Introduction
The severity of the maintenance problem
and repair of industrial pipeline
reinforcement (PTA) arose with the beginning
reforming the national economy
country and the formation of market relations.
As a result of the transformations,
a sharp increase in the cost of PTA, which
rapidly approaching the global
level. Limited amount of financial
consumer resources PTA made them
look for a way out of a difficult situation,
when replacing worn fittings with
new became heavy economic
burden. Under these conditions, consumers
fittings and remembered the possibility
repairs and started
carry out spontaneously at low technical
level, but setting the task of creating a system
maintenance and repair
PTA. This situation has created a demand
on-technical means of carrying out
repair, technological processes,
methods for evaluating the effectiveness of
repairs, regulations on the organization
repair production, standards for
quality assurance, etc.
A necessary condition for normal
functioning of the technical
maintenance and repair is
interaction of performers, armed
design and technological
repair documentation, technical
means - in the form of technological
equipment, technological equipment,
means of diagnostics, testing and
control over the repair process. In the market
economic efficiency
is the dominant factor
defining interest in
launch and daily maintenance
normal functioning of the system
maintenance and repair.
About the feasibility of the repair
PTA testify structure
technological processes, results
technical and economic calculations and
practical efficiency data
operation of specialized
departments and organizations that carry out
maintenance and repair of PTA.
The cost of conducting small, medium
and overhauls are in
range from 7% to 50% of the cost of a new
fittings, which allows quite definitely
argue that in modern economic
conditions and at the present level
quality of pipeline fittings
well organized and adequate
least technically equipped process
repair is economically beneficial to the consumer
fittings.
Properties of gate valves, their possibility
use in various industries
depend on numerous factors. TO
the most important factors are
constructive design of the base
parts such as body, wedge, cover,
material used for these parts,
ways of obtaining blanks, weight and size
specifications.
The operation of valves involves not
only the process itself
functioning of the product, it is also
supervision of the condition of pipelines
systems, technological equipment
and pipeline fittings. for supporting
in working order of the equipment,
pipeline fittings and permanent
security is carried out
constant supervision, technical
maintenance and repair.
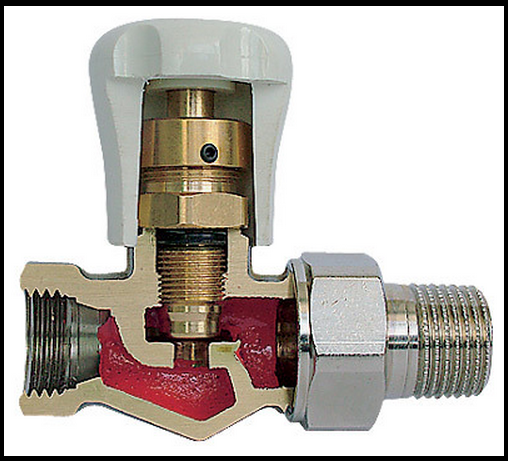
Wedge gate valves from the provision position
tightness in the gate and resource
tightness are the most difficult
object from all types of valves.
They belong to the four-surface
systems. To ensure tightness
in them it is necessary to accurately make four
surfaces. In this case, the surfaces must
exactly positioned relative to each other
friend. the largest technological
the challenge is to ensure accuracy
shutter angle parameters. For achievement
precision in the technological process
repair must be used or
specialized technological
tooling for universal equipment,
or specialized repair
equipment. Technological methods
must ensure the quality of all
sets of metric parameters.
Description of the technological process
Partial disassembly of the valve for the purpose of repair, replacement of the spindle or wedge is carried out without dismantling the valve from the pipeline in the absence of working medium pressure. Disassembly is carried out in the following order:
- set the wedge to the upper position OPEN and remove the casing and pointer (for the electric drive JSC Tulaelektroprivod);
- set the wedge to the middle position, lowering it by 3/4 of the full stroke if the valve is in the OPEN position or raising it by ¼ of the full stroke if the valve is in the CLOSED position;
- remove the electric drive;
- unscrew the plug by 2-3 turns and make sure that there is no medium pressure in the pipeline;
- remove the cover fasteners;
- Raise the assembly until it exits the housing. Take the knot aside and set the wedge in a vertical position on the pads;
- remove the spindle head from mating with the upper groove of the wedge, after which the assembly is installed in a horizontal position on the linings. If necessary, the removed assembly can be completely disassembled.
After inspecting and repairing parts and assemblies, assemble the valve in the following order:
- lubricate and place the sealing ring in the groove on the end of the housing;
- sling the cover assembly with the spindle and the stand in a vertical position, carefully insert the spindle head into the corresponding groove of the wedge and lower the assembled unit into the housing cavity. Lower the unit slowly, guiding the wedge along the guides between the body nozzles
The wedge must be installed in the same orientation relative to the body nozzles;
- install the cover fasteners and evenly tighten it with a torque in a diametrically-cross pattern:
Mcr.=(70±7) kgf. m - for DN 500;
Mcr \u003d (120 ± 12) kgf. m - for DN 600;
Mcr \u003d (140 ± 14) kgf. m - for DN 700,800;
Mkr. =(190±19) kgf. m - for DN 1000,1200;
Next, install the electric drive of the valve and check the operation of the valve.
Complete disassembly of the valve for repair of the seal assembly is carried out only after the valve has been dismantled from the pipeline.
After assembly, the gate valve must be pressurized with pressure Pn = 12.0 MPa with the gate open in accordance with the rules in force at the facility in operation.
Repair of valves on pipelines
Repair of fittings and pipelines
The main defects of pipelines are density violations in flanged, coupling and fitting connections. Eliminate leakage by tightening flanges, fittings. If the leak continues, the connection is disassembled, the sealing surfaces, gaskets are checked, seals are replaced if necessary, cracks in the pipes. Eliminate malfunctions by applying clamps, linings, welding with electric or gas welding. Cracks in copper pipes are sealed with soldering.
When repairing pipelines, the connections are thoroughly cleaned of dirt, grease, residues of intermediate products and washed. Irregularities of the sealing surfaces are cleaned with files, needle files, scrapers, rubbed with abrasive pastes and powders. Threaded connections of pipelines are sealed with linen thread, tow, red lead, whitewash and special pastes.
Repair of pipelines (categories are indicated in Table 20) is carried out taking into account the requirements of the Rules for the Design and Safe Operation of Steam and Hot Water Pipelines, approved by Gosgortekhnadzor on 10.03.70.
The requirements of the Rules do not include pipelines with parameters of category 1 with an outer diameter of less than 51 mm and categories 2, 3 and 4 with an outer diameter of less than 76 mm; drain, purge and exhaust, from non-metallic materials; floating structures, nuclear power plants and special installations.
For the repair of pipelines subject to the Rules, only materials permitted by them are used. Materials that do not have passports or certificates can only be used after testing and control.
Manufacture, installation and repair of pipelines and their elements should be carried out by enterprises or organizations that have the necessary technical means and trained personnel.
The manufacture and repair of pipelines subject to registration with the bodies of the Gosgortekhnadzor of the USSR can only be carried out by organizations that have permission from the local bodies of Gosgortekhnadzor; pipelines of category 1 with a conditional passage of more than 70 mm, as well as 2 and 3 categories with a conditional passage of more than 100 mm. Other pipelines are registered at the enterprise - the owner of the pipeline.
An operating permit for a newly installed or repaired pipeline is issued by a district inspector of the USSR Gosgortekhnadzor (for a pipeline registered with boiler supervision authorities) and for pipelines not registered with boiler supervision, by a person at the enterprise responsible for the good condition and safe operation of pipelines.
When repairing, it is allowed to use all industrial welding methods that provide the necessary operational reliability of pipeline welded joints. Welders with a certificate are allowed to weld. Welding work is carried out at an ambient temperature of at least 0°C. When installing the pipeline, it is allowed to use welding at a temperature of minus 20 ° C (with a thickness of welded elements up to 16 mm). In bad weather, the welder and the welding site must be well protected.
Armature failure. The most common defects are wear and damage to gland seals; seizure of sealing surfaces; wear of the valve seat and valve disc; spindle thread wear. Measures to eliminate them are indicated in Table. 21.
THE VALVE IS FULLY ADJUSTABLE FROM 0 TO 100 .
The whole range and without narrowing.
given the very dirty risers - the best choice for durability.
For the 1st time, they put it on installation in Berdsk - to the system administrator Kenguryakh.

Initial data: riser 1 inch And the desire of the customer kenguraha : When installing a new radiator, I would like to keep the flow area as much as possible.
There are several methods without narrowing the riser:
Kangaroo is not Australia!
This is not a simple Berd sysadmin: he worked for a long time at the Institute of Mathematics at the Academy, in short Associate Professor - and very jumpy! What are they doing there? Are they calculating the correct equipment for heating installation? This kangaroo quickly and briskly jumped over the smoked one: at 3/4 of the tap, there is also a narrowing - let's put the tap on 1 inch!  kenguraha: I would like to be able to regulate the heat transfer of the radiator. What options are there for this, given the diameter of the riser?
kenguraha: I would like to be able to regulate the heat transfer of the radiator. What options are there for this, given the diameter of the riser?
Okay, I think: right now, we will quickly break off this mathematician: there is always a narrowing on the thermostatic control valve:
purely constructive - additional hydraulic resistance:
In the maximum open state, it passes 3 times less water than a full-bore faucet.

And there is a hole in the old woman: it turns out that there is a wedge valve for sale - full bore.
Fully adjustable from 100% to 0% (full range and no narrowing).
Summary: The Australian Jumping Kangaroo is better at:
Photo of real installation: Minsk cast-iron radiator is a classic.
The order was made in the style of nostalgia: "boiler room from a scoop" - we are all made in the USSR.
Taps and valves, pipe bends and no modern bimetal: everything is specially selected according to the design of that era.


An alien battery from another galaxy - celestial, cosmic hue.
Blatnoy, an elite radiator of "blue blood" - fans of acrylic bathtubs do not understand this.
And lovers of polypropylene (cellophane layers) on heating will generally spit.

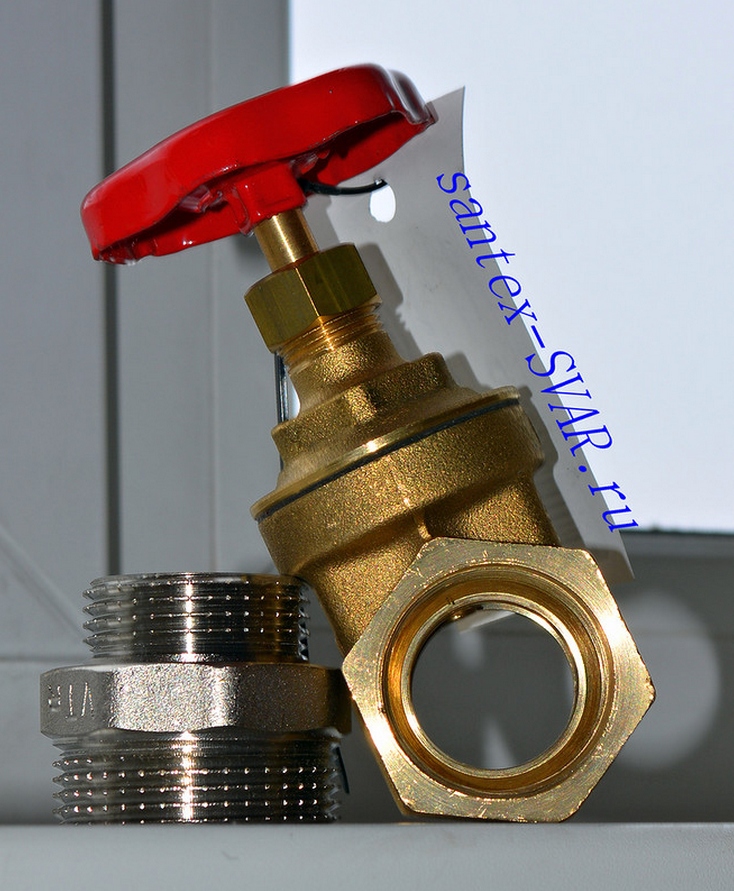
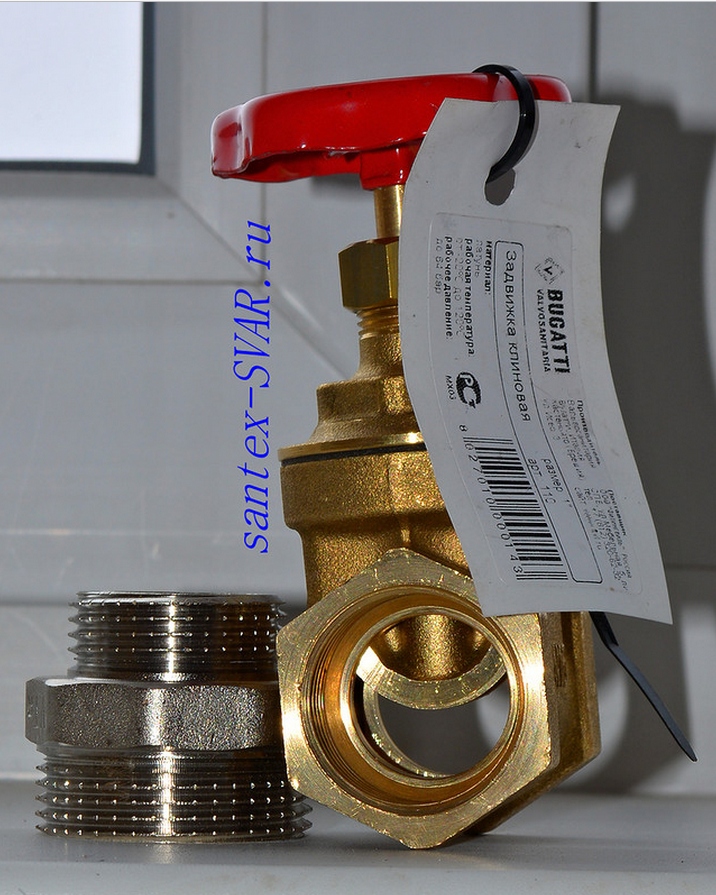
Part wear and recovery methods
The fittings requiring repair are dismantled, washed and sent assembled to a repair company. Here it is disassembled and defects are fixed. The most common reasons for shut-off valves to fail are leakage due to corrosion, nicks, dents of foreign bodies on the sealing surfaces, as well as deformation of the valve body under the influence of external loads and temperature deformations.
The internal cavity of the body is inspected for the detection of shells, cracks and other defects. Non-through defective places in the body are cut to the full depth to bare metal. Before cutting cracks, holes with a diameter of 8-10 mm are drilled at their ends. The edges adjacent to the cutting points are cleaned with a file and a metal brush. After etching with a 10% nitric acid solution, the cracks are welded by electric arc welding and thermally treated.
When inspecting the parts of the shutter, check the tightness of the sealing ring (seat) in the body and the cleanliness of its surface. The shutter (gate, discs), spindle, bushing, stuffing box cavities, bushing head and fasteners are checked for nicks, scuffs, scratches and other damage. Damaged parts are discarded and refurbished.
Various sinks, cavities, scuffs and other damage to the sealing surfaces are eliminated by turning, grinding and lapping on the machine. Defects with a depth of more than 0.5 mm on the sealing surface are eliminated by preliminary cutting of the defective place and surfacing of metal on it, followed by processing. If the damage depth is less than 0.5 mm, then grinding with an abrasive wheel and lapping is carried out.
Leaks between the body and the seat are eliminated depending on the type of attachment. If the saddle is fixed in the body by pressing, then it is machined out of the body and replaced with a new one, which is welded to the body with preliminary cutting of the landing site.
If the saddle is seated on a thread, then it is unscrewed using special keys and fixtures. If there is a normally preserved thread, a new seat is screwed in with the same device, but with a large tightening torque.
If the thread for the seat has significant wear, then it is bored to a larger size with simultaneous boring for welding.
A new ring is pressed into this place and welded. If the rings are welded into the valve, then they are turned on a lathe in a special device, where both surfaces are turned in one installation.
After that, the body of the valve goes to the grinding and lapping of the rings. Both sides of the wedge in this case are built up and machined in the fixture in one setting. The wedge is adjusted along the valve body on a horizontally sharpening and lapping machine.
The processing of sealing rings of wedge gate valves can be carried out not only on a lathe, but also on a horizontal boring machine.
Before repair, the spindle is cleaned of traces of the old gland packing, soot and dirt, washed in kerosene or gasoline. The sealing surface of the spindle must be mirror-smooth.
Not deep dents and scuffs, with a depth of more than 0.08 - 0.15 mm, are eliminated by lapping with EOI paste or grinding powders diluted in oil.
The inner surface of parts mating with the spindle is also checked for cleanliness and lack of ovality.One of the labor-intensive operations in the repair of fittings is the grinding of sealing surfaces. Lapping of flat parts of reinforcement (saddle, wedges) is carried out on a plate.
Lapping can be done both manually and mechanically. The design of the laps is selected depending on the shape of the surfaces to be lapped and the size of the conditional passage.
When mechanically lapping the sealing surfaces, lapping machines or attachments for drilling machines are used.
Lapping machines have a reciprocating - rotational movement of the lapping machine with a rotation ahead of it in one direction. Electrocorundum or silicon carbide of various grain sizes is introduced into the lapping paste. Lapping is carried out to a light matte color of the sealing surfaces.
The “pencil” method used in practice is that thin transverse risks are applied to the prepared surfaces of the dies, wedge or plug (for taps). If, after mating the lapped surfaces and their mutual movement, the risks are everywhere erased, then it is considered that a good grinding has been achieved.
After replacing the gasket and gland packing, the assembled valve is sent for testing of finished products.