List of regulatory documents
Building regulations
SNiP II-12-77 Protection against
noise. Design standards.
SNiP 2.08.01-89* Residential
building. Amendment 1 BST 7-93 Amendment 2 BST 12-94 Amendment 3 BST 9-99 (ed.
1995 with revisions 1 and 2)
SNiP 2.08.02-89*
Public buildings and structures. Change 1 BST 10-91 Change 2 BST 7-93
(ed. 1993 with revisions 1 and 2)
SNiP 2.09.04-87
Administrative and household buildings. Change 1 BST 5-94 Change 2 BST 4-95
(ed. 1995 with revisions 1 and 2)
State standards
GOST 12.1.036-84. SSBT.
Noise. Permissible levels in residential premises and public buildings
GOST 12.1.050-86. SSBT.
Methods for measuring noise in the workplace
GOST 12.1.001-83.
Ultrasound. General safety requirements.
GOST 12.1.003-83*. SSBT.
Noise. General safety requirements.
GOST 12.1.012-78. SSBT.
Vibration. General safety requirements. SSBT. Means and methods of noise protection.
Classification.
GOST 12.1.029-80. SSTB.
Means of protection for workers. Classification.
GOST 12.4.011-75. SSBT.
Methods and means of vibration protection. Classification.
GOST 12.4.046-78. Materials and products. Construction
sound absorbing and soundproof. Classification. "General technical
requirements"
GOST 23499-79.
Building. Materials and products. Sound absorbing and soundproof.
Nomenclature of indicators.
GOST 4.209-79. materials
polymeric rolled and tiled floors. Methods for determining soundproofing
properties.
GOST 24210-80. materials
polymer roll for floors.
GOST 27019-86.
Accelerated method for determining sound insulation properties,
GOST 16297-80. materials
soundproof and sound absorbing. Test methods.
GOST 20444-85. Noise.
Transport streams. Methods for measuring noise characteristics.
GOST 22906-78. Noise. Methods for measuring the sound insulation of outdoor
enclosing structures.
GOST 23337-78. Noise.
Methods for measuring noise in a residential area and in residential and
public buildings. Amendment 1 IUS 4, 1982
GOST 12.2.098-84. SSBT.
The cabins are soundproof. General requirements. Noise. Methods for measuring sound insulation
observation and remote control booths in industrial buildings.
GOST 23426-79. Defence from
noise in construction. Noise mufflers. Methods for determining acoustic
characteristics.
GOST 28100-89. Methods
measurements of sound insulation of casings.
GOST 23628-79. The change
1 BST 12, 1985
GOST 24146-85. auditoriums.
Reverberation time measurement method.
GOST 27296-87. Defence from
noise in construction. Sound insulation of enclosing structures of buildings. Methods
measurements.
GOST 27679-88. Defence from
noise in construction. Sanitary fittings. Laboratory method
noise measurements.
Sanitary standards
SN 4396-87 Sanitary standards for permissible sound volume
sound-reproducing and sound-amplifying devices indoors and on
open areas.
SN 2.2.4/2.1.8.562-96 Noise on
workplaces, in the premises of residential, public buildings and on the territory of residential
buildings. Ministry of Health of Russia, M. 1997
SN 2.2.4 / 2.1.8.562-96 "Industrial vibration, vibration in residential and
public buildings "Ministry of Health of Russia, M. 1997
SanPiN 2.2.4 / 2.1.8.582-96 "Hygienic requirements when working with sources of air and
contact ultrasound for industrial, medical
and household purposes. Ministry of Health of Russia, 1996
SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.567-96 "Sanitary and protective
zones and sanitary classification of enterprises, structures and other objects”.
SN 2.2.4 / 2.1.8.583-96 "Infrasound at workplaces, in residential and
public spaces and residential areas. Ministry of Health of Russia, M. 1997
Moscow city building codes
MGSN 2.04-97 Permissible
noise levels, vibrations and sound insulation requirements in residential and public
buildings, M. 1997
MGSN 3.01-96 Residential
building.
2
For noise insulation of structural noise, it is recommended to use soundproof panels as the main element in the construction of structures. The panels are produced under various brand names, such as FonStar, Sonoplat, Tycho, SoundGuard and others. The choice is yours. We can only recommend Ticho Group products in terms of price-quality ratio. .
Vibroacoustic sealant is used when filling joints in the construction of floating floors, cladding and framed partitions. The material provides a high degree of vibration isolation, does not cause metal corrosion, has good adhesion to most building materials such as brick, concrete, ceramics, wood. The cured sealant is odorless, but when working with it, ensure good ventilation of the premises and avoid contact with skin and eyes.
Silica fiber gaskets are a lesser known material used for soundproofing rooms with high fire safety requirements. This material is safe for humans and non-flammable.
It is important to note that the presence of one type of sound insulation does not guarantee peace and quiet in your house or apartment - you need to skillfully arrange these materials in order to achieve a really significant effect.
How to protect yourself from the effects of noise useful tips
Spend 1 to 2 hours in silence every day. Since noise negatively affects not only hearing, but also the nervous system, a person simply needs to spend at least 1-2 hours every day in complete silence. Find a quiet and secluded place where no one will disturb you. Turn off gadgets, forget about TV, computer and radio. Take this time to meditate or just lie down with your eyes closed. Your nervous system will be very grateful to you, and you will be surprised to notice that the irritation, the cause of which you could not find, has disappeared without a trace!
Get out in nature more often. The quiet rustle of leaves, the beautiful singing of birds and other sounds of nature will help you take a break from the noisy city and restore peace of mind. It has been proven that auditory cells recover much faster after stress in such natural conditions.
Replace windows, put a second front door. Soundproofing the floor, ceiling, and walls minimizes street noise and helps you build relationships with your neighbors, who like to play bowling early in the morning, and in the evening, for the fifth year in a row, they are doing a major overhaul in the apartment.
Don't listen to music too loudly. Music that is too loud causes permanent damage to your hearing. The problem is that loud music lovers don't care about it until it's too late. Therefore, you should always remember about hearing hygiene!
Buy quality earplugs. Properly selected earplugs can remove approximately 25-35 dB of noise. When making a purchase, be sure to make sure that the earplugs are made from materials that are safe for human health.
Start rearranging furniture. If you want to increase the level of noise isolation in your home, then move a large closet to the wall, and place the bed so that it is as far away from the wall as possible.
Buy new curtains. Properly selected curtains can drown out street noise. Choose curtains from velveteen, velvet, linen, thick cotton, brocade, any other "heavy" material.
A massive lambrequin will not only make an unobtrusive accent on the excellent taste of the owners of the home, but, like curtains, it will perfectly dampen the noise from the street.
Lay a fluffy carpet on the floor. It will perfectly block the noise from below. Carpet will help make your steps more muffled and quiet.
Check plumbing and heating pipes. If you find gaps there, then they must be sealed with cement and treated with sealant.
Although we cannot completely hide from annoying noise that interferes with enjoying the silence, it is in our power to do everything possible to protect our hearing from intrusive sounds to the maximum.Never forget about hearing hygiene, because it is easy enough to lose it, but it is not always possible to restore it!
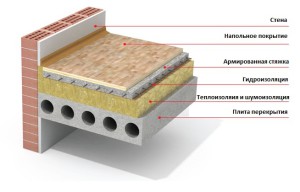
Floor soundproofing panel systems ZIPS.
Another option for soundproofing the floor is the ZIPS-floor frameless system. These are sandwich panels that are laid on a pre-leveled floor. The disadvantage of this solution is the need to level the floor surface before installing the panels (the presence of wet work) and poor sound insulation of the low-frequency component of penetrating noise. The floor will rise 8-11 cm, depending on the type of panels.
Often, however, the home owner does not need to renovate the entire old floor. This allows for additional insulation between the screed and the floor covering. “These mats are two to six millimeters thick and give a good percussive sound,” says Herzig.
It is important to adjust the insulation on the appropriate surface. “Typically: soft floor – soft insulation, hard floor – hard insulation,” Wallenberg says.
If the wrong insulation is selected, the floor covering may be damaged. “If the insulation is too soft, for example, there is an unpleasant impression from the furniture or the chair.”
Peace and quiet - every resident of an apartment building or a house located near a noisy highway dreams of this. Fortunately, soundproofing materials, combined with their proper use, will help get rid of all kinds of noise. This will be discussed - how to properly apply soundproofing.
Insulation of airborne noise in rooms
Modern construction of load-bearing building envelopes and ceilings most often involves the creation of two types of sound insulation. In the process of designing buildings, its value in the range of 45–55 dB is taken into account. It is achieved by a certain massiveness of the wall thickness and is called its own soundproofing structure.
However, the noise level has increased significantly in recent decades and the recommended coefficient is not enough to create comfortable conditions in residential premises. This requires an insulation index of walls and ceilings with a minimum value of Rw = 62 dB. This figure is 8 dB higher than even the most stringent existing standards. Nevertheless, acoustic comfort is provided only upon its achievement, through the creation of additional noise reduction systems.
A separate standard has been established to ensure air sound insulation, but even in this case it is recommended to increase the upper bar of a given index (SNiP-23-03-2003), which is Rw = 52 dB, by at least 5 dB more.
But even such protection does not prevent the sounds of a loudly turned on neighbor's TV from penetrating into the bedroom, especially at night.
Therefore, in order for the stay in the apartment to be truly comfortable, in terms of the penetration of extraneous noise into it, it is necessary to use additional materials.
1
Often, by noise, many people mean only one type of sound - air. These are the sounds that come to us from the outside: passing cars, screams of children in the yard, barking dogs, a construction site nearby. However, there is also an impact type of noise (hammering nails into the wall, the notorious drilling in the neighborhood, rearranging furniture) and structural noise - in this case, the sounds are transmitted directly through the building structure, the elements of which are joined rigidly and without the use of soundproofing pads.
Soundproofing. In our own apartment, house or office, we expect a calm atmosphere of a room that protects us, and perhaps also from disturbing noises from outside. Only when we find these rest areas can we find a healthy, healthy lifestyle and performance-oriented work.
Basic principles of soundproofing airborne, impact and structure-borne noise
Good soundproofing of ceilings, walls and floors is an important feature of high quality rooms.However, if sound transmissions are transmitted through components, they should be prevented by appropriate measures so that noise pollution does not lead to health problems.
A person feels comfortable with sound vibrations within the limit of 25 decibels.
, although sanitary standards somewhat overestimate this rate - up to 30 dB at night and up to 40 dB during the day. Of course, each person has his own standards of perception - someone calmly endures all 60 dB, but more decibels can make you seriously nervous.
Soundproofing – body sound and air sound
First we have to divide the sound into two regions. This is one of the air sounds transmitted by pressure waves as air vibration and perceived directly by the human ear. Airborne sound waves are, among other things. from a radiolane, a musical instrument, or a human voice.
Impact and airborne noise
The second dimension for noise protection is cabinet sound. It propagates through solids, for which in the house, in particular. Ceilings, walls and floors. A particular form of cabinet sound is impact sound, which can cause serious problems for the user in the lower room.
For this, soundproofing was invented - its task is to reflect noise, not to allow them to pass through walls and other obstacles into your environment. Good for those who have thick walls - by themselves they perfectly reflect sound vibrations. However, this hardly applies to most panel houses and new buildings. In addition to sound insulation, there is also sound absorption - the ability of materials to absorb sound waves. Most granular, fibrous or cellular materials just have this ability.
Rest with suitable soundproofing measures
In order to minimize the propagation of sound in residential construction and renovations, certain measures are mandatory. The most important are the separation of components and the exclusion of bend-resistant building materials, but the use of flexible materials with high mass.
The greater the mass of the material, the better it isolates sound. In this case, loose masses such as sand are better than solid masses. Positive insulation properties are also provided by cellulose, fibreboard, cellulose and hemp insulation materials. Excellent sound insulation, in turn, comes down to the built-in mass and porous structure of the material.
Among such materials, soft, semi-rigid and hard are distinguished. Soft sound absorbers are made of fiberglass or mineral wool, as well as felt and ordinary wool. These include pumice and vermiculite - the so-called porous aggregates. Semi-rigid materials include plates made of the same fiberglass or mineral wool, as well as materials with a cellular structure, for example, polyurethane foam. By the way, their sound absorption coefficient is slightly higher than that of soft ones, but their specific gravity is greater.
Airborne noise is the easiest to deal with - porous and fibrous materials that can be mounted both outside and inside the building are saved from it. In addition, they have another property - thermal insulation, so their use is doubly beneficial. Impact noise can also be "plugged" with closed-cell materials by laying them around the perimeter of walls and ceilings. But structural noise is a more significant problem, because the materials must be laid at the construction stage.
JOINTS AND KNOTS
4.17 Joints between internal
enclosing structures, as well as between them and other adjacent
structures should be designed in such a way that after
construction was absent during operation
buildings did not have through cracks, crevices and leaks, which drastically reduce
soundproofing fences.
Joints in which in the process
operation, despite the design measures taken, mutual
movement of joined elements under the influence of load, temperature and
shrinkage deformations, should be designed using durable
sealing elastic materials and products glued to joined
surfaces.
4.18 Bearing elements of floors
should be supported on internal and external walls or wound into them. free
adjoining load-bearing elements of floors to walls is not recommended.
At junctions without
winding the joined element, a figured joint is recommended,
preventing mutual displacement of elements and supplemented by the use
sealing material. The same junction design should be taken in
places of passage through holes in the ceilings of vertical self-supporting
elements, such as ventilation units.
Joints between carriers
wall elements and ceilings based on them are designed with filling
mortar or concrete. If as a result of loads or other influences
opening of seams is possible, measures must be taken in the design to avoid
allowing the formation of through cracks at the joints.
4.19 Joints between carriers
elements of internal walls are designed, as a rule, with filling with mortar
or concrete. The mating surfaces of the joined elements must form
cavity (well), the transverse dimensions of which provide the possibility
densely filling it with mounting concrete or mortar to the entire height of the element.
It is necessary to provide measures to limit the mutual movement of docked
elements (device of keys, welding of embedded parts, etc.). Connecting
details, releases of fittings, etc. should not interfere with the filling of the joint cavity
concrete or mortar. It is recommended to fill joints with non-shrinking
(expanding) concrete or mortar.
4.20 acoustically homogeneous and
double partitions, based on the load-bearing structures of the floor, should
be installed on sealing and leveling materials (cement-sand
mortar, cement pastes, etc.). In places where they adjoin the ceiling, there should be
the use of sealing material is provided for the entire depth of the joint
(drawing ).
The junction of partitions to the outer and inner walls should be decided
similar to the connection to the ceiling.
4.21 Carrier conjugation
elements of internal walls with external walls should be carried out with
by inserting the inner wall into a groove or into a joint between the elements of the outer wall and
the device of a monolithic joint, excluding the formation of through cracks.
4.22 When designing a joint
between the prefabricated elements of the interfloor ceiling within the premises should be
arrange the joint monolithic, excluding the formation of through cracks and
place sealing gaskets made of sealing materials at the joint
(drawing ).
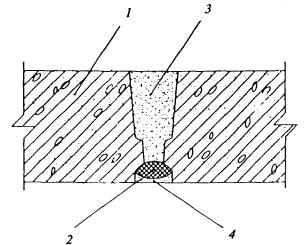
1 - the bearing part of the floor; 2 — partition element;3 — sealant
(sealing gasket or cord);4 — solution
Figure 16 - Scheme of a constructive solution for the junction of a double partition to
overlap
1 - prefabricated floor element; 2 — sealant; 3 — mounting
concrete; 4 — solution
Figure 17 - Scheme of a constructive solution
located within the premises of the junction of the elements of the floor using
sealing material
4.23 Joint design in double
walls located within the premises should not create a rigid connection
between the layers of the wall. At the junction in the gap between the layers of a double wall
a sealing bar with soundproof gaskets should be placed.
4.24 When designing prefabricated
structural elements must take such a configuration and dimensions
abutting sections that provide placement, sticker, fixation and
required compression of sealing materials and products when their application
provided for in this Code of Practice.
When sizing
gaps and cavities (wells) in the joints, tolerances should be taken into account when
production and installation of prefabricated elements With so that, with possible
under adverse conditions, reliable sealing of the joint was ensured,
provided by the project.
The need for additional sound insulation from special materials in certain rooms
Since the sound insulation provided by the main building materials is not enough, measures should be taken to strengthen it with special ones - soundproofing.
The assessment of the effect produced by them is calculated by the standards provided for the additional restriction from airborne noise. They are much lower than those applied to load-bearing structures and are in the coverage ∆Rw = 0–20 dB.
The calculation is made on the basis of the coefficient of anti-noise limitation of slabs and walls, both enclosing and partitioning. The choice of the insulation method is influenced by the appointment of rooms and the proximity to auxiliary premises: bathrooms, elevator shafts, etc.
As practice shows, increasing sound insulation by building partitions with bricks turned out to be ineffective. Since this leads to the fact that the index increases slightly, by no more than 6 dB, but the pressure on the structural part of the base doubles. The area is also lost, since the laying in half a brick has a width of 120 mm.
Much more useful in this sense isolating systems, purposefully prepared to perform the function of dampening sounds. They give good results. Prefabricated structures are made from special materials, forming a serious barrier that serves to prevent the penetration of interference.
This is a device of multilayer false walls, with a low mass, with alternating layers of sound-reflecting and sound-absorbing building materials.
This methodology is based on the fact that the sound wave that has passed through the first barrier is first absorbed, then reflected by the foil material, after which it changes direction, is again absorbed by the sound absorber and attenuates. Theoretically, this technique looks ideal, but in practice its flawless implementation is difficult.
Noise concept and main types
From a physiological point of view, noise is any sound that is undesirable for human hearing and has a negative effect on our health. If we consider noise from a physical point of view, then it is a random combination of sounds of different strength (intensity) and frequency. These sounds occur during certain vibrations in gaseous, liquid, solid spheres.
If we classify noise according to the nature of its occurrence, then we can distinguish the following types of it:
- hydraulic;
- mechanical;
- electromagnetic;
- aerodynamic.
According to the nature of propagation in the room, the following types of noise are distinguished:
- airborne - noise that is emitted directly into the air (talking, crying of a child, TV, music center, radio, etc.);
- structural - noise that arises from a mechanical impact and is heard at a considerable distance from the source (walking on the floor, which is heard in an adjacent room, vibration caused by the operation of an elevator, fan, pump, hand-held power tools, etc.);
- shock - noise that is created as a result of direct contact of objects (impacts on the floor, wall, knocking on pipes, etc.) and spreads over long distances.
Noise level is usually measured in decibels (dB). Sound in decibels has the following strength:
- in the forest - 12 - 26 dB;
- human whisper - 20 - 30 dB;
- while cooking on the stove - 36 - 45 dB;
- during a normal conversation - 40 - 50 dB;
- in the elevator - 36 - 44 dB;
- in an average office - 55 - 65 dB;
- outdoors - 75 - 85 dB;
- baby crying - 76 - 82 dB;
- during the operation of the music center - 84 - 88 dB;
- in industrial factories - 75 - 115 dB;
- during operation of the chain saw - 100 - 105 dB;
- during the operation of the jackhammer - 118 - 126 dB;
- during the takeoff of a jet aircraft - 120 - 130 dB;
- near the bell of a meter horn (vuvuzela) - 130 - 140 dB;
- during rocket launch - 145 - 150 dB;
The sanitary standards state that during the daytime, near houses and buildings, the noise level should not exceed 55 - 58 dB, and from 11 pm to 7 am - 45 - 48 dB.In apartments, during the day, the noise level should not exceed 40 dB, at night - 30 dB.
3
For protective materials of this kind, such an indicator as measured in dB is typical. The second indicator is the degree of sound absorption, which is measured from 0 to 1. The closer this degree is to one, the better the material. As already mentioned, thick walls themselves protect the comfort of our home from extraneous sounds. However, to increase the massiveness of walls and ceilings is a task too difficult for the layman, and inefficient.
In most cases, drywall acts as a rigid material - its thickness is optimal for interior work, when it is important to preserve as much living space as possible. Drywall plays the role, while a layer of soft material takes on sound absorption
As already mentioned, these include glass wool, mineral wool, polyurethane foam and other cellular formations. For effective sound absorption, the layer of material in a multilayer structure must be at least 50 mm and make up at least half of the entire structure.
The task, as well as in the house, is performed by an acoustic ceiling - also a multilayer structure that reduces the energy of sound vibrations and absorbs them. This requires the formation of an air space between the floor and the ceiling area - it is filled with pressed mineral or fiberglass boards.
After all, there is a cheaper polyethylene foam! Quite often, laminate flooring manufacturers offer it along with their products. Polyethylene foam is used both for soundproofing floor coverings and floating floors, and for sealing joints. It is resistant to almost all solvents, it is in good contact with cement and other finishing materials. However, when wetting the space filled with polyethylene foam, good conditions are created for mold colonies. In addition, prolonged loads lead to a loss of material thickness (up to ¾ of the original value), which in turn leads to a loss of soundproofing properties.
The composite material, consisting of two layers of polyethylene film and expanded polystyrene beads, is an improved version of the use of polyethylene. The top layer provides protection against moisture penetration into the structure. The lower film lets air and steam into the space between the films, but from there they are removed through the seams. Such ventilation prevents the accumulation of moisture and mold. The composite material does not deform and serves for a long time - from 20 years. When laying, the use of adhesives is not required.
The cork-rubber backing consists of cork and rubber granules. This material perfectly dampens the vibration of household appliances and other appliances. It is effective to lay such a substrate both under elastic and hard floor coverings: linoleum, parquet, laminate, tile. However, the cork-rubber coating needs additional protection from moisture, since it serves as a medium for the emergence and development of mold.