with an incandescent bulb 220V 60W. The photos below show lighting options with both light sources.
10 watt LED only
60 watt incandescent bulb only
Draw your own conclusions. Of course, the LED loses in color temperature (after all, 6000K), but in terms of brightness per watt of power consumption, it surpassed its rival by several times.
Another good feature is a very wide angle of light, almost 170 degrees. The era of LEDs with lenses has passed, now even a reflector is not required to obtain normal lighting. The design of the light emitter of the LED device is such that the light is emitted evenly over the entire hemisphere.
It seems interesting to use this 10-watt LED either in a powerful LED flashlight (which was done), or together with an LED driver in the body of a burned-out fluorescent energy-saving lamp. But do not forget about sufficient heat dissipation - the dimensions of the radiator must be at least 10 square meters. cm.
I will not talk about the price of the LED, since the cost of LED devices is constantly decreasing. Check online stores. In the following articles, we will conduct interesting experiments with the most powerful LED of several tens of watts! LED Forum
Application area
Super bright 10W LEDs are widely used in various lighting applications. All areas can be conditionally divided into general and special purposes. The general purpose includes the operation of LEDs in lamps, lamps, spotlights, and the special purpose is the use for lighting in greenhouses and aquariums. The second option is the so-called phytolamps and not only. The trick is that the emission spectrum of this LED is optimal for plant growth, both on land and in water. And besides algae and fish, lighting with 10 watt LEDs has a positive effect on the development of corals, so aquarium lovers are frequent consumers of this radio component. All these wonderful properties are manifested in a certain combination of crystal colors. As for the use of the described semiconductor device for general-purpose lighting devices, in addition to household lamps, the LED is excellently used for the manufacture of headlights for a car, traffic lights, and road lighting.
For decoration purposes, multi-colored 10-watt LEDs are used in landscape design, to illuminate buildings, swimming pools and street advertising.
Standard selection method
It is used only when the height of the room is less than 3 m. It is implemented as follows:
- Determine the area of the room. For example, it is 25 m².
- Multiply the resulting figure by 100 watts. According to SNiP, this figure is the norm. The document says that 100 watts should be generated for every square meter. It turns out that the heat source should create 2,500 W or 2.5 kW.
- The received power is divided by the heat transfer of one section of the battery. This step is performed when it is planned to install a sectional radiator or battery. As you know, cast iron, aluminum and bimetallic heating devices have such a design. If the battery has a section with a heat dissipation of 150 W, then you need to buy a device with 17 sections (2500/150 = 16.6, rounded up only).
With panel radiators, the situation is somewhat different. They are a one-piece structure that cannot be increased or decreased. Therefore, their full power is taken into account. However, installing one large 2.5 kW heatsink would be a bit of a misstep. This is because a different calculation method is used for these batteries.
Some features of the standard method
However, if the room has an increased heat loss, then the total power of the heating devices (in our case, the figure is 2.5 kW) must be adjusted.
The adjustment should be like this:
- An increase in the final figure by 20% in the case when the room is a corner one (that is, two walls are external).
- Increase in total power by 10% in case of bottom connection of the radiator.
- Reducing the total amount of heat by 15-25% if metal-plastic windows are installed in the room.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=mVNWfHKN-Pw
Materials for manufacturing
Radiators for cooling LEDs vary in design and material.
Ambient air can take no more than 5-10 W from a single surface
When choosing a material for the manufacture of a radiator, the following condition should be taken into account: its thermal conductivity must be at least 5-10 W.Materials with a smaller parameter will not be able to transfer all the heat that air can take.
For the manufacture of radiators, aluminum, copper or ceramics are traditionally used. Recently, products made of heat-dissipating plastics have appeared.
Aluminum
The main disadvantage of an aluminum radiator is the multi-layer design. This inevitably leads to the appearance of transient thermal resistances, which have to be overcome by using additional heat-conducting materials:
- adhesive substances;
- insulating plates;
- materials that fill air gaps, etc.
Aluminum Heatsinks for 1W LEDs
Copper
Copper has a higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, so in some cases its use for the manufacture of radiators is justified. In general, this material is inferior to aluminum in terms of lightness of construction and manufacturability (copper is a less pliable metal).
It is impossible to manufacture a copper radiator by pressing - the most economical - method. And cutting gives a large percentage of waste of expensive material.

Copper radiators
Ceramic
One of the most successful options for a heat sink is a ceramic substrate, on which current-carrying traces are pre-applied. LEDs are soldered directly to them. This design allows you to remove twice as much heat compared to metal radiators.
Bulb with ceramic heatsink
Heat-dissipating plastics
Increasingly, there is information about the prospects for replacing metal and ceramics with thermally dissipating plastic. Interest in this material is understandable: plastic costs much less than aluminum, and its manufacturability is much higher. However, the thermal conductivity of ordinary plastic does not exceed 0.1-0.2 W / m.K. It is possible to achieve acceptable thermal conductivity of plastics through the use of various fillers.
When replacing an aluminum radiator with a plastic one (of equal size), the temperature in the temperature supply zone increases by only 4-5%. Given that the thermal conductivity of heat-dissipating plastic is much less than aluminum (8 W/m.K versus 220-180 W/m.K), we can conclude that the plastic material is quite competitive.
Bulb with thermoplastic heatsink
Radiator area calculation
At the very beginning, you need to figure out how much primer and paint you need to use to paint the battery. This can be found by calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe heating radiator. Next, look at the recommendations indicated on the can of paint. They always indicate how much paint can go per 1 sq. m. It is impossible to independently measure the area of \u200b\u200bthe battery. This does not need to be done, because manufacturers indicate the heating surface area of \u200b\u200bthe section. Since each square centimeter of the section is heated, this area and the area of the entire surface of the section.
One edge of the MS-140-500 battery has an area of 0.244 sq. m. The modification of this model with a center distance of 300 mm has sections with an area of 0.208 square meters. m.
To determine the total surface area of a cast iron battery, you must:
- Find out the model name of the installed battery and preferably the manufacturer (this is because the sections produced by manufacturers of the same models have different depths and widths).
- Set heating area 1 fin .
- Multiply the number of sections by the area. If there are 10 fins in the MS-140-500 radiator, then the surface area will be 2.44 sq. m.
Having made the calculation, determine the amount of composition and primer, buy them and paint. Paint should be taken with a margin, because everyone applies a layer with a different thickness.
Methods for calculating radiators
So, it’s worth starting with the calculation of batteries. The minimum required number may depend on several parameters at once:
Scheme of installation of heating radiators.
- area of the premises;
- ceiling height;
- wall material, the presence of holes, the number of windows, that is, from the heat loss of the house.
The simplest calculation, which does not take into account many of the above factors, can be considered the one that is performed according to the following formula:
- K is the required number of battery sections;
- P is the total area of the heated premises for which the selection is being made;
- M1 is the power of one section.
In the formula, the difference is multiplied by 100. This figure was not taken by chance. Long-term practice has shown that the minimum power required for one area unit (1 sq.m) of a heated room in order to maintain normal temperature conditions in it is about 100 watts.
It is worth noting that for non-residential buildings, but in need of heating, this figure can take a value of 50 watts.
To carry out the selection according to the formula, one constant is missing - the heating power of one section. Of course, it can also be calculated, but it is quite complicated and time consuming.
Since all cast-iron heating batteries are approximately the same size, an average power value of about 150 watts was taken over many years of practice.
Now, having all the data, you can choose the required number of radiator sections.
However, this is only the simplest formula. Since each room individually has its own heat loss indicators, additional coefficients are usually added to the formula. For example, if the room has two external walls, that is, it is angular, then a factor of 1.2 is entered.
Then the formula will take the form:
Let the room have an area of 9 square meters and be located in the center of the house, but with two outer walls. It is necessary to carry out the selection of heating elements for this room.
So, K \u003d (9/150) * 100 * 1.2 \u003d 7.2, that is, 8 sections.
It is worth noting that this calculation is only valid for ceilings no higher than 2.7 meters. It should also be said that it is more correct to calculate based on the volume of the room.
Approximately the same principle is based on the second approximate calculation. It has long been calculated that one section of the battery is capable of heating approximately 1.8 square meters. m of floor space. Moreover, this figure is true only for ceilings that do not exceed 2.7 m in height.
Manufacturers
The leaders in the production of high-power LEDs, such as LED 10 W, are dispersed in three parts of the world. Among them are the American company Cree (which we have already mentioned and demonstrated a sample of its products), the Japanese Nichia (a pioneer in the field of LED technology), as well as the German Osram (more known to the domestic buyer).
Branded LED products are more expensive than their noname counterparts, but no one guarantees quality in the second case.
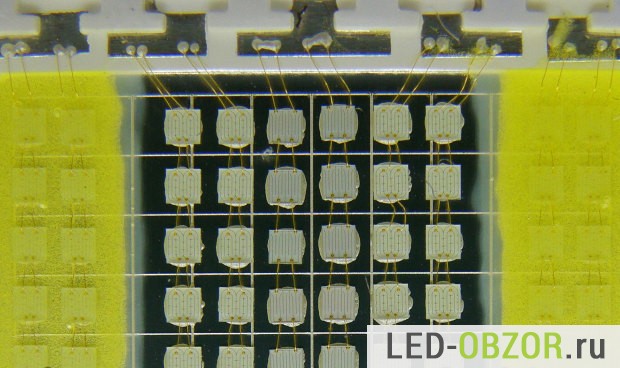
Consider what features you will encounter when deciding to purchase Chinese cheap 10-watt LEDs. First, if you compare carefully, then 9 matrix crystals themselves are smaller than those of high-quality modules. This, of course, will affect the light output during their work. Secondly, the strong unevenness of the glow of each crystal. This is noticeable, however, only at a reduced current, but, nevertheless, this feature affects the degradation rate of the entire LED module.
10 watt fakes from China
In the picture you can see the uneven glow of the individual crystals of the module, and how it levels out with an increase in current
Thirdly, in low-quality LEDs, the conductors connecting the crystals are very thin, and can break due to careless movement, which will interrupt the functioning of at least one triple of consecutive crystals.
Summarizing the above, I would like to highlight the theses of the article that are important for memorization. 10 W LEDs as light emitting sources are widely used in practice for the manufacture of car lamps, flashlights, spotlights and other lighting devices.
Radiator cooling is critical to the normal operation of the LED. Power is supplied from a 12V source through a driver (voltage stabilizer)
A well-known brand guarantees uninterrupted operation during the entire declared period, and problems may arise with Chinese inexpensive counterparts.
LED design, options
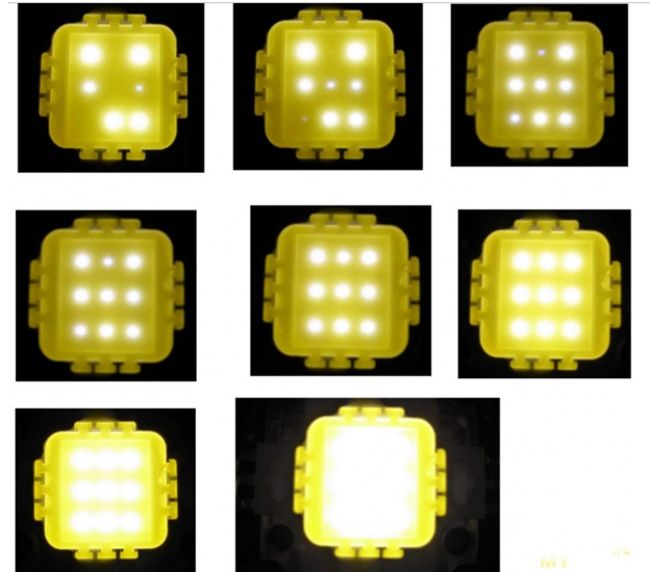
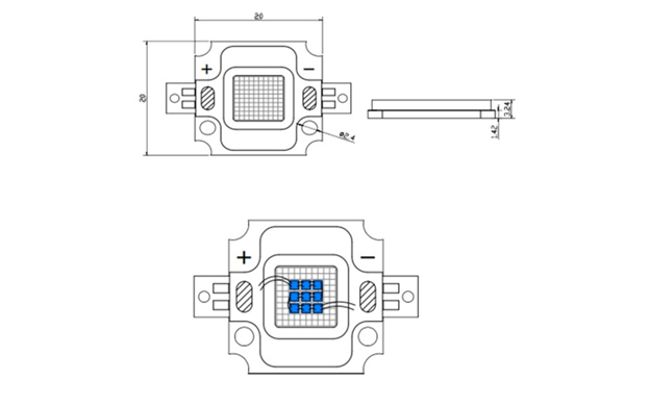
The COB 10 W LED is a compact chip-on-board module. The fundamental difference from SMD is that several crystals are placed together on a board and covered with a common layer of phosphor. This significantly reduces the cost of the matrix. It consists of 9 crystals: three parallel chains with three crystals connected in series in each. Externally, LED 10 W may differ in the shape of the conductive substrate. For example, a Cree LED looks like the one shown in the figure. Its substrate has the shape of a star and is made of aluminum.
The body of the module is made of heat-resistant plastic, and the lens is made of epoxy resin. Classic LED 10 W looks like it is shown in the diagram, but in practice the overall dimensions vary depending on the manufacturer.
Do not forget that the LED is a polar element, so pay attention to the markings during installation. A prerequisite for the adequate functioning of the 10 W LED is the presence of a heat sink
You can organize it using an aluminum or copper radiator. Lubricate the LED substrate with thermally conductive paste or hot melt adhesive for better heat dissipation. Sometimes a cooler is additionally mounted, which provides air circulation to cool the radiator fins.
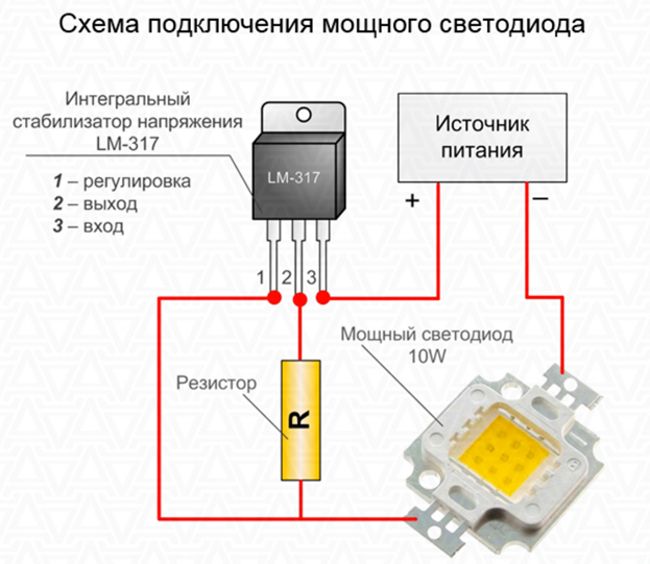
In the video you can see the test of the 10W LED and recommendations for connecting such an element. Here's what the 10W LED connection diagram should look like.
The power source can be a car battery, a computer power supply, or a specially purchased 12-volt source. In order to avoid overheating (despite the heatsink) and protect the LED, it is imperative to connect it not directly to the source, but through any voltage regulator. The diagram shows the integrated voltage regulator LM-317, but you can use another one with suitable parameters. With the help of a conventional roll and a resistor, you will provide yourself with guaranteed 12 V at the output and the current will not exceed 1 A, which is the key to the durability of your device.
The combination of a resistor and a stabilizer is called an LED driver.
Why diodes need cooling
Despite the high light output, LEDs emit light for about a third of the power consumed, and the rest is released into heat. If the diode overheats, the structure of its crystal is disturbed, begins to degrade, the luminous flux decreases, and the degree of heating increases like an avalanche.
Causes of LED overheating:
- Too much current;
- poor stabilization of the supply voltage;
- bad cooling.
The first two reasons are solved by using a quality power supply for LEDs. Such sources are often referred to as an LED driver. Their feature is not in voltage stabilization, but in stabilization of the output current.
The fact is that when overheating, the resistance of the LED decreases and the current flowing through it increases. If you use a voltage stabilizer as a power supply, the process will turn out to be an avalanche: more heating - more current, and more current - this is more heating, and so on in a circle.
By stabilizing the current, you partially stabilize the temperature of the crystal. The third reason is poor cooling for LEDs. Let's consider this question in more detail.
For engines with spark ignition 140180 Wm2deg
φ
- coefficient taking into account pollution
radiator surface
v
calculations is taken equal to 0,7…0,8;
Δt
– temperature
difference between coolant and
external environment (air), in calculations
accepted - Δt=40…45.
Calculation of liquid
pump
circulation
coolant flow is determined
according to the formula:
 ,
,
m3/With;
where
WITHwell
– heat capacity
liquid, j/kg·hail,
for
water WITHwell
\u003d 4.2 J / kg·hail,
for antifreeze
WITHwell
\u003d 2.09 J / kg·hail;
pwell
is the density of the liquid, kg/m3,
for water Rwell
=1000kg/m3
ΔtR
–temperature
liquid drop in the radiator, is taken
in calculations equal to 10…12
deg.
Estimated
pump performance:
VR
=Vc
/ ηn
, m3/With;
where
ηn-pump delivery coefficient, taking into account
leakage of fluid from the pressure chamber into
suction, is taken equal to0,8…0,9.
Power for
pump drive:
 ,
,
kW;
where
Δp -pressure,
created by the pump (in calculations
accepted 0.05 ... 0.1 MPa);
ηm
– mechanical efficiency pump (0,7…0,9).
Fan calculation
Performance
fan is determined by the formula:
 ,
,
m3/With;
where
Rv
- air density at its average
temperature in the radiator:
 ,
,
kg/m3;
Tcr.v
– average air temperature in the radiator,
taken into account 320…330K,
Rv
–specific
gas constant for air
–287J/kg.grad,
WITHv
—
heat capacity of air1000J/kg.grad,
Δtv
—
temperature
air difference in the grate
radiator - (25 ... 30).
Power,
spent on the fan drive:
 ,
,
kW;
where
ηv
– efficiency fan,
for
stamped fans - ηv=0,2…0,4,
for
cast fans - ηv=0,55…0,65;
Δрglad
– air path resistance
radiator, is accepted in rkaccounts -
600…1000Pa.