What is hard water
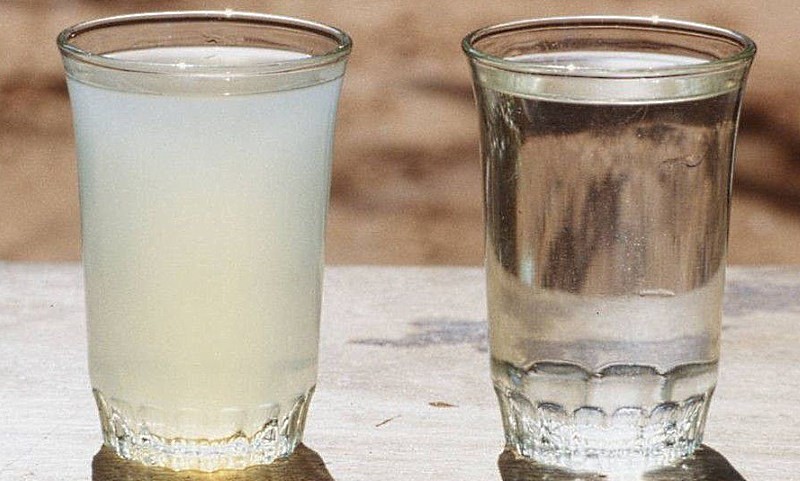
Hard experts call a liquid that contains a lot of salts. Magnesium and calcium are found in it in the form of sulfates, sometimes in the form of bicarbonates. Elements are also found in the form of chlorides. The bitter taste testifies to the increased rigidity. Outwardly, high rates are indicated by the sediment formed at the bottom of the kettle and on the water heating elements.
The liquid is only not contaminated with surface runoff and agricultural waste, but this does not affect the softness.
The indicator depends on the soil horizons through which the resource passes. In the sandy layers, the liquid is softest, and in the limestone horizon it is the hardest. The salt content also increases when water passes through dolomite and gypsum deposits.
Ways to soften hard water
In order to soften too hard well water, several methods can be used. We consider each in more detail.
The easiest way to soften water from a well / well is to boil it. However, it is impossible to boil the liquid in the huge quantities necessary for the normal operation of the water supply system in the house. Therefore, only the use of water softening filters installed on the site of the water supply system will be relevant.
Ion exchange filter
Such a filter contributes to a better softening of water from a well or well. The device is a structure, inside which there are sodium cations in the form of special resins. Their adsorbing ability perfectly neutralizes calcium and magnesium salts, however, such a filter requires constant renewal of sodium crystals (with a regularity of 1 time in 2-4 months, depending on the amount of softened water).
There are such types of ion exchange filters:
- Devices in the form of a simple flask. Suitable for softening small amounts of water and are considered the most economical option.
- Filters with replaceable cartridges. Convenient and compact systems for installation on the water supply system in front of the water point.
- The filter is regenerative. It is a cylinder in which a reservoir with sodium crystals is located. Such a system is considered the most expensive among the listed reagent filters.
If such systems cope well with large volumes of water, then the disadvantages are:
- The need for constant replenishment of stocks of sodium crystals;
- The need to connect filters to the sewer to discharge a saline solution saturated with calcium and magnesium salts;
- In addition, softened water using such a system is not suitable for use in food.
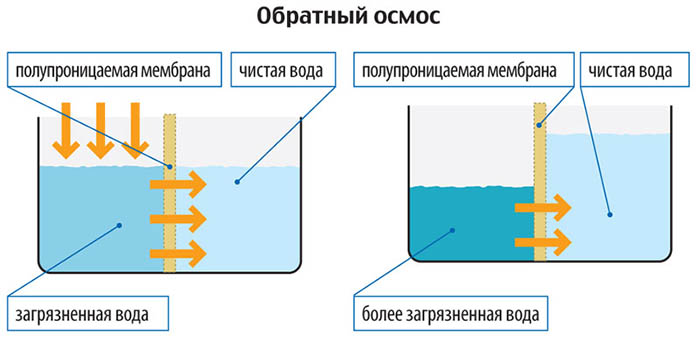
Reverse osmosis filters
These water softening systems are considered the most advanced. Water is purified from inclusions of calcium and magnesium salts here due to a dense membrane through which hard water is driven under high pressure. All harmful impurities settle on the walls of the reverse osmosis membrane, and water is supplied to the water supply system already softened and suitable for domestic and food use, but only after additional saturation of the liquid with useful minerals. Additional mineralization takes place here in the osmosis filter housing thanks to special mineralization cartridges.
An important characteristic of the reverse osmosis membrane of such a filter is its ability to pass liquid molecules, but retain crystals of harmful impurities. The disadvantages of a reverse osmosis system include:
The disadvantages of a reverse osmosis system include:
- The need for constant pressure in the water supply system, equal to 3 atm. and more;
- High price for filters.
Folk ways of softening
Our grandmothers also faced the problems of hard water, and they at least guessed about the dangers of using it. Therefore, there are enough simple and affordable ways to soften in the piggy bank of folk wisdom. We present the most popular of them.
Boiling (and not in an electric kettle, but on a stove, since the desired effect of the decomposition of hardness salts can be achieved only with prolonged heating)
After this, the liquid should be allowed to settle for a day, and only then it should be carefully drained without stirring up the sediment at the bottom.
Freezing is a more gentle way that will allow you to at least partially preserve useful substances in water and not spoil the taste. A transparent container of water must be sent to the freezer and monitor its freezing. As soon as 75-80% of the total volume turns into ice, the vessel is taken out and the liquid residue is drained - salts are concentrated in it, which give high rigidity.
Settling. You just need to pour water into any container and remove it away from sunlight for 3-6 days
After that, you need to carefully drain the upper layers without disturbing the sediment. Such water is not suitable for drinking, but for domestic use it is quite
The addition of silicon or shungite - minerals that literally absorb hardness salts. Our great-grandfathers lined wells with flint to soften the water stored in them. A simpler way is available to us: you just need to lower the sterile stones of silicon or shungite into a container with drinking water. Natural absorbents will absorb salts in 2-3 days, although many recommend increasing this period to a week.
Saponification is one of the ways to prepare water for washing. It will be necessary to grate 15-20 g of laundry or toilet soap and dilute it in 0.5 liters of water until completely dissolved and foam appears. This amount is enough for a bucket of liquid, after which you need to stand everything for at least a night - the soap will react with the salts and send them to sediment. In the morning, the solution is carefully poured into another container and boric acid (2-3 tablespoons) is added to it.
What do you need to soften water?
Ideally, to take advantage of all of our recommendations, you'll need your refrigerator's freezer, peat, ash, and a simple household cleaning filter. At the same time, if you don’t have any items from this list, you don’t need to be upset. There are other simpler ways to purify water.
1. Boiling
At the initial stage, plain water from the tap will have to be boiled. This will get rid of the so-called "temporary hardness" of water. This term refers to hydrocarbon liquid. In the process of boiling unfiltered water, bicarbonates precipitate.
Almost certainly, you have observed such scale inside a kettle or dishes more than once. And the color of the sediment will depend on the percentage of iron contained in the water. It happens that water saturated with iron acquires a yellowish or reddish hue. This is clearly visible to the eye.
The result is that the water acquires a “permanent hardness” (water quality). Naturally, such water is already losing its iron content.
2. Freezing
The technique of freezing ice is used already when we have received water with "constant hardness". The essence of the method is the gradual freezing of water. After about 10% of the initial liquid volume remains unfrozen water, the remainder must be drained.
The remaining ice must be melted to obtain softened water. Salts that are not able to crystallize will leave with the drained ten percent of the unfrozen water. The hardness of water depends on the number of salts.
Minerals and, possibly, useful salts leave the water. And this is also the other side of the coin.
3. Filtering
The following technique will be useful to those readers who are ready to install water filters. The variety of different filters today rolls over, but you can choose the most accurate filter by evaluating the condition of a particular tap water.
To obtain the results of a chemical analysis of your home's running water, the easiest way is to contact your local Sanitary and Epidemiological Station or an independent (but certified) center. Information of this kind can also be provided by direct sellers of filters - water treatment companies with which you are going to cooperate.
In this case, filters can be very different:
- built into the water system of your home;
- dressed on the crane;
- external (water filters, carbon filters);
- any others.
4. Technical cleaning
In this case, we are talking about technical water, but not drinking water! Modern gels, detergents, powders, shampoos, etc. are able to soften water, for example, for showering, washing dishes or laundry.
Liquid soap, shampoo occupies a special category here, since they can contain almost any softening components on a natural basis (minerals, fruits, herbs, etc.).
It is clear that these products are not suitable for drinking water, but it will not be difficult to protect the skin of the hands, head, and body from the effects of hard water.
5. Water for irrigation
Natural additives in the form of ash and peat will help soften the water, for example, for watering indoor plants or flowers in the garden. In any case, it is better to water the plants with soft or softened water.
In dachas, rainwater collected in advance is often used, and this is also not accidental. In addition, peat and ash are excellent fertilizers that will ensure the harmonious growth of your plants.
Good to know
Why soften water? Is there any information that will help to understand the issue a little deeper? Certainly! There she is. The main thing is the advantages of soft water:
- Significant savings in detergents, including toothpaste, because they foam better and are less consumed.
- Save energy by reducing the number of washes and cleanings.
- Extending the life of water pipes and household appliances.
- Long-term preservation of the original quality and characteristics of clothing.
Any, even the most expensive method or method of softening water pays off. As described in the above benefits. But the most important thing is health. You can't buy it. You can't save on it. And any disease is better to prevent than to cure. Water is the easiest way to prolong life and its quality. To do this, it is enough to control its purity and softness!
From advertising, we know that too hard water leads to the appearance of scale and the rapid failure of washing machines. Manufacturers don't lie. Excessive rigidity harms not only household appliances, but also health: it makes hair thin and brittle, accelerates skin aging, contributes to the development of diseases of the kidneys and the genitourinary system, and creates an additional load on blood vessels. Depending on the situation, you can soften the water in different ways, in this article we will review the most affordable home remedies.
Theory.
Water hardness is a parameter that characterizes the concentration of calcium and magnesium salts in the composition. It is measured in units of mol / m3 (mol per cubic meter) or degrees of hardness (accepted in Russia) - mg-eq / l (milligram equivalent per liter). The higher this figure, the worse.
According to the hardness value, water is divided into:
- soft (0-2 ° W) - in nature it is found in swampy areas with peat bogs, and melted snow that is not polluted by other substances also falls into this group. Interestingly, it is very difficult to wash off the soap with soft water.
- medium (2.1-7 ° W) - the most common;
- hard (7-10 ° W) - harmful and dangerous to health;
- superhard (more than 10°F) - in natural conditions it is found in lakes of karst caves, it is impossible to drink such water.
Depending on the substances contained, the hardness of water is:
- constant - caused by the presence of chlorides, phosphates, silicates, sulfates and nitrates of magnesium, calcium in water, which do not decompose when boiled, mainly these substances are removed only by filters;
- temporary - occurs in most cases, due to magnesium and calcium bicarbonates, which decompose when heated, forming scale deposits on pipes and heating devices, which leads to increased energy costs and breakdown.
Features of hard water
Water becomes hard from dissolved salts - calcium and / or magnesium compounds (the cations of the latter are much less common). There are other elements, the presence of which may affect the final indicators of hardness, for example, manganese, strontium, barium
But their influence is so insignificant that it is simply not taken into account.
The general hardness index is usually divided in accordance with the composition of the salts:
- Carbonate or temporary hardness - determines the content of Ca and Mg bicarbonates in water at a pH level exceeding 8.3 units. It can be easily dealt with by prolonged boiling - after an hour, the salts will simply disintegrate under the influence of high temperature and precipitate.
- Non-carbonate hardness is called constant, because it is not so easy to get rid of it. It is determined by the content of stable salts of various acids, which do not decompose and must be removed by other methods, such as reverse osmosis.
In sum, these two indicators just give the overall stiffness, although it is difficult and expensive to calculate them separately. Usually, special reagents or indicator strips are used to determine the actual salt content.
But you can find out that your system has hard water without laboratory tests. In the process of use, it delivers a lot of problems that are simply impossible to ignore:
- White marks on washed clothes;
- Weak foaming of detergents, and as a result - their inefficiency;
- Scale on the walls of the kettle (and imagine what happens to the heating elements of boilers, washing machines and dishwashers);
- Constantly appearing plaque on the mixer and sink.
Hard water also causes considerable harm to the human body. The feeling of skin dryness after contact with such an environment is nothing more than washing off the protective lipid film from its surface. And the use of this water inside without preliminary softening can provoke urolithiasis.
But this does not mean that water softening should be total, even if it is used for drinking and cooking. A liquid completely devoid of salts leads to a deficiency of calcium and magnesium ions in the body, which negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system. The harm and benefits of drinking water hardness is one of the medical paradoxes. But it is allowed simply - compliance with the measure.
“Resoftened” water can also harm steel pipes of plumbing and heating systems - because of it, they are more exposed to corrosive wear and serve less than pipelines transporting harsh media.
Methods to soften water
1. Boiling.
The easiest affordable way to get rid of temporary stiffness without the use of chemicals and complex devices. At high temperatures, bicarbonates and calcium sulfate decompose, precipitating on the bottom of the dishes and heating elements. Softened water is suitable for any purpose: drinking, washing, washing, etc.
Bring the water to a boil, leave for 2-3 minutes, then cool to the desired temperature.
Flaws:
- only the temporary hardness of water is partially reduced;
- limited - it is very difficult to provide all domestic needs with boiled water;
- after some time, due to a layer of scale, heating systems and containers have to be changed or cleaned;
- when boiling water, useful substances evaporate;
- heating requires a significant amount of energy.
2. Settling.
After 1-2 days in a place protected from direct sunlight, it softens water from wells and wells, intended for watering flowers and indoor plants.It can be used for drinking water treatment, but only if the initial hardness is only slightly higher than normal.
3. Freezing.
An effective method that does not change the structure of water, as a result of which all useful substances remain in the composition. Put water in the freezer, when ice appears on the walls of the container, drain the liquid in the center.
Use the melted ice as drinking water or for watering flowerpots.
Disadvantage: it is difficult to prepare large volumes of water with this method.
4. Food and soda ash.
Thanks to its chemical properties, baking soda softens water and reduces acidity.
Add 2 teaspoons of food or 1 teaspoon of soda ash to 10 liters of water, mix well and wait for sediment to appear at the bottom. While cooking, add 1 teaspoon of baking soda to 3 liters of water so that cereals and vegetables boil better.
Flaws:
- water softened with soda cannot be used as drinking water (except for boiling);
- difficulty in the constant processing of large volumes of water.
5. Vinegar and citric acid.
Partially reduce hardness, but significantly increase acidity, as a result of which these products are not recommended for drinking water. Often they are used for cosmetic purposes.
To soften the water for washing your hair, add 1 tablespoon of vinegar (1 teaspoon of citric acid or the juice of one lemon) to 2 liters of water, mix. Let stand 4-5 minutes before use.
6. Rock (cooking) salt.
It is also sodium chloride, which dissolves calcium and magnesium salts contained in water, preventing the appearance of scale on heating devices. Due to changes in chemical composition and taste, this method is not recommended for drinking.
Basically, salt softens water intended for dishwashers. For ease of use, manufacturers supply salt in the form of granules and tablets, but in most cases, the composition of the proposed substance is no different from table salt.
7. Chemicals.
First of all, these are the well-known brands Calgon, Finish and others, which are sold in the form of powder or tablets. Apply according to instructions. Sold in household chemical stores.
Disadvantage: soften water only for washing.
8. Filters.
Versatile systems designed to quickly soften large amounts of hard water and remove harmful impurities. They can operate independently or be connected to the water supply. They differ in design and principle of operation.
Types of water hardness reduction systems:
-
filter jug
- designed for a volume of 1-3 liters, suitable for drinking water purification, tea or coffee preparation. Works with a special cartridge. Depending on the intensity of use and the initial hardness of the water, it lasts up to 2 months, then it requires replacement of the filter cartridge. -
Ion exchange systems
- filter and soften water of any hardness with the help of special ion-exchange resins and saline solution (substances are in different tanks). These filters are characterized by high performance and relatively easy maintenance. Disadvantages: not suitable for drinking water, require periodic replacement of reagents and connection to the sewer. -
Magnetic and electromagnetic softeners
- are installed on highways or on water pipes in the form of overlays. Under the influence of a magnetic or electromagnetic field, hardness salts lose their ability to be deposited in the form of scale and drain into special sedimentation tanks. Disadvantage: not suitable for drinking water treatment.
Folk methods
No opportunity or desire to use the latest miracles of professional development? Then you can use the "grandmother's" methods. They are tested by time and people.
- A large amount of water is difficult to clean and soften with a filter. The simplest and most effective method to deal with impressive volumes is settling for several days.Most often, this method is used to soften liquid from a well or well intended for irrigation or washing. If the latter is produced by means of a unit, it is recommended to purchase a special one.
- Infusion on peat. A bucket of water will need 100 g of peat, which is placed in a canvas bag. Water should be infused for about a day, after which it can be used to water plants.
- silicon liquid. Pure silicon stones are placed in glass or enameled dishes, poured with water at the rate of 100 g per 10 liters, put in a shaded place for 2-3 days, covered with gauze. Drain and use only the top layer of liquid. The bottom layer covering the stones contains harmful substances. After the procedure, the stones must be thoroughly washed and dried. Ready water is recommended to be stored in a cool place, but not in the refrigerator. Also, do not boil it, otherwise it will lose its positive properties.
- Store-bought liquid, rain or melt water can make softer hard water from a tap. To do this, mix them. The proportions depend on the purpose of use.
- Flax decoction. Used for swimming. Infused with flax seeds. For 1 liter boiling water is taken 4 tsp. seeds. The broth is boiled for about 5 minutes, then infused for an hour.
Where does hard water come from
Water hardness refers to the high concentration of calcium and magnesium salts (chlorides, sulfates and bicarbonates) dissolved in it. Chlorides and sulfates are not destroyed by boiling and do not form a precipitate, so they are responsible for the overall (constant) hardness index. Hydrocarbonates, on the contrary, decompose under the influence of high temperature, forming scale. These substances determine the degree of temporary (variable) hardness. According to GOST, water is divided into three categories: soft (up to 2°F), medium (2-10°F) and hard (more than 10°F). The cause of hard water in the well can be deposits of gypsum, dolomite or limestone - alkaline earth metal salts seep into the mine or well and dissolve in the liquid. As a rule, the concentration varies depending on the season: it decreases in the cold season and increases in the heat. Only artesian wells, equipped according to all the rules and isolated from the upper drains, can boast of a stable composition of water.
Best Answers
Mikhail Tyrkin:
Sulfur-coal and ion-exchange filters are used for these purposes in boiler houses and CHPPs. Sulfo-coal is cheaper, ion-exchange has a longer resource. There are household analogues, I saw it myself! The prices are great too. Search, choose! In both types it is necessary to periodically add table salt, depending on the hardness and consumption. I think it will be in the instructions. My advice: Take a bottle of water from the well and, having arrived in the city, go into the boiler room (a tall pipe will indicate) - there you will measure hardness for a chocolate bar in mg / mol - you will know!
woman*:
Of course have. Any detergent (bath foam, shower gel, etc.)
Denis:
Calgon!!!
Alexandr Ilin:
Sky Angel:
Water hardness can be reduced by boiling as mentioned above, which will remove hydrocarbons, but sulfate will remain. It can be removed with lime, but is unnecessary. A It is better to use ion-exchange resins for filtration. These ion exchange resin filters are designed for your type of water and are relatively long lasting.