Do I need to ground the heated towel rail
First you need to know that grounding (the construction of ground loops with your own hands) is not required if:
- 1. You are using an electric heated towel rail (such heated towel rails are usually equipped with special plugs in which there is a ground wire, all this is connected to a socket, and the sockets themselves must already be connected to the ground loop).
- 2. You live in a private house or apartment and have a separate heating system.
Grounding the heated towel rail is mandatory in the following cases:
- 1. If your dryer is connected to the heating system with a plastic pipe. Inside the metal-plastic pipe there is aluminum, which conducts electric current: at the junctions where the fittings are located, the electrical circuit is broken. Accordingly, such a heated towel rail must be connected to the ground loop, or to the hot water riser.
- 2. If your hot water system is made of plastic pipes.
How to ground a heated towel rail
All electric heated towel rails, as mentioned above, are connected to a grounded outlet, while such dryers have a ground wire with a separate contact on the plug. Since heated towel rails are usually installed in the bathroom, you should inspect the outlet to which it will be connected. Such an outlet must be in a special protective case that prevents moisture from entering the outlet itself.
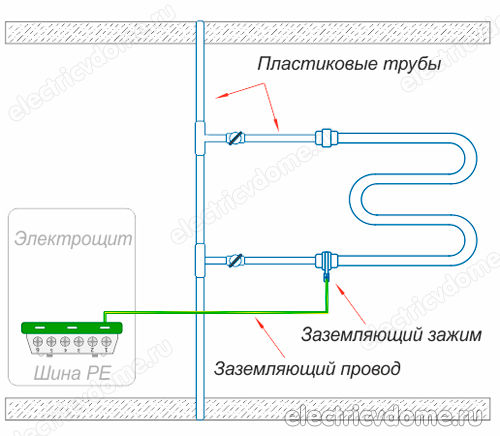
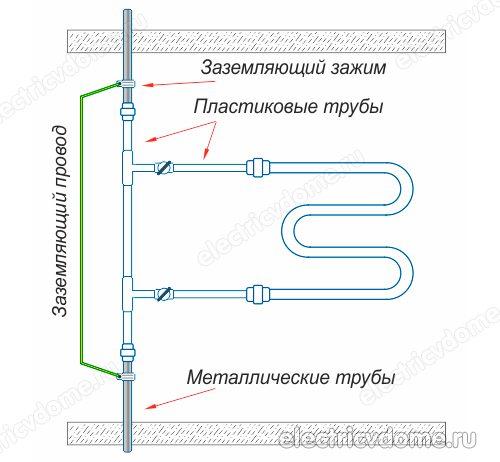
There are 2 main ways to ground a heated towel rail:
- 1. Using a potential equalization system, which must be installed by hand, then ground this system to the common ground of the electrical panel. This should be done if communications made of polymers (metal-plastic pipes) are used instead of metal communications in a house or apartment.
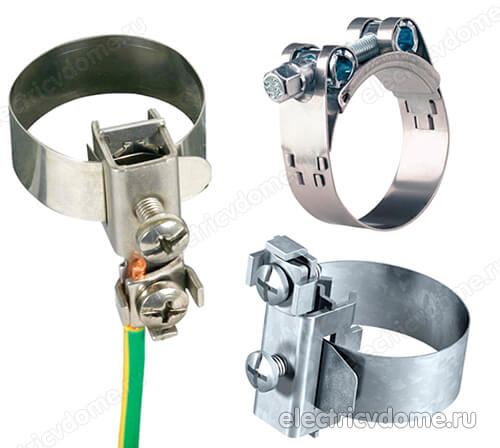
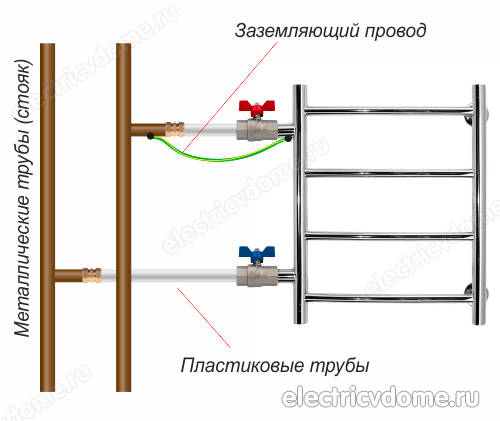
- 2. Grounding directly the pipe of the body of the heated towel rail with an ordinary wire to a steel riser.
To implement the grounding of the heated towel rail in the second way, you first need to get a clamp, after removing all insulating materials from it. This clamp must have a terminal for connecting the wire. Then the clamp is attached to the pipe of the heated towel rail body.
An ordinary copper wire is taken, which should have a cross section of 4 mm2. This wire is connected on one side to the clamp terminal, its other end must be connected either to the ground of the electrical panel or to a steel riser. In addition, do not forget to connect other devices in your bathroom to the ground loop.
| Such methods do not require a lot of time for their implementation, but in return they get a long and uninterrupted operation of the heated towel rail, and in the future the question “how to ground the heated towel rail” will not cause difficulties. |
Friends also watch the video for what you need to ground the heated towel rail.
Related content on the site:
- About grounding in simple words
- Why is the bath grounded?
- The design of the grounding device
Causes of electrocorrosion
The appearance of Foucault eddy currents is a rather complex and unpredictable phenomenon. In hot water supply systems, and sometimes in the heating system, such currents appear due to many reasons that seem to be unrelated.
In general, eddy currents are formed with a potential difference. When building a house, all metal structures are connected to a common ground loop, and earlier in construction they used grounding along the loop, but now they are content with the potential equalization method.
When plastic systems are installed in an apartment instead of the existing metal system, the potential difference arises due to a ground break (for example, there is one potential on a heated towel rail, and a completely different one on a riser). Hence the potential difference, hence the stray currents. They can also occur as a result of a short circuit, lack of grounding of nearby electrical household appliances, be it a washing machine, and so on.
Even the presence / absence of tram tracks in the immediate vicinity plays a role. Stray currents also occur when there is a violation of the insulation of the electrical wiring, a network break, or grounding made to the heating system.
All this leads to electrical corrosion of plumbing, it is also caused by the proximity of two different materials, especially stainless and black steel. The place through which the charge passes into the heated towel rail, as a result, undergoes an electrochemical reaction, so damage occurs there. Such problems are usually solved by directly grounding the heated towel rail itself.
When buying a water heated towel rail, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the rules for its operation, in particular, pay attention to whether it is necessary to ground the heated towel rail or not, in order to take this point into account during the repair, and not after the repair is completed
Why ground a water heated towel rail
After plastic pipes began to replace ordinary metal ones, they began to ignore their grounding, mistakenly believing that a metal pipe and a metal-plastic pipe have the same electrical conductivity. This is not true. There is no contact between the metal-plastic pipe and aluminum: they are not connected.
Practice shows that 90 percent of heated towel rails begin to leak precisely in the case of replacing metal hot water systems with their plastic counterparts (for example, polypropylene). Old metal pipes are replaced with modern plastic ones in order to reduce eddy currents. However, corrosion continues to show itself.
The first symptoms of electrical corrosion are the appearance of rust spots on the heated towel rail, and rust appears even on devices made of stainless steel. In general, all metal electrical products in contact with water are subject to both electrochemical and galvanic corrosion. Electrocorrosion occurs in the presence of stray currents. As a result, the metal is simultaneously exposed to electric current and water, after which metal breakdowns appear, and corrosion begins to spread from there.
When two different metals come into contact, one of which is more reactive than the other, both metals enter into a chemical reaction. Pure water is a very poor conductor of electric current (dielectric), but due to the high concentration of various impurities, water turns into a kind of electrolyte.
Do not forget that temperature has a great influence on electrical conductivity: the higher the water temperature, the better it conducts electricity. This phenomenon is known as "galvanic corrosion", it is she who methodically makes the heated towel rail unusable.
The need for anti-corrosion protection
Protecting metal from influences that have a destructive effect on its surface is one of the main tasks facing those people who work with mechanisms, units and machines, ships and construction processes.

The more actively a device or part is used, the more likely it is to be exposed to the destructive effects of atmospheric conditions, liquids that one encounters during operation.Many branches of science and industrial production are working on protecting metal from corrosion, but the main methods remain unchanged and consist in creating protective coatings:
- metal;
- non-metallic;
- chemical.
Non-metallic coatings are created using organic and inorganic compounds, their principle of operation is quite effective and differs from other types of protection. To create non-metallic protection in industrial and construction production, paints and varnishes, concrete and bitumen, and high-molecular compounds are used, which have been especially actively adopted in recent years, when polymer chemistry has reached great heights.

Chemistry has contributed to the creation of protective coatings by methods:
- oxidation (creation of a protective film on the metal using oxide films);
- phosphating (phosphate films);
- nitriding (saturation of the steel surface with nitrogen);
- cementation (compounds with carbon);
- bluing (compounds with organic substances);
- changing the composition of the metal by introducing anti-corrosion additives into it);
- modification of the surrounding corrosive environment by introducing inhibitors that affect it.
Electrochemical corrosion protection is the reverse process of electrochemical corrosion. Depending on the shift of the potential of the metal to the positive or negative side, there are anodic and cathodic protection. By connecting a protector or a direct current source to a metal product, cathodic polarization is created on the metal surface, which prevents the destruction of the metal through the anode.
Electrochemical protection methods consist of two options:
- the metal coating is protected by another metal, which has a more negative potential (that is, the protecting metal is less stable than the one being protected), and this is called anodizing;
- the coating is applied from a less active metal, and then it is and is called cathodic.

Anode corrosion protection is, for example, galvanized iron. Until all the zinc from the protective layer is used up, the iron will be relatively safe.
Cathodic protection is nickel plating or copper plating. In this case, the destruction of the protective layer leads to the destruction of the layer that it protects. Attaching a protector to protect a metal product is no different from the reaction in other cases. The protector acts as an anode, and what is under its protectorate remains intact, using the conditions created for it.
What is corrosion
The process of destruction of the upper layer of a metallic material under the influence of external influences is called corrosion in a broad sense.

The term corrosion in this case is only a characteristic of the fact that the metal surface enters into a chemical reaction and loses its original properties under its influence.
4 main signs by which you can determine that this process exists:
- a process that develops on the surface and eventually penetrates into the metal product;
- the reaction arises spontaneously from the fact that the stability of the thermodynamic balance between the environment and the system of atoms in the alloy or monolith is disturbed;
- chemistry perceives this process not just as a reaction of destruction, but as a reaction of reduction and oxidation: when entering into a reaction, some atoms replace others;
- the properties and characteristics of the metal during such a reaction undergo significant changes, or are lost where it occurs.
Metal protection methods
Electrochemical corrosion is one of the main obstacles encountered in the way of human activity. Protection from the impact of destructive processes and their flow on the surface of structures and structures is one of the permanent and urgent tasks of any industrial production, and any household activity of a person.

Several methods of such protection have been developed, and all of them are actively used in the daily life cycle:
- Electrochemical protection - electrolytic according to the principle of operation, the use of chemical laws, protects the metal using the anode, cathode and tread principle.
- Electrospark processing using various installations - non-contact, contact, anode-mechanical.
- Electric arc spraying is the main advantage in the thickness of the applied layer and the relative cheapness of the process.
- Effective anti-corrosion treatment is the removal of contaminants and cleaning of the treated surface, followed by the application of an anti-corrosion and then an additional protective layer to the surface.
All these methods have been developed in the process of human activity in order to protect tools, vehicles and transportation at the junction of several industrial sectors, and using scientific achievements.
Electrochemical corrosion, which is a natural process of destruction of the metal surface under the influence of neutral or aggressive environmental factors, is a complex problem. Machine-building, transport, and industrial enterprises, vehicles suffer losses from it. And this is a problem that requires daily resolution.
Types of corrosion
Depending on the type of metal and the redox reaction that occurs with it, corrosion can be:
- uniform or uneven;
- local and point (some sections for some reason reacted, while others did not);
- ulcerative, also known as pitting;
- subsurface;
- cracking;
- intercrystalline, arising along the boundaries of the metal crystal.
Also, depending on what kind of external factors affect the surface, corrosion can be chemical and electrochemical. Chemical corrosion occurs as a result of some reactions under the influence of chemical interactions, but without the participation of electric current, and can even be inherent in oil and gas. Electrochemical is distinguished by certain processes, it is more complex than chemical.

On the video: corrosion of metals.
Causes and signs of electrochemical corrosion
Electrochemical corrosion differs from chemical corrosion in that the destruction process takes place in the electrolyte system, which causes an electric current to arise inside this system. Two conjugate processes, anodic and cathodic, lead to the removal of unstable atoms from the crystal lattice of the metal. During the anodic process, ions go into solution, and electrons from the anodic process fall into a trap to an oxidizing substance and are bound by a depolarizer.
Thus, depolarization is the removal of free electrons from the cathode sites, and the depolarizer is the substance that is responsible for this process. The main reactions occur with the participation of hydrogen and oxygen as depolarizers.
There are many examples of electrochemical corrosion of various types, which affects metal surfaces in nature and under the influence of various conditions. Hydrogen works in an acidic environment, while oxygen works in a neutral one.
Almost all metals undergo electrochemical corrosion, and on this basis they are divided into 4 groups, the value of their electrode potential is determined:
- active ones corrode even in an environment where there are no oxidizing agents;
- medium-active enter into an oxidation reaction in an acidic environment;
- inactive ones do not react in the absence of oxidizing agents in both neutral and acidic environments;
- do not react - high stability (noble metals, palladium, gold, platinum, iridium).
But the same reaction can also take place in water, in solutions of bases, salts and acids. In the highly specialized difference in atmospheric corrosion, soil and aeration, marine and biological (occurring under the influence of bacteria) are distinguished.
There is even electrical corrosion, which occurs under the influence of electric current, and is the result of stray currents that occur where electric current is used by a person to carry out certain activities.
In this case, the homogeneous metal surface is destroyed due to thermodynamic instability to the environment. And heterogeneous - due to the composition of the crystal lattice, in which the atoms of one metal are held tighter than the atoms of foreign inclusions.These reactions differ in the rate of ionization of ions and the reduction of oxidative components of the environment.
The destruction of metal surfaces during electrochemical corrosion consists in the simultaneous occurrence of two processes: anodic and cathodic, and the differences between the processes are that the dissolution occurs at the anodes, which are in contact with the environment through many microelectrodes that are part of the surface of any metal and are closed to myself.