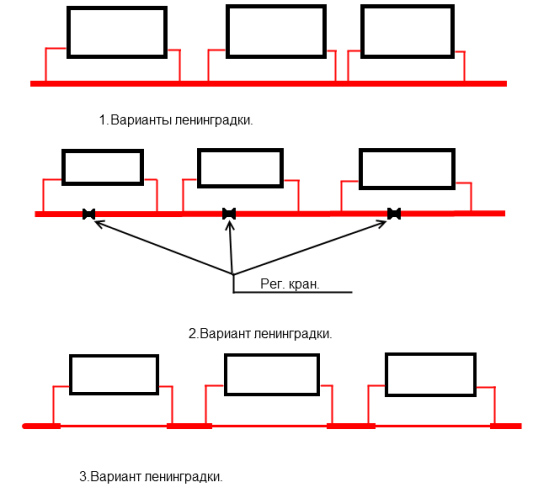
Characteristics of Leningradka
When choosing an installation, you should pay attention to the fact that it differs in the way the coolant circulates:
- Water moves forcibly. Leningradka with a pump increases circulation, but at the same time consumes electricity.
- Water moves by gravity. The process is carried out due to physical laws. Cyclicity is provided by the temperature difference and under the action of gravity.
The technical characteristics of Leningradka without a pump are inferior to forced ones in terms of the speed of movement of the coolant and the speed of heating.
To improve the properties of the equipment, it is equipped with various devices:
- Ball valves - thanks to them, you can adjust the temperature level for heating the room.
- Thermostats direct the coolant to the desired zones.
- Valves are used to regulate the circulation of water.
These add-ons allow you to upgrade even a previously installed system.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of using include:
- Profitability - the cost of the elements is low, installation can be carried out independently. During operation, energy is saved.
- Availability - parts for assembly are available at any hardware store.
- The heating system of a private house in Leningradka is easily repaired in case of breakdowns.
Among the shortcomings are:
- Installation features. To equalize heat transfer, it is necessary to add several sections to each radiator located far from the boiler.
- Inability to connect to a horizontal installation of underfloor heating or heated towel rails.
- Since pipes with a large cross section are used when forming an external network, the equipment looks unaesthetic.
How to mount correctly?
Installing Leningradka is quite feasible with your own hands, for this, 1 of the methods is selected:
1. Horizontal. A prerequisite is the laying of a floor covering in the structure or on top of it, it is necessary to choose at the design stage.
The supply network is installed at a slope to ensure the free movement of water. All radiators must be located on the same level.
2. Vertical is used in case of using forced type equipment. The advantage of this method lies in the rapid heating of the coolant even when installing pipes with a small cross section. Functioning occurs due to the installation of a circulation pump. If you want to do without it, then you should purchase pipes with a large diameter and place them under a slope. The Leningradka vertical water heating system is mounted with bypasses, which allow repairing individual elements of the equipment without shutting it down. The length must not exceed 30 m.
Features of the installation of the Leningradka heating system are reduced to following the sequence of work:
- Install the boiler and connect it to a common line. The pipeline must run around the entire perimeter of the building.
- The expansion tank is a must. To connect it, a vertical pipe is cut. It should be located near the heating boiler. The tank is installed above all other elements.
- Radiators are cut into the supply network. They are supplied with bypasses and ball valves.
- Close the equipment on the heating boiler.
A video review of the Leningradka heating distribution system will help you understand the order of work and follow their sequence.
“A few years ago we moved to live outside the city. We have a single-pipe heating system installed in a two-story house similar to Leningradka. For normal circulation, I connected the equipment to the pump. There is enough pressure for heating the 2nd floor, it is not cold. All rooms are well heated.Easy to install, no expensive materials required.
Grigory Astapov, Moscow.
“When choosing heating, I studied a lot of information. According to reviews, Leningradka approached us due to the savings in materials. Radiators chose bimetallic. It works smoothly, fully copes with the heating of a two-story house, but the equipment should be cleaned periodically. After 3 years, our radiators stopped working at full capacity. It turns out that garbage was clogged on the approaches to them. After cleaning, the operation resumed.
Oleg Egorov, St. Petersburg.
“The Leningradka heating distribution system has been working with us for more than a year. Generally satisfied, easy installation and easy maintenance. I took polypropylene pipes with a diameter of 32 mm, the boiler runs on solid fuel. We use antifreeze diluted with water as a coolant. The equipment fully copes with the heating of a house of 120 m2.
Alexey Chizhov, Yekaterinburg.
Horizontal installation
This installation scheme is simple, but it has its own nuances that must be taken into account when performing work. So, the highway should be either in the floor structure, or on top of it.
It is necessary to pay special attention to the thermal insulation of the system, otherwise it will not be possible to avoid high heat transfer.
When laid in the floor, the coating will be mounted directly under the system. When using a one-pipe system, the installation order can be reworked already in the course of work.
The supply line must be mounted at an angle in order to make the necessary slope for the circulation of the liquid. In this case, the heating batteries are placed on the same level. It is still worth installing Mayevsky taps on radiators, with their help it will be possible to remove air bubbles from the system.
In which houses is it profitable to install single-pipe pumping systems
Reducing the length of heating pipes relative to two-pipe schemes is inherent in multi-storey residential buildings, industrial buildings (workshops, warehouses), characterized by lengths of heating circuits of hundreds of meters. The use of a "single pipe" in them really saves heating pipes. Widespread use in individual construction is explained by a misunderstanding of the real cost-benefit ratio of this type of heating by customers and heating practitioners.
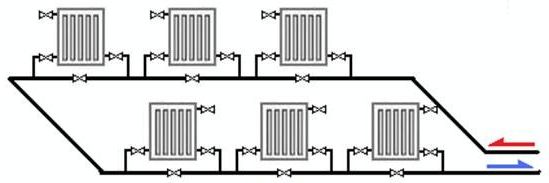
In small two-story houses with an area of \u200b\u200babout 100 sq.m (50 sq.m - first floor, 50 sq.m - second), a “single pipe” is often mounted, which works well with short circuits containing 4-5 heaters. Large houses with many radiators are not well suited for single-pipe schemes, although objects with a dozen batteries in a storey circuit do work, as in the mixed vertical-horizontal single-pipe scheme shown below.
Single-pipe system of mixed (vertically - horizontal) type.
1 Description of system features
It is rightly noted that there are a large number of technological schemes focused on solving one single issue - heating a private house.
There are single-pipe and two-pipe systems, horizontal and vertical. Single circuit and multi circuit. Each option offers its pros and cons and none is perfect.
A Leningradka-type heating system is one of the most popular solutions when it comes to arranging a heating circuit in a private house of one or two floors.
It is also suitable for multi-storey buildings, but its efficiency will drop, since it strongly depends on the length of the contour.
What is this Leningrad system? In fact, the principle of its operation and the layout of the pipes is very simple.
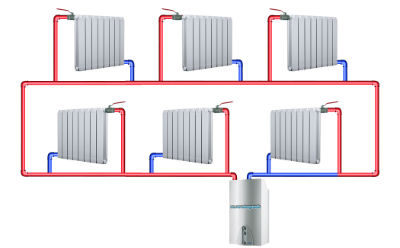
This is a single-circuit single-pipe piping layout with serial connection of radiators.
Single-circuit, means that the Leningrad is connected to only one boiler or boiler and works exclusively for space heating, operating with the circulation of a heat carrier, most often water or antifreeze.
It is also single-pipe, that is, it consists of one pipe, straight or with branches (bypasses). The one-pipe scheme assumes the movement of the carrier in a clear direction.
Serial Connection Diagram
Water or antifreeze leaves the boiler, passes through the entire chain of radiators, and then closes on the boiler or mixing unit through the same pipe. The peculiarity of the scheme is that they try to place radiators in it along the entire circuit so that the distance between the last radiator and the boiler is minimal.
The system is designed in such a way that the media cools down over time, that is, in the extreme sections, the temperature can be significantly lower. Leningradka solves this problem quite elegantly, by operating with forced circulation, temperature sensors and bypasses.
The layout of the Leningradka system also leaves you some room for maneuver. You can choose any option.
As for the specific components of the heating system, Leningradka works best with plastic or metal-plastic pipes, as well as forced circulation of the flow generated by a pump.
1.1 Pros and cons
Leningradka, like any other heating scheme, is not a universal candidate. It is suitable for some tasks and not suitable for others,
For a better understanding of priority areas, one should understand what pros and cons it carries. This is what we'll do.
- Simplicity and conciseness;
- The ability to carry out installation by hand;
- Pipe layout is selected according to your taste and desire;
- thrift;
- High efficiency at low cost;
- Almost ideal for heating a one-story or two-story house;
- The ability to isolate each node, making the heating circuit completely autonomous and independent.
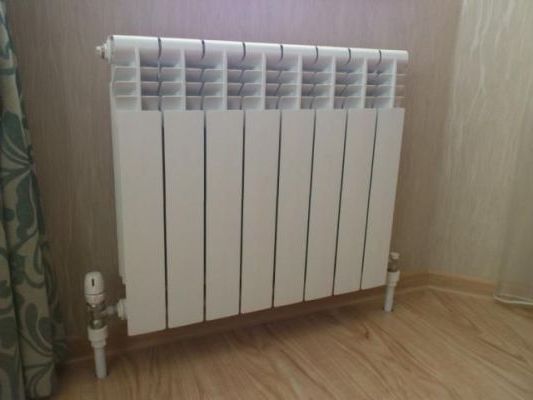
Radiator in Leningrad with inlet taps and thermostats
- The temperature of the carrier decreases in proportion to the length of the line;
- If the lower wiring is selected and the length of the pipes is more than 50 meters, then it is necessary to engage in forced circulation using a pump, otherwise there is a risk of clogging the system and stopping the movement of the carrier;
- Fully stuffed piping with bypasses, insulated radiators and temperature control valves will still cost you a pretty penny.
The disadvantages of such a system are much less, but they still exist. We also note that Leningrad does not function in the best way if it is necessary to provide heating for huge buildings with a large number of storeys. Even there it can be adapted, but the results will not be as impressive.
Nevertheless, in a medium-sized house, this scheme shows itself as well as possible, plugging most of the competitive solutions into the belt.
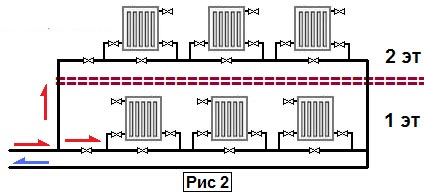
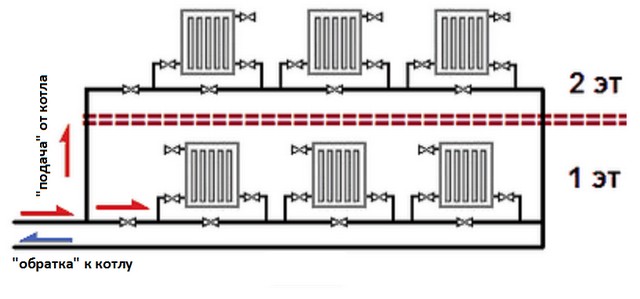
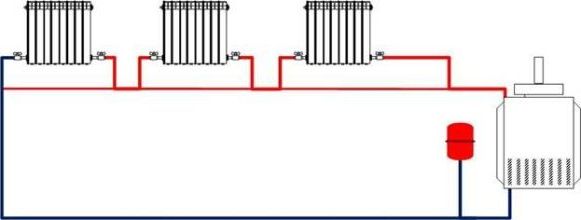
Single-pipe heating system of a two-story house with a circulation pump
Includes floor circuits with horizontal single-pipe wiring connected by vertical risers of "supply" and "return", the latter are spatially separated or combined into a two-pipe riser. The circulation pump is included in the return line ("return") in front of the heating boiler.
The simplest one-pipe heating system for a two-story house, the circuit of which contains two circuits of 3 radiators, is shown below.
Single-pipe horizontal system of a 2-storey house with a pump.
The flow rate of the coolant along the horizontal line is N times greater (N is the number of radiators connected in series) required by the two-pipe scheme. A "single-tube" having the same number of heaters with a "two-tube" is equipped with a circulation pump of greater power.
Pros and cons of this heating system
It is not in vain that Leningradka is very popular, because it has many important advantages:
- Possibility of laying the supply pipeline under the door opening;
- Low cost of arranging the system;
- A simple and inexpensive installation that you can even handle with your own hands;
- Leningradka provides for a minimum number of pipes on the surface, so communications will not spoil the interior of the room;
- The system can be connected even to two heating devices;
- If necessary, you can repair the system;
- There are separate elements on the market for the Leningradka, which will help to replace failed nodes without any problems;
- The system allows you to make a "warm floor" in the house.
With one ring at the outer walls, you will go around your entire house. With this method of installation, the supply pipe goes from the center of Leningrad, passes through the entire room and goes back.
It would be unfair not to talk about the shortcomings. This system also has them, but there are not many of them, and with proper planning and installation of minuses, you can avoid:
Radiators that go at the end of the system must have a large number of sections. Such a solution will make it possible to make a uniform heat transfer of all batteries in the house;
The scheme of a horizontal Leningradka is quite complicated, and it is almost impossible to make a warm floor and install heated towel rails in it. Therefore, if you need such elements, it is better to use a vertical scheme;
The single-pipe version of the Leningradka will work effectively only at high pressure of the heat source.
Operating principle
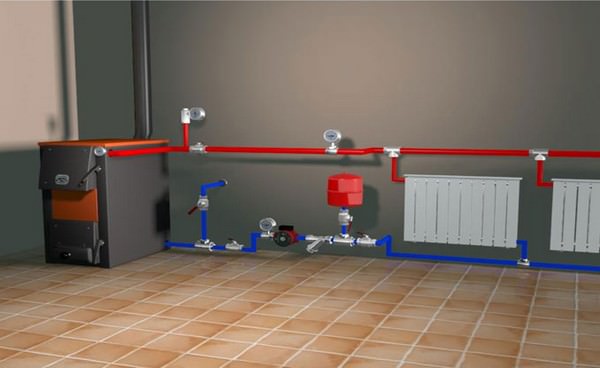
The classic Leningradka system is a set of heating devices that are connected by a single pipeline. A coolant circulates throughout the circuit, in the role of which water or antifreeze acts. With the advent of new heating equipment, the system was improved, made it manageable and expanded its functionality.
Depending on how the pipeline is located, the heating scheme is divided into two groups:
- horizontal;
- vertical.
The location of the pipes can be upper and lower. In the first case, the heat transfer efficiency is higher, but installation is more difficult. The lower installation of the system is easier to make, while it is imperative to install a pump.
The circulation of the heat carrier in the circuit can be carried out in two ways - natural and forced with the help of a pump. There are also open and closed systems.
The recommended number of heating devices when installing the Leningradka system is 5. This value can be increased to 6-7 by first performing the appropriate calculations. Installing more radiators will not be effective, and its cost will be unreasonably high.
How to equalize uneven heating of radiators
The usual way to equalize their heat transfer during unequal heating is to gradually increase the thermal power (or, equivalently, the number of sections) of radiators in the direction of the coolant in the circuit. If the power of the first heater in the circuit is taken as 100%, then the next one has 110%, and so on up to 150-200% of the power of the last one (depending on the number of consecutive radiators).
When performing a single-pipe heating system for a two-story house, the scheme of which includes a main pipe, the diameter of the latter is taken large. So, when making connections to radiators with a DN16 metal-plastic pipe, for eight to nine heaters in a storey circuit, you should take a "trunk" with DN40. The Du32 pipe will work, but the stability of the system will decrease. This means that any change in the coolant temperature will lead to its imbalance, i.e. a noticeable change in the difference in heating temperatures of neighboring radiators in the circuit.
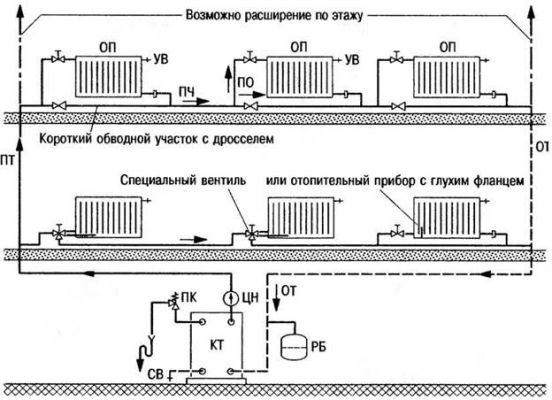
Schemes of "single tubes" with so-called radiator piping are common. "bypasses", as shown in the photo below.
Connecting a radiator in the "Leningrad" scheme with a bypass.
These are sections of smaller diameter included in line breaks under radiators, sometimes with an installed flow control device (needle valve, etc.). Control valves are also installed in one (or both!) Inlets to the radiators.It turns out that instead of a continuous line of the same diameter, there is a pipe of variable diameter. At the same time, practical installers mistakenly believe that in order to branch the coolant flow into two components in the tee of the supply to the radiator, it is necessary to narrow the main passage for it. This is not true, since a pressurized fluid will fill any free volume it encounters in its flow path.
Of course, if in such a scheme with many flow control devices you constantly engage in manual control of the heating of each device, then you can, spending a lot of time, constantly achieve their uniform heating. But is the game worth the candle? If you make a “single-pipe”, then radiators should be connected to a line of a constant large diameter, ensuring their stable operation with a slight decrease in the heating of devices along the circuit.
Conclusion
If radiators in a single-pipe scheme are connected to a main pipe with a diameter at least twice the diameter of the connections to them (with the appropriate size of the fittings), then at the cost of such material costs, it is possible to reduce the temperature in the chain to 8-10 devices. In a two-pipe scheme, the same result is achieved with a small diameter of all heating pipes.
How to implement alternative heating of a private house
Two-pipe heating system of a private house - classification, varieties and practical design skills
One-pipe and two-pipe heating distribution in a private house
Selection of pipes by diameter
How to choose the materials that make up the Leningrad heating system
Pipe diameters are one of the main characteristics that it is important to choose correctly. In general, the diameter used depends on many factors, including the area of \u200b\u200bthe house, the rate of cooling of the coolant, heat loss, circulation rate, etc.
All this is quite difficult to calculate, so it is better to determine which pipes are needed according to the nominal pressure. So, if 10 atmospheres are enough for the system to work, then pipes of 25 millimeters can be used. When the pressure is at the level of 20-25 atmospheres, it is better to install pipes at 32 millimeters.
Automatic regulation of heating system parameters


- How to pour water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular Russian-made outdoor gas boiler
- How to correctly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes in case of malfunction
Recommended reading
What batteries are better to choose for heating a private house? Heating project for a two-story house: choosing a scheme and connection method What does the heating scheme of a one-story house with forced circulation look like? Greenhouse heating - types of systems and sources of heating
2016–2017 — Leading heating portal.All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement entails legal liability. Contacts
Schemes and principle of operation
The Leningrad heating system of a private house provides for the sequential installation and connection of heating devices. The coolant in the form of ordinary water or non-freezing liquid moves through all the batteries, and along this path its temperature drops. As a result, inside the batteries farthest from the boiler, the water will not be so hot. As already mentioned, this problem is solved by increasing the number of sections.
For heating a small house on 1-2 floors, a single-pipe system is perfect. If the scheme provides for laying pipes under the floor level, then care should be taken to isolate them; roll materials are used for this. If this is not done, there will be large heat losses.
The scheme of operation of a single-pipe system for a two-story building is quite simple, the coolant enters the batteries and begins to move to the upper point. When the liquid cools, it will begin to descend to the bottom. At the same time, the processes of heating and cooling take place simultaneously, so the Leningrad plant works without interruptions.
121LO
5-, 10- and 9-storey houses of the 121LO series are being built to the present. The ceilings here reach 280 cm. There are balconies even on the first floor.

Panel five-story building 121 series
The floor plans are comfortable. Few change them. Yes, this is practically and impossible, since the interior walls here are load-bearing.

Typical section layout
The maximum that can be done is to use the balcony as a living space. Usually they arrange a recreation area there or put a desktop with a computer.
Several design options for such balconies:
All series have a problem with poor sound insulation. But in new houses, the issue is partly resolved by sealing the internal joints of the panels with silicone.
In any case, when buying an apartment in a building with a Leningrad layout, you will have to think about soundproofing the walls, ceiling and floor.
adblock detector
Advantages and disadvantages
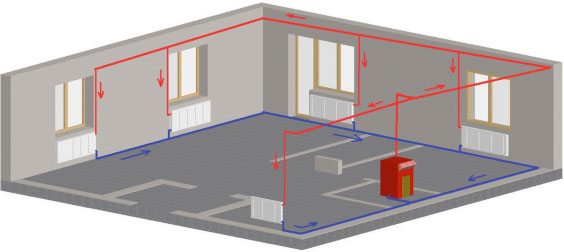
The heating system "Leningradka" has its positive and negative sides. The pluses include:
Ease of wiring and installation. Significantly reduced the amount of installation work. You can install without resorting to the help of specialists.
High efficiency.
Profitability. Pipe consumption is 30% lower than other heating systems. In addition, you do not need to purchase expensive equipment.
The introduction of adjusting elements (bypasses, ball valves) made it possible to improve the circuit and adjust the temperature regime in different rooms.
Adding new elements makes it easier to repair and replace without turning off the entire heating system in the house.
Versatility. The system can be used in one- and two-story houses. The difference in schemes will be small.
Reliability. The heating system will function without failure.
At the lower location in a building with one floor, you can hide the pipes in the thickness of the floor
At the same time, it is important to observe the measures of thermal insulation and tightness of the joints.
"Leningradka" has proven itself well in one-story buildings with a small area.
The main disadvantages include the complexity of the calculations. The number of sections, pipe diameters depend on many parameters, including the individual characteristics of the house, so there may be problems with the correct determination of parameters. Difficulties also arise when balancing the system. This may require additional equipment and repairs. The system cannot be carried out in large apartment buildings due to its inefficiency.
Series 1LG
The houses of this series are panel.
1LG 502
Brezhnevka 1LG 502 was built from 1963 to 1972. These are five-story buildings with two or more entrances and a ceiling height of 250 cm.
Balconies and loggias are not in all apartments. Houses without a garbage chute with four apartments per floor.

Most apartments in the 502 series do not have balconies.
House structure:
- Exterior walls made of expanded clay concrete panels 303 mm thick in three layers with ceramic mosaic cladding. Internal - single-layer 140 mm.
- Overlappings are continuous, 120 mm thick. The covering of the last floor is ribbed.
- Flights of stairs on the central stringer.
- Bathrooms from a solid reinforced concrete cabin, separate, spacious.

Layout of the section of the house 1LG 502
1LG 504D-MK
In 1975, the 502 series from Lenproekt was replaced by another standard version of panel apartment buildings - 1LG-504D-MK. They were built before 1989. These were two to eight access 12-story buildings. Some have two uninhabited floors downstairs.

12-storey building 504 series
All apartments, starting from the 2nd floor, have balconies. The height of the premises has increased to 270 cm.
Standard layout of the section and apartments:
1LG 600
Houses of the six hundredth series were built in the Leningrad, Tyumen, Pskov and Chelyabinsk regions for 22 years from 67 to 89. Curvilinear brick inserts appeared in them, designed to dampen gusts of wind in coastal areas. Because of this, they are called "ships".

House 600 series
Houses of the Leningrad layout are the most popular in the secondary housing market.
They were built in old neighborhoods with good infrastructure. They have an elevator and a garbage chute.
Disadvantages - poor sound insulation and small six-meter kitchens in the first houses. Later, this omission was corrected and the area of the kitchens was increased.
In the northern regions, many hotel-type houses of the 1LG-600A / UR-25 modification were built for small-family hostels. These are 108-apartment nine-story buildings that have little in common with the main series.

Houses with three sections connected perpendicularly are called "trefoils"
In addition to them, there were several modifications:
- 9-storey for 54, 180, 252, 322 apartments;
- 12-storey apartments with 54 and 72 apartments;
- 15-storey buildings with 90 apartments.
Section plan and most common layouts:
1LG-602
The standard project went into series in 1966. Five- and nine-story houses for 216, 252, 288 and 324 apartments without a technical floor were built until 1982. Entrances - 6-9. Loggias appeared at the ends. The windows became three-framed.

Five-story building of the 602 series
In the 72nd, turning and corner sections appeared in the houses of this series. In the 75th, experiments were carried out with the front facing of wall panels. The shape of the canopies above the entrance to the entrance, the design of the ventilation ducts, and the layout of the bathrooms have changed.

Typical floor plan
The soundproofing of the apartments has become better than in the houses of the previous series. The disadvantage is the impossibility of redevelopment of apartments.
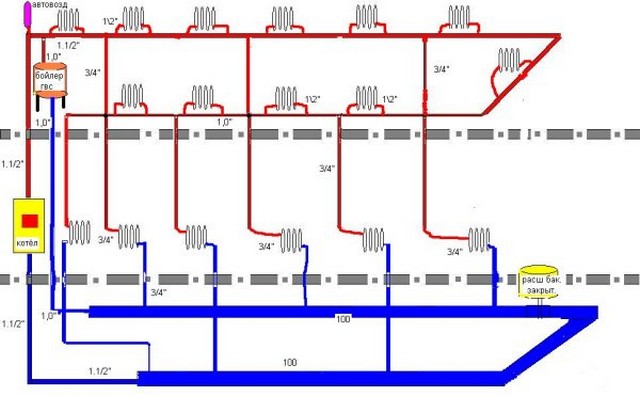
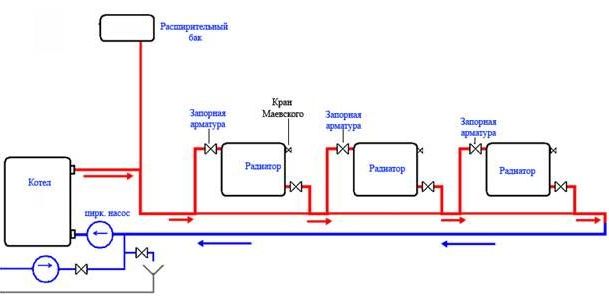
Heating Leningradka open wiring diagram
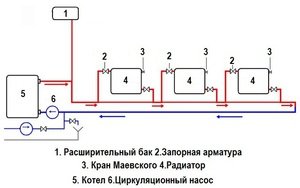
Due to the heating of water in the heating system, according to the laws of physics, it expands in volume. Therefore, to remove its excess in the circuit, an expansion tank is installed. At the same time, in an open heating system, such a structural element is connected to the air in the room through a special pipe. After the coolant cools down, it enters the system again from the expansion tank.
Very often, to increase the efficiency of heating, a single-pipe system is equipped with a circulation pump. which is installed in front of the boiler on the return pipe.Thanks to this addition, the heating rate of a private house, both one-story and two-story, increases significantly, since the coolant begins to circulate according to the forced principle.
To facilitate filling the heating system with water, a cold water supply pipeline is connected at the place where the return pipe passes through the locking mechanism and the cleaning filter. Also, at the lowest point of the system, a drain pipe with a tap at the end is mounted. Such a device allows, if necessary, to drain the entire coolant from the system.
In private housing construction, standard radiators with a lower connection diagram are usually used. In addition, each battery for removing air congestion is equipped with a Mayevsky crane. In addition, in private houses for "Leningrad" they often use a serial diagonal method of connecting batteries.
But, despite the popularity of such heating wiring diagrams, they have a common significant drawback - they do not provide for adjusting the heat transfer level of each individual battery. To solve this problem, there is a radically different way to connect radiators.
To improve the operation of the heating system by adjusting the heat of each radiator, parallel connection of all batteries to the riser is used. At the same time, each heating device is equipped with shut-off valves at the inlet and outlet pipes. Also, in a section of the riser parallel to the battery, which in such a situation acts as a bypass, a needle valve is mounted to adjust the intensity of the water flow through the heating battery. This was achieved thanks to the laws of physics, because when the locking mechanism is fully opened, the coolant will not flow up the battery, overcoming gravity. This leads to the fact that with an increase in the degree of opening of the valve, the temperature in the battery decreases.
Principal features of the functioning of Leningradka

Since in the provided scheme it is possible to lay the pipeline below the level of the floor surface, it is necessary to worry about high-quality thermal insulation. If this issue is neglected, then the efficiency of the Leningrad heating system will drop significantly and, in addition, the structural elements of the floor will overheat greatly, since the temperature of the coolant in the pipe is quite high.
Mounting Features
 For concealed installation, thermal insulation of the walls is required
For concealed installation, thermal insulation of the walls is required
The arrangement of the Leningradka single-pipe system requires care in calculations and execution. For its implementation, it is necessary to pre-calculate the dimensions of the pipes, the number of sections in the radiator, prepare the premises and do a number of other works.
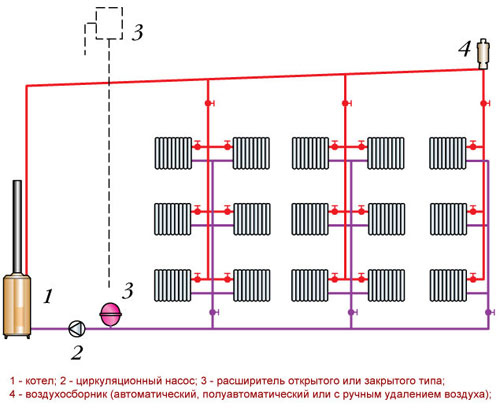
The system consists of the following mandatory elements:
- boiler;
- pipeline;
- sections of heating batteries;
- expansion barrel;
- tees.
If the Leningradka heating system with forced circulation is organized, another pump will be required. To improve the capabilities, ball valves (2 pieces per battery) and bypasses with a needle valve are used.
The main line can be mounted in the plane of the wall or on its surface
When inside walls, floors or ceilings, it is important to make high-quality thermal insulation. Otherwise, heat losses will increase and the temperature in the radiators will be lower.
This is due to microcracks that are formed in the process of wall chasing.
The place of installation of the expansion tank and boiler is selected in advance. The tank should be placed above the level of radiators - for example, in the attic. The boiler is usually mounted in the basement.
Material selection
 Pipes are selected taking into account the length of the line, the temperature of the coolant, the method of installation
Pipes are selected taking into account the length of the line, the temperature of the coolant, the method of installation
The amount of heat in the radiator depends on the material of the pipes. Polypropylene or metal products are usually used.
Heating in a private house from polypropylene pipes "Leningradka" is easy to do with your own hands
It is important to consider that such pipes are not suitable for installation in houses located in the northern regions. It has to do with the properties of the material.
Polypropylene melts when it reaches +95°C, which increases the risk of pipe rupture at maximum heat transfer of the system.
Metal products are more difficult to assemble, since components are required to be welded, but their quality and reliability are at a high level. They are able to withstand high temperatures. Differ in durability.
The diameter of the pipe depends on the number of heaters. If 4-5 radiators are installed in the house, pipes with a diameter of 25 mm and a bypass of 20 mm are needed. With the number of batteries equal to 6-8, a 32 mm line and a 25 mm bypass are selected. In the case of a gravity system, pipes with a diameter of 40 mm or more are purchased. The size also depends on the number of batteries in the circuit.
Connecting elements and pipes to each other
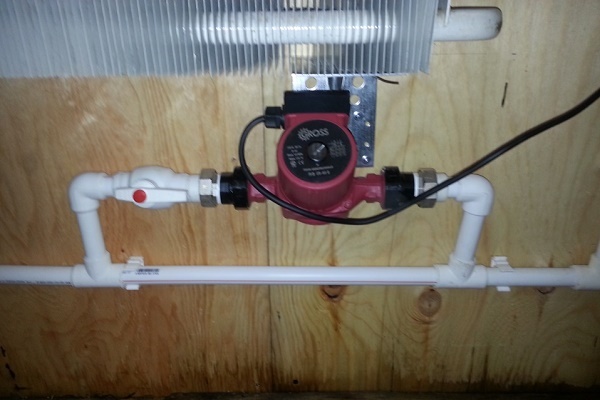

Bypasses are built into the assembled line. They are manufactured separately with taps, the distance between which is calculated with an error of 2 mm. It is allowed to have a backlash for trimming 1-2 mm. If this distance is increased, the system may leak. To determine the exact dimensions in the radiator, angle valves are turned out, the distance between the centers of the couplings is measured.
Tees must be welded or attached to the branches. One hole must be allocated for bypasses. The second is selected according to the distance between the central axes of the taps.
Welding parts
Metal pipes are connected by welding. To do this, the master must have special equipment and skills to work with it. Otherwise, the installation should be entrusted to professionals.
When welding, it is important to ensure that no internal influx is formed. This will reduce the amount of coolant that enters the radiator.
With the formation of sagging, the work should be redone.
After welding of all parts, the radiators are placed on the wall with the help of angle valves and couplings. Bypasses with taps are placed in the strobes. Their length is measured, the excess is cut off.
Final works
Before starting the heating system, it is necessary to remove excess air. To do this, open Mayevsky taps
It is important to visually inspect all connections
After that, the assembled circuit is tested and balancing is performed. The temperature should be equalized in all radiators using a needle valve.