Step-by-step instructions for adjusting the temperature
To ensure a comfortable stay in the room, you need to perform some basic actions.
- Initially, on each battery, it is necessary to bleed the air until water flows in a trickle from the tap.
- Then you need to adjust the pressure in the batteries.
- To do this, in the first battery from the boiler, you need to open the valve by two turns, in the second - by three, and then in the same way, increasing the number of turns of the opened valve on each radiator. Thus, the coolant pressure is evenly distributed over all radiators. This will ensure its normal passage through the pipes and better heating of the batteries.
- In a forced heating system, control valves will help to pump the coolant, control the rational consumption of heat.
- In the flow system, the temperature is well regulated by the thermostats built into each battery.
- In a two-pipe heating system, it is possible to control not only the temperature of the coolant, but also its amount in the batteries using both manual and automatic control systems.
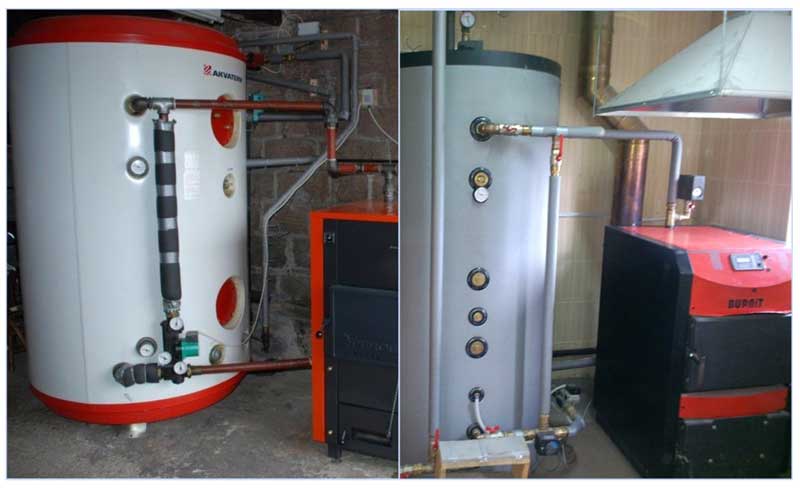
Bypass in the piping system of a solid fuel heating boiler
The main difference between a solid fuel boiler and a gas boiler is the high combustion temperature of heating materials (charcoal and coal, firewood, peat briquettes, pellets) and the impossibility of adjusting it.
If solid fuel heating boilers are heated, they reach very high temperatures within a short time, and the interaction of hot air with cold heat carrier leads to too large a temperature difference. This factor negatively affects the strength characteristics of materials separating sources, leading to their accelerated wear - cast iron does not like such temperature changes and can crack, and steel is subject to increased corrosion. In addition, rapid high-temperature heating contributes to the formation of condensate on the surface of the chimney, on which soot incoming with smoke settles.
The only technically acceptable and competent way out is to reduce the time period for the interaction of hot air in the boiler with a cold coolant. To solve this problem, a small heating circuit of a solid fuel boiler is created, in which a small amount of liquid circulates. Moving in a vicious circle through the bypass jumper, the water quickly warms up, after which it gradually enters the main system through a slightly opening thermostatic valve set to a certain temperature. Hot water is mixed with the main coolant and gradually heats it up, ensuring a smooth start of the entire system without sudden temperature changes. This technique significantly extends the service life of all equipment, reduces the frequency of preventive maintenance for cleaning chimney channels, and increases the efficiency of the system.
Rice. 14 Bypass in the piping system of a solid fuel boiler
Use cases
Bypasses have several purposes.
Temperature control in the radiator
To control the temperature in a system with a bypass, the following elements are installed on the heater (after the shut-off valve):
- Control valve for manual temperature change. Turning the knob changes the area of the orifice in the valve. Accordingly, the amount of HP entering the heater and its temperature also change.
- Valve with thermal head for automatic temperature change. The regulator sets the position corresponding to the desired temperature. To increase the temperature, the valve is moved to the “open” position and the HP passes through to heat the heater.Otherwise, the valve is moved to the "closed" position so that the heater cools down.
Both elements regulate the flow of coolant through the heater, directing its excess around the radiator through a shunt jumper.
Operation without power supply
If the gravity heating system is equipped with a central heating valve with a bypass, then in the event of a power outage, the circulation of the HP continues through the bypass. With a non-return valve on the bypass, this happens automatically, the ball valve must be opened manually.
Attention! If the ball valve is not opened in time when the pump is stopped (while the solid fuel boiler is running), this can lead to circulation disturbance and damage to the boiler equipment. Therefore, for the central heating, an uninterruptible power supply is installed with a battery life of 5-10 minutes
This is enough time to open the tap after a power outage.
Therefore, an uninterruptible power supply with a battery life of 5-10 minutes is installed for the CN. This is enough to have time to open the tap after a power outage.
Improvement of the one-pipe system
For a comprehensive modernization of a single-pipe system, technical solutions are used:
- Each radiator in the house is equipped with a shunt jumper and a valve with a thermal head for uniform heating of all heaters.
- Each riser after the last battery is equipped with a special thermostatic regulator with an external temperature sensor. When the regulators on the riser batteries are closed, the return temperature is higher than the calculated one. In order not to waste the heated HP in vain, the thermostatic regulator closes the riser. This allows you to balance all the risers in the house in terms of HP flow depending on the temperature.
As a result of a comprehensive modernization, the actual consumption of HP can be reduced from 500 liters per hour to 100 liters per hour while maintaining a comfortable temperature.
Some installation features
Using information from the Internet when designing a system and doing your own installation, remember that a large amount of material read and watched video increases your chances of successfully completing what you started. But the best way to organize heating with your own hands would be to attract, at a minimum, a professional practitioner for consulting support.
To ensure high-quality heating of the extreme radiators in the chain, the number of their sections should be increased.
For the gravity version of the system, pipes of significant diameter are necessarily used. And the total length of the circuit should not exceed 30 m.
The installation of the supply main pipe must be carried out at a slight slope. The radiators themselves are installed at the same height and do not distort the “geometry” of the room at all.
The vertical wiring of the "Leningrad" and the long "horizontal" will definitely require the introduction of a circulation pump into the system.
When installing a supply pipe in the thickness of the floor with your own hands, you should remember about the need to insulate it with heat-insulating roll materials. This will save you significant money during the operation of the system and will not lead to overheating of the "underground" space.
Photo of a needle type crane
ball valve
Only needle-type valves should be used as shut-off valves on bypasses and auxiliary circuits of the system. They are able to smoothly regulate the flow of fluid through themselves. The use of ball valves is not allowed here, as they are not designed for "semi-open" operation. They are either closed or completely open. Only in these two positions is their long-term performance preserved. There are enough videos on the net on this subject.
Finishing a long stream of thoughts, we want to note that the single-pipe “Leningradka”, which has long been proven for decades of use, with a modern “upgrade” with a circulation pump and control valves on bypasses, allows you to get the benefits of a more complex heating system with its real simplicity and low investment. Ensure its proper installation with your own hands and spend the cold seasons in the warmth and comfort of your private home.
Rules for installing a bypass in a heating system
It is desirable that specialists take up the installation of the bypass on the heating battery. They will mount all the equipment according to the established rules and standards, carry out pressure testing of the system, and check for defects. But if a situation arises when you need to put the jumper on your own, use a number of rules that will help you do this.
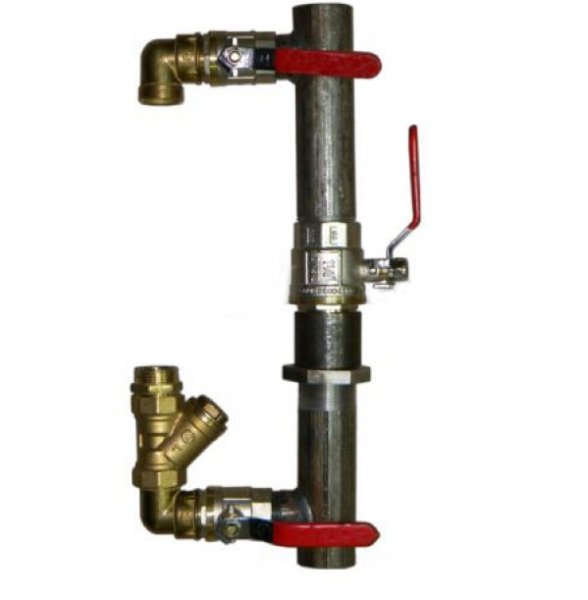
- The decisive role in the installation of the jumper is played by the correctness of the calculations made. The bypass diameter must be one size smaller than the pipe diameter. You can take a ready-made jumper, or make it yourself.
- If you have not previously mounted such elements, it is better to take a ready-made jumper. This will keep the chance of errors to a minimum.
- The bypass must not be installed directly on the riser. It should be moved closer to the radiator. However, you can not install it back to back, as this can lead to improper operation of the heating system and overheating of the return current. As a result, the effect of the jumper installation becomes minimal.
- After installing the bypass, it is necessary to carry out a pressure test with a pressure 1.5 times higher than the calculated one and check the system for leaks.
Installation and connection
After studying the design and purpose of the bypass, it is necessary to find out the features of its installation. When installing a device in a system, certain factors are taken into account, among which the most important are the following:
- the bypass diameter is smaller than the diameter of the supply and return pipes (if the inlet has a diameter of 3/4″, then the bypass is 1/2″);
- the temperature at the bypass installation site is the lowest;
- maximum approach to the radiator and removal from the riser;
- installation in a horizontal position, which avoids airing;
- the possibility of rapid dismantling of the radiator requires the installation of locking elements, for which ball valves are used.
Connected outlet pipe.
Installing a bypass channel for a radiator
When connecting new radiators to an old one-pipe system, it is first necessary to ensure that the coolant is drained. Next, the radiator body kit is assembled. The grinder cuts off old cast-iron batteries, with the help of pipe wrenches, unnecessary parts of the pipe with a non-working tap are unscrewed. Then a thread is cut and a structure is assembled, the elements of which are a tee, an extension and ball valves with an American.
The radiator screens are attached before it is mounted on the wall. When assembling a heating system with a bypass, you must remember to maintain the required center distance of the radiator. At the last stage, the pipes are cleaned and painted.
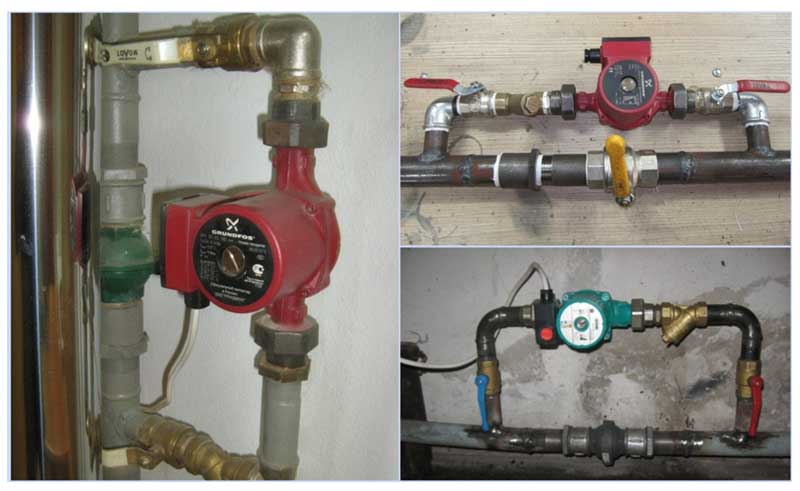
Installation with circulation pump
If it is necessary to install a circulation pump in the system, a cleaning filter is used to protect the expensive blower mechanism from impurities in the coolant. The protective properties of the filter are provided by a metal mesh that traps large particles of contaminants. The filter has a special container for collecting contaminants, equipped with a cleaning hole. When installing, it is recommended to place the filter with the drain hole down. A cleaning filter is mounted directly in front of the pump inlet.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=22c2iR87zxw
When using a circulation pump, a check valve is used as shut-off elements, without which the coolant will pass only in a small circle.However, a ball valve is more reliable than a valve that ensures the automatic operation of the system. In the old one-pipe schemes, the second option is applicable.
In the first case, the bypass in the heating system is installed both on the return and on the supply pipeline, and in the second - only on the return pipe.
Possible causes and procedure for replacing the bypass section
During the operation of the heating system, it may be necessary to replace the bypass channel. The need for this operation is due to the failure of the device or the need to install additional components in its composition. When using modern polypropylene pipelines, the first option is unlikely, therefore, in most cases, replacement is carried out to install a check valve or ball valve.
The order of the operation depends on how the bypass section is connected to the circulation pipeline. With a detachable threaded connection, the bypass section is connected to the inlet and outlet pipes through tees. When dismantling, it is necessary to unscrew the nut with a drive or "American". If it is planned to complete the bypass, the length of its pipe must be reduced by an appropriate amount.
Principle of operation
The work of the bypass consists in the complete or partial direction of the coolant bypassing the main pipeline. A bypass channel is needed in two cases:
- for radiators of a single-pipe heating system;
- for circulation pumps.
Faucet bypass.
Despite the general principle design, in each case the bypass has a different purpose. For the radiator, it acts as a thermostat, directing excess water around the heater. When installed as a piping of the circulation pump, the bypass is switched on in the absence of power supply. In both of the above cases, it provides an additional function - it allows you to dismantle the device without stopping the entire system, which may be necessary for repairs or if a pump or radiator is planned to be replaced.
Main functions
The diameter of the bypass installed between the radiator pipes at the inlet and outlet is smaller than the diameter of the supply pipe. It is this installation that allows the system to remain operational during the repair and replacement of components and parts, as well as for their cleaning.
Battery design diagram.
Also, the bypass accelerates the supply of coolant when filling the system or in the process of emptying it. A bypass is used in single-pipe heating systems, installing it as close as possible to the heating battery, but as far as possible from the riser. In this case, it becomes possible to regulate the temperature of the water in the radiator, changing the intensity of its supply. A control valve or thermostat is installed between the bypass and the radiator.
Signs of high quality
A quality certified bypass will have the following characteristics:
- no damage at the joints;
- high reliability of threaded connections.
The principle of operation of the Leningradka heating circuit
The advent of modern heating equipment and new technologies has made it possible to improve Leningradka, make it manageable and increase its functionality.
The classic "Leningradka" is a system of heating devices (radiators, converters, panels) connected by a single pipeline. A coolant circulates freely through this system - water or a mixture of antifreeze. The boiler acts as a heat source. Radiators are installed around the perimeter of housing along the walls.
The figure shows the implementation of the closed circuit "Leningradka" with an upper pipe supply and forced circulation. One pipeline connects the boiler, radiator batteries, the coolant moves through it, its direction is indicated by arrows.The red color indicates the pipeline that gives off heat, the blue color indicates the pipe through which the cooled coolant moves
The heating system, depending on the location of the pipeline, is divided into two types:
The piping of the system can be located below, above and diagonally. The top pipes are considered the most efficient in terms of heat transfer, while the bottom pipes are easier to install.
When connecting heating devices to the heating main at the bottom, it is necessary to provide for a narrowing of the pipes in the area necessary to direct the coolant to the radiator
The circulation of the coolant can be forced (using a circulation pump) or naturally. Also, the system can be closed or open type. The features of each type of system will be discussed in the next section.
The one-pipe heating system referred to as "Leningradka" is suitable for one-, two-story residential buildings of a small area, the optimal number of radiators is up to 5 pieces. When using 6-7 batteries, it is necessary to make rigorous design calculations. If there are more than 8 radiators, the system may not be efficient enough, and its installation and modification may be unreasonably expensive.
The diagonal connection option in a single-pipe circuit, although it allows you to increase the heat transfer of the system by 10 - 12%, but does not eliminate the "skew" in the temperature regime between the first from the boiler and the extreme batteries
What is a bypass in a heating system
Bypass - Russian pronunciation of the English word "bypass", translated means to bypass, bypass, detour, detour. The device plays a similar role in the pipeline system - it creates a bypass for the working fluid, becoming a kind of jumper bypass between the entry and exit points of the included heat exchange devices.
Structurally, the part is a short pipe section made of a material similar to pipes, installed at a small distance from the inlet and outlet fittings of the connected heat exchanger. The pipe section can be welded in the case of using metal pipes, fixed to threaded fittings when using a metal-plastic, soldered into a polypropylene line.
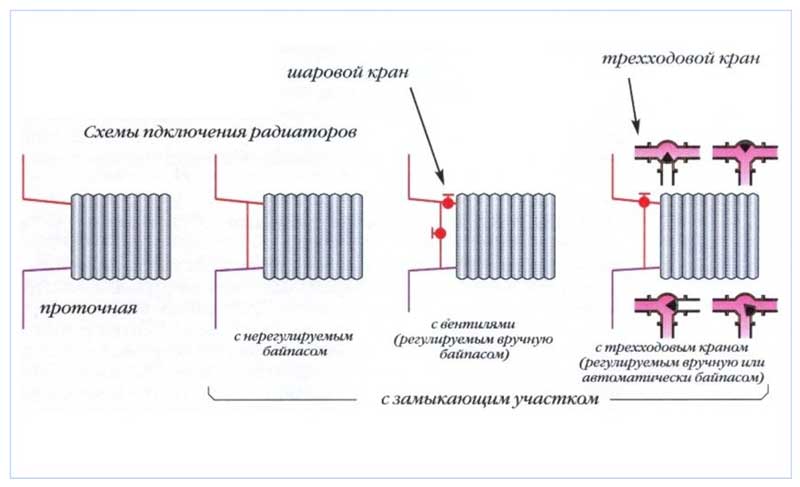
Rice. 2 Radiator connection diagrams
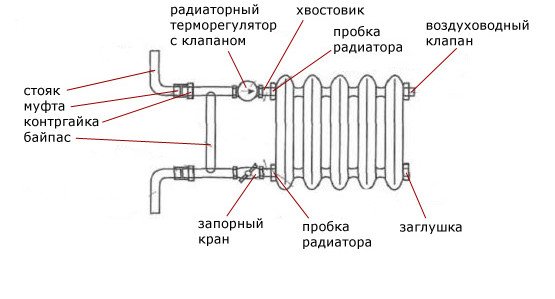
Bypass in the piping of the heating radiator
When installing a jumper node, the following basic rules are observed:
- The jumper is placed as close as possible to the inlet radiator fittings - this contributes to more efficient heating of the heat exchangers as a result of the passage of large volumes of coolant through them.
- Shut-off ball valves must be placed at the inlet and outlet of the batteries, allowing them to be disconnected from the network for maintenance and repair work without draining the coolant and stopping heating.
- When using pipelines made of modern materials - metal-plastic or polypropylene for heating individual residential buildings, it is better to install a control valve in the bypass bypass. With it, you can reduce the flow passing through the jumper, as well as adjust the heating temperature of all radiators in the line by changing the cross section of its passage channel.
Rice. 8 Examples of installing a control valve between bypass
What is the bypass on the radiator for?
As noted earlier, the use of a bypass with heating radiators is effective only in single-pipe schemes, the part allows you to achieve more uniform heating of all heat exchange units. Also, the presence of a bypass allows you to supply water to subsequent heat exchangers in case of failure or shutdown of one of them.
Using a tap installed in the jumper, you can manually adjust the system so that all radiators heat up evenly.To do this, the cross section of the bypass to the heat exchangers closest to the boiler is increased, and at the most distant radiators it is reduced, thus controlling the flow passing through the batteries.
Rice. 9 Tying the radiator with a polypropylene and metal-plastic pipe
Independent installation of the bypass in the radiator piping
Before installing the bypass, you can consider factory samples - the industry produces finished products for radiator heat exchangers, in which the distance between the connecting inlet fittings corresponds to the standard axial dimension from the upper and lower connection points of the radiators.
The task of how to make a bypass to the heating system has different solutions depending on the material of the pipes used. Usually, self-assembly of this element does not cause any particular difficulties for any owner (with the exception of polypropylene pipes) who has minimal plumbing skills and the necessary tools (you need one or two adjustable wrenches).
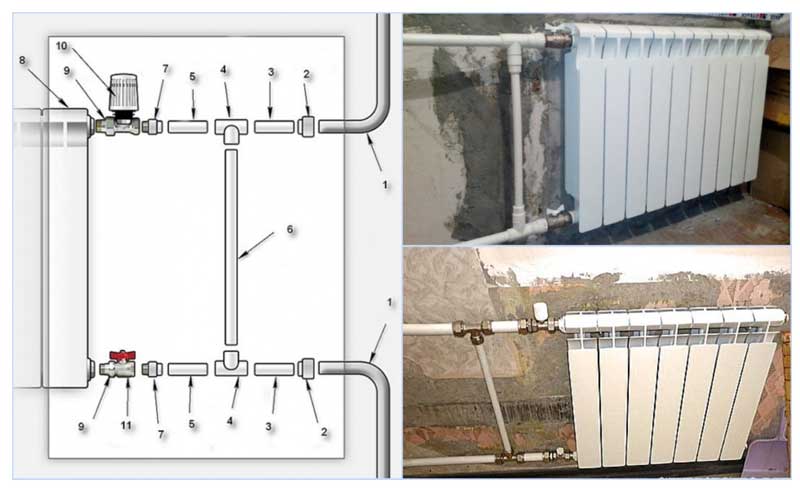
Figure 8 shows the installation of a bypass in a polypropylene water line, which is connected to the riser 1 through adapters 2. Bypass 6 is connected through a tee 4 connected to the main by pipe sections 3 and 5. To a thermostat 10 connected to a radiator 8 through an American 9 , a pipe section made of polypropylene is connected using a fitting adapter from metal to polypropylene 7, in the same way the line is connected to the shut-off valve 11.
In this scheme, all pipes have the same outer size, therefore, the operation of such a design is inefficient (the internal channel section of the bypass pipe in a single-pipe connection should be smaller), for its normal operation, a control valve must be inserted into section 6, reducing the through channel opening.
Similarly, a jumper-bypass is mounted on the battery when using metal-plastic, the structure can be assembled most quickly using compression fittings (Fig. 8).
It should be noted that in the diagram in Fig. 8 pipe sections 5 are optional, the tee can be connected directly to the ball valve and thermostat by extending section 3.
If metal pipes are used in heating for water supply, the bypass jumper can be placed directly near the taps on the inlet and outlet battery fittings by connecting two tees to them. It is easy to make the diameter of the bypass jumper smaller than the main line with a small cross-section bypass pipe, while it is not necessary to put a shut-off valve in the jumper.
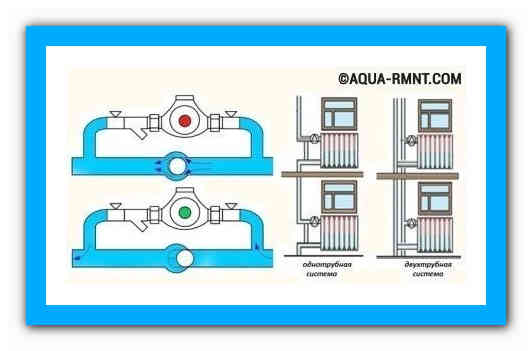
Rice. 10 Parallel bypass branch in the circuit of the circulation pump
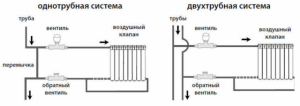
Types of heating systems and the principle of adjusting radiators
Handle with valve
In order to properly adjust the temperature of the radiators, you need to know the general structure of the heating system and the layout of the coolant pipes.
In the case of individual heating, adjustment is easier when:
- The system is powered by a powerful boiler.
- Each battery is equipped with a three-way valve.
- Forced pumping of the coolant has been installed.
At the stage of installation work for individual heating, it is necessary to take into account the minimum number of bends in the system. This is necessary in order to reduce heat loss and not reduce the pressure of the coolant supplied to the radiators.
For uniform heating and rational use of heat, a valve is mounted on each battery. With it, you can reduce the water supply or disconnect it from the general heating system in an unused room.
- In the central heating system of multi-storey buildings, equipped with a supply of coolant through a pipeline from top to bottom vertically, it is impossible to adjust the radiators. In this situation, the upper floors open windows due to the heat, and it is cold in the rooms of the lower floors, since the radiators there are barely warm.
- More perfect one-pipe network.Here, the coolant is supplied to each battery with its subsequent return to the central riser. Therefore, there is no noticeable temperature difference in the apartments of the upper and lower floors of these houses. In this case, the supply pipe of each radiator is equipped with a control valve.
- A two-pipe system, where two risers are mounted, provides the supply of coolant to the heating radiator and vice versa. To increase or decrease the coolant flow, each battery is equipped with a separate valve with a manual or automatic thermostat.
Device Mounting Recommendations

Thus, using accessible and functional regulators in the heating system, it is possible to achieve significant results in matters of energy saving and to achieve a smooth distribution of heat from heaters in a house or apartment.
The regulation of the heating battery depends on the heating system installed in the apartment. If you cannot do it yourself, it is best to invite specialists who will do everything at the highest level.
Bypass examples
Example #1 - adjusting the coolant
The functional purpose of the bypass is to return excess coolant from the heating battery to the riser when its quantity is changed by means of a manual or automatic thermostat. In other words, through the bypass, the coolant is transported parallel to the shut-off and control valves. Without the presence of this element, it is impossible to repair the battery when the heating system is in working condition. The bypass also speeds up the process of filling or emptying the system.
This is how the bypass can be integrated into the heating system
Example #2 - running the system without electricity
Installing a bypass in a heating system is especially relevant when installing modern heating systems that involve the use of circulation pumps. People who encounter heating installation for the first time often ask craftsmen or consultants in stores: “How will the system work if the electricity fails?”. After all, everyone is used to the fact that a standard floor boiler, operated in the past, was not connected to electricity. And equipping the heating system with a circulation pump makes it volatile.
That's it, in such situations, the bypass comes to the rescue. Its role is very simple - at the time of a power outage in the network, the consumer must turn off the coolant supply valves to the pump and open the valve on the central pipe. By the way, this can happen automatically if a bypass with a valve is used. These simple manipulations put the heating system into natural circulation mode.
Installation of devices on the bypass should be carried out towards the coolant in the following sequence:
- filter;
- check valve;
- circulation pump.
It is important to note that the introduction of a bypass into the riser near the circulation pump must be carried out using shut-off valves. And the element itself is better to install horizontally
In this case, the system will be protected from air accumulation.
Schematic representation of a bypass pipe built into the heating
Example #3 - resuscitation of one-pipe heating
Yes, a single-pipe heating system is obsolete today, but it can still be found quite often in Soviet-built buildings. Moreover, there are such miracles when such heating functions very efficiently and in apartments in winter, it’s just hot.Installing a bypass will also help to correct the situation. In principle, there is nothing complicated in this work, but it is still worth observing some conditions:
- The bypass should be located at the maximum distance from the vertical section of the pipe, that is, as close as possible to the battery.
- The bypass pipe can be made directly at the installation site - a pipe, a tee and welding will be required. Or you can purchase such an element ready-made and install it on threaded connections.
- The radiator inlet and bypass must be separated by an expansion valve or radiator thermostat.
By installing such a device, you will get a banal "temperature controller in the house."
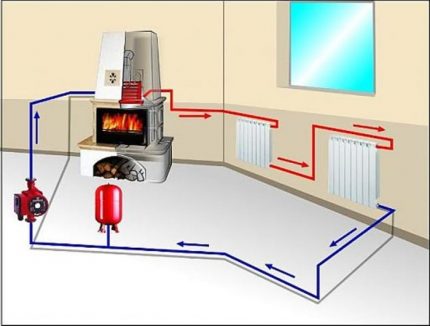
Bypass in the boiler room
In boiler piping schemes, a bypass line is also necessary in 2 cases:
- as a bypass for a circulation pump;
- for organizing a small circulation circuit for a solid fuel boiler.
A pump installed on a bypass pipeline is found in heating systems quite often, sometimes even without special need. The fact is that a one-pipe or two-pipe heating system, originally conceived with forced circulation, can never function when the pump is turned off. She does not have large slopes and increased pipe diameters for this. But the bypass for the pump is exactly what is needed so that the water can flow in a straight line, while the pumping device is not working.
Hence the conclusion: when connecting a system designed for forced circulation to the boiler, it is not necessary to put the pump on the bypass. Turning off and removing the unit in any case will stop the movement of the coolant, so the pump is installed in a straight line.
Another thing is a system adapted to the natural movement of water. It often happens that in order to increase efficiency, they do not just build in a pump, but install a bypass system with a check valve on the line. This allows you to automatically switch to natural circulation in the event of a power outage, which is reflected in the diagram:
While the pump is running, it presses the valve on the back side with its pressure and does not let the flow flow in a straight line. One has only to turn off the electricity or close one of the taps, as the pressure disappears and the bypass valve opens a direct path to the coolant, the convective movement of water is restored. You can safely remove the pump or clean the sump, the operation of the system will not be disturbed by this, it will simply switch to another mode.
Well, the last place of application of the bypass is the small circulation circuit of a solid fuel boiler with a mixing unit. Here, a jumper connected to a three-way valve allows the heat generator to warm up to a temperature of 50 ºС in order to avoid low-temperature corrosion on the steel walls of the furnace. In this case, the bypass circuit looks like this:
The principle of operation is simple: the valve does not let cold water from the system into the boiler until the coolant circulating through the bypass line is heated to the required temperature. Then the valve opens and passes cold water into the circuit, mixing it with hot water. Then condensation does not form on the walls of the furnace and corrosion does not occur.
Sometimes a bypass is needed in the water supply system. For example, to remove for repair, washing or replacing a heated towel rail in the bathroom. Since it is connected to the DHW riser, its dismantling in an apartment building will create a lot of inconvenience. It is easier to foresee this in advance and put a jumper with a tap when installing the heater.
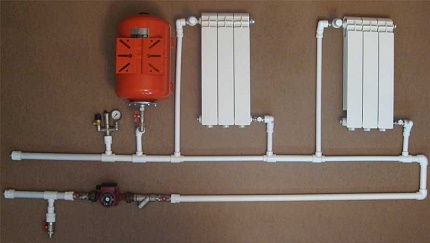
Bypass in the circulation pump assembly
In modern heating, circulating electric pumps are gradually replacing distributions with natural circulation due to their advantages: the rapid movement of the fluid flow and the regulation of its speed, which allows for accelerated heating of a cold room.An important advantage is the ability to program operating modes, the safety of a closed circuit when using poisonous antifreeze antifreeze - ethylene glycol.
The only drawback is the dependence on the circulation pump - if there is no electricity supply or if it breaks down, the heat supply becomes impossible. The use of a simple jumper between the sections of the forward and reverse branches with an installed electric pump allows you to get rid of this problem, creating a workaround for the working fluid. When connecting, it is better to install the element horizontally, although in practice you can also find a vertical bypass.
Sometimes a shut-off valve is cut into the bypass pipe, while the other two taps are mounted at the inlet and outlet of the unit with a circular pump - this makes it easy to dismantle the pumping equipment without draining the water for repair, maintenance, replacement.
How to do the installation yourself
From the materials you will need:
- drive 1+14″ 200 mm complete with coupling and locknut - 1 pc.;
- threaded outlets 34″ - 2 pcs.;
- ball valve 34″ - 2 pcs.;
- sump 34″ - 1 pc.;
- corners 34″ - 2 pcs.;
- circulation pump 34″ - 1 pc.;
- ball valve 1+14″ — 1 pc.;
Mounting process:
- Assemble the TsN piping (pump, angles, taps, sump, threaded outlets).
- Cut the sling into two halves approximately in the middle of the central section (without thread).
- Connect both halves to a 1+14″ tap.
- Mark and make holes on the halves of the drive for 34 ″ bends to the central valve.
- Disassemble the assembled piping TsN.
- Weld 34″ bends to the halves of the run.
- Finally assemble the TsN piping with sealing of the threaded connections.
- By adjusting the squeegee clutch, set the distance sufficient to install the central pump with gaskets (do not install the pump itself). Pack the coupling and lock it with a lock nut.
- Cut a section out of the return pipe (for bypass welding).
- Weld the assembled bypass to the return pipe section.
- Install CN.
Is a check valve required?
The valve is needed when installing a shunt jumper with a central heating valve in a gravitational heating system to automatically start natural circulation when the central heating is turned off.
Bypass functions in the heating system
Let us clarify that a bypass is a pipeline designed to flow water around a certain section of the highway where any equipment is installed. In heating schemes, it can be found in two places:
- in single-pipe systems as a jumper on radiators;
- on the distribution manifold of water heated floors.
As you know, in a single-pipe heating system, the heat transfer of the first battery affects the operation of the next one, and so on. This applies to both vertical and horizontal layouts. If the bypass setting in the heating system is not done, then the radiators will be connected in series. As a result, the first of them will take away the maximum amount of heat, the second - all that is left, and only the cooled coolant will fall to the share of the third.
To prevent this from happening, the supply and return near each battery is connected by a jumper, whose task is to direct part of the coolant around the radiator. In this case, the principle of operation of the bypass is to transfer the same part of the heat to the near and far heaters and reduce their dependence on each other. How this is implemented can be seen in the figure:
Important. In the shown vertical system, the bypass device is provided so that the diameter of the pipe is smaller than the main line and slightly offset from its axis to the side
The goal is to prevent the coolant from passing under the influence of gravity in a straight line, past the radiator. In a horizontal system, the main pipe itself is a bypass, while it does not move anywhere and everywhere remains the same flow area.
In the heating system, a bypass is needed to evenly distribute heat across the batteries, as well as to carry out their repair or maintenance. If for some reason it is necessary to disconnect and remove the heater, then it is enough to simply close the 2 taps installed at the inlet and outlet of the coolant. Then the water will go along the bypass through the jumper.
But the bypass for heating on the collector of the water-heated floor plays a different role. Here, the bypass line is part of the mixing unit with a three-way valve. The task of the node is to prepare the coolant of the required temperature for supply to the heating circuits of underfloor heating. Indeed, in these circuits, the water temperature does not exceed 45 ºС, while in the supply line it can be 80 ºС.
In normal mode, the three-way valve passes hot water from the system to the warm floor in a limited amount. The rest of the coolant passes through this automatic bypass, mixes with cold water from the collector and returns back to the boiler. Since the temperature difference between the main and the collector is significant, the bypass line is used constantly. It turns out that without it the normal functioning of underfloor heating is impossible.