Factors affecting pressure
Measuring devices of the elevator unit room mark any violation of the supply or drainage of water from the building.
Increased pressure in the heating batteries of an apartment building can be created by the following factors:
- the temperature of the hot resource is too high against the established norm;
- the diameter of the piping has been reduced due to the unauthorized reconstruction of the apartment heating scheme by the residents;
- formation of air pockets in the end radiators of the floors;
- the use of centrifugal pumps of greater power than provided for by the plan;
- part of the system is not working or blocked.
A decrease in agent pressure also indicates a problem with the heating circuit.
When the onslaught falls, it is necessary to pay attention to such possible aspects:
- emergency situations when supply pipelines break;
- malfunction or unsatisfactory operation of the circulation pump;
- failure of the safety block;
- rupture of the resonator of the expansion tank.

Silting or clogging of the filter in front of the elevator assembly also contributes to the pressure drop.
A leak
Leakage of water from the heating circuit is the most common factor in reducing the onslaught of the coolant. Most often, breaks occur at the junction of pipes with a boiler and heating equipment.
A rush is also possible in other arbitrary places if the owner of the apartment or house did not conduct a visual inspection before the start of the season, or installed defective elements.
Hot agent leakage can occur in several ways:
- Through the rupture of the diffuser of the expansion tank. Such an accident cannot be visually determined due to the presence of water inside the tank. To check, you must press your finger on the valve that pumps air into the tank. When water flows out of the spool, we can talk about a membrane crack.
- When the resource boils in the heat exchanger - through the relief valve.
- Microcracks, corrosive parts of measuring instruments, loose connections can also contribute to pressure drop and water leakage.
The correct method for determining a possible leak is to turn off the circulation pump. In this case, the static pressure indicator will differ from the calculated characteristics.
Air outlet
After filling the artificial heating system with water, its onslaught decreases when the air exits the circuit. Pre-boiling preparation - deaeration of water with chemical reagents - will help to avoid such a problem.
The latter reduce the amount of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the coolant to the calculated level. The heating circuit is filled with a slow supply from below - through a relief valve, with cold water.
Aluminum radiators
The installation of lightweight batteries - aluminum, leads to the reaction of oxygen with the metal, while forming an oxidizing film. The released hydrogen leaves through an automatic air vent.
A similar process is often observed in newly installed aluminum batteries, and the reaction stops after the entire inner surface of the radiator is covered with a film.
Therefore, after installing new heating equipment, you should pay attention to the fact that the pressure in the central heating may drop and you will have to supplement the volume of the heating agent
Adaptation of the heating pressure process
After the reconstruction of the old or the installation of a new heating circuit, the first few days will be determined by a steady decrease in the pressure of the carrier. This is considered normal due to air escaping from radiators and pipes. After forced deaeration of the circuit, the pressure stabilizes.
If the latter will constantly decrease within 30 days, you need to pay attention to the expansion tank, the incorrect calculation of its capacity.The emergency valve of the tank can be constantly activated and thereby cause the agent to be discharged and cooled down, which leads to a decrease in the onslaught.
If the membrane expansion tank is in good condition and the atmosphere is falling, it is necessary to check the tightness of the system.
Limit values of pressures Pf, causing various degrees of destruction of individual structural elements of buildings
|
Рf, |
building elements |
|
0,5 — 3,0 |
Partial |
|
3,0 — 7,0 |
Complete destruction |
|
12 |
Partitions, |
|
15 |
Overlappings |
|
30 |
brick and |
|
70 |
metal |
|
90 |
Reinforced concrete |
Then
by the nature of the destruction of individual
elements of the building are judged by the degree
destruction of the building as a whole. Wherein
known descriptions of degrees are used
building destruction. May also
use strength data
buildings to the effects of nuclear explosions
explosion. However, in this case, the values
causing varying degrees of destruction
buildings, increase by 1.5
1.7 times.
Volume
blockage of a completely destroyed building
determined by the formula
 ,
,
m3, (6.18)
where
A, B, H - length, width and height of the building, m;
-
blockage volume per 100 m3
construction volume of the building, accepted:
for
industrial buildings -
= 20 m3;
for
residential buildings -
= 40 m3.
Volume
blockage of a building that received a strong
degree of destruction,
taken equal to half of the volume
blockage of a completely destroyed building.
Quantity
areas requiring strengthening (collapse)
damaged or destroyed structures,
taken at the rate of one plot per
building that was badly damaged.
Quantity
accidents at IES
taken equal to the number of destroyed
inputs of communications into the building (electrical,
gas, heat and water supply). Besides
In addition, the possibility of destruction is checked
head elements of communications and lines
supplies. Communication input is considered
destroyed if the building received a complete
or severe destruction. At
in the absence of initial data,
assume that each building has four
communication input.
Length
littered driveways
estimated taking into account the width of the streets and
fragmentation range. Without
given the width of the streets is taken equal to:
30 m - for trunk lines; 18 m - district;
10 - 12 m - driveways and lanes. Range
debris scattering
destroyed buildings is determined for
estimates of the blockage of entrances.
The fragmentation range is taken
half the height of the building.
Height
obstruction
calculated to select the method of conducting
rescue work. If the blockage height
is 4-5 m, then more efficient
is the excavation of galleries in the rubble, with
rescue operations from
filled cellars. Height calculations
blockage is carried out according to the formula.
 , m (3.58)
, m (3.58)
where
H is the height of the building, m;
—
blockage volume per 100 m3
volume of the building;
To
- the indicator is equal: for an explosion outside
buildings - 2; inside the building - 2.5;
Maximum
debris weight and size,
load capacity and reach
boom cranes can be taken in
according to table. 3.23
Table 3.23
GOST, SNiP and other terrible documents what pressure should be in the heating system of an apartment building
Before designing a heating system, you should familiarize yourself with the regulatory documents. Just in case, it is better to invite specialists to help with the creation of the harness.
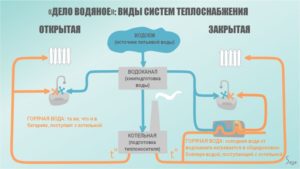
Types of pressure in the heating system
There are three indicators:
- Static, which is taken equal to one atmosphere or 10 kPa / m.
- Dynamic, taken into account when using a circulation pump.
- Working, emerging from the previous ones.
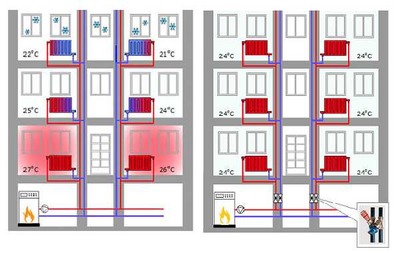
Photo 1. An example of a strapping scheme for an apartment building.Hot coolant flows through red pipes, cold coolant flows through blue pipes.
Working value
It is characterized by regulatory documents and is the sum of two components. One of them is dynamic pressure. It exists only in systems with a circulation pump, which is not often found in apartment buildings. Therefore, in most cases, a value equal to 0.01 MPa for each meter of pipeline is taken as a working one.
Minimum value
It is chosen as the number of atmospheres at which water does not boil if heated above 100 °C.
| Temperature, °C | Pressure, atm |
| 130 | 1,8 |
| 140 | 2,7 |
| 150 | 3,9 |
The calculation is made as follows:
- determine the height of the house;
- add a margin of 8 m, which will prevent problems.
So, for a house with 5 floors of 3 meters each, the pressure will be: 15 + 8 = 23 m = 2.3 atm.
What should be the GOST and SNiP standards for apartment buildings
The documents stipulate the ranges that provide heating for the building. The figures are calculated to maintain a temperature of about 20 ° C with a humidity of about 40%.
To achieve them, a project is being developed at the stage of preparation for construction. There are three working pressure values:
- 2-4 atm for houses up to 5 floors;
- 5-7 for 6-9;
- 12 and above for 10-story and large buildings.
Factors determining indications
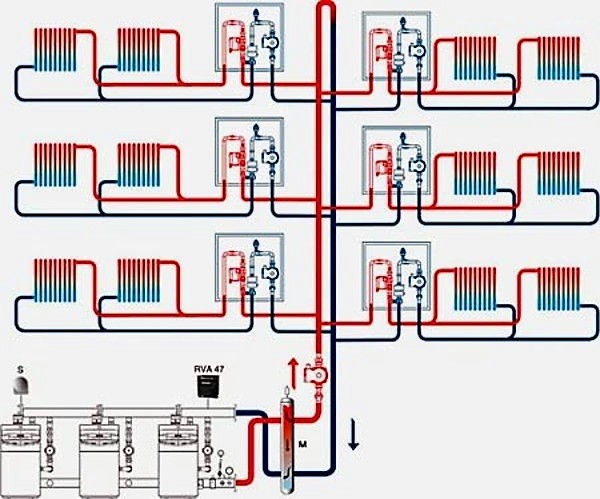
Modern houses are equipped with elevators that divide the network into parts. Their purpose is to mix streams of water of different temperatures. They are equipped with regulators that control the nozzles. This affects the determination of pressure: a partially closed assembly changes the indicator.
The following factors also interfere with achieving the values \u200b\u200bspecified in GOST:
- The power of the appliances installed in the building rarely matches the calculations made before starting work.
- Equipment status. During operation, it wears out.
- Pipeline diameter. Sometimes, during repairs, the piping section is replaced by choosing a different size, which leads to a pressure drop.
- Location of the apartment: the farther from the highway and the boiler, the greater the chance of a decrease in readings.
Checking the norm in multi-storey buildings
It is carried out by manometers at three points:
- on the supply, near the boiler, as well as on the return at a similar point;
- near all equipment used: pumps, filters, regulators, etc.;
- on the highway near the boiler room and at the outlet to the house.
Requirements for indicators are defined by GOST and SNiP.
Ways to raise the pressure
In an apartment building, it is impossible to solve such a problem on your own. The best thing to do is get the air out of the pipes. And they can also help:
- Loosening threads by breaking welded joints.
- Feed stop in different parts of the strapping.
- Reduce system power for a short period of time.
- Inspection of the valves for the passage of the working fluid.
- Applying soap to joints.
Useful video
Watch a video that shows exactly how heating is supplied to a multi-storey residential building.
Pressure drop
Important! The problem is sought by turning off the parts of the harness one by one
If it is not detected, attention is switched to the equipment. More details about the differences are written in SNiP
- supply location;
- pipe diameter;
- check valve is present.
Sweet fiction or reality: is it possible to connect individual heating in an apartment?
Why is it hot in the kitchen and cold in the bedroom? Adjustment of heating batteries in the apartment
What is the secret of her work? Features of the heating system in a multi-storey building
Economic heating without overpayments! How to put counters for heating in an apartment?
Autonomous apartment heating - easy! Features of disconnecting from central heating in an apartment building
Trust, but verify: heat meters for heating in an apartment building, the principle of operation of devices
Pressure rate
Compared to the heating main, where the water pressure is 12 atm, the pressure in the heating system of the building is somewhat less - about 10 units.Poorly adjusted configuration, losses are reduced to 5.5 atmospheres.
Between heating periods, an index exceeding the static index is maintained in the pipes. This protects the wiring from oxygen ingress and the corrosion process. The minimum value of the above condition depends on the height of the residential building with a margin of 3-5 meters.
Differences between static and dynamic pressure
The pressure of artificial heating of MKD has several main types.
These are represented by:
- static pressure. Indicates the force with which the water column presses on the inner walls of pipes, radiators, depending on their height. When calculating zero (0), the surface pressure of the liquid is taken.
- The dynamic indicator arises due to the movement of a hot carrier inside pipelines, batteries.
- The working state consists of the two previous indicators, which ensure the trouble-free operation of all elements of the heating structure.
The last characteristic has its own conditions, which are expressed by coefficients:
- low-rise buildings with a closed type of circulation - 0.20-0.40 mPA;
- one-story buildings with natural circulation of hot media and an open model - 0.10 mPa for every 10.0 m of water column;
- high-rise buildings - approximately 1.0 MPa.
The role of the static onslaught is expressed by the pressure of the liquid in the closed heating circuit on the batteries of the apartment and its wiring, depending on the number of floors. If we take this formula as a basis, then for every 10 meters of height there is one additional atmosphere.

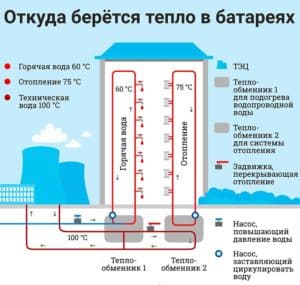
Additional pressure is dynamic. The latter is due to the onslaught of water on pipelines, batteries during the movement of a hot carrier. When installing a closed circuit of artificial heating of a building with a centrifugal pump, it is necessary to take into account the joint - static and dynamic pressure, a feature of the equipment. For example, a cast iron radiator is designed for a working use of 0.6 mPa.