What gas is used in residential buildings
Natural gas is a conditional concept that is used for a combustible gaseous mixture extracted from the bowels and delivered to consumers of thermal energy in liquid form.
The composition is varied, but methane always predominates (from 80 to 100%). In addition, the composition of natural gas includes: ethane, propane, butane, water vapor, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium. An indicator of the quality of natural gas is the amount of methane. All other components of natural gas are nasty additives that create polluting emissions and destroy pipes. Natural gas for residential buildings is not recognized by the senses in any way, so strongly smelling gases are added to it - odorants, which perform a signal function.
Norms and rules
To determine the required distance from the gas pipe, after the development of a residential building project, citizens of the Russian Federation apply for the appropriate permit (approval) to the local gas distribution organization. For a definite answer, you need to know the type of gas pipeline and what pressure is applied when it is supplied. If there is no data on the type of gasket and on the pressure in the pipes, it is impossible to give an unambiguous answer.

SNiP 42-01-2002 is one of the logical results of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation "On Technical Regulation" No. 184, adopted in December 2002. In November 2008, it was accepted Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 858, according to which the current codes of practice were developed and approved. This joint venture was approved at the legislative level in an updated version and was named joint venture 62.13330.2011.
The most democratic type of fuel in terms of cost has become widespread and has become a public energy resource. Its widespread use has led to the urgent need for the development of regulatory documents, in which you can find the permitted distances.

Starting from 2010, SNiP registered by Rosstandart:
- are legislative documents, the observance of which is mandatory;
- is checked by supervising organizations designed to ensure the safety of such structures;
- may be the basis for a decision on a lawsuit;
- recognized as a weighty reason for imposing an administrative penalty on the fact of violation.
SP 62.13330.2011 regulates the distances that must be observed depending on the type of laying of the main gas pipeline or its branches and the pressure of liquid fuel in the pipes.

If the gas is supplied in cylinders, only the prescribed fire safety regulations must be observed. More economical and volumetric transportation in pipes provides for differentiated requirements for different types of supplies and pressure levels during their implementation.

Main gas pipelines. High, medium and low pressure gas pipelines Glossary
The gas pipeline is an important element of the gas supply system, since 70.80% of all capital investments are spent on its construction. At the same time, 80% of the total length of distribution gas networks falls on low pressure gas pipelines and 20% on medium and high pressure gas pipelines.
Gas pipeline classification by pressure
In gas supply systems, depending on the pressure of the transported gas, there are:
- high-pressure gas pipelines of category I (operating gas pressure over 1.2 MPa);
- high-pressure gas pipelines of category I (operating gas pressure from 0.6 to 1.2 MPa);
- high-pressure gas pipelines of category II (operating gas pressure from 0.3 to 0.6 MPa);
- medium pressure gas pipelines (operating gas pressure from 0.005 to 0.3 MPa);
- low pressure gas pipelines (operating gas pressure up to 0.005 MPa).

Medium pressure gas pipelines through gas control points (GRP) supply gas to low pressure gas pipelines, as well as industrial and municipal enterprises. Through high-pressure gas pipelines, gas flows through hydraulic fracturing to industrial enterprises and medium-pressure gas pipelines. Communication between consumers and gas pipelines of various pressures is carried out through hydraulic fracturing, GRSH and GRU.
Location of gas pipelines (classification)
Depending on the location, gas pipelines are divided into external (street, intra-quarter, yard, inter-workshop) and internal (located inside buildings and premises), as well as underground (underwater) and above-ground (above-water). Depending on the purpose in the gas supply system, gas pipelines are divided into distribution, gas pipelines-inlets, inlet, purge, waste and inter-settlement.
Distribution pipelines are external gas pipelines that provide gas supply from main gas pipelines to gas input pipelines, as well as high and medium pressure gas pipelines designed to supply gas to one object.
The inlet gas pipeline is considered to be the section from the point of connection to the distribution gas pipeline to the disconnecting device at the inlet.
The inlet gas pipeline is considered the section from the disconnecting device at the entrance to the building to the internal gas pipeline.
Inter-settlement pipelines are distribution gas pipelines located outside the territory of settlements.
The internal gas pipeline is considered to be the section from the gas pipeline-inlet (inlet gas pipeline) to the place of connection of a gas appliance or a thermal unit.
Materials for gas pipelines
Depending on the material of the pipes, gas pipelines are divided into metal (steel, copper) and non-metallic (polyethylene).
There are also pipelines with natural, liquefied hydrocarbon gas (LHG), as well as liquefied natural gas (LNG) at cryogenic temperatures.
The principle of construction of distribution systems of gas pipelines
According to the principle of construction, distribution systems of gas pipelines are divided into ring, dead-end and mixed. In dead-end gas networks, gas flows to the consumer in one direction, i.e. consumers have a one-way supply.
Unlike dead-end networks, ring networks consist of closed loops, as a result of which gas can be supplied to consumers through two or more lines.
Reliability of ring networks is higher than dead-end ones. When carrying out repair work on the ring networks, only a part of the consumers connected to this section is turned off.
Of course, if you need to order gas supply to the site or perform gasification of an apartment building, instead of memorizing the terms, it is more profitable and more efficient to turn to reliable certified contractors. We will carry out work on conducting gas to your facility with high quality and within the agreed time frame.
LLC "GazComfort"
Office in Minsk: Minsk, Pobediteley Ave. 23, bldg. 1, office 316АOffice in Dzerzhinsky: Dzerzhinsk, st. Furmanova 2, office 9
Types of gas pipelines
Hydrocarbon gases in the world community are recognized as a more promising type of raw material than oil, and much more productive than coal. For the transportation of LPG - liquefied hydrocarbon gases - special conditions are required, as well as for storage. Sometimes they are called, depending on the origin, LPG (petroleum) or LNG (natural). Today, all three abbreviations are understood to mean the same as LPG, but these mixtures sometimes have significant differences in composition, and this suggests the need for the development of separate standards for LNG.

Due to the potential explosion hazard, special rules are imposed on the laying of networks. Exists:
- special SP 62.13330.2011 "Gas distribution systems" (revised and supplemented edition of SNiP 42-01-2002);
- an auxiliary table (B.1*), which indicates the minimum distances resulting from the set of rules;
- FNiP "Safety Rules for Facilities Using Liquefied Petroleum Gases" (PB was approved by Order No. 558 dated November 21, 2013);
- recently adopted GOST 9.602-2016 “Unified system of protection against corrosion and aging. Underground structures”, related to the protection of gas distribution systems.

The distance from residential and public buildings to the gas pipeline can be found in the "Rules for the Protection of Gas Distribution Networks", approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 20, 2000 No. 878. The main requirements for any pipelines are reliability and safety in operation.
Much depends on the ability of the entire complex to ensure industrial safety rules at any stage, as well as the ability to turn off individual sections for repair and safety work.

Main gas pipelines
Installed to move raw materials over long distances. They are classified as dangerous structures because high-pressure gas flows through them. The first category involves up to 10 MPa, the second - up to 2.5 MPa. Gas compressor stations are needed to maintain high pressure along the transportation route. Gas distribution stations reduce pressure to supply hydraulic fracturing, from where fuel is delivered directly to the consumer.

Distribution networks
Distribution gas pipelines are laid from the GZRS to the consumer in compliance with the necessary safety rules. This means that they support the setting of low, high or medium gas pressure. The permissible distance from the gas pipeline to the foundation of the building (structure) is regulated taking into account the requirements of the set of rules.
The need to maintain a certain distance is dictated by the number of outlets, single-stage or multi-stage, outlet gas pressure (low, medium - from 5 kPa to 0.3 MPa, high - from 0.3 to 1.2 MPa).
The photo shows a gas pipe.

Laying methods
The technical characteristics of the gas pipeline are regulated by the relevant GOST. The material is selected based on the category of the system, i.e. the supply pressure, and the installation method: underground, above ground or installation inside the building.
- Underground is the safest, especially when it comes to high pressure lines. Depending on the class of the transferred gas mixture, laying is carried out either below the freezing level of the soil - wet gas, or from 0.8 m to the ground level - dry gas.
- Aboveground - implemented with unremovable obstacles: residential buildings, ravines, rivers, canals, and so on. This method of installation is allowed on the territory of factories.
- The gas pipeline in the house - the installation of the riser, as well as the gas pipe in the apartment, is carried out only in an open way. It is allowed to place communications in strobes, but only if they are interrupted by easily removable shields. Easy and quick access to any part of the system is a prerequisite for security.
Norms and SNiP gas supply
An indicator of the quality of natural gas is the amount of methane. All other components of natural gas are unpleasant additives. There is another characteristic, according to which the gas pipeline is divided into categories - this is the gas pressure in the system.
What gas is used in residential buildings
Natural gas is a conditional concept that is used for a combustible gaseous mixture extracted from the bowels and delivered to consumers of thermal energy in liquid form.
The composition is varied, but methane always predominates (from 80 to 100%).In addition, the composition of natural gas includes: ethane, propane, butane, water vapor, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, helium. An indicator of the quality of natural gas is the amount of methane. All other components of natural gas are nasty additives that create polluting emissions and destroy pipes. Natural gas for residential buildings is not recognized by the senses in any way, so strongly smelling gases are added to it - odorants, which perform a signal function.
What is the gas pressure in the gas pipeline of a residential building
A gas pipeline is the entire path that gas passes through pipes from a place of storage to a consumer. Gas pipelines can be divided into land, surface, underground and underwater. In terms of the complexity of the conducting system, they are divided into multi-stage and single-stage.
There is another characteristic, according to which the gas pipeline is divided into categories - this is the gas pressure in the system. For gas supply to cities and other settlements, the pressure is:
- low - up to 0.05 kgf / cm2;
- medium - up to 0.05 to 3.0 kgf / cm2;
- high - up to 6 kgf / cm2;
- very high - up to 12 kgf / cm2.
This difference in pressure is due to the purpose of the gas pipeline. Most of the pressure is in the main part of the system, the least - inside the house. For a system with a certain pressure, there is its own GOST, which is strictly forbidden to deviate from.
Norms of gas consumption for home heating
The norms of natural gas consumption by the population are determined in the following areas of its use:
- cooking for 1 person per month;
- water heating with autonomous gas and water supply in the absence or presence of a gas water heater;
- individual heating of residential premises and outbuildings;
- for the needs of keeping pets;
Norms of gas for heating are calculated on the basis of consumption in equal shares by months of the whole year. They are measured in cubic meters per 1 m2 of heated area or per 1 m3 of heated volume. If the building is multi-storey, then the calculation is made for each floor separately. As a rule, attics, basement floors, as well as some basements are considered to be heated rooms.
SNiP gas supply for residential buildings
The requirements of SNiP in this area are as follows:
- Gas consumption is determined by the following indicators: for cooking with gas - 0.5 m3 per day; for hot water produced by a gas water heater - 0.5 m3 per day; for heating from a gas heating apparatus - 7 - 12 m3 per day.
- The gas pressure within the internal gas pipeline of an individual residential building cannot exceed 0.003 MPa.
- Above-ground gas pipelines on the site of a residential building should be located where there is no access for vehicles and the passage of people. They are placed at a height of at least 0.35 m from the ground to the bottom of the pipe.
- When entering a house, a low-pressure gas pipe is equipped with a shut-off device located at a height of up to 1.8 m from the ground.
- The distance between pipelines located in close proximity to the gas pipeline should allow access for repair and maintenance purposes.
- Any gas storage should be dug into the ground to a depth determined by a distance of 60 cm from the surface to the tank if the ground freezes in winter, and 20 cm if there is no freezing. If storage facilities are installed where the groundwater level does not allow them to be buried, then the tanks must be isolated from water and ensure their immobility. The low-pressure gas pipeline is laid underground, except in the situation of permafrost.
- Inside the house, the gas pipeline must be open. Otherwise, it is allowed only if the gas pipes are located near special ventilation, and are closed with shields that can be removed without special work and devices.
- Where building structures intersect, the gas pipeline is placed in special cases. Their ends should be placed at least 3 cm from the floor. The pipes must not come into contact with the case (gap 5 cm). These 5 cm must be covered with elastic materials.
- Disconnect devices are placed in front of meters and gas consuming devices.
Norms of gas consumption for home heating
Restrictions in the consumption of utilities can be manifested in minimum tariffs, allowable power and resource release rates. The need for the existence of norms appears where there are no accounting counters.
The norms of natural gas consumption by the population are determined in the following areas of its use:
- cooking for 1 person per month;
- water heating with autonomous gas and water supply in the absence or presence of a gas water heater;
- individual heating of residential premises and outbuildings;
- for the needs of keeping pets;
Norms of gas for heating are calculated on the basis of consumption in equal shares by months of the whole year. They are measured in cubic meters per 1 m 2 of the heated area or per 1 m 3 of the heated volume. If the building is multi-storey, then the calculation is made for each floor separately. As a rule, attics, basement floors, as well as some basements are considered to be heated rooms.
Gas production
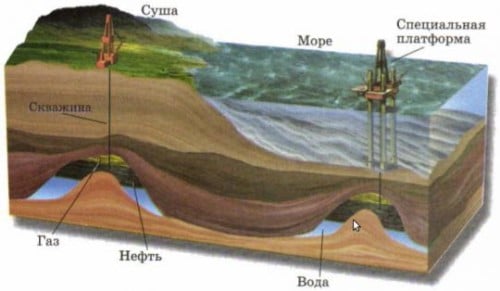
The gas lies in the earth's crust at a distance of 1-6 km from the surface, so geological exploration is carried out first. Deep in the bowels of the planet there are very small pores and cracks that contain gas. The mechanism of natural gas movement is simple: methane is displaced from high pressure pores to lower pressure pores. Wells are evenly installed over the entire area of the deposit. Since the pressure underground is many times greater than atmospheric pressure, the gas itself goes into the well.
Preparation and transportation
Gas is not immediately allowed through the pipeline, first it is prepared in a special way in boiler houses, thermal power plants and chemical plants. They are dried from water vapor and cleaned of impurities: hydrogen sulfide (causes corrosion of pipes), water vapor (causes condensate, interferes with the movement of gas). The pipeline is also prepared: with the help of nitrogen, an inert environment is created in it. Further, the gas moves through large pipes with a diameter of 1.5 m (at a pressure of 75 atmospheres). Since during transportation the potential energy of the gas is spent on the friction forces between the particles of the gas itself and on the friction between the pipe and methane, there are compressor stations that raise the pressure inside the pipe up to 120 atmospheres. Underground gas pipelines are laid at a depth of 1.5 m so that the structure does not freeze.
Types of gas pipelines
- Trunk. The pressure in the system is 6-12 atmospheres maintained until the gas distribution station, which reduces the pressure to the desired level.
- Medium pressure lines. The pressure in the system is 3-6 atmospheres.
- Low pressure lines. The pressure during operation is from 0.05 to 3 atmospheres. This is the pressure in the gas pipe in an apartment or in a private house.
Distribution and control devices
- The gas pressure regulator is equipment for controlling the flow of the working medium.
- Gas control systems automatically shut off the gas supply.
- The reduction unit reduces the fuel pressure.
- The switch redistributes the main stream into separate branches.
- Pressure gauges and flow meters allow you to monitor the parameters of the system.
- Filters clean the gas mixture from impurities.
All these devices ensure the safety of main pipelines and are part of the automatic parameter control system.
Security zones
If there is a construction of complexes or buildings that are not involved in the activities of the gas filling station system, the observance of the security zone, the length of which depends on the type of protected structure, will certainly be taken into account. Its dimensions:
- outside - 2 m on each side, even in cramped conditions;
- from the underground - 3 m from the delimiting gas pipeline;
- CNG stations and gas filling stations are limited to a vicious circle with a radius of at least ten meters from the established boundaries of the complex of capital construction projects.
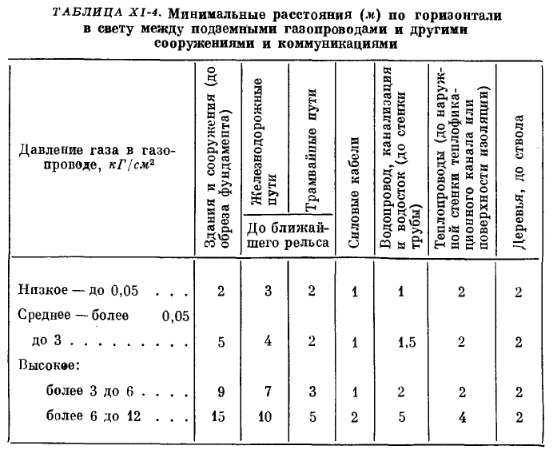
Regulatory distances - this is the norm of distance from the gas pipeline to communications. Water supply, power lines, roads and railroad tracks must be at a certain distance, which is regulated by the reference table. The minimum horizontal distances in the light are taken into account (they depend on the pressure of the gas pipeline) and other existing requirements - electrochemical protection, climatic features, the presence of PUE and high-voltage lines, etc.
The distance from buildings and structures to the gas pipeline must strictly comply with the standards. Remote standards are regulated by the pressure of the supplied gas and the type of gas pipeline built. For low pressure aboveground, only a protection zone is required, due to existing operating rules. If necessary, it should be reconstructed.
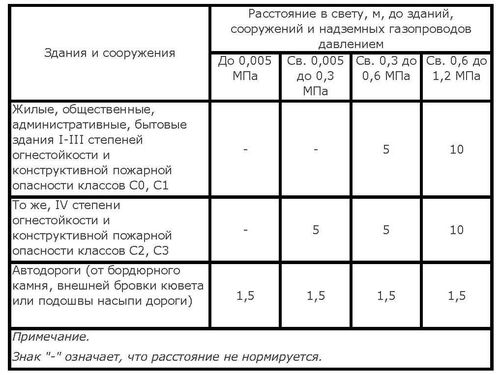
Nuances
An additional application requires compliance with distances from boiler rooms, as fire hazardous industrial structures. Two pipes - only 4 meters away from the residential building. Windows and roofs require at least 0.2 meters, and up to the door - 50 cm.
Distancing from warehouses may be regulated by the enterprise, but it should not be less than in SNiP 2.07.01-89 and SP 42.13330.2011. The same applies to laying at the foot of the slope, which can be regulated by the builders and the administration of Russian Railways (sometimes the distance from the gas pipeline to the railway lines decreases, but less than the standard is not allowed, especially near the embankment).
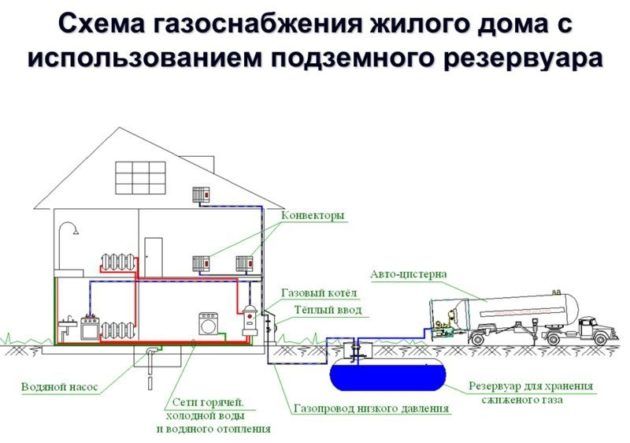
LPG tanks are taken into account separately. There are several types of them. For example, according to their orientation in space, they are divided into vertical and horizontal, according to their location - underground and surface LPG tanks, single-walled and double-walled LPG tanks - according to the degree of endurance of the structure. The volume, location and type of the complex regulate the distances. The standard GPC has a maximum pressure value.

With regard to tank installations, the standards of SP 62.13330.2011 are taken into account, but in each specific case, the minimum distance is taken into account depending on the characteristics of a particular gas tank. Underground deepen by 0.6 m, and the light distance between them is 0.7 m
A gas consumption metering station is a prerequisite when using such installations; mixing units, if necessary, are mounted 10 meters away
Underground ones are deepened by 0.6 m, and the light distance between them is 0.7 m. A gas consumption metering point is a prerequisite when using such installations;

The design of buildings of any plan should be carried out near the gas pipeline only with the knowledge of controlling and supervisory organizations, which calculate the norm depending on the type of structures and the pressure supplied by valuable chemical raw materials and fuel.
The average gas pressure in the gas pipeline is how much
To study the mode of operation of gas pipelines, gas pressure measurements are carried out at least twice a year, during the period of the highest flow rate (in winter) and the lowest one (in summer). Based on the results of measurements, maps of pressures in gas networks are compiled.These maps determine those areas where there is the greatest pressure drop of the gas.
On the way to the city, gas distribution stations (GDS) are being built, from which gas, after measuring its quantity and reducing pressure, is supplied to the distribution networks of the city. The gas distribution station is the final section of the main gas pipeline and is, as it were, the border between the city and main gas pipelines.
During a technical inspection, they monitor the oil level in the gear boxes, gearbox and counting mechanism, measure the pressure drop at the meters, and check for tight connections of the meters. Meters are installed on vertical sections of gas pipelines so that the gas flow is directed through the meter from top to bottom.
The gas enters the reception point at a pressure of 0.15-0.35 MPa. Here, first, its quantity is measured, and then it is sent to receiving separators, where mechanical impurities (sand, dust, corrosion products of gas pipelines) and condensed moisture are separated from the gas. Next, the gas enters the gas purification unit 2, where hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide are separated from it.
To check the operation of gas pipelines and identify areas with the highest pressure drop, gas pressure measurements are carried out. For measurements, gas control points, condensate-state collectors, inputs to houses or directly gas appliances are used. On average, one measuring point is chosen for every 500 m of the gas pipeline. All work on measuring gas pressure is carefully planned and carried out according to special instructions, which are approved by the chief engineer of the trust or office.
On fig. 125 shows a gas supply scheme for a large industrial enterprise. Gas from the high-pressure gas pipeline through a shut-off device / in the well is supplied to the central gas control point of the GRP 2. Gas flow is measured and reduced in it. In this case, high-pressure gas is supplied to shops No. 1 and 2, medium-pressure gas to shops No. 3 and 4 and the boiler room, and low pressure gas to the canteen (through the GRU). With a larger number of workshops and their considerable remoteness from the central hydraulic fracturing station, cabinet GRU 7 can be mounted in the workshops, ensuring the stability of gas pressure in front of the burners of the units. At high gas consumption in the shops, gas consumption metering units can be installed to control the rational and economical gas combustion.
To select part of the main gas and transfer it through the outlet gas pipelines under the necessary pressure to intermediate consumers, gas distribution stations (GDS) are built. Pressure regulators (spring or lever action), dust collectors, condensate collectors, installations for gas odorization (that is, giving it an odor) and measuring the amount of gas supplied to the consumer, shutoff valves, connecting pipelines and fittings are installed on the GDS. The mass of piping and fittings for GDS with a capacity of 250-500 thousand m per hour reaches approximately 20-40 tons.



