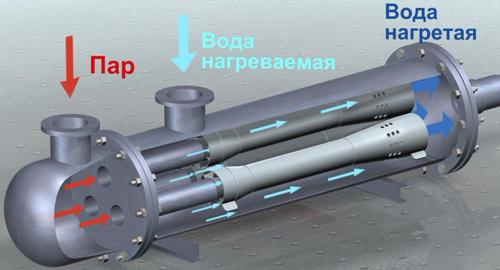
Advantages of vertical shell-and-tube heat exchangers over plate heat exchangers when using steam in the primary circuit
- the ability to work at high steam pressures and temperatures (up to 250°C) without the need for steam reduction - significantly lower the cost of piping;
- lack of consumables (gaskets) - higher reliability;
- the ability to control the load on the condensate side - a wider range of load control in automatic mode, the use of condensate heat (lower steam consumption), the operation of the heat exchanger at a constant pressure, regardless of the load value;
- small footprint due to vertical design;
- low weight due to the lack of a massive frame and base;
- large heat exchange surface with small dimensions due to tubes twisted into a bundle;
- long service life without maintenance - from several years to tens of years;
- possibility of use as a vapor cooler or as a condensate cooler;
- no special thermal insulation design is required, traditional thermal insulation coatings for pipelines are suitable.
The best recuperative heat exchanger
Hot and cold coolants move in different channels, heat exchange occurs through the wall. The heat flux at each point of the wall keeps the same direction.
CEEVT (Russia)
It is a device inside which hot and cold carriers move through different channels. In this case, the heat exchange between the working media occurs through the wall, and the heat flow in each section retains its direction.
"CEEVT"
Products differ depending on the direction of movement of the working media. Under the brand "CEEVT" they produce:
- direct-flow - parallel movement of coolants in one direction;
- countercurrent - parallel oncoming traffic is organized inside.
- cross-flow - interacting media move mutually perpendicular.
Countercurrent modifications
The counterflow tubular heat exchanger operates at a pressure of 4 Pa. The tubes of the models are installed in a horizontal position. On average, the throughput is at the level of 140 liters of liquid per minute. It is also worth noting that there are modifications with two racks. The lids are usually made in small diameters. Pipes are used from stainless steel, but there are also brass counterparts.
Many modifications can boast excellent performance. Heat exchangers of this type are well suited for vegetable oil pasteurization. Some experts claim that the models have good tightness. However, they have several disadvantages. First of all, we are talking about large sizes.
Additionally, it is important to consider the complex maintenance of these units, since the racks must be replaced periodically. It is also required to constantly check the strength of the flange
Classification and operation of steam heat exchangers
Classification can be made according to differences in the design of steam-water heat exchangers, according to their performance characteristics and purpose. In terms of characteristics, heaters are divided into
- produced in accordance with GOST 28679-90;
- heaters with improved characteristics.
The division into
- low pressure heaters and
- high pressure heaters.
According to the device, steam-water heat exchangers are divided into
- flow heaters;
- capacitive heaters,
and also on
- models;
- with one-, two-, four-way, etc. water flow in the tube bundle;
- with straight or U-shaped pipes, various types of expansion joints, etc. - almost all types of common.
The division by purpose (for hot water supply or heating, household, municipal, industrial) is largely conditional, and depends on the technical parameters of the heater of a certain model - its maximum performance, temperature regime, dimensions, etc.
Features of horizontal modifications
Models of this type are the most common. For industrial enterprises, a tubular (horizontal) heat exchanger is great. The conductivity indicator for models, as a rule, does not exceed 130 liters per minute. A tubular heat exchanger is often found in dairy enterprises. The tubes in this case are fixed on special plates.
Some enterprises install modifications on wide stands. Heat exchange tubes are used in different diameters. Flanges are usually located at the front of the structures next to the covers. The coolant temperature in this case depends on the throughput of the model. Branch pipes of branch connect with adapters. The production of tubular heat exchangers is mainly established in the USA.