VIDEO ipt>
heating cable requirements
Based on state standards, it is important not to forget about the following general requirements for a heating cable:
If the floor heating system will be used in the apartment, then it should be an additional, and not the main source of heating.
In wooden houses with a wooden base, it is necessary to mount such a wire, the power of which will not exceed 2 kW.
For heating ramps or stairs located outside the premises, a wire is used, the rated power of which is 4 kW.
To equip one circuit, you must use a continuous piece of cable. It is advisable to mount one circuit in one room if its area does not exceed 25 m2.
Wire transfer from one room to another is not allowed. In the transition area, it can simply break.
For laying the product, you must use only those parts and accessories that are sold with it in the kit.
The device of a single-core warm floor
The main element of a single-core underfloor heating is a cable with a certain diameter. The core material is nichrome, galvanized, brass or other metal. When electricity is supplied, the resistance heats up the core.
For maximum safety during operation of the system, it is wrapped with two or four layers of insulators:
heat-resistant layer, the material for which is polyvinyl chloride, fluoroplastic, silicone rubber, or cross-linked polyethylene;
shell made of aluminum foil and copper mesh, which protect against electromagnetic radiation;
the outer layer of plastic that protects against mechanical damage;
copper ground, which is connected to the supply cable.
If everything is done correctly, then the heating core will warm up no more than 80 degrees. The insulator withstands from 100 degrees.Different manufacturers have their own insulation system, so when buying, you can separately ask what material it is made of and how many layers.
Deviations about single-core. Solid and stranded wire, what's the difference
Quite often you can hear how they are trying to compare these two types of cable products and find out which wires are better, stranded or solid? Let's say right away that such a formulation of the question is generally incorrect and shows the incompetence of the questioner. After all, you can also ask: “Which is better, a shovel or a hammer?”, And the answer does not depend on objects, but on the type of activity that will be carried out with the help of a certain tool.
The choice of the type of conductor in a cable or wire is equally dependent on 1) location and 2) operating conditions. Therefore, instead of breaking spears, it is better to “get acquainted” with the candidates for selection, find out their features and differences, and only then decide which is much better.
What is solid and what is stranded wire
In the truest sense of the word, the expression "solid and stranded" does not apply to this issue, since the word "cores" refers to the total number of conductors in a cable or wire, and not to the structure of an individual core. It would be correct to say single-wire or multi-wire core. But, for some reason, the expression "stranded" stuck. For the veracity of the information, we will use the correct term, but we will also not condemn those who have become accustomed to a different option, this is not our business.
Single-wire wire - having only one core as a conductive element, with a cross section from the standard range (0.5-1-1.5-2.5-4, etc. mm sq.)
Stranded wire - as a conductive element - these are several conductors intertwined with each other, having a total cross section in the same standard values. It is allowed to interweave a non-conductive thread (usually resembling kapron) into conductive cores to further increase the elasticity of the entire cable.
Features of each of the two types of wires
Both a flexible blade of grass and a rigid tree can withstand a hurricane, therefore we must also understand that the same properties of wires (under certain circumstances and installation requirements) can also become both a disadvantage and an advantage. And, instead of arguing about “best”, we will present the full picture, pointing out the features of each type of vein that help in choosing the right one in specific situations.
1. Single-wire core.
Bottom line: no matter what “home-grown” electricians say, in most household electrical systems it is more efficient and competent to use wires with single-wire cores. In most, but not all, consider the other side of the coin.
2. Stranded core.
Applications for solid and stranded wires
So a reasonable conclusion suggests itself: each of them is good if it is in its place. The properties indicated above, without dispute or hesitation, show where it is more appropriate to use each type of wire.
Stationary wiring of power cables in houses, apartments and industrial facilities with medium and large cross-sections of cable cores is preferably performed with single-wire conductors (if there are no special requirements). On electrified railways, all contact wires have just such a design, serving reliably and for a long time.
Electric cables can be divided into single-core and multi-core, they are also called hard and soft, or solid and flexible. Whatever you call them, the first have one vein, and the second have several veins. single core and many
Two-core electric floor
A two-core cable is slightly different from a single-core cable in its design. In such a cable, 2 wires insulated from each other (cold and heating) run in parallel under the outer sheath. These wires are attached to one side of the heating section.
There are no differences between the 2 compared heating elements in terms of quality and service life. However, a two-core floor has a plug at each end of the section, which connects and reinforces them. 2 other parts are similarly connected using a coupling and cold ends of the wire.
A two-core cable floor is easier to install, as it already has a ready-made end for connecting to the mains. And the end of a single-core cable after laying must be returned to the connection point (loop).
The main criteria that influence the choice are: the type and size of the room in which such a structure will be installed and the thickness of the screed. Experts recommend using a single-core system in small and warm rooms, and a two-core floor for potentially cold, damp and spacious rooms. In apartments, cottages and private houses for the installation of underfloor heating, as a rule, a two-core underfloor heating is used. And in public, office and non-residential premises, it would be more expedient to use a single-core cable, since electromagnetic radiation occurs around almost any conductor with electric current, which is unsafe for both people and animals. In a single-wire cable, current flows in one direction, creating harmful electromagnetic radiation.
A two-core cable has 2 wires with mutually directed electromagnetic fields that cancel each other out. There are no differences between the two systems in terms of quality and service life.
It should also be taken into account that when using such a cable heating structure, the floor height will rise by 5-10 cm. The electric cable heating system is universal and suitable for many types of coatings (linoleum, tile, carpet, laminate, natural stone). It helps evenly and correctly distribute warm air throughout the room thanks to the regulator. Modern developments and technologies make it possible to shield the heating conductors of the cable as much as possible. To date, underfloor heating is an environmentally friendly, economical, practical and very convenient solution for warming your home.
How to install floor heating
Before starting installation, it is necessary to make a “warm floor” project. It indicates the power of the equipment. The data is calculated according to the norm: 1 kW of energy is required for heating per 10 m2. If a two-core underfloor heating is additional heating, only 10% of the room should be heated for the full effect, then, accordingly, the indicator will be different, 10 W per 10 m2.
The cable is connected to electricity. The passport to the equipment must indicate what voltage it works on. If home wiring does not provide for the use of high-power appliances, then it is recommended to make new wiring in the house. Some systems operate from 230 V. How is cable heating installed?
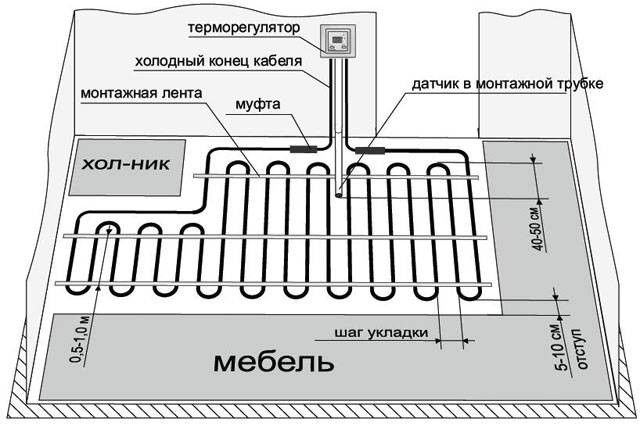
The room provides a place on the wall for the installation of a thermostat and an automatic device. A recess is made on the surface of the wall, which is equipped with a plastic box. It will contain electrical wires and a control unit for the heating system.
Before laying the cable, it is necessary to level the base. Perform a concrete screed, equip it with heat-insulating material. A damper tape is strengthened along the perimeter of the room. It will keep the heat in the room, compensate for the expansion of the heating elements at the time of heating.
If the room is located on 2 or more floors, then the thickness of the insulation can be 2-3 cm. It is recommended to use a material with a reflective surface.
In the marked area, mats are placed to which the cable is attached. The upper part of the mat is covered with a protective film. Connect all elements of the system one by one.
If it is necessary to lay a separate cable, then metal tapes are installed on the thermal insulation for fastening. Sections are laid with a certain step. It is calculated by the formula: S room / L cable length.
The ends of the wires must be insulated. To do this, use a shrink film.
A temperature sensor is placed on the surface of the heated area. The distance from the wall to the sensor is 60 cm.
The sensor and all wire outputs are connected to the network.
Perform system testing.
A screed with a depth of at least 20 mm is laid on the floor.
Two-core warm floor
The underfloor heating system has been used for many years. She has proven herself well both in country cottages and in city apartments. Cable heating is not difficult to install. It is necessary to calculate the electricity costs associated with heating the home. As additional heating, the cable is used in the children's room, in the bathroom, in the bathroom.
How is the installation
The next step after choosing the power is to determine the model of the warm floor.
Two types of products with a fundamental difference in installation:
integral mats with fixed heating elements;
cable, which are mounted with the desired step.
How to choose? In standard-configured rooms, you can safely mount mats. They can be either with single-core or with two-core cables. The second type will provide faster heating of rooms. The larger the diameter of the conductor, the higher the temperature level will rise when the equipment is turned on to the maximum.
The specifics of installing a single-core system provides for a mandatory circuit closure. Both ends of the cable must be connected to a power source. When the areas are large, it is convenient to lay with a “snake”, so this condition is difficult to comply with. But for a small room is quite suitable. Moreover, the price of single-core systems is small.
At a two-core warm floor, the circuits are closed according to a different system. Two wires are connected at the ends. The thermostat is also powered when both conductors of the heating elements are connected. Models are more complex and therefore more expensive. At the same time, they allow solving the problem of warming large areas.
Advice. The level of electricity consumption by a warm floor is directly proportional to its power. In this regard, it is necessary to correctly calculate the load on the wiring. If there is a mismatch, the wiring must be replaced.
If the room has a complex configuration, then a two-core underfloor heating will solve the problem, since there is no need to return the cable back to the thermostat. The installation process of the equipment will take about 4-5 hours, no more.
It is believed that both options for underfloor heating are harmless to humans. However, a two-core cable for underfloor heating creates an electromagnetic field 300 times less than the norm, a single-core cable - 60 times. For this reason, in large kitchens and living rooms, where people stay longer than in other rooms, it is more expedient to use two-core cables. Single-core - in bathrooms, corridors and loggias.
When laying equipment, one should take into account how much heat energy will go into the subfloor. So, for example, in apartments and houses on the second floors and above, there is no need to build powerful thermal insulation, a foil layer is enough. But above basements or on cold floors in households, the surface must be thoroughly insulated, otherwise part of the heat will go "to nowhere". With the loss of heat, kilowatts of electricity go away. Therefore, it is better not to save on a heat insulator for the floor.
Some misconceptions about the warm field
The most common misconception is that many people think that the effect of a warm floor will be felt 10-15 minutes after it is turned on. This is not so, the floor will become warm only after a few hours, because the concrete slab needs to warm up first. Even if a floating screed with thermal insulation is arranged, it should take 3-4 hours to warm up to 30-40 degrees. Therefore, if you are planning an electric heated floor in the bathroom, you should know that in order to feel a comfortable temperature under your feet, you need to turn on the warm floor in advance, 3-4 hours in advance. In general, a warm floor is not relevant for short turns, it will be useful when turned on for long hours.
In connection with the need for "warming up", there are many myths about energy consumption.In fact, energy consumption is easy to calculate. To do this, the total floor power in kilowatts must be multiplied by the number of working hours.
Example: Heated floor in the corridor, installed in the place where they take off their shoes and leave shoes, area is about 2 m2, cable length is 24 m, power is 440 watts. In kilowatts, 440 W is 0.44 kW, multiply by 24 hours: 0.44 * 24 \u003d 10.56 - ten and a half kilowatts / hours will be consumed by this floor during continuous operation for one day.
It is worth adding that there are “smart” thermostats on sale that can turn on the warm floor a few hours before your arrival. Naturally, to do this, you must first program the thermostat.
Mounting methods
The heating cable must eventually be covered on all sides with mortar/tile adhesive, this can be achieved in three ways:
fill . The most correct way in my opinion. It consists in pouring a mini-tie 1-2 cm over the mounted cable. The resulting screed will be suitable for any floor covering. To implement this option, a couple of centimeters of height should be provided when pouring the main screed, in places where there will be a warm floor. For work, mixtures are used that allow pouring such thin layers. If the screed is initially poured into one level and raising the floor level is unacceptable, then this method is not suitable.
Glue layer . When the tile is laid, and everything else is permissible to raise the level of the subfloor by 1-2 cm (do not forget, the tile itself will add at least 1 cm), the tile is placed on top of the cable on a thick layer of glue. It is necessary to consider this option as a last resort, because there will be a significant drop at the border of the warm zone.
Shtroblenie . The most difficult and dreary way, however, when raising the screed level is unacceptable, is the surest. First you need to mark the lines where the heating cable will go. It is also necessary to take into account the strobe for the corrugation with a temperature sensor and the coupling with a cold connecting cable. After marking, you need to attach some kind of thread / rope to the lines to check the length of the strobe. You need to be sure that the entire cable will fit into the future strobe, otherwise you need to change the layout.
After chasing, the dust is carefully removed and the surface is primed. The wire is laid in a strobe, the depth of the strobe should allow applying 3-5 mm of coating solution over the cable.
The temperature sensor in the corrugation is also mounted in the strobe, the corrugation must be plugged from the end (wrap it with electrical tape). The end of the corrugation should be located between the heating conductors, not far from the edge of the heating zone (but not at the edge). The optimal distance of the temperature sensor is 30-50 cm from the edge, deep into the warm area.
When the wire is laid, the strobes are sealed with tile adhesive, or a mixture of self-leveling floor. If you plan to lay linoleum, it will not be superfluous to apply a finishing layer of 1-2 mm of self-leveling floor.
Floors should be checked or operated no earlier than one month after completion of all wet processes with the floor (pouring, laying tiles). Switching on earlier will not damage the cable itself, but may cause cracking of the grout/adhesive.
Conclusion
The heating cable is recommended for underfloor heating. The most preferred application is a direct heating system or "thin floor".
Among the variety of heating cables, it is best to use a two-core resistive cable in terms of price-quality ratio.
The choice of the desired cable with the required power density, its length and laying step are obtained as a result of calculations.
It is unacceptable to change the length of a resistive cable section (except for zonal cable).
Which wire is better in terms of parameters solid or stranded
stupid question section and separation of channels or phases
For what purpose? For fixed electrical wiring, single-core is better, as it is more resistant to corrosion. The stranded one has a more developed surface, therefore the oxidation area is larger. And the price of stranded wire is higher.
and depending on what for ... If the cord for equipment, a portable extension cord, etc. is obviously multi-stranded with its much greater resistance to repeated bends and twists .. A single-core simply cannot stand such "liberties", breaking off somewhere at a 5-7 sharp bend , but on the other hand, when the wire is motionless (for example, in a cable channel or on brackets on the wall, etc.), it retains its shape better and does not sag, and the lower cost also matters ...
Strange electricians surround you. VVG 3X2.5 and PPVS 3X2.5 is it a single-core wire or not? 🙂 Maybe the question is about single-wire and multi-wire CORE. Multiwire for change is preferable.
Here the question is posed in such a way that it is more preferable in terms of cost and ease of installation. Suppose it is necessary to lay a cable in hard-to-reach, inconvenient places, the customer chooses a cable or wire with a solid core, as it is cheaper. Although mounting it is often more difficult and longer than flexible. To mount, suppose, the wiring in the apartment with a wire with a multi-wire residential, on the contrary, is more time consuming. The cable is selected primarily according to the cross section of the core, and the material of the conductor.
It just doesn't get better. Sometimes better for some purposes. For mass power low-frequency installation, single-core is better because it is stupidly cheaper. And if the frequency is so high that the skin effect begins to affect, then the losses in the stranded will be much lower, even if it is more expensive. If money is not taken into account, then another plus of a single-core is that it is easier to mold it and clamp it into a terminal. And stranded that it is much softer and bends better. In general, it all depends on your goals.
Everything is driven by technology. And so it doesn't matter. Look inside any household equipment - most of the conductors are made of single-core wires. And only where flexibility is needed, there is a stranded one.
Temperature regime
The temperature of the electric floor depends on the sensor and programmer. It is these devices that set the necessary heating. But we must remember that each heating cable for underfloor heating has an optimal temperature, which should not exceed its limit:
The maximum temperature of the cables is 65°C, but they usually operate at an average temperature of 30°C. Protective insulation will withstand no more than 100 ° C;
The operating temperature of an electric mat depends on its brand. Usually it ranges from 80 to 104°C. For example, the temperature of a cable mat is a maximum of 60°C, while a carbon mat is 55°C. The maximum operating temperature of the film mat is 55°C, although the film itself can withstand up to 250°C, then it begins to melt.
There are many ways of electric floor heating. In each case, the choice of a heating element must be made individually, taking into account the type of flooring, floor design features, installation complexity and other factors.
VIDEO
VIDEO Characteristics of a two-core cable
As the main heating, it is preferable to lay a two-core cable on the floor. It is more powerful, gives off more heat. The two-wire wire diagram has the following characteristics:
the basis is 2 cores; electricity flows through them; they are a heating device;
each core is separated by fluoroplastic insulation;
a drainage rod passes over it; he is able to draw off excess energy and prevent the main veins from overheating; overheating occurs when the wire is “locked” by furniture or carpet; drainage is connected to a temperature sensor and gives a signal to the system about an increase in temperature;
all 3 rods are enclosed in a foil screen made of aluminum;
the top protective layer is a thick fiberglass or polypropylene shell; it withstands temperatures over 100 0C.
VIDEO Which cable is better two-core or single-core
The difference between a single-core and a two-core cable is as follows:
The need to install a thermostat. The self-regulating cable does not require the installation of a temperature sensor and regulator. In this case, heating is carried out in separate sections.
The presence of an electromagnetic field. Some varieties of single-core cables have a high-quality Teflon coating. The protective layer effectively reduces the level of radiation. The remaining types of single-core wire create an electromagnetic field of greater intensity, so they are recommended for use in walk-through rooms, hallways, balconies, baths, saunas, etc. In warm two-core floors, radiation is completely absent, which makes operation completely safe for living quarters: bedrooms, children's rooms, etc.
Some manufacturers, in an effort to reduce the cost of self-regulating underfloor heating, change the internal structure, leaving only a heating matrix and minimal insulation. The correct method for selecting a self-regulating cable is related to the need to determine whether the cable has external insulation and a copper shield layer. The presence is indicated by the marking CT, CF, CR.
Characteristics of a single-core wire
A single-core cable is most often used as additional heating. It is laid for floor heating in small rooms, in the kitchen, in the bathroom or in the bathroom. The intensity of heating is not high power. If there is a need to conduct heating in a large room, then it is necessary to provide a long cable, lay it in frequent turns on the floor.
A single-core cable is a system based on one core, a core. An electric current passes through it. When heated, it is a heating device. The core is made of brass, galvanized steel or chrome.
The rod is wrapped with insulating material. It can be fiberglass, fluoroplastic, polyvinyl chloride sheath. Use 3-4 insulating layers.
A reflective screen is laid on the insulation. It is designed to block electromagnetic radiation. Most often, a thin layer of aluminum is used.
The outer sheath of the cable is a protective film made of fiberglass or cross-linked polyethylene. They use a heat-resistant, water-repellent material that protects the cable from external influences, including mechanical ones.
The cable system "warm floor" is recommended to be used under a hard floor cladding. Despite the fact that the heater will be under the screed, it can be very vulnerable. It is not recommended to use linoleum or carpet as a finishing coating. An additional hard layer is required to securely protect the cable. As a protective layer, sheets of fiberboard or plywood are used. Cable heating is widely used in Moscow, in apartments and country houses.
If you install furniture on the floor without first protecting the cable, then "locking the wire" may occur. The bottom surface of a cabinet or sofa will contribute to overheating of individual sections of the cable. The system will automatically catch the increased load, and may turn off.
To control this process, it is recommended to install several temperature sensors in the floor covering. This will allow you to determine in which area the temperature began to decrease. Furniture is installed on legs. The distance between the bottom panel of the cabinet and the floor is recommended to be kept at 5 cm.