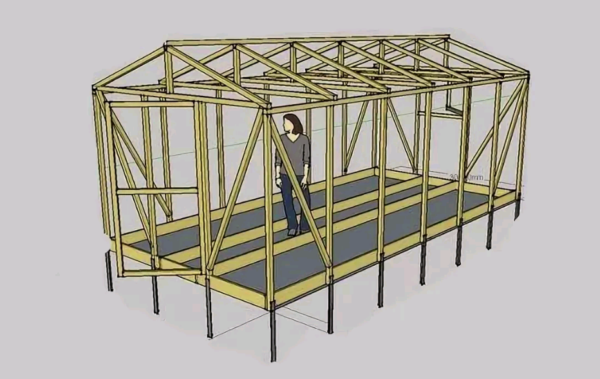
Device beds in greenhouses 3 to 6
Usually compact greenhouses 3x6 m are widely in demand in suburban, suburban areas. Here are the key features of such greenhouses.
It is necessary to place the greenhouse in an open place
It is important to organize a convenient approach to it.
The beds usually go along the long sides, along the walls.
In order for the lighting to be of better quality and longer, the long side must be turned to the west.
It is important to create conditions for comfortable care of the beds. The height of the ridges relative to the track is usually a maximum of 40 cm.
It is advisable to leave tracks at least 45 cm wide
Only in such conditions is a full-fledged effective work possible.
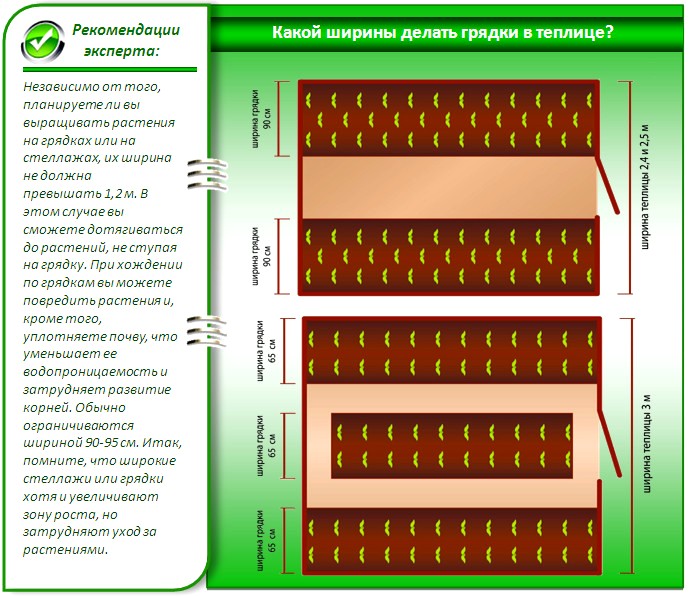
The beds are best done at 60 or 90 cm. Wider beds are used with paths on both sides, and when approaching from one side, beds 60 cm wide are suitable.

How to calculate the size of the greenhouse, drawing up a drawing
Drawing up a preliminary plan is necessary in order to understand the amount of material needed and the general course of action for the construction of a greenhouse on the land.
What you need to consider when calculating the greenhouse:
- Foundation. Its installation depends on the size and purpose of the structure. If it is a stationary structure, then a strip foundation is performed. If the structure is periodically moved, then the base is made of wood and light;
- Frame size. The material that is taken when you need to calculate the greenhouse also matters. It will be a material that is durable for decades or wooden structures that will last 2-3 seasons, but will make the greenhouse much heavier. It is fashionable to make from aluminum profiles that can stand for decades and not succumb to corrosion and destruction. At the same time, the material has a small weight; any shape of the frame can be made from it;
- Design. The calculation of the greenhouse is made depending on the shape of the future structure. It will be a gable structure, arched or single-sided. The cost of the future greenhouse also depends on this;
- How many windows are expected in the design. Calculate the greenhouse, taking into account the need to ensure air circulation in the room. Thus, the optimum temperature and humidity will be maintained in the greenhouse.
At the base of a capital structure, it is recommended to use:
- Concrete
- Bricks.
If it is planned to erect a light structure or an arched structure, then the frame is installed on:
- Rubble stone;
- Rubble.
The frame of the calculated greenhouse can be built from metal profiles, pipes, wooden bars, PVC pipes can be used. But it should be understood in advance that metal and wood are short-lived building materials. They need to be treated with special solutions that will protect the frame from destruction for some time.
The most optimal frame material in the calculation of the greenhouse is considered to be metal treated during manufacture with an anti-corrosion compound.
An important point on how to calculate the size of the greenhouse is the location of the heating equipment. To create the optimal temperature regime, electric circuits, a "warm floor" system, converter heating, heating with infrared lamps are used. The choice depends on the financial capacity of the gardener and the purpose of growing the crop. Vegetables for sale should grow warm to be beautiful and in large quantities.
4. Heat consumption for heating water for watering plants
By
VNTP-N-97 "Consumer water consumption standards
agricultural
water supply" water consumption for irrigation
crops is defined as:
where
— weighted average irrigation rates
agricultural crops when irrigated
sprinkling method;
—
irrigation area, ha;
—
number of days of watering.
Quantity
heat to heat water to a temperature
25°С:
3.5. Heat consumption in
in general for the greenhouse SPK "Druzhba"
Complete
meaning:
where
1.13 - coefficient taking into account losses
for own needs of the boiler house.
Power
boiler room:
3.6. Annual
fuel consumption for heating
,
where
—
lower calorific value of fuel,
- efficiency
heat generating plant
-coefficient,
taking into account heat losses in thermal
networks
for
central boiler houses operating on
liquid and gaseous fuels
Calculate
annual reference fuel consumption
,
then:
For
recalculation of conventional fuel consumption in
natural use thermal
equivalent
,
then
,
At
use as fuel
natural gas
:,
then
fuel consumption
-
Definition
heat loss of the barn.
4.1.
Supply air calculation for
livestock buildings
barn
designed for 100 heads, size 120 × 15 × 3 m,
windows 80 size 1.2×0.8.
Walls
double layer brick
-weight
cows (dairy direction) 400kg,
-number
cows 100 .,
-humidity
φn=0.8
and φext=0.7,
-temperature
tn=-26C
and text=10С,
-volume
premises V=120×15×3=5400
m3
One
cow excretes:
- free
heat 1618.5 W,
- carbonic acid
126 l/h,
- water
vapor 404g/h.
1) Selection
SO2:
LCO2=(n m CP)/(WITH1-WITH2)=(100·400·1)/(2-0.3)=23530
m3/h
n-number
cows,
WITHn-number
SO2
excreted by a cow per 1 kg, l/h kg
WITH1- maximum allowable
CO concentration2
indoors is 2 l/h
WITH2- maximum allowable
CO concentration2
in the atmosphere is 0.3 l/h.
m-mass
1st cow, kg
WITHalive—
carbon dioxide content per head,
l/h
2) Consumption
air:
Lw=W/(ρ(dext
–
dn))=256875/(1.2(8,3-0.4))=20386
m3/h
W-moisture release,
g/h
ρ-density
air is equal to 1.4 kg/m3
dext—
internal air moisture content
equal to 9.4 g/kg dry air.
dn—
the external moisture content of the air is
0.4 g/kg dry air
W=Walive+WSpanish=40400+6060=46460
g/h
Walive
=Σwiniα=404 100 1=40400
g/h
wi—
quantity produced per 1 head
water vapor 404 l/h
ni-number
cows
Alpha
- correction factor =1
WSpanish=ξ WFri=0.15·40400=6060
g/h
Choice
fan is produced according to the flow and
by force. The fan is chosen with a margin
in 15-20%.
n=Lco2/V=23530/5400=4.3≈5
take
Lco2
,
because max.
3)
Mine calculation:
Accept
height h=3m
Speed
in mine
Vsh=2.2
√h(text-tn)/273=2.2√3(10+26)/273=1.34
m/s
Accept
shaft size 0.5×0.5=0.25 m2
Total
mine area
Fw=Lco2/(3600 Vw)=23530/(3600·1.34)=4,9
m2
Number
mines
N=Fsh/0.25=4,9/0,25=6,4≈19,6
mines.
What to consider when calculating the greenhouse
Installing a greenhouse on a personal plot involves preliminary preparation of the land allotment, drawing up a drawing and preparing building material. At the same time, the calculation of the greenhouse should be carried out even during the period when it is cold, in order to immediately begin construction with warming.
First of all, you need to understand where the structure will stand. It is necessary to calculate the size of the greenhouse to fit inside:
- Necessary communication systems;
- Equipment;
- Seedling.

The choice of frame material and covering sheet is also important. Today, we can note the trend towards the construction of polycarbonate greenhouses. If you need a budget option, then a thickened polyethylene film is used.
When calculating the greenhouse, try to place the structure in a place protected from wind and draft. Enough sunlight must get inside the structure, which is necessary for the growth and fruiting of plants.
To get a good harvest, the greenhouse is located on the sunny side of the land.
You should not count on a large greenhouse, since a small design is enough to provide optimal conditions for plants. The optimal size is considered to be 3 meters wide, 6 meters long. It is necessary to make a calculation of the greenhouse and its location so that there is room for placing beds with other vegetables in the open ground
The number of family members who will use the fruits from the greenhouse should be taken into account. Seedlings should be enough to meet the needs of each of them
If you calculate the greenhouse as a business, then the dimensions should allow you to place large volumes of seedlings.
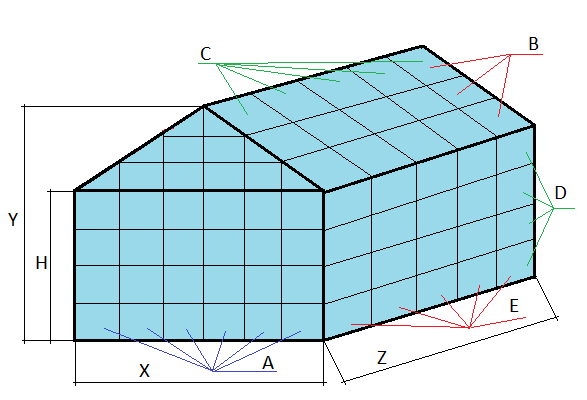
Instructions for a calculator for calculating a rectangular greenhouse
Specify the desired drawing scale.
Fill in the parameters of the greenhouse in millimeters:
X - The width of the greenhouse, is selected according to your wishes and goals (want to pamper the household with fresh products or build a greenhouse for a mini business) and depends on the budget for construction and the availability of space on the site. Factory greenhouses are produced in widths from 1800 to 6000 mm. For comfortable work in the greenhouse, the X value should be chosen at least 2400 mm. This width is optimal, because it allows you to equip a passage (600 mm) and arrange racks with seedlings or beds on both sides up to 900 mm (it is difficult to reach beyond the specified distance for plant care).
Z - Greenhouse in length, can be any, if the size of the site and the budget of the building allow. When choosing a Z value, one should take into account the standard dimensions of the material that will be used for glazing. For example, if polycarbonate is used, the value of the Z length should be a multiple of 2100 mm. For a greenhouse covered with polyethylene film, it is advisable to choose a length that is a multiple of 1000 mm.
When choosing the size of the greenhouse and its placement on the site, one should take into account the nature of the landscape (the slope of the site, the presence of water bodies, the level of soil freezing, the height of groundwater), orientation relative to the cardinal points (strongly affects the illumination and, as a result, productivity), the quality of the land in the place where the greenhouse is planned to be installed. In this case, the location of the greenhouse near buildings and tall trees should be avoided.
Y - Total height of the greenhouse (from the floor to the roof ridge). The height of the greenhouse is chosen based on the convenience of working in it (the determining factor is the height of the worker plus free space) and should be higher than the side walls. The optimal height above the aisle is not less than 2200 mm, since working in a low room is inconvenient and tiring.
H - The height of the walls of the greenhouse is chosen not less than 1500 mm for ease of operation and care of plants.
A - The number of vertical sections on the facade of the greenhouse. The A value should be selected taking into account the dimensions of the glazing material and the required load-bearing capacity of the framework. The greater the width of the greenhouse, the greater the number of vertical sections needed for structural stability.
B - The number of cells of the roof slope of the greenhouse from the eaves to the ridge. It should be chosen based on the type of glazing material and to exclude the possibility of its sagging. The minimum B value for a small greenhouse is 2.
C - The number of sections of the roof slope, depends on the material used for covering. The larger the value of C, the higher the bearing capacity of the roof of the greenhouse. You should also consider the standard dimensions of glazing materials (polycarbonate, glass).
D - The number of vertical cells of the walls is selected taking into account the length of the greenhouse and the dimensions of the glazing material. The higher the D value, the higher the bearing capacity of the greenhouse frame.
E - The number of horizontal cells of the walls of the greenhouse is set, taking into account its length of the greenhouse and the dimensions of the material that is planned to be used for glazing.
The capabilities of the online calculator for calculating a rectangular greenhouse allow you to select the optimal sizes of sections and cells, changing their number, while their dimensions will be displayed on the drawings of the greenhouse.
Click Calculate.
The calculator will help you calculate the area, volume and perimeter of a rectangular greenhouse. As well as the area of the roof, side and facade walls and the total area of glazing, which is necessary for the purchase of cladding material in the right amount. In addition, you will find out the length of the materials needed to make the frame of the greenhouse. This data will help determine the cost of building a greenhouse and decide whether to build it yourself or buy a finished greenhouse from a manufacturer.
Peculiarities
It has the following number of advantages:
Simplicity of design. Water heating - . Making such a greenhouse heating system with your own hands is quite simple;
Versatility in fuel selection
Ultimately, it doesn't matter how the water is heated.You can burn ordinary firewood, and coal, and household waste
If the area where the greenhouse is installed is gasified, then gas can also be used. Heating water with electric heating elements is also quite a suitable option;
. This is manifested in the fact that after the cessation of the heat supply to the boiler, the heat is stored for a long time. This feature of water systems eliminates sudden temperature changes;
The use of water heating makes it easy to realize the heating of air and soil;
Space heating with a water system does not reduce air humidity. This is especially important in the cold season, when air humidity is already very low.
is the risk of defrosting in the event of an emergency. This usually happens when the heating in the greenhouse has been interrupted and the water has not been drained from the pipes. Turning into ice, the water expands, which leads to the destruction of structures filled with water.
In order to implement any greenhouse heating, it is necessary to take into account the overall energy efficiency of the building. Any enclosing structures have heat transfer, and the lower this characteristic, the less energy is required to maintain the required temperature inside the greenhouse. The heat preservation champion is cellular polycarbonate. Its cellular structure has a very low thermal conductivity. In second place are film barriers, but in terms of their mechanical characteristics, the film is not suitable for structures operated in winter. Glass comes last.