Classification of one-pipe heating systems
In this type of heating, there is no separation into return and supply pipelines, since the coolant, after leaving the boiler, goes through one ring, after which it returns to the boiler again. Radiators in this case have a sequential arrangement. The coolant enters each of these radiators in turn, first into the first, then into the second, and so on. However, the temperature of the coolant will decrease, and the last heater in the system will have a temperature lower than the first one.
The classification of single-pipe heating systems looks like this, each type has its own schemes:
- closed heating systems that do not communicate with air. They differ in excess pressure, the air can only be discharged manually by means of special valves or automatic air valves. Such heating systems can work with circular pumps. Such heating may also have a lower wiring and a corresponding circuit;
- open heating systems that communicate with the atmosphere using an expansion tank to release excess air. In this case, the ring with the coolant should be placed above the level of the heating devices, otherwise air will collect in them and the water circulation will be disturbed;
- horizontal - in such systems, the coolant pipes are placed horizontally. This is great for private one-story houses or apartments where there is an autonomous heating system. Single-pipe type of heating with lower wiring and the corresponding scheme is the best option;
- vertical - the coolant pipes in this case are placed in a vertical plane. Such a heating system is best suited for private residential buildings, consisting of two to four floors.
Bottom and horizontal wiring of the system and its diagrams
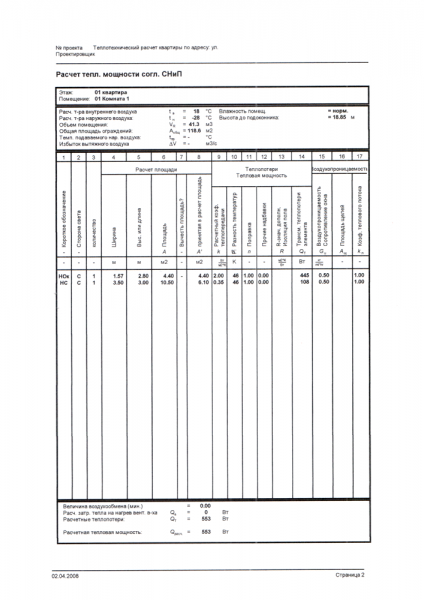
The circulation of the coolant in the horizontal piping scheme is provided by a pump. And the supply pipes are placed above or below the floor. A horizontal line with a lower wiring should be laid with a slight slope from the boiler, while the radiators must be placed all on the same level.
In houses with two floors, such a wiring diagram has two risers - supply and return, while the vertical circuit allows for more. During forced circulation of the heating agent using a pump, the temperature in the room rises much faster. Therefore, to install such a heating system, it is necessary to use pipes with a smaller diameter than in cases of natural movement of the coolant.
On the pipes that enter the floors, you need to install valves that will regulate the supply of hot water to each floor.
Consider some wiring diagrams for a single-pipe heating system:
- vertical feed scheme - can have natural or forced circulation. In the absence of a pump, the coolant circulates by means of a change in density during the cooling down of the heat exchange. From the boiler, water rises to the main line of the upper floors, then it is distributed through the risers to the radiators and cools in them, after which it returns to the boiler again;
- diagram of a single-pipe vertical system with bottom wiring. In the scheme with the lower wiring, the return and supply lines go below the heating devices, and the pipeline is laid in the basement. The coolant is supplied through the drain, passes through the radiator and returns down to the basement through the downcomer. With this method of wiring, heat loss will be much less than when the pipes are in the attic. Yes, and it will be very simple to maintain the heating system with this wiring diagram;
- scheme of a single-pipe system with an upper wiring. The supply pipeline in this wiring diagram is located above the radiators. The supply line runs under the ceiling or through the attic. Through this line, the risers go down and radiators are attached to them one by one. The return line goes either along the floor, or under it, or through the basement. Such a wiring diagram is suitable in the case of natural circulation of the coolant.
Remember that if you do not want to raise the threshold of the doors in order to lay the supply pipe, you can smoothly lower it under the door on a small piece of land while maintaining the general slope.
Single pipe heating system pros and cons
Advantages
A single-pipe heating system has both advantages and disadvantages. Among the advantages are the following:
- the possibility of covering the entire area of the building with the help of a closed ring, which does not depend on the layout of the building;
- the ability to connect certain additional devices to the heating system, for example, underfloor heating, heated towel rails or equipping a built-in circulation pump;
- it is possible to direct the coolant in one direction or another. For example, in the course of circulation, colder rooms, which are often ventilated, can be sent first. In the same two-pipe systems, this function is reduced to the location of the boiler;
- ease of installation work. There are not so many materials, and the cost of their purchase and the work themselves will be significantly lower than when installing a two-pipe system;
- with thoughtful placement of heating devices and proper piping, the difference in temperatures in different rooms can be minimized, but this phenomenon cannot be completely dealt with.
Flaws
The disadvantages of a one-pipe system are:
- the presence of special requirements for the diameter of the key pipeline;
- in the first radiator, the temperature will be the highest, and in subsequent ones it will be lower due to the constant admixture to the coolant flow from the radiators that have already been passed;
- the last radiators should have a larger area than the first, so as not to be too cold;
- it is better not to install more than 10 radiators on one branch, since uniform heating in this way will not work.
Alignment of the temperature regime occurs due to a change in the number of radiator sections and the installation of special jumpers, thermostatic valves, valves, regulators or ball valves. It is advisable to have a circulation pump available, and in order for hot water to pass through pipes and radiators better, you need to install a special overclocking collector. In two-story houses, it is not needed.
If the wiring is of the upper type, then the supply pipe is capable of creating natural pressure, however, with such a scheme, you need to install pipes with a large diameter, and this will negatively affect the appearance of your interior. Therefore, if it is possible to put the wiring node under the floor covering, it will be much better.
We also recommend that when installing radiators in a two-story building, in order to regulate heating, connect the batteries in parallel with the installation of taps at the inputs. Also, so that the temperature on the second floor is evenly distributed, instead of radiators, you can purchase a system of underfloor heating.
As you can see, a single-pipe system in terms of operation can have a number of difficulties. For example, it requires high pressure indicators, and in order for it to work normally, it is desirable to use a powerful pump, and this is not only unnecessary trouble, but also high costs. In addition, a one-story building will require a vertical spout and an expansion attic tank.
However, despite this, the advantages of this solution are still greater.
What is heating
Considering the heating of an apartment building, you can not boast of a large selection. All houses are heated approximately according to the same scheme.Each room has a cast-iron heating radiator (its dimensions depend on the size of the room and its purpose), which is supplied with hot water of a certain temperature (heat carrier) coming from a thermal station.

However, the entire water supply scheme may vary depending on which heating distribution is provided in a particular building - one-pipe or two-pipe. Each of these options has certain advantages and disadvantages. To better understand this issue, you need to know exactly everything about the first and second. So let's briefly describe them.
- Single pipe heating system. Its design is simple, and, therefore, reliable and cheap. But still, she is not very in demand. The fact is that, getting into the heating system of the house, the coolant (hot water) must pass through all the heating radiators before it enters the return channel (it is also called the "return"). Of course, heating all the radiators in turn, the coolant loses temperature. As a result, reaching the last user, the water has a relatively low temperature, which is why in the last room it can differ significantly from the temperature in the one it first enters. This often causes dissatisfaction among residents. Therefore, the described heating system of a multi-storey building is used relatively rarely.
- Two-pipe heating system. It is deprived of those shortcomings that are inherent in the heating system described above. The design of this system is significantly different. Hot water, having passed through the heating radiator, does not enter the pipe leading to the next radiator, but immediately into the return channel. From there, it immediately goes back to the thermal station, where it will be heated to the desired temperature. Of course, this option requires significantly higher costs both during installation of the system and during maintenance. But this scheme of the heating system allows you to ensure the same temperature in all heated buildings. Example of a two-pipe heating system
It also makes it possible to install a heating meter. By installing it on a heating radiator, the owner can independently regulate the level of its heating and, accordingly, reduce the cost of paying heating bills. In a single-pipe heating system, this option is not possible. By reducing the amount of hot water passing through your radiators, you can thus cause a lot of trouble to the neighbors, to whom the coolant enters through your apartment. That is, the rules of heating in this case will be frankly violated.
Of course, it is impossible to change the type of heating system in an apartment, it requires titanic efforts and a lot of work that will affect the whole house. But still, it will be useful for every apartment owner to know about the pros and cons of different types of heating systems.
This video provides a broad overview of various heating systems.
Features of gravity flow systems
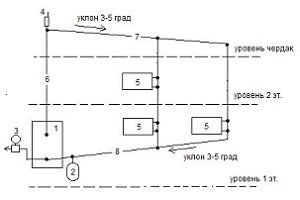
• maximize the acceleration point;
• use wide supply pipes;
Further, from the beginning of the first divergence to each subsequent one, a pipe of smaller diameter is connected by a step equal to it, which involves inertial flows.
There are also other features of the installation of gravity systems. So, pipes should be laid at an angle of 1-5%, which is affected by the length of the pipeline. If there is a sufficient difference in heights and temperatures in the system, horizontal wiring can also be used.
It is important to ensure that there are no areas with a negative angle, since they cannot be reached by the movement of the coolant, due to the formation of air pockets in them
So, the principle of operation can be based on an open type or be a membrane (closed) type.If you make the installation of a horizontal orientation, it is recommended to install Mayevsky taps on each radiator. because with their help it is easier to eliminate air jams in the system.
Watch the video in which the specialist talks about the conditions for the possibility of using a gravity-flow, pumpless, gravitational heating system:
The principle of operation of a gravity heating system
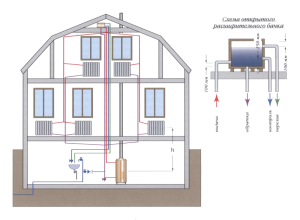
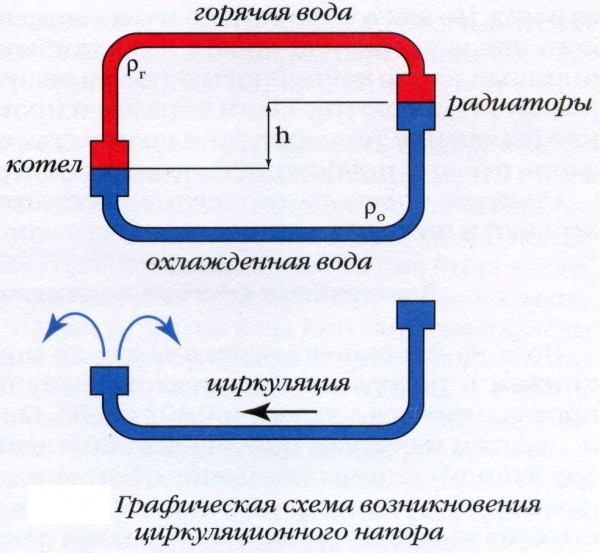
The principle of operation of heating looks simple: water moves through the pipeline, driven by hydrostatic pressure, which appeared due to the different masses of heated and cooled water. Another such design is called gravity or gravity. Circulation is the movement of cooled down in batteries and heavier liquid under the pressure of its own mass down to the heating element, and the displacement of light heated water into the supply pipe. The system functions when the natural circulation boiler is located below the radiators.
In open circuits, it communicates directly with the external environment, and excess air escapes into the atmosphere. The volume of water increased from heating is eliminated, constant pressure is normalized.
Natural circulation is also possible in a closed heating system if it is equipped with an expansion tank with a membrane. Sometimes open-type structures are converted into closed ones. Closed circuits are more stable in operation, the coolant does not evaporate in them, but they are also independent of electricity. What affects circulation pressure
The circulation of water in the boiler depends on the difference in density between the hot and cold liquids and on the magnitude of the height difference between the boiler and the lowest radiator. These parameters are calculated even before the installation of the heating circuit. Natural circulation occurs because the return temperature in the heating system is low. The coolant has time to cool down, moving through the radiators, it becomes heavier and with its mass pushes the heated liquid out of the boiler, forcing it to move through the pipes.

Scheme of water circulation in the boiler
The height of the battery level above the boiler increases the pressure, helping the water to overcome the resistance of the pipes more easily. The higher the radiators are located in relation to the boiler, the greater the height of the cooled return column and with the greater pressure it pushes the heated water up when it reaches the boiler.
The density also regulates the pressure: the more the water warms up, the less its density becomes in comparison with the return. As a result, it is pushed out with more force and the pressure increases. For this reason, gravity heating structures are considered self-regulating, because if you change the temperature of the water heating, the pressure on the coolant will also change, which means that its consumption will change.
During installation, the boiler should be placed at the very bottom, below all other elements, in order to ensure sufficient pressure of the coolant.
Power calculation
The effective heat output of the boiler is calculated in the same way as in all other cases.
By area
The simplest way is the calculation recommended by SNiP for the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. 1 kW of thermal power should fall on 10 m2 of the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. For the southern regions, a coefficient of 0.7 - 0.9 is taken, for the middle zone of the country - 1.2 - 1.3, for the regions of the Far North - 1.5-2.0.
Like any rough calculation, this method neglects many factors:
- Ceiling heights. It is far from being the standard 2.5 meters everywhere.
- Heat leaks through openings.
- The location of the room inside the house or against external walls.
All calculation methods give large errors, so the thermal power is usually included in the project with some margin.
By volume, taking into account additional factors
A more accurate picture will give another method of calculation.
- The thermal power of 40 watts per cubic meter of air volume in the room is taken as the basis.
- Regional coefficients apply in this case as well.
- Each standard size window adds 100 watts to our calculations. Each door is 200.
- The location of the room near the outer wall will give, depending on its thickness and material, a coefficient of 1.1 - 1.3.
- A private house, in which below and above there are not warm neighboring apartments, but a street, is calculated with a coefficient of 1.5.
However: and this calculation will be VERY approximate. Suffice it to say that in private houses built using energy-saving technologies, the project includes a heating power of 50-60 watts per square meter. Too much is determined by heat leakage through walls and ceilings.
Development of a heating system project
The heating device, starting from the introductory system and ending with heating radiators, is created immediately after the skeleton of an apartment building is built. Of course, by this time, the heating project for an apartment building must be developed, tested and approved.
And it is at the first stage that a number of difficulties often arise, as in the performance of any other, very complex and important work. In general, the heating system of an apartment building is complex.
The power of the heating system may depend on the strength of the wind in your area, the material from which the building is built, the thickness of the walls, the size of the premises and many other factors. Even two identical apartments, one of which is located on the corner of the building, and the other in its center, require a different approach.
After all, a strong wind in the winter season quickly cools the outer walls, which means that the heat loss of a corner apartment will be much higher.
Therefore, they must be compensated by installing larger heating radiators. Only experienced specialists who know exactly how all the equipment is arranged and how it works can take into account all the nuances, choose the best solutions.
A beginner who decides to calculate the heating system in an apartment building will be doomed to failure from the very beginning. And this will lead not only to a significant overspending of resources, but also put the lives of the inhabitants of the house in danger.
Centralized heating system
No one will argue with the fact that the centralized system of heat supply to apartment buildings, in the form in which it currently exists, to put it mildly, is obsolete.
It is no secret that losses during transportation can reach up to 30% and we have to pay for all this. Refusing central heating in an apartment building is a complicated and troublesome procedure, but first, let's figure out how it works.
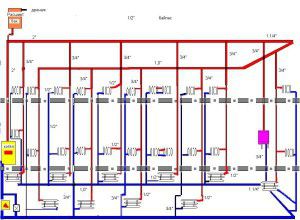
Heating a multi-storey building is a complex engineering structure. There is a whole set of drains, distributors, flanges that are tied to the central unit, the so-called elevator unit, through which the heating is regulated in an apartment building.
Two-pipe heating scheme.
It makes no sense now to talk in detail about the intricacies of the operation of this system, since professionals are engaged in this and a simple layman simply does not need this, because nothing depends on him here. For clarity, it is better to consider the scheme for supplying heat to an apartment.
bottom filling
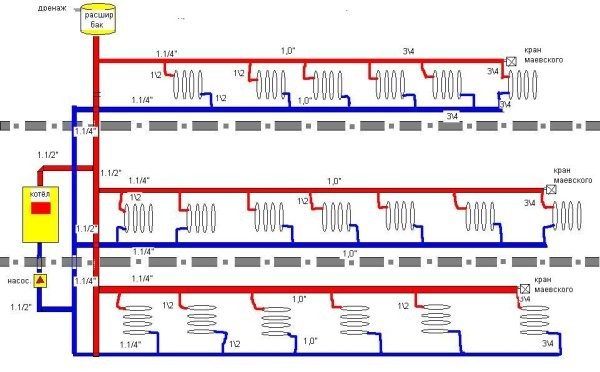
As the name implies, the distribution scheme with bottom filling provides for the supply of coolant from the bottom up. Classical heating of a 5-storey building, mounted exactly according to this principle.
As a rule, the supply and return are installed along the perimeter of the building and run in the basement. The supply and return risers, in this case, are a jumper between the highways. This is a closed system that rises to the last floor and descends again to the basement.
Two types of bottling in comparison.
Despite the fact that this scheme is considered the simplest, putting it into operation is troublesome for locksmiths. The fact is that at the top of each riser, a device for bleeding air, the so-called Mayevsky crane, is installed.Before each start, you need to release air, otherwise the air lock will block the system and the riser will not be heated.
Important: some residents of the extreme floors are trying to move the air release valve to the attic so as not to encounter housing and communal services workers every season. This change can be costly.
The attic is a cold room, and if heating is stopped for an hour in winter, the pipes in the attic will freeze and burst.
A serious disadvantage here is that on one side of the five-story building, where the input passes, the batteries are hot, and on the opposite side they are cool. This is especially felt on the lower floors.
Radiator connection option.
Top filling
The heating device in the nine-story building is made on a completely different principle. The supply line, bypassing the apartments, is immediately taken out to the upper technical floor. An expansion tank, an air release valve and a valve system are also based here, which allows cutting off the entire riser if necessary.
In this case, the heat is more evenly distributed over all the radiators of the apartment, regardless of their location. But another problem comes up here, the heating of the first floor in the nine-story building leaves much to be desired. After all, having passed through all the floors, the coolant comes down already barely warm, you can only deal with this by increasing the number of sections in the radiator.
Important: the problem with freezing water on the technical floor, in this case, is not so acute. After all, the cross section of the supply line is about 50 mm, plus in the event of an accident, it is possible to completely drain the water from the entire riser in a few seconds, just open the air vent in the attic and the valve in the basement
Temperature balance
Of course, everyone knows that central heating in an apartment building has its own clearly regulated standards. So during the heating season, the temperature in the rooms should not fall below +20 ºС, in the bathroom or in the combined bathroom +25 ºС.
Modern heating of new buildings.
In view of the fact that the kitchen in old houses does not have a large quadrature, plus it is naturally heated due to the periodic operation of the stove, the permissible minimum temperature in it is +18 ºС.
Important: all the above data are valid for apartments located in the central part of the building. For side apartments, where most of the walls are external, the instruction prescribes an increase in temperature above the norm by 2 - 5 ºС
Heating regulations by region.
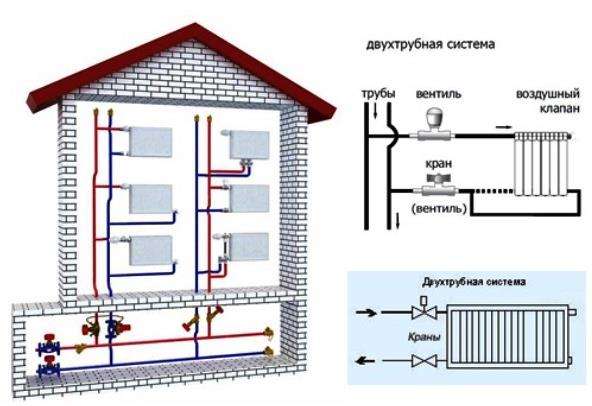
Two-pipe heating system with top wiring
Installing a two-pipe heating system with top wiring minimizes or completely eliminates many of the above disadvantages. In this case, the radiators are connected in parallel.
For its installation, much more materials are needed, since two parallel lines are installed. A hot coolant flows through one of them, and a cooled coolant flows through the other. Why is this overflow heating system preferred for private houses? One of the significant advantages is the relatively large area of the room. The two-pipe system can effectively maintain a comfortable temperature level in houses with a total area of up to 400 m².
In addition to this factor, for a heating circuit with top filling, the following important performance characteristics are noted:
- Uniform distribution of hot coolant over all installed radiators;
- The possibility of installing control valves not only on the battery piping, but also on separate heating circuits;
- Installation of water floor heating system. A collector hot water distribution system is only possible with two-pipe heating.
To organize forced top filling in the heating system, it is necessary to install additional units - a circulation pump and a membrane expansion tank. The latter will replace the open expansion tank. But the place of its installation will be different.Membrane sealed models are mounted on the return line and always on the straight section.
The advantage of such a scheme is the optional observance of the slope of the pipelines, which is characteristic of the upper and lower distribution of heating with natural circulation. The required pressure will be created by the circulation pump.
But does a two-pipe forced heating system with an upper wiring have any disadvantages? Yes, and one of them is dependence on electricity. During a power outage, the circulation pump stops working. With a large hydrodynamic resistance, the natural circulation of the coolant will be difficult. Therefore, when designing a scheme for a single-pipe heating system with an upper wiring, all the required calculations must be performed.
You should also take into account the following features of installation and operation:
- When the pump stops, reverse movement of the coolant is possible. Therefore, in critical areas, it is necessary to install a check valve;
- Excessive heating of the coolant can cause the critical pressure indicator to be exceeded. In addition to the expansion tank, air vents are installed as an additional protection measure;
- To increase the efficiency of the heating system with the upper piping, it is necessary to provide for automatic replenishment with coolant. Even a small decrease in pressure below normal can lead to a decrease in radiator heating.
The video will help you visually see the difference for various heating schemes:
Most of the heating systems of multi-apartment and private houses are built exactly according to this scheme. What are its advantages and are there any disadvantages?
Can a do-it-yourself two-pipe heating system be installed?
Convector in a two-pipe heating system
Types of heating systems with gravity circulation
Despite the simple design of a water heating system with self-circulation of the coolant, there are at least four popular installation schemes. The choice of wiring type depends on the characteristics of the building itself and the expected performance.
To determine which scheme will work, in each individual case it is required to perform a hydraulic calculation of the system, take into account the characteristics of the heating unit, calculate the pipe diameter, etc. You may need the help of a professional when doing the calculations.
Closed system with gravity circulation
In the EU countries, closed systems are the most popular among other solutions. In the Russian Federation, the scheme has not yet been widely used. The principles of operation of a closed-type water heating system with pumpless circulation are as follows:
- When heated, the coolant expands, water is displaced from the heating circuit.
- Under pressure, the liquid enters a closed membrane expansion tank. The design of the container is a cavity divided by a membrane into two parts. One half of the tank is filled with gas (most models use nitrogen). The second part remains empty for filling with coolant.
- When the liquid is heated, pressure is created sufficient to push through the membrane and compress the nitrogen. After cooling, the reverse process occurs, and the gas squeezes the water out of the tank.
Otherwise, closed-type systems work like other natural circulation heating schemes. As disadvantages, one can single out the dependence on the volume of the expansion tank. For rooms with a large heated area, you will need to install a capacious container, which is not always advisable.
Open system with gravity circulation
The open type heating system differs from the previous type only in the design of the expansion tank. This scheme was most often used in old buildings. The advantages of an open system is the possibility of self-manufacturing containers from improvised materials.The tank usually has modest dimensions and is installed on the roof or under the ceiling of the living room.
The main disadvantage of open structures is the ingress of air into pipes and heating radiators, which leads to increased corrosion and rapid failure of heating elements. Airing the system is also a frequent "guest" in open circuits. Therefore, radiators are installed at an angle, Mayevsky cranes are required to bleed air.
Single pipe system with self-circulation
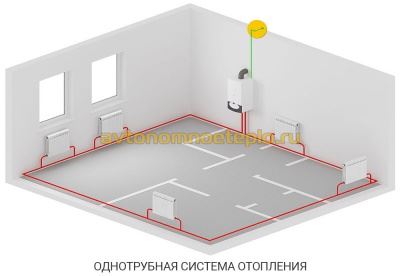
This solution has several advantages:
- There is no paired pipeline under the ceiling and above the floor level.
- Save money on system installation.
The disadvantages of such a solution are obvious. The heat output of heating radiators and the intensity of their heating decreases with distance from the boiler. As practice shows, a single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation, even if all slopes are observed and the correct pipe diameter is selected, is often redone (by installing pumping equipment).
Two-pipe system with self-circulation
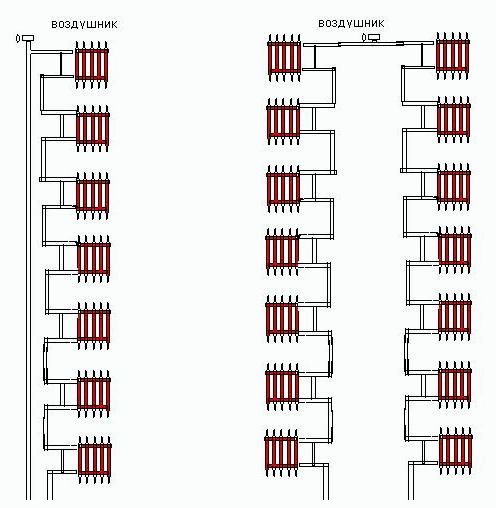
The two-pipe heating system in a private house with natural circulation has the following design features:
- Supply and return flow through separate pipes.
- The supply pipe is connected to each radiator via an inlet.
- The battery is connected to the return line with the second eyeliner.
As a result, a two-pipe radiator type system provides the following advantages:
- Uniform distribution of heat.
- No need to add radiator sections for better warm-up.
- Easier to adjust the system.
- The diameter of the water circuit is at least one size smaller than in single-pipe schemes.
- Lack of strict rules for installing a two-pipe system. Small deviations regarding slopes are allowed.
The main advantage of a two-pipe heating system with lower and upper wiring is the simplicity and at the same time the efficiency of the design, which allows you to level errors made in the calculations or during installation work.
general information
Basic moments
The absence of a circulation pump and moving elements in general and a closed circuit, in which the amount of suspensions and mineral salts is finite, makes the service life of this type of heating system very long. When using galvanized or polymer pipes and bimetallic radiators - at least half a century.
Natural heating circulation means a fairly small pressure drop. Pipes and heaters inevitably provide a certain resistance to the movement of the coolant. That is why the recommended radius of the heating system we are interested in is estimated at about 30 meters. Clearly, this does not mean that with a radius of 32 meters the water will freeze - the border is rather arbitrary.
The inertia of the system will be quite large. Several hours may elapse between the ignition or start-up of the boiler and the stabilization of the temperature in all heated rooms. The reasons are clear: the boiler will have to warm up the heat exchanger, and only then will the water begin to circulate, and rather slowly.
All horizontal sections of pipelines are made with a mandatory slope in the direction of water movement. It will ensure the free movement of cooling water by gravity with minimal resistance.
What is no less important - in this case, all air plugs will be forced out to the upper point of the heating system, where the expansion tank is mounted - sealed, with an air vent, or open.
All air will collect at the top.
Self-regulation
Home heating with natural circulation is a self-regulating system. The colder it is in the house, the faster the coolant circulates. How it works?
The fact is that the circulation pressure depends on:
Differences in height between the boiler and the bottom heater. The lower the boiler is relative to the lower radiator, the faster the water will overflow into it by gravity. The principle of communicating vessels, remember? This parameter is stable and unchanged during the operation of the heating system.
The diagram demonstrates the principle of operation of heating clearly.
Curious: that is why the heating boiler is recommended to be installed in the basement or just as low as possible indoors. However, the author has seen a perfectly functioning heating system in which the heat exchanger in the furnace furnace was noticeably higher than the radiators. The system was fully operational.
Differences in the density of water at the outlet of the boiler and in the return pipeline. Which, of course, is determined by the temperature of the water. And it is precisely thanks to this feature that natural heating becomes self-regulating: as soon as the temperature in the room drops, the heaters cool down.
With a drop in the temperature of the coolant, its density increases, and it begins to quickly displace the heated water from the lower part of the circuit.
Circulation rate
In addition to pressure, the circulation rate of the coolant will be determined by a number of other factors.
- Wiring pipe diameter. The smaller the internal section of the pipe, the greater the resistance it will provide to the movement of fluid in it. That is why for wiring in the case of natural circulation, pipes with a deliberately oversized diameter are taken - DN32 - DN40.
- Pipe material. Steel (especially corroded and covered with deposits) resists the flow several times more than, for example, a polypropylene pipe with the same cross section.
- The number and radius of turns. Therefore, the main wiring is best done as straight as possible.
- The presence, quantity and type of valves. a variety of retaining washers and pipe diameter transitions.
Each valve, each bend causes a pressure drop.
It is precisely because of the abundance of variables that an accurate calculation of a heating system with natural circulation is extremely rare and gives very approximate results. In practice, it is enough to use the recommendations already given.
House heating scheme
It has already been said above that most modern houses in cities are heated using a centralized heating system. That is, there is a thermal station at which (in most cases with the help of coal) heating boilers heat water to a very high temperature. Most often it is more than 100 degrees Celsius!
Water is supplied to all buildings connected to the heating main. When connecting the house to the heating plant, inlet valves are installed to control the process of supplying hot water to it. A heating unit is also connected to them, as well as a number of specialized equipment.
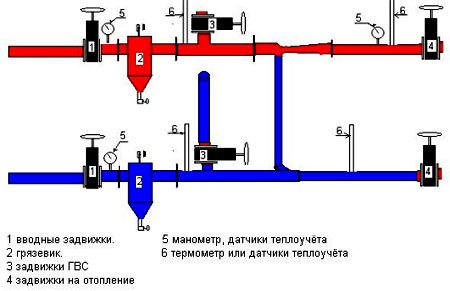
Water can be supplied both from top to bottom and from bottom to top (when using a one-pipe system, which will be discussed below), depending on how the heating risers are located, or simultaneously to all apartments (with a two-pipe system).
Hot water, getting into heating radiators, heats them up to the required temperature, providing its required level in each room. The dimensions of the radiators depend both on the size of the room and on its purpose. Of course, the larger the radiators are, the warmer it will be where they are installed.