Gas welding technology secrets
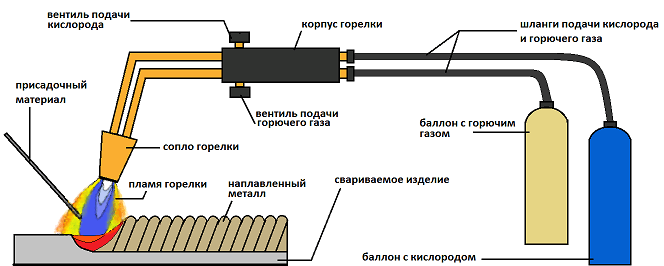
The source of energy in this method is a gas cylinder. Copper welding, made using this technology, allows you to get a reliable and high-quality connection. Due to the fact that copper has a high thermal conductivity, a flame with enhanced power should be used. Recommended values:
- 150 liters per hour with a pipe thickness of less than 10 mm;
- 200 liters per hour - for all other products.
Some tricks, following which, welding of copper with a gas cylinder will be successful, correct and of high quality:
- All actions must be performed quickly, without interruption. In this way, the contact of the melt with oxygen can be minimized and unwanted cracks can be avoided;
- It is better to use a restorative flame;
- It is necessary to direct the flame to the pipe at a right angle;
- As an additive, it is recommended to use copper wire or any other metal wire, provided that it contains deoxidizers;
- The edge of the pipe must be cleaned to bare metal;
- The heat of the gas burner should be distributed in such a way that the additive melts before the pipe;
- To increase the strength of the weld, after welding, the product must be forged. This is done in a cold state, provided that the wall thickness of the product does not exceed 5 mm;
- Then the seam should be annealed at a temperature of 500 - 550 degrees;
Temperatures below 500 degrees will be detrimental to copper, it will provoke a loss of strength characteristics.
The last step will be lowering into cold water.
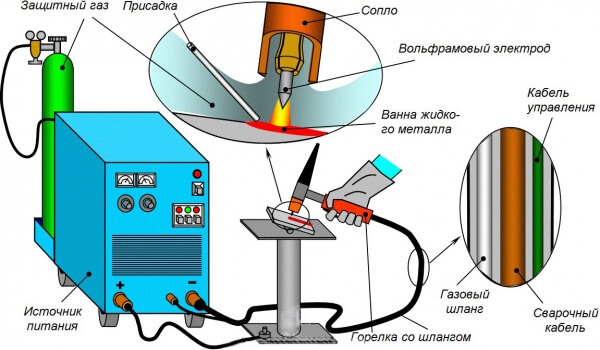
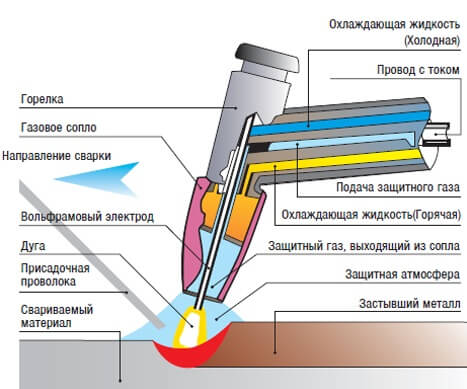
Argon arc welding of copper, also referred to as TIG, is performed using argon, or a mixture of argon and helium. In addition, for the implementation of the welding process, both in industrial and at home, tungsten electrodes will be required.
Tungsten electrodes are non-consumable and are characterized by good arc stability.
Features of the connection:
- If tungsten electrodes are used, welding must be carried out at direct current;
- It is better to clean the electrodes to bare metal before welding;
- During operation, it is recommended to direct the electrodes to the surface of the seam;
- In some cases, consumable electrodes may be used.
The TIG welding technology is shown in more detail in the figure:
Arc welding of copper allows you to make a high-quality connection with the right technology.
The main methods of welding copper with stainless steel
Stainless steel and copper are quite different in their compositions, the most common way to weld them is argon-arc. It is also possible to use electric arc, very rarely - ultrasonic welding.
Manual argon arc welding
This type of welding is performed with increased welding current, this is due to the high thermal conductivity of copper. In some cases, the use of a steel lining is acceptable. The essence of manual argon arc welding is the formation of a weld by melting the filler material.
For welding, non-consumable tungsten electrodes are taken. If another gas (nitrogen) is used instead of argon, then graphite electrodes must be used. Argon is 38% heavier than oxygen, which allows it to be successfully displaced from the welding area.
Argon-arc technology makes it possible to achieve iron content in the weld up to 10%. And if you apply cold welding, then its content will be more than 10%. To increase the final strength of the seam, it is additionally alloyed with zinc.
Required equipment:
- inverter or other power source suitable for argon arc welding;
- tungsten electrodes;
- argon;
- reducer;
- filler material;
- protective items (welding mask, gloves, etc.).
https://youtube.com/watch?v=6zZS5FoNzPs
Electric arc welding technology
This versatile welding method can also be used to weld copper to stainless steel. Electric arc welding must be performed using a high current source with low voltage. The technology of the electric arc method simultaneously allows the melting of the electrode metal (or filler material) and the metal to be joined, as a result of which a weld pool is formed.
An arc discharge occurs between the electrode and the metal. Melting occurs due to the local distribution of thermal energy of the arc, forming a weld pool and protective slag.
Necessary equipment:
- source of power;
- consumable or non-consumable electrodes;
- hammer, chisel;
- metal brush;
- filler material;
- protective clothing (mask, gloves).
ultrasonic welding
This type of welding is used only in industrial areas. The essence of this method is the conversion of electrical vibrations into mechanical ones. It is most often used for welding plastics, but it can also be used for non-ferrous metals.
Equipment:
- source of power;
- mounting bracket;
- vibration conversion system;
- drive to increase the pressure force.
How to solder copper pipes with your own hands
In the private sector and in production, only two methods are used for soldering products made of copper and alloys:
- Soldering at high temperature, the so-called "hard soldering", when the solder melts in the range of 600C-900C. To solder a copper part, they use refractory solder, and you get a strong, reliable seam that can withstand heavy mechanical loads;
- Low-temperature "soft" soldering (≤ 450C) is used in everyday life. Low-melting solder is used to connect tubes or seal cracks.
To get a reliable result, use the following tool for soldering copper pipes:
- Pipe cutter, grinder, electric jigsaw, hacksaw;
- Beveler, which cleans the cut ends of copper pipes;
- Soldering iron - electric of different power, gas, or old design, heated on an open fire. Also, sometimes soldering is carried out with a gasoline blowtorch or a gas welding torch. Electric soldering irons are suitable for hard and soft soldering, gas soldering irons are better suited for working with hard solders and appropriate additives such as borax;
- Expander - a device that expands the end of one product so that it can be inserted into the edge of the second;
- Solder is selected for each mode. For hard soldering of the heating main, copper wire with phosphorus impurities is suitable, for low-temperature connections - tin solder with lead additives;
- Additives (flux) can be liquid and solid, acidic or alkaline, and are designed to clean soldered surfaces from oxides. The most common flux in everyday life for soldering copper products is rosin and borax.
If a large area is being repaired, then to control the melting temperature of the solder, they use a building industrial hair dryer with nozzles of various designs that allow you to control the flow and direction of hot air. Of the tools and fixtures, they also use sandpaper, a metal brush, rags, and brushes.
Features of working with copper
Although copper parts can be welded using special electrodes, it is still best to use non-consumable tungsten electrodes for these purposes.
Such electrodes “weld” the seams well, unlike welding with conventional electrodes, they are strong, even and clean.
There are several types of tungsten non-consumable electrodes: EVL and EVI. EVL are lapped electrodes, and EVL are iterated electrodes.
Iterated tungsten electrodes are used for welding copper parts with argon.If the thickness of copper parts welded with argon exceeds 5 mm, then a mandatory cutting of the edges is used.
Without cutting the edges, the entire thickness of the metal cannot be heated, since copper has a high thermal conductivity.
You should be aware that for metal with a thickness of 5–12 mm, one-sided cutting is used, and if the thickness of the metal is greater than the specified one, then both edges of the workpiece are cut.
The quality of the weld also depends on the impurities contained in copper - the purer the copper, the better the weld. In addition to tungsten electrodes, filler wire is also used.
The filler wire isolates the parts to be welded from oxygen, which still enters the welding area.

The material of the filler wire must necessarily correspond to the composition of the metal that is supposed to be welded.
Therefore, as an additive, it is best to use a wire containing any rare earth materials.
Such materials completely remove oxygen from the seams, but do not remain in the composition of the seam, like manganese impurities.
Unfortunately, rare earth filler wire is very expensive, which is why few dare to use it, preferring inexpensive copper wire.
Copper welding on automatic or semi-automatic submerged arc welding
When welding copper to improve weld quality and productivity in industry
apply. The process is carried out on automatic or hose semi-automatic machines.
manually or mechanized. Welding of thin copper is successfully performed under
flux with a non-consumable electrode.
Preparation of metal for welding
Edges must be cleaned. Butt joints of copper 6-8 mm thick are assembled
for welding with a gap of 1-1.5 mm. For larger thicknesses, a V-shape is recommended.
cutting with a total opening angle of 60°. In this case, welding is performed without
technological gaps.
When welding copper with a gap, the butt joint is assembled on a backing, otherwise
molten metal will flow out through the gap. The best results are obtained
when using flux pads, however, it is worth remembering that a strong preload
linings to the metal leads to a deterioration in the formation of the root of the weld.
Before welding copper products, it is recommended to preheat.
With a small thickness of the metal being welded, it is possible to confine oneself to the local initial
heated. When welding a large thickness of metal or with a large joint length, it is recommended
concomitant heating during the welding process. The heating temperature is 250-300°C.
Wire for automatic welding of copper
For welding, copper wire grades M1, M2 and M3 are used. If the wire is thin
(up to 3 mm), then it is pre-hardened. If it is impossible to get a hardened
thin copper wire, then use a more elastic wire made of bronze grades
BrOF 4-0.3, Br.X-1, or Br.KMts 3-1. It should be noted, however, that the use
copper wire reduces the risk of cracking in the weld.
When automatically welding copper with a thin wire, it will be more technologically advanced to use
automatic machines with a wire-drawing mechanism equipped with two pulling
rollers. Along with thin wire, you can use a wire with a diameter of 3.4.5 mm.
Wire with a diameter of more than 5 mm is not used for automatic welding of copper,
because this requires special power sources.
Through the wire, it is possible to alloy the weld metal by introducing various
deoxidizers - silicon, manganese, phosphorus, etc. But, the best results are obtained
alloying through fluxes, especially ceramic ones.
Fused and non-fused fluxes for welding
Of the fused fluxes, the fluxes of the following grades are most widely used:
1. AN-348A, OSC-45 and AN-348 - high-silicon manganese;
2. AN-51, AN-10 - low-silicon manganese;
3. AN-20 - low-silicon, manganese-free.
That allow
alloy the weld metal and introduce deoxidizers into its composition. Composition of ceramic
fluxes K-13 and ZhM-1, used in automatic welding of copper, is indicated in the table.
Welding heating pipes what and how to cook Let's figure it out together
Heating pipe welding is one of the most reliable types of joining. The process of connecting structures is carried out using special devices under the influence of high temperature. This type of welding is used for both metal and plastic pipes.
If there are no welding skills, it is preferable to seek help from specialists.
Some docking methods can be done independently with the help of the necessary tools and observing safety precautions. Welding heating pipes by a welder can cost you a very high price. At the same time, the cost of the welding machine is low.
Note: the price depends on the diameter of the pipes, the number of joints, passes, and the price will also be increased if the pipes need to be welded at a height, in cramped or cold conditions.
Welding of plastic pipes
It is possible to cope with the welding of plastic pipes on your own; this process does not require special knowledge and skills.
Plastic Pipe Welding Machine
To work with such material, you need:
- scissors for cutting pipes;
- special nozzles;
- welding machine.
When working with plastic, it is necessary to be careful and accurate, since such material is easily damaged or spoiled by thermal exposure.
The temperature during welding should not exceed 1800 C, since above this indicator the plastic can melt and spill into the pipeline. Also, the use of low temperatures in the docking process threatens with a leaky connection, gaps may form, which will entail leakage during operation.
The process of welding polypropylene pipes, see below
Remember that it is very important that water does not get into the place of soldering, the author of the video pays special attention to this, he also says that the pipeline must be filled with water no earlier than one hour after the end of work
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Qw2Nvx1gtO0
Electric welding of metal pipelines
For welding metal heating pipes, a joint method with a gap of 2-3 mm is used.
With such a connection, the edges of the pipes should not melt; the joining is carried out with a fused wire in the gap.
It is advisable to select pipes of equal size for stronger and more reliable welding.
The surface of pipelines must be cleaned before work is performed. The ends of the pipes must be even. The pipe installation scheme, the size of the required sections should be thought out in advance, in connection with this, it is necessary to cut metal structures.
The welding process is carried out in a circle. Depending on the thickness of the pipes, several layers of welding are used, but not less than two. Before a new seam, the slag must be removed.
The video below shows how to weld gapped steel pipes in two passes. Very detailed and helpful video.
Gas welding
Gas welding of pipes is a more expensive type of connection than electric welding.
When using a gas tool, the connection occurs using molten metal on the surface of the seam.
Shows how to connect pipes using gas welding
To produce a seam, the circumference of the pipes along the intended seam is divided into 4 conditional segments, along which the seam is filled. When welding in four segments, each worked part is turned down.
Welding, as a docking method, is regulated by GOST, SNiP for thermal networks.
When performing gas welding, safety measures must also be taken. It is necessary to put on a protective suit, and a special helmet-mask must be put on the head and eyes. All work must be carried out away from flammable objects.
Cold welding
Also known is such a connection method as cold welding of heating pipes.
A man applies cold welding to a pipe joint
It is an epoxy adhesive with steel powder. Used as putty. The method allows gluing virtually any materials, including plastics and metals. This method of welding is most often used for individual seams or for closing gaps.
By the way, you can weld not only pipes with cold welding. For example, Victor from the video below repaired the ax handle in this way. Quite helpful and informative.
You can check the tightness of any seam using a soap solution that is applied to the joint. Air is supplied through the pipe. If there are gaps, then bubbles appear at the joints.
We hope that the article was useful and relevant to you. We will be very grateful if you click on the social network buttons below. Let others read this material.
Features of copper welding
As we wrote above, there are some features of the welding of copper and its alloys, due to which the process of joining metals is significantly more complicated.
Let's list the main nuances that you need to pay attention to
First, copper has a very high thermal conductivity, which means that you need to use an arc capable of delivering high heat output and symmetrically removing heat from the welding zone. Also, because of this feature, it will not be possible to use any types of seams. We recommend using butt joints for welding copper parts.
Secondly, when melted, copper begins to drain quickly, because of this it is extremely difficult to make ceiling and vertical seams, since the metal rapidly flows down at the slightest overheating. To avoid this problem, the weld pool must be kept as small as possible and the molten metal must be cooled rapidly.

Thirdly, when welding copper using butt welds and in the lower position, it is imperative to use graphite, asbestos linings or flux pads. This is necessary to avoid burns through the metal.
Fourth, being in the molten state, copper actively absorbs oxygen and hydrogen. This leads to the formation of hot cracks and pores form in the seam. All this worsens the quality of the seam, reliability and aesthetic component suffer. To avoid this, careful protection of the welding zone is necessary. Gas solves this problem.
Fifth, copper is extremely prone to oxidation, while the oxide film is very refractory and difficult to get rid of. This problem is solved by using a filler wire containing phosphorus, manganese and silicon in its composition.
And finally, the last thing you need to know. Copper differs from other metals in a large coefficient of linear expansion. This means that the metal is easily deformed and is particularly prone to hot cracking. This problem can be solved relatively simply: the part must first be heated in an oven or with a burner to a temperature of 300 degrees Celsius.
Despite all the difficulties, welding copper at home is possible. But first, the metal needs to be properly prepared, we will talk about this later.
Equipment and mechanisms for pipe welding
For a qualitative result, several simple conditions must be met. During welding, the temperature should be 425 degrees or less, but in no case more. The most important condition is that during soldering they should be at the very minimum distance between themselves, for the capillary method this nuance is very important. Now we were talking about pipes with participation in the soldering of hard soldering, but when using soft soldering, the soldering temperature should be less than 424 degrees. 
1. Classical soldering is used most often.It can be used to solder pipes made of copper, tinplate and brass, if you want to weld them for water supply, then unfortunately this soldering will not work. 2. Soft soldering is used when joining parts with brass sleeve. 3. Hard soldering is used in heating and plumbing system. Soldering with this type of welding does not require the use of sleeves. 4. Soldering of copper and phosphorus is used and the participation of flux. No need to use with nickel and bronze pipes 5. Soldering with silver content.
Copper Pipe Welding Tools
1. Thread for pipes. Needed to cut them into pieces. You can choose the type of cutting according to its diameter. It is worth noting that the higher the price, the larger the pipe cutter for copper pipes. 2. Chamfering mechanism. They come in two types: a pencil or a round case.
3. A pipe expander is used during pipe expansion to fit a specific coupling. You need to choose it depending on the size of the diameter of the pipeline. Take note! In order for the work with the participation of this tool to be successful, first create softness for the pipes. 4. Brushes and sponges for cleaning mechanisms from excess. 5. Burners with gas supply. Used and selected depending on the pipeline material. Sequence of work during welding of copper pipes 1. To begin work, we will prepare the outer walls of the pipelines. We clean them with a special brush or brush from dust and dirt, giving it a shiny appearance.
2. If the work will be carried out when mounting parts in water supply and heating systems, where the highest temperature reaches no more than 110 degrees, then in such cases the use of couplings is not required. Instead, a pipe expander is used, which expands it in order to form sufficient space between them. Now we insert it with an extension into another pipe, and we fill the space with the help of soldering. 3. Using a burner with a gas supply, after we have connected the pipes, we heat them along the entire length. Heat must be distributed evenly and over the entire diameter of the pipeline. 4. To understand when they are warm enough, you just need to bring a small bar to them. If it begins to melt upon contact, then the joints are considered sufficiently heated. To improve the final work, we warm up the soldering rod well. 5. If the outer walls of the pipes are warmed up well and have acquired a sufficient temperature, then attach a soldering rod to it and then you will see how the solder fills the space between the pipelines using the capillary method. 6. After welding, the connected parts are laid on a surface with an even coating. In this state, they should be at least an hour, after this time they can be used.
Manual welding with carbon and graphite electrodes
Manual welding of copper with carbon and graphite electrodes is used to a limited extent
and mainly for low-responsibility products. Let us dwell briefly on its technology.
It is advisable to use carbon electrodes when welding copper, up to 15 mm thick.
For larger thicknesses, graphite electrodes are used. Carbon and graphite electrodes
sharpen on a cone 1/3 of its length. Welding is carried out on a direct current direct
polarity in a long arc. The current density at the electrode is 200-400 A/cm2.
The filler rod is not immersed in the weld pool, but kept at a distance of 5-6 mm
from it at an angle of 30° to the product. The electrode is held at an angle of 75-90° to the product.
To protect the metal from oxidation, a flux is used, consisting of 94-96% of fused
borax and 4-6% metallic magnesium. The flux is applied to the filler rod, preliminarily
wetting it in liquid glass.
If the thickness of the welded metal exceeds 5 mm, the butt joint is welded
with cutting edges with a total angle of 70-90 °. The gap between the edges is 0.5mm. welding
performed on a graphite or asbestos lining. The electrode is tilted at an angle
forward" at 10-20 ° from the vertical. Metal up to 5 mm thick is forged without
heating, and with a greater thickness - with heating up to 800 ° C and subsequent rapid
cooling. Welding is recommended to be done in one pass to ensure
the best mechanical properties of the seam.
Features of the welding process
Welding copper has significant differences compared to welding ferrous metals. This process can cause some difficulties due to lack of experience and if the procedure is performed at home. The main difficulties are associated with the characteristics of non-ferrous metal, namely:
- Good electrical conductivity;
- High thermal conductivity;
- Reaction with gases circulating in the atmosphere;
- tendency to oxidize;
- High fluidity in the molten state;
- Increased coefficient of linear expansion.
Welding of copper can be complicated by the influence of oxygen absorbed from the atmosphere.
Some non-ferrous metal impurities further complicate welding. These are the following substances:
- Lead;
- Bismuth;
- Sulfur.
Depending on the method of obtaining energy, copper welding can be:
- gas;
- Argon-arc.