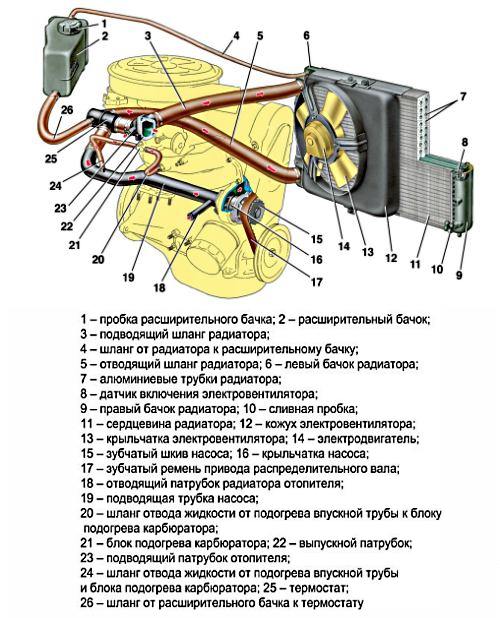
what to do if the heating boiler boils
Boiler boiling
2. At some point, the nearby circuits also stop heating, and all the batteries become cold, and the boiler boils.
The heating system is boiling. Why? Conclusion
3. Then I achieve the desired result in different ways: I feverishly twist the central plug in the pump, releasing steam and coolant, turn the pump on and off, the last time it all lasted more than 2 hours, the process is generally uncontrollable. It seems that the pump works for itself and does not pump anything, I do everything at random.
4. Then at some point, everything suddenly breaks through, the batteries ALL instantly become hot, and the temperature in the boiler drops to 60 degrees. Further, everything can remain and work well for several hours, or again after 2-3 hours the batteries can cool down and the temperature in the boiler rises.
Heating scheme
Unfortunately, you did not indicate whether this was the first launch after installation, or whether the heating system worked successfully before. We will assume that the design and installation were carried out correctly, the capacity of the compensation tank and the sections of pipelines were chosen correctly. The floor-by-floor wiring diagram you sent is simple and should ensure satisfactory circulation of the coolant. By the way, connecting a radiator on a ladder to a vertical line is irrational, the right decision would be to connect after the riser.
There may be several reasons for the fact that the temperature of the coolant periodically rises to a critical level, and the radiators remain cold:
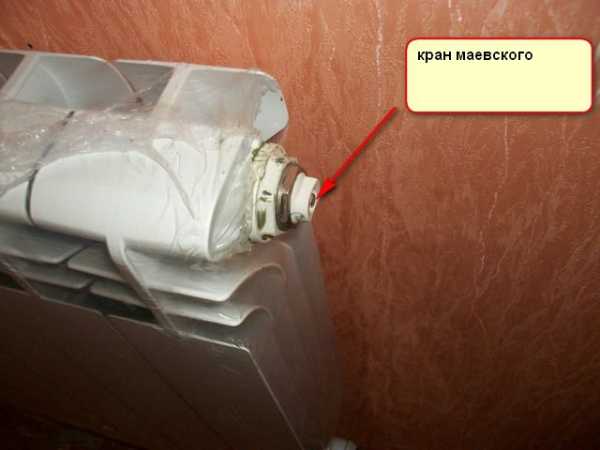
Most often, such problems are created by a “plug”, air or mud. Air is especially actively released in the first month after filling the system; it is recommended to bleed it daily. The air blower (Maevsky crane) should be installed on each heating device. Automatic air vents are mounted at the top of the heating mains, in the boiler room, on the boiler itself, on the collectors (you, judging by the diagram, do not have them). Airing the system is the most common cause of unstable heating operation. We recommend that you start the test with a thorough deflation, first at the top, moving down. If the air has to be bled frequently, and the pressure in the system drops, the tightness is broken somewhere.
An air blower should be installed on each heating radiator
A mud “plug” can also interfere with the free flow of the coolant. The first step is to check the filter, if any. Also, air vents, especially needle-shaped ones (Maevsky taps), can also clog dirt and sludge.
Such a device combines the functions of an automatic air blower and a mud filter. Easy to maintain, ensures cleanliness and normal gas composition of the coolant
The reasons for the unstable operation of the heating may also lie in your circulation pump. Although, more often it fails immediately and permanently. Whether the pump is working can be checked by placing a hand on the body. A slight vibration should be felt. To begin with, we recommend checking and cleaning the electrical contacts. The reason may lie in the wear of parts of the electric motor or in the formation of lime deposits if untreated tap water is used as a coolant.
Why does a gas boiler boil
During normal operation of the equipment, the coolant in the circuit is heated to a predetermined temperature. After that, naturally or forcibly due to the pump, it is carried through the heating system. This is how the radiators in the room warm up. Then the liquid moves along the return circuit and returns to the boiler.
In case of overheating of the coolant, thermal sensors are triggered. As a result, the operation of the device is blocked.What to do if the boiler boils? To restore the heating, it is necessary to find the cause of the breakdown. Sometimes the self-diagnosis system displays an error code
:
- E01 for " ";
- E02 for ;
- A03 for "";
- 01 for ;
- F20 for "";
- 16 for etc.
But if this did not happen, you can identify the problem by external signs.
What causes overheating:
- Clogged filters;
- accumulation of air;
- Blockage of the heat exchanger with scale;
- Problems with the circulation pump;
- Failure to comply with the regulations for the room where the equipment is installed.
When the boiler is turned on, water boils. what to do
Water in the heating boiler may boil due to the fact that the rate of its heating in the boiler exceeds the rate of heat transfer in the heating system of the house. This can happen for several reasons:
insufficient circulation rate of the coolant or its absence;
insufficient amount of coolant (water) in the system - most often happens in open systems with an expansion tank;
exceeding the power of the heating boiler compared to the total power (heat output) of the radiators for heating the house, taking into account losses - in the absence of a boiler draft (power) control system;
improper installation of the heating system.
If the circulation rate of the coolant is insufficient, the heated water does not have time to transfer the heat received in the boiler to the system and can heat up in the boiler to the boiling point. This can occur in heating systems with natural circulation of the coolant if the correct pipe installation slopes are not observed, or less often if their diameter is insufficient. With a forced circulation system, this can happen if the circulation pump is not selected correctly, is defective, does not work, or there is no electric current supplied to it.
Also, the water in the boiler may boil if for some reason there is not enough water in the system and air has entered it. If the heating system is with natural circulation and with a conventional expansion tank, this sometimes happens and in this case you just need to add water. Depending on the design of the heating system, sometimes it is required to bleed air from the system or some part of it (in the absence of an automatic valve).
To increase the circulation of water in the heating system, it is necessary to redo the heating system or, best of all, install a circulation pump. Even if the pipe slopes are not quite correct or in their absence, the circulation pump will provide the necessary circulation.
Water in the heating system can also boil if the installed boiler is much more powerful than the heat transfer capacity of the entire system, especially if there is no or malfunction of the automatic control (draft) air supply system. In this case, it is necessary to install a semi- or automatic draft control system, replace the boiler (if it is self-made without a draft control system) or increase the number or power of radiators. Also, as an option, you can install an indirect water heater (boiler) in the system, which will take part of the heat from the system to heat water and serve as a kind of heat accumulator.
OBI sells a special liquid (similar to ANTIFREEZE for a car) specifically for the heating system in private homes - I myself recently saw it in OBI at Belaya Dacha
Good day. urgently need to call the masters to repair the heating system. We had the same problem last year. we ourselves could not solve it, called these masters http://toutletoutim.fr/
A simple look at the problem.
The expansion tank plays an important role in the cooling system. Its main function is to dampen pressure fluctuations in pipelines resulting from an increase (decrease) in the volume of antifreeze during heating (cooling). Due to the presence of such a container, mechanical loads on the elements of the system are reduced, water hammer and the appearance of air pockets are prevented.
In fact, the tank makes up for the lack of fluid in the lines during cooling and serves to receive excess when heated. Structurally, it is made in the form of a plastic sealed container.
A mandatory design detail is a safety valve for releasing excess pressure into the atmosphere.
When antifreeze is heated, it expands, filling the free space of the tank, and the intensity of evaporation increases. This leads to an increase in pressure in the volume. An increase in pressure above the threshold value triggers the built-in valve.
The only situation when antifreeze is thrown out of the expansion tank is that the valve does not cope with the performance of its assigned functions.
Principle of operation
Schematically, the OS heating circuit can be represented as a long vertical ring. One side of the ring
- with hot water (supply riser from the boiler to the RB), other side
- with cold (riser with return from radiators). The density of a hot coolant is less than a cold one - water expands when heated.
Therefore, the weight of water and the pressure of the water column in the cold part of the circuit will be higher than the weight of the water and the pressure of the column in the hot branch.
According to the law of communicating vessels, the fluid will tend to balance the pressures - transition from a cold branch to a hot one.
Since the circuit is such a closed ring, circulation or gravity flow of the coolant occurs.
- The feed riser is maximally insulated over the entire height.
- The boiler is located as low as possible on the last radiator.
-
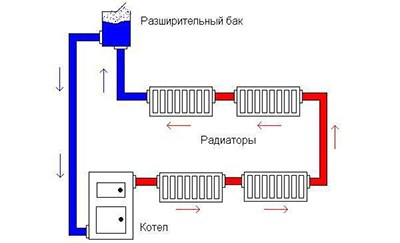
The circuit has a tank for the output of excess volume of heated coolant
- expansion tank (to ensure low density and low pressure of the water column in the heated branch).
With natural circulation
The coolant moves during natural circulation under the action of circulation pressure Pн
(in mm water column):
Pn \u003d H x (pcold - pgor).
-
H
- height difference between the boiler and the last radiator, m; -
phol
is the density of water in the cold return pipe, kg/m³
; -
pgor
is the density of the water in the hot supply riser, kg/m³
.
During circulation along the circuit, the coolant spends part of the pressure to overcome the hydraulic resistance of pipes, radiators, and valves. Therefore, when designing the OS, choose materials with low hydraulic resistance
so that in total they do not exceed the calculated pressure Pn
(do not lock the system).
Important!
There is air in the OS coolant, which is mixed in the expansion tank. To remove air, pipes are made with a slope of at least 3-5 mm per
m. pipes.
With pump circulation
To increase the natural head, a circulation pump is included in the OS circuit.
Exists two pump taps
to an existing OS:
-
On the return pipe in front of the boiler.
At the same time, the expansion tank is reconnected to the return pipe in front of the pump (in the suction zone). -
On the top feed pipe
immediately after the connection point of the expansion tank.
Reference!
The tie-in place of the pump is equipped bypass
with flap check valve.
Single pipe
One-pipe system with natural circulation is done only with the upper distribution of the coolant.
All radiators in the riser of a single-pipe OS are connected in series - The output of one battery is connected to the input of the other.
- Few pipes.
- Ease of installation.
-
System imbalance
- the upper batteries are hot, the lower ones are cold. To equalize the temperature regime, the lower radiators are installed with a large number of sections. -
Impossibility of thermoregulation
due to the high resistance of the control valves.
You will also be interested in:
Two-pipe
The two-pipe system is characterized by the fact that each radiator is suitable two pipes
: one delivers hot coolant from the supply riser, the other discharges chilled water to the return riser.
- Temperature balancing of all batteries.
- The radiator can be replaced without shutting down the boiler.
- Increased pipe consumption.
- The complexity of installation.
Top feed
Hot water is supplied from the boiler up the vertical riser to the attic
or under the roof, from where it is bred along the sunbeds to the vertical radiator branches (both single-pipe and double-pipe). After passing through the radiators, the cooled coolant is collected in the return line and enters the boiler.
Bottom feed
At the bottom supply, the heated coolant enters into the radiator branches from the bottom up.
The supply and return pipelines are laid next to each other at floor level.
Attention!
Such a system does not clutter up the room with an abundance of pipes, but requires the installation of Mayevsky cranes
for each air outlet radiator. Advantages:
Advantages:
- Ease of installation.
- Durability.
- Circulation does not require electricity.
-
Self-regulating system
- the speed of the coolant depends on the temperature in the rooms.
Flaws:
-
Not suitable for all spaces
- you need an attic where an expansion tank is placed and horizontal pipes are laid. -
Requires the lowest possible location of the boiler
- in a pit or basement. - Slow heating at startup.
-
Unpresentable appearance
(iron pipes of large diameter, cast-iron radiators). - Short range - no more than 30 meters from the boiler.
-
Inability to use antifreeze
due to the poisonous vapors.
Expansion tank
Located in the attic. Since the attic is usually an unheated room, the tank must be insulated, otherwise the water in it may freeze in winter. The tank compensates for temperature fluctuations in the water level. In addition, sometimes water can boil in the system (it happens if you start heating the boiler too quickly), and the bubbles significantly increase the volume. For this, the excess volume in the expansion tank serves.
It is desirable to provide for the possibility of draining excess water from the tank when overfilled. To do this, water can be brought either to the sewer, or simply to the street.
It should be borne in mind that water from an open system evaporates. Therefore, it is necessary to replenish the system with water. You can do this manually, periodically climbing into the attic and adding water, or you can make an expansion tank in the likeness of a toilet bowl - with automatic topping up of water.
But this is rarely done. Usually just use the container.
It is better to close the top of the tank with a lid so that water evaporates less.
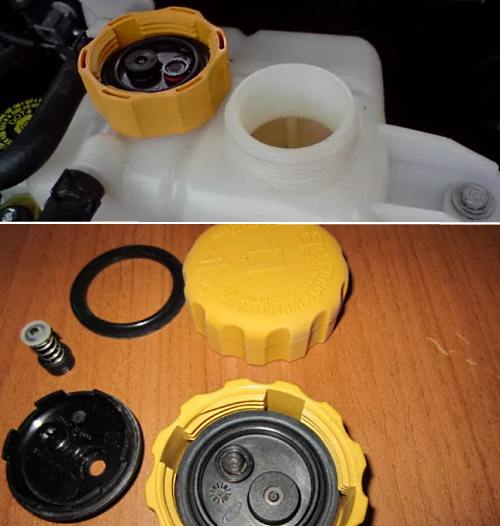
Expansion tank device
Structurally, this container is very simple. The material of manufacture is translucent plastic. Also, a sensor can be additionally built into the tank, which signals the driver about a critical decrease in the coolant level.
On top of the tank is closed with a lid, in which a valve is installed to regulate the pressure. If the pressure in the system rises, then the valve is activated.
Also on the wall of the tank there is a level indicator in the form of "minimum" and "maximum" marks, allowing you to control the liquid level.
It is important to understand that on a cold engine, the level should not fall below the minimum. It is also not allowed to exceed the maximum level
As for the tank lid with a valve, it hermetically closes the container on a cold ICE. However, when the engine reaches operating temperature and the coolant heats up, the pressure naturally rises in the cooling system and in the tank.
If the pressure rise reaches an average of 120 kPa, the valve opens. When the pressure drops to an average of about 83.4 kPa, the valve closes. Such valve operation is necessary in order to avoid rupture of pipes, damage to the radiator, etc.
In parallel with this, after the engine cools down, the pressure in the system begins to fall, the coolant volume decreases and a vacuum is created.When the pressure drops, on average, below the mark of 3 kPa, the inlet valve of the expansion tank opens to take in air. As a result, the pressure difference is leveled, and the missing volume of liquid is compensated from the tank.
Why are not all batteries in gas heating. What to do if the batteries get cold and the heating boiler boils
A change in the temperature regime of heating operation can be caused by a number of internal reasons. Many of them negatively affect the efficiency of the system, increasing energy costs. In such cases, a reasonable question arises - why does the heating not heat up: radiators, batteries, pumps, systems? The first step is to find the cause of the problem.
General heating problems
The principle of operation of any heating system is the efficient transfer of thermal energy from an energy carrier (gas, solid fuel, diesel, etc.) to water in pipes. The task of heating devices (radiators, batteries, pipes) is to transfer the received heat to the room.
And if the heating battery does not heat up, the reasons for this may lie both in the design itself and in the parameters of the system as a whole. Consider the common reasons for the decrease in the efficiency of the heating system:
- Low efficiency of the boiler heat exchanger. Water is not heated to the desired temperature;
- A specific heating battery does not heat well. Possible reasons - incorrect installation, the formation of air pockets;
- Changing the technical characteristics of the system - an increase in hydrodynamic resistance in certain sections of the pipeline, a decrease in the passage diameter of pipes, etc. Most often, the consequence of such phenomena is that the heating circulation pump is very hot.
In some cases, not one, but several of the listed problems occur. Often the main cause is the root cause of the appearance of the following. Thus, the formation of an air lock affects the increase in hydrodynamic resistance, and as a result, there is an increased load on the circulation pump.
The radiator does not heat up
Most often, problems with normal heat transfer occur in heating radiators. This is due to their specific design - the coolant does not move through one pipe, as in the transport line, but is distributed over several.
In what cases does the heating radiator not heat up? There are several factors that directly affect the correct operation of the battery.
Air pockets in heating
There are several reasons for the appearance - exceeding the temperature regime, evaporation of water, etc.
It is important that the consequence of this is the appearance of places in the line that are not filled with coolant. Most often these are radiators.
To eliminate them, it is necessary to install a Mayevsky crane - an air valve that releases excess air from the device.
How to determine why the heating radiator does not heat well? The simplest method is the temperature difference on the surface. In the place of formation of an air lock, it will be much lower, thereby preventing the normal passage of the coolant. To fix it, follow these steps:
- With the help of a screwdriver or a rotary lever, the Mayevsky tap is opened;
- Add water to the system until the coolant begins to flow out of the tap together with air;
- Shut off the water supply.
After the surface of the radiator should heat evenly. Otherwise, repeat the procedure.
Heating appliances
In systems with natural circulation, only radiators can be used, as well as thick pipes as radiators (they have less hydraulic resistance).
But alas, convectors cannot be used - natural circulation simply will not go through them.
Summarizing the above, an open system is the last century.Slow heating, high inertia of the system, a large amount of soluble air, bulky pipes, low efficiency make it unattractive for modern heating systems. So it is used in extreme cases - for example, in areas where power is often cut off.
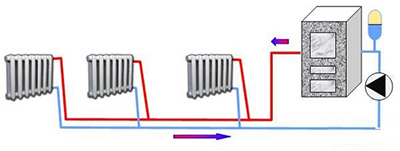
The most popular now are closed systems with forced circulation of the coolant, two-pipe or collector-beam.
Let's analyze the situation when water boils in the heating boiler, and it turns off in emergency mode due to overheating of the coolant. Consider several types of boilers and common causes of such a problem in them.
An open heating system with natural circulation has a number of features
- There is a lot of dissolved air in the system, which can lead to corrosion of internal metal elements in the system.
- Large inertia of the system. After turning on the heating, the house heats up slowly. It is necessary to warm up the system gradually, otherwise the water will simply boil in the boiler, while it will still be cold in the radiators.
- House warms up evenly
- Large temperature difference between supply and return
- Fuel consumption is higher (low efficiency) than in a closed system with a circulation pump
- Independence from electricity
- The system is simple, there is practically nothing to break in it. Fairly simple installation.
- Aesthetically not too good, because. pipes of large diameter are used, and sometimes pipes of increased diameter are used as radiators
- The system is quite cumbersome
- Do not use antifreeze in the system
- Water from the system gradually evaporates, so it must be topped up periodically. It is advisable to install automatic topping up.
- The boiler must be installed at the lowest point in the system. Best of all - in the basement, or in some recess.
- The expansion tank is installed at the highest point in the system. If you install it in the attic - it must be insulated.
- Silent operation, due to the lack of a circulation pump
But nevertheless, this system has been successfully used and is being used when installing heating in small private houses with a height of 1 or 2 floors.
Let's describe the whole system in order:
Boilers with automatic ignition.
The water circulation in the heating circuit is disturbed.
Due to the slow movement of the coolant in the heating system, the water in the heat exchanger overheats and the boiler stops in emergency mode. The speed of movement of the liquid in the system can be affected by a decrease in the efficiency or breakdown of the pump, contamination of the filter installed on the "return" of the heating circuit, incorrect operation of the three-way valve.
The performance of the circulation pump is reduced due to contamination of the turbine blades or the internal cavity.
Photo 1 - gas boiler circulation pump module with automatic ignition.
For its revision it is necessary:
- Stop smoothly by moving the water temperature regulator knob to the extreme zero position and wait for the process to complete, turn off the power to the boiler.
- Dismantle the front of the housing.
- Determine the location of the pump.
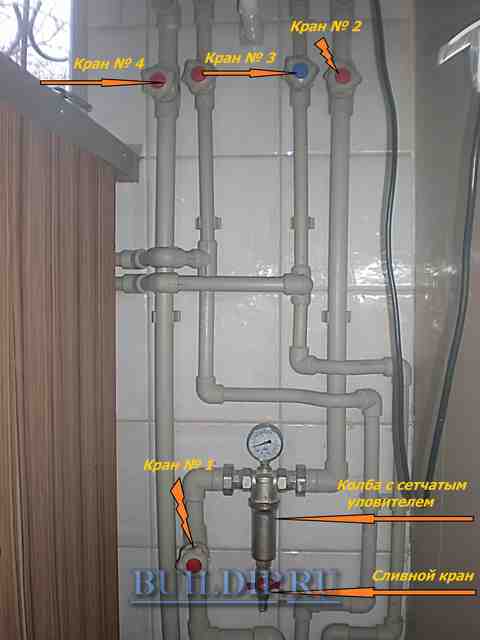
- Close the shut-off valve (No. 2, No. 3, No. 4 photo 2) of the supply, return line, cold water supply.
- Drain water from the boiler through the drain cock and leave it in the open position.
- Loosen pump fasteners until air enters the circuit to drain residual fluid from the system.
- Dismantle the fastener, power plug and remove the module (engine with turbine).
- Clean the blades, the inner cavity and the rubber seal of the mechanism from dirt.
- Assemble the pump.
- Open the cold water supply tap.
- Slightly open the make-up valve to check the tightness of the hydraulic part of the boiler.
- Open the supply and return valve.
- Fill the system with water up to a pressure of 1 bar.
- Turn on the boiler in circulation mode to remove air.
Photo 2 is an example of piping of a heating system.
In boilers with electronic control, if the pump breaks down, the corresponding fault code will be displayed on the dashboard, which is decoded using the boiler passport or electronic catalogs posted on the manufacturer's website.
Checking and cleaning the filter:
- Gently stop the boiler.
- Using the taps (No. 1, No. 2) installed in front of the filter and behind it, shut off the water supply.
- Using the drain cock of the filter, remove water from the isolated area.
- Unscrew the flask and clean the strainer.
- Assemble all filter components.
- Open previously closed valves.
- If the system pressure drops, energize the circuit.
- Switch the boiler to the venting position.
Checking the three-way valve.
In double-circuit wall-mounted gas boilers, switching from heating mode to hot water position is carried out using a three-way valve. It consists of a servo drive (motor with a gearbox), a stem, rubber seals, a valve and a housing with inlets and outlets. A malfunction of this device can lead to a cessation of the circulation of the coolant and, as a result, an overheating of the heat exchanger is formed.
To check the condition of the three-way valve, it is necessary to smoothly stop the boiler and de-energize the system. Check the condition of the engine, and for this, connect the ohmmeter probes to the power terminals. If it shows 80 - 300 ohms, then the engine is working, and if other indications (0 or 1), then it is faulty.
The three-way valve may not switch due to jamming of the actuator gearbox, or due to deformation of the valve itself. If violations of the valve operation are detected, it is changed to a serviceable one, or is subject to revision.