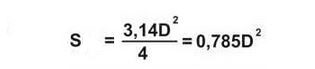Which SIP wire to choose for connecting a country house and a plot
SIP cable is a reliable and versatile conductor of electric current, which has found a wide area of its direct use. Its versatility lies in the fact that it can be used extremely effectively in a variety of situations. It is also characterized by the convenience of its gasket and a wide range of models. But due to their huge variety, many people do not know which SIP wire to choose for a summer residence. The article deals with the solution of this issue.
Purpose of SIP cable
This type of cable line can be used in networks of a wide variety of voltages, which can vary from 220 V to 20 kV. The key feature of SIP is the simplicity of its installation. It does not need reinforcement, holds its shape well and does not sag even under its own weight. Therefore, when conducting overhead lines in the country, it is better to use SIP cable. Also, this version of the conductor is characterized by excellent insulation, which eliminates the possibility of a short circuit.
Varieties of SIP cable and scope
Today, in the local electrical market, the buyer can find the following types of SIP cable:
- SIP1. Based on the use of several cores, the zero cable is not insulated;
- SIP2. There are two cores, the neutral cable is insulated, used for laying overhead lines. They can be used as main power supply lines between settlements. It can be applied practically in any climatic features. Under the influence of low temperatures, the insulating layer is not deformed. Withstands temperatures up to +900 degrees;
- SIP3. The insulation of this type of cable is based on the use of polyethylene. Can also be used in cold and hot environments;
- SIP4. This modification of the cable does not have a carrier core. The design feature is the use of two or four cores. It is used directly for wiring in the house or for supplying electricity to the building itself;
- SIP5. They have a high degree of security, there is double insulation. Often used for laying power lines between cities.
As you can see, each type of cable has its own technical and operational characteristics. Depending on the features of use, as well as the method of laying the cable line, you can choose for yourself the most optimal version of this practical and reliable conductor of electric current. We hope that you now know which SIP wire to choose for a summer residence.
The material was prepared with the support of our partner Trade House "BaltikKabel"
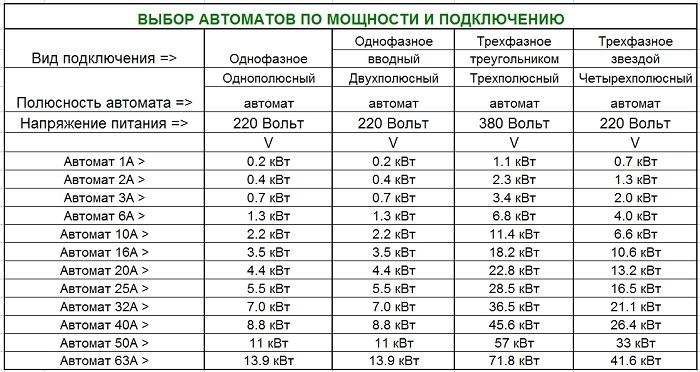
Circuit breaker calculation
You can choose machines with the calculation of the load current or the cross section of the wiring.
Calculation of the machine for current
We calculate the total power of the loads on the machine. We add the power of all consumers of electricity, and according to the following formula:
we get the rated current of the machine.
P is the total power of all consumers of electricity
U - mains voltage
We round the calculated value of the received current up.
Calculation of the machine according to the cross section of the wiring
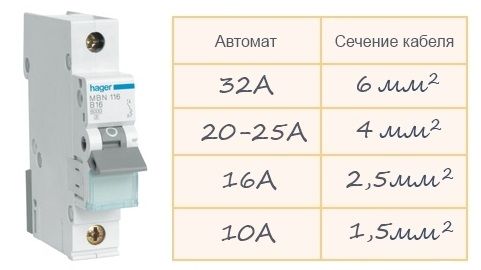
To select the machine, you can use table 1. The current selected for the cross section of the wiring is reduced to the lower value of the machine's current to reduce the load on the wiring.
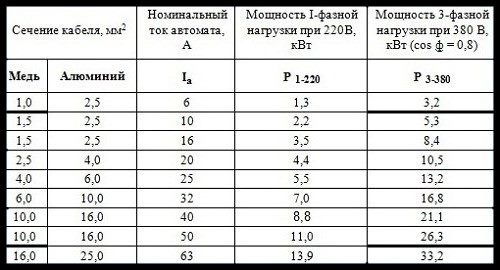
Choice of rated current according to the cable section. Table #1
For sockets, the machines take a current of 16 amperes, since the sockets are designed for a current of 16 amperes, for lighting the best option for a 10 ampere machine. If you do not know the cross section of the electrical wiring, then it is easy to calculate it using the formula:
S - wire section in mm²
D - wire diameter without insulation in mm
The second method of calculating the circuit breaker is more preferable, as it protects the wiring diagram in the room.
On the given simplified graph, the current ratings of the automata are indicated on the horizontal scale, on the vertical scale, the active power value for a single-phase power supply of 220 Volts, the calculation for a voltage of 380 Volts and / or a three-phase power supply will differ significantly and the given graph for others, except for 220 Volts and a single-phase power supply, capacity is invalid. . To select an automatic machine suitable for the selected rated power, it is enough to draw a horizontal line from the power selected on the left to the intersection with the green column, looking at the base of which you can select the nominal value of the machine for the specified power. The desired time current characteristic and the number of poles can be selected by going through the picture to the selection table of automata curve C, as the most universal and frequently used characteristic.
what wire size is needed for 3 kW
What wire size is needed for 3 kW
In the section Other services to the question How to determine what should be the cross-section of the wire for a water heater with a power of 3.5 kW? given by the author Kochegar2 the best answer is The cable usually consists of 2-4 strands. The cross section (more precisely, the cross-sectional area) of the core is determined by its diameter. Based on practical considerations, at low current strengths, the cross section of a copper core is taken at least 1 mm2, and aluminum - 2 mm². At sufficiently high currents, the wire cross-section is selected according to the connected power.
Simply put, if you have a 3.5 kW instantaneous water heater, then you need to connect it with a wire rated for at least 15.9 A, and for a copper wire, the cross section must be at least 2.5 mm².
For aluminum wires, the cross section should be a step higher, since their conductivity is approximately 62% of the conductivity of copper ones. For example, if, according to calculations for copper, a cross section of 2.5 m⊃m is needed; 2, then 4 mm² should be taken for aluminum, but if 4 mm² is needed for copper, then 6 mm² for aluminum, etc.
In general, it is better to choose a larger cross section than according to calculations - what if you need to connect something else? In addition, it is necessary to check whether the wire size is consistent with the maximum actual load, as well as with the current of the protective fuses or circuit breaker, which are usually located near the meter.
Come here
Reply from 22 replies
Hey! Here is a selection of topics with answers to your question: How to determine what the wire size should be for a 3.5 kW water heater?
What denomination to put a 4-pole machine on a 380V socket?
tell me for a welding inverter with a power of 5.5 kW Which extension cord on the coil to choose, with what section? tags: technology
What cable section is needed for a 6 kW EVN. for 380 V. copper cable.
We know the SECTION of the wire and VOLTS, how to calculate how many watts the wire can withstand? for example, a cross section of 0.75, 12 volt tags: Experienced Dedovsk
Reply from Koshak
take 6*3 you won't go wrong
Answer from Ѐuslan Globazh
take with a margin of more than 20a
Reply from Ololosha
well, consider the student the power divided by the voltage, we get the current strength of 15.9 amperes at a voltage of 220 volts, and then 4mm * 2, I think that's enough, because suddenly there will be short-term interference
Reply from Bosston
for 4 kW, we take a cross section of a copper core of 4 sq. mm, the rated current of the protection device is 31.5 Amperes.
And you can also determine according to the table of rated protection currents and the cross section of the supply wires
Reply from Alisha
it is very easy to determine :) - 3 * 2.5
By the way, do not forget that the water heater must be connected to a grounded socket, i.e. into the outlet from the washer (if any :)), if not, then buy a 16-amp machine (see how it looks next to the meter) and a waterproof socket with grounding and call an electrician - he will connect everything.
Reply from 2 replies
Hey! Here are some other threads with relevant answers:
in the bathroom there is a boiler and a washing machine, a copper wire of 2.5 mm, there is a 16A machine on the shield.should I change the tags to 25A: Vehicles Districts of Van
Will VVG 4x16 withstand a load of 50 kW? or you need to pick up a VVG 4x25 cable ??? tags: Technique Cable production
Who can tell from knowledgeable electricians how the cable is connected to the meter in Khrushchev ?! tags: Khrushchev technique
What is the current and voltage in ordinary Russian sockets? tags: technology
https://youtube.com/watch?v=0o9x-5mPCuY
How to choose a SIP wire. Choosing the right self-supporting insulated wire
Self-supporting wires are the optimal solution for both high and low voltage networks.
The popularity of this type of cable is associated with the ease of installation, convenience and safety of operation and the minimum number of interruptions in the supply of electricity due to emergencies.
Before choosing a SIP brand cable, you should decide for what purposes it is needed and in what conditions it will be used.
What types of wires exist
Sip -1 and Sip -2 are mainly used for main transmission lines or their branches with a voltage of 0.6-1 kV;
Sip - 3 is also used for air lines, but is designed for much higher loads - 10 - 35 kV;
SIP - 4 does not have a carrier core, it is laid mainly along the walls of buildings and structures, and its main area of \u200b\u200buse is branches from highways for supplying electricity to end consumers.
How to choose a section?
The cross section of the wire should correspond as much as possible to the power of the connected load. Too thin wires will have a higher resistance, respectively, they will get very hot, which leads to significant energy losses during transmission, and can also be the cause of insulation destruction, short circuits and even fire.
How to choose the right one? Regulatory documents and tables indicating voltage and current strength for different types of SIP will help to select a cable with the characteristics necessary for the consumer.
The key characteristic for choosing a wire is the strength of the current that can pass through it.
For different sections, this indicator is different:
- 16 mm2 - 100 A;
- 25 mm2 - 130 A;
- 35 mm2 - 160 A;
- 50 mm2 - 195 A;
- 70 mm2 - 240 A;
- 95 mm2 - 300 A;
- 120 mm2 - 340 A;
- 150 mm2 - 380 A;
- 185 mm2 - 436 A;
- 240 mm2 - 515 A;
In proportion to the increase in the cross-sectional area, the maximum allowable current strength, for the load from which this wire is designed, also changes. In addition, wires of different sections can withstand different intensity and duration of heating during operation.
If the task is to bring electricity to the house using a vulture, it is important to choose the right option. Usually a wire with a minimum cross section of 16 mm2 is more than enough
A smaller cable is simply not produced, and a larger one is not needed for domestic power consumption.
In a standard household power supply network, there are no significant overloads, and the ambient temperature does not go beyond - 50 - + 60 degrees.
Choice of wire insulation
In addition to the characteristics of the conductive and load-bearing cores, it is worth paying attention to the insulation of the wires, more precisely, to the material of its manufacture. For regions with high ultraviolet radiation intensity, light-stabilized polyethylene insulation is recommended.
If there is a risk of significant external heating during operation, non-combustible insulation should be preferred. If significant sudden temperature changes are possible, there is a risk of snow sticking or icing of wires, then in such conditions, wires with thermoplastic insulation will be the most durable and work properly.
For regions with increased intensity of ultraviolet radiation, insulation made of light-stabilized polyethylene is recommended. If there is a risk of significant external heating during operation, non-combustible insulation should be preferred.If significant sudden temperature changes are possible, there is a risk of snow sticking or icing of the wires, then in such conditions the wires with thermoplastic insulation will be the most durable and work properly.
When operating in high humidity conditions, the use of sealed wires is preferable.
Production and sale
There are many cable manufacturers, and it is up to the consumer to decide which wire to choose specifically from all varieties. As for quality, it cannot be said that any of the major domestic or foreign manufacturers is significantly higher or lower in this indicator.
All requirements for SIP wires are presented in the corresponding GOST, and if the products of a particular enterprise do not comply with it, it simply will not enter the market.
Directly, the manufacturer mainly carries out wholesale sales of the cable; for small volumes, you will have to resort to the services of dealers or intermediaries. And decent companies are always ready to provide documentation confirming their cooperation with a particular manufacturer, as well as indicating the quality of the goods.
The choice of cable for electrical wiring in the apartment
For home wiring, a three-core cable is chosen, one conductor goes to ground. The core is the current-carrying part of the wire, it can be single- or multi-wire. The cores have standard sections, covered with an insulating polymer or rubber sheath, sometimes with a protective cotton braid on top. Wire strands are made of copper, aluminum or steel.
The best option for new electrical wiring in the apartment is copper wire. It is more reliable, more durable, the electrical performance of copper is better than that of aluminum.
As for the brand of cable, the most commonly used cable is VVG and VVGng - flat-shaped copper wires, in double PVC insulation ("ng" refers to non-combustible wire insulation). Designed for wiring inside buildings, outdoors in the ground when laying in tubes, operates at an ambient temperature of -50 to +50°C. Service life up to 30 years. Available in 2-, 3- and 4-wire cable with core cross section from 1.5 to 35.0 mm2
(Please note that with the designation AVVG, the cores in the wire are aluminum.)
Analogous to the Russian VVG - NYM cable, round shape, with copper conductors and non-combustible insulation, complies with the German standard VDE 0250. Technical characteristics and scope are almost the same. The cable is available in 2-, 3- and 4-wire with a core cross-section from 1.5 to 4.0 mm2.
It is more convenient to lay a round cable through walls - holes are drilled slightly larger than the diameter of the cable. For internal wiring, a VVG flat cable is more convenient.
Lightweight and cheap aluminum wires are indispensable for laying overhead electrical wiring, with proper connection they have a long service life, since aluminum almost does not oxidize. Aluminum wiring can be encountered during repairs in old houses. When it is required to connect additional energy-intensive devices, the ability of aluminum wiring to withstand a large load is determined by the cross section or diameter of the wire cores (see table).
Long-term permissible current loads on aluminum wires are several times less than when using copper wires and cables of the same cross section.
| Wire diameter, mm | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1,6 |
1,8 |
2,0 |
2,3 |
2,5 |
2,7 |
3,2 |
3,6 |
4,5 |
5,6 |
6,2 |
| Wire section, mm2 | ||||||||||
|
2,0 |
2,5 |
3,0 |
4,0 |
5,0 |
6,0 |
8,0 |
10,0 |
16,0 |
25,0 |
30,0 |
| Max. current at cont. load, A | ||||||||||
|
14 |
16 |
18 |
21 |
24 |
26 |
31 |
38 |
55 |
65 |
75 |
| Max. load power, watt (BA) | ||||||||||
|
3000 |
3500 |
4000 |
4600 |
5300 |
5700 |
6800 |
8400 |
12000 |
14000 |
16000 |
Electric installation work. Wires, cables and tools
Before talking about the rules for installing internal lines (groups) of house wiring, it is worth understanding the types of wires and their purpose.
An electrical wire is an insulated or uninsulated conductor of electric current, consisting of one or more wires (most often copper or aluminum).
The installation wire is an insulated electrical wire for electrical installation and hidden or open wiring.
Electric cable - several insulated electrical wires enclosed in a common protective sheath, and sometimes on top of it in a protective cover - a steel spiral tape (metal hose) or a metal braid.
An electrical cord is a flexible cable with multi-wire flexible conductors, designed to connect electrical appliances to the network through sockets.
Bare wire may only be used for overhead lines.
The cross section of the wire must be selected depending on the current passing through it (or power consumption).
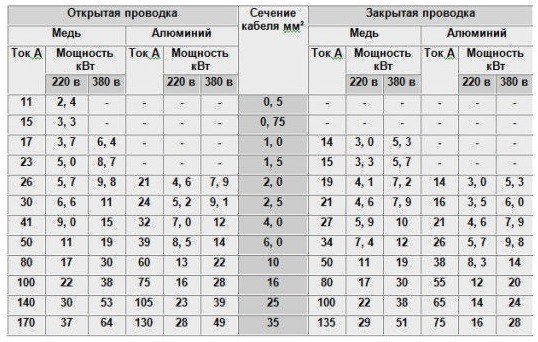
For copper wires, the permissible current load is up to 8 amperes per square millimeter of cross section, and for aluminum wires - up to 6 amperes.
How many kilowatts can withstand SIP
Looking through the simplicity of the Internet for electrical installation, I found a topic on one forum with a discussion of “whether the sip 4x16 15 kW can withstand it.” The question arises because 15 kW 380 volts are allocated to connect a private house. Well, people are wondering if it’s not enough to lay 16 squares on a branch from the overhead line? I looked at the PUE, but for some reason I didn’t find anything on the topic of SIP power.
There is only a plate 1.3.29 "Permissible continuous current for bare wires according to GOST 839-80". And it shows that the maximum allowable current for a cross section of 16kv. mm. wire type AC, AKS, ASK outdoors is 111 amperes. Well, at least something to start with.
How many kilowatts can withstand SIP 4x16?
But then there is GOST 31943-2012 "Self-supporting insulated and protected wires for overhead power lines." At the end of the guest, in paragraph 10 of the instruction manual, there is a sign
How many kilowatts can withstand SIP - table:
| SIP 4x16 | 62 kW | 22 kW |
| SIP 4x25 | 80 kW | 29 kW |
| SIP 4x35 | 99 kW | 35 kW |
| SIP 4x50 | 121 kW | 43 kW |
| SIP 4x70 | 149 kW | 53 kW |
| SIP 4x95 | 186 kW | 66 kW |
| SIP 4x120 | 211 kW | 75 kW |
| SIP 4x150 | 236 kW | 84 kW |
| SIP 4x185 | 270 kW | 96 kW |
| SIP 4x240 | 320 kW | 113 kW |
Method of calculation (update from 19.02.2018)
We take plate 10 and from it we find that one vein of a vulture is 16 sq. mm. withstands - 100 amperes. Next, we take the following calculation formulas:
for single-phase load 220V P=U*I
for three-phase load 380V P=(I1+I2+I3)\3*cos φ*1.732*0.38
update dated 02/19/2018 As for the calculation of power for a three-phase load, it is necessary to understand that a lot depends on the type of consumers (more precisely, what kind of load they provide active or reactive, it depends on what cos φ needs to be substituted into the formula, in this case for calculations it is equal to 0.95 )
Dear visitors of the site and I probably would not have noticed your sharp, but technically correct comments on the article if, just today, a person called me with the question: “what kind of vulture do I need under 120 kW?”. According to the plate, SIP with a cross section of 50 mm square is perfect for him. Even if we omit the fact that the length of the line affects the voltage drop (it has 150 meters), do not forget that the load on the phases can vary, as can be seen from the formula - the average value for the three phases is taken there. Here you just need to understand that the phase current can exceed the maximum allowable values for a given wire section.
Therefore, if the value of the load you need is closer than 10% to the table, you should choose a larger section of the vulture from the list. Let me explain with an example of 120 kW. According to the table, for this three-phase load, SIP with a cross section of 50 mm conductive wires is suitable, but this is less than 10%. That is, 121kW * 0.9 = 109 kW. Accordingly, you need to choose SIP 3x70 + 1x54.6.
At the beginning of the topic, the question was raised: "Will a 4x16 15kW sip withstand"? Therefore, for a private house, we multiply 220Vx100A = 22kW by phase. But do not forget that we have three phases. And this is already 66 kilowatts in total for a residential building. What is a 4-fold margin relative to the issued technical conditions.
Selection of the cable section according to the current strength
The following table will help you calculate the cross section of a copper cable by current strength:
For example, with closed wiring, to connect devices with a total current strength of 17.5 A, a wire with a cross section of at least 2 mm2 is required.
When calculating the cross section of a wire by current strength, it does not matter whether it is AC or DC, as well as the magnitude and frequency of voltage changes in the wiring.
For more rigorous calculations of the cross-sections of the cores of cables, wires in terms of power and current strength, each factor is taken into account - the method of laying electrical wiring, length, type of insulation, etc.All these indicators are regulated by the Electrical Installation Rules (PES).
In general, the electrical wiring in the apartment must necessarily meet the requirements of safety, reliability and efficiency. Electricity is a very serious matter. And if you are not confident in your experience and knowledge, the best solution is to turn to the services of specialists.
Call! +7 (343) 219-22-56
Energomodul LLC
|
household appliance |
Power consumption depending on the model of the electrical appliance, kW (BA) |
Consumed current, A |
Note |
|---|---|---|---|
|
incandescent lamp |
0,06 – 0,25 |
0,3 – 1,2 |
|
|
Electric kettle |
1,0 – 2,0 |
5 – 9 |
Continuous operation time up to 5 minutes |
|
electric stove |
1,0 – 6,0 |
5 – 60 |
Above 2 kV, separate wiring is required |
|
Microwave |
1,5 – 2,2 |
7 – 10 |
During operation, the maximum current is consumed intermittently |
|
Electric meat grinder |
1,5 – 2,2 |
7 – 10 |
During operation, depending on the load, the consumed current varies |
|
Toaster |
0,5 – 1,5 |
2 – 7 |
|
|
coffee grinder |
0,5 – 1,5 |
2 – 8 |
During operation, depending on the load, the consumed current varies |
|
Coffee maker |
0,5 – 1,5 |
2 – 8 |
|
|
Electric oven |
1,0 – 2,0 |
5 – 9 |
During operation, the maximum current is consumed intermittently |
|
Dishwasher |
1,0 – 2,0 |
5 – 9 |
The maximum current is consumed from the moment of switching on until the water is heated |
|
Washing machine |
1,2 – 2,0 |
6 – 9 |
The maximum current is consumed from the moment of switching on until the water is heated |
|
Iron |
1,2 – 2,0 |
6 – 9 |
During operation, the maximum current is consumed intermittently |
|
A vacuum cleaner |
0,8 – 2,0 |
4 – 9 |
During operation, depending on the load, the consumed current varies |
|
Desktop computer |
0,3 – 0,8 |
1 – 3 |
During operation, the maximum current is consumed intermittently |
|
Power tools (drill, jigsaw, etc.) |
0,5 – 2,5 |
2 – 13 |
During operation, depending on the load, the consumed current varies |
Which machine is 15 kW 3 phase
Being the owner or owner of non-residential premises is not easy. A wide range of issues immediately arise, which are sometimes very difficult to solve on their own. One of such global tasks is power supply. The further operation of the premises will directly depend on the solution of this problem.
Before embarking on the implementation of technological connection, it is worth deciding which devices will be connected to the electrical network, as well as how often and for how long they will be operated. All power receiving devices will make up the total load of the network, the value of which can both fit into the value of the allowed power, and exceed this value.
In order to ensure the safety of your facility in terms of the operation of power receiving devices, you must install an appropriate machine. Choosing the right one is quite difficult, as there are many related questions. For example, which machine to put on 15 kW? For 15 kW 3 phases, how many amperes should the machine be at the input of the electrical installation? First of all, it must be said that a 15 kW machine in 3 phases takes a voltage of 380V. Therefore, a 15 kW machine requires an introductory 25A machine. How to meet all these requirements? Let's figure it out.
Cross-section of wires with closed and open wiring
Another point is the type of wiring you plan to use. Open wiring is mounted on surfaces or in pipes fixed on top. Hidden electrical wiring is laid in the voids of floors, in channels or grooves cut in walls, in insulating and steel pipes inside structural elements.
With closed wiring, the requirements for the cable cross-section are somewhat higher than with open wiring, since without air access, the cable heats up more under load.
Knowing the rated current, the type of cable and wiring, you can proceed to the calculation of the cross section of the wires. Two parameters are taken into account: the permissible continuous current load and the voltage loss in the wires connecting the consumer to the current source. The longer the wire, the greater the loss in throughput it incurs (then the cross-sectional diameter of the current-carrying core is increased).
For individual rooms or appliances that do not require high power, the second indicator can be ignored (voltage losses will be too small).
Automaton calculation parameters
Each circuit breaker primarily protects the wiring connected after it. The main calculations of these devices are carried out according to the rated load current. Power calculations are carried out when the entire length of the wire is designed for the load, in accordance with the rated current.
The final choice of rated current for the machine depends on the wire section. Only then can the load be calculated. The maximum current allowed for a wire with a certain cross section must be greater than the rated current indicated on the machine. Thus, when choosing a protective device, the minimum wire cross-section present in the electrical network is used.
When consumers have a question about which machine to put on 15 kW, the table also takes into account a three-phase electrical network. There is a method for such calculations. In these cases, the rated power of a three-phase machine is determined as the sum of the powers of all electrical appliances planned to be connected through a circuit breaker.
For example, if the load of each of the three phases is 5 kW, then the value of the operating current is determined by multiplying the sum of the powers of all phases by a factor of 1.52. Thus, it turns out 5x3x1.52 \u003d 22.8 amperes. The rated current of the machine must exceed the operating current. In this regard, a protective device with a rating of 25 A will be most suitable. The most common ratings of machines are 6, 10, 16, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63, 80 and 100 amperes. At the same time, the compliance of the cable cores with the declared loads is specified.
This technique can be used only in cases where the load is the same for all three phases. If one of the phases consumes more power than all the others, then the rating of the circuit breaker is calculated from the power of this particular phase. In this case, only the maximum power value is used, multiplied by a factor of 4.55. These calculations allow you to choose the machine not only according to the table, but also according to the most accurate data obtained.
When designing the electrical network of a new house, in order to connect new powerful devices, in the process of upgrading the electrical panel, it is necessary to choose a circuit breaker for reliable electrical safety.
Some users are careless about this task, and may not hesitate to connect any existing machine, if only it works, or when choosing, they are guided by the following criteria: cheaper, so that it doesn’t hit too hard, or more powerful, so that it doesn’t knock out once again.
Very often, such negligence and ignorance of the elementary rules for choosing the rating of a safety device leads to fatal consequences. This article will introduce the main criteria for protecting electrical wiring from overload and short circuit, in order to be able to choose the right circuit breaker according to the power consumption of electricity.
Expert answers
vasily zelenkov:
And what is the tension? it depends on it, for example, a 2000W kettle with which cord is powered and the starter at ZAZ 0.78kw, and there will be wires THICKER.
Evgeniy:
220 - 10 squares is enough, 380 - 4 should be enough (per core)
Seryoga Sribny:
10mm2 copper, open wiring 220v. If closed 16mm2.
Vitaly Petrov:
If the three-phase motor is 380V, four-core copper cable is 6mm square (each core).
Alexander Zatsarinny:
What kind of load: single-phase or three-phase? What cable cores: aluminum or copper? How will the cable be laid: along structures, in the ground, in a pipe or how?
marina jivaga:
Alexandr Yyh:
Every electrician ironically "knows" that 1 Current follows the path of least resistance. 2 Ground resistance must be 4 ohms. 3 The wire holds 10 amps per square. —
The misconception about "amps per square" stems from the fact that most electricians are only familiar with apartment wiring where the cross section ranges from 2.5 mm2 to 6 mm2 and the use of "amperes per square" in this case does not give gross errors.
But if we use tables from the PUE to determine, we see
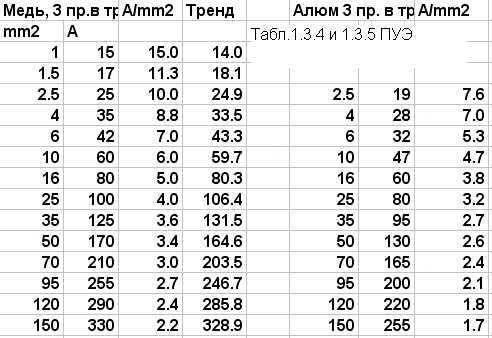 |
that the long-term permissible current of the wire in terms of "amperes per square" changes for copper from 15 A / mm2 for a section of 1 mm2, to less than 2 A / mm2 for large sections, and for aluminum from 8 A / mm2 to less than 2 A / mm2. Considering the high price of large-section cables, it is better to use not dubious “amps per square”, but PUE tables to select a cable.
In this case, if there are no additional conditions, Table 1.3.5 is suitable. Permissible continuous current for wires with rubber and PVC insulation with aluminum conductors
The cosine phi of the consumer is not specified in the conditions. If we assume that the cosine phi is equal to one, that is, there are almost no motors, almost all the power goes to heating, then
120 kW/(3*0.22 kV)= 180 amps A 120 mm2 three-core aluminum cable holds 190 amps, that's it. A drop at 200 meters somewhere around 5 ... 6 volts does not create a problem. When choosing a cable, do not forget about the zero core.
If there are many motors, then the cosine phi can be somewhere around 0.4 ... 0.5. In this case, the current will be two or more times more and it will not work with one cable. You can put a reactive compensator directly on the consumer's tires, but then if it fails, the consumer will not be able to work.
If this is not a course book, but a real installation, then you must not forget to regularly check the heating of the contacts throughout the circuit and, in case of strong heating, not only crimp, but also clean off the oxide from aluminum at the point of contact.
bruho:
In general, they dance not from power, but from current. If on one phase 220, then about 5 amps per kilowatt. So this is about 120 kilowatts 600 amps ... for copper it turns out 40 square .. but this is all about ..
Rashid Gabbasov:
It is necessary to consider by current and not by power. Suddenly you have 600 volts 3 phases and not 380. Or maybe there is a step-down trans and you supply 6kv.
navigator:
Usually for ALUMINUM cables…. accept current density up to 15 A \ sq. mm…. in the case of a 3-phase current, it is reduced by sq. root of 3….t. e. will be less than 10 A \ sq. mm ... as they say here - 5 A per 1 KW .... t. that is, approximately - roughly 600 A ... and dividing by 10, we get that we need a section of 70 square meters closest to GOST. mm