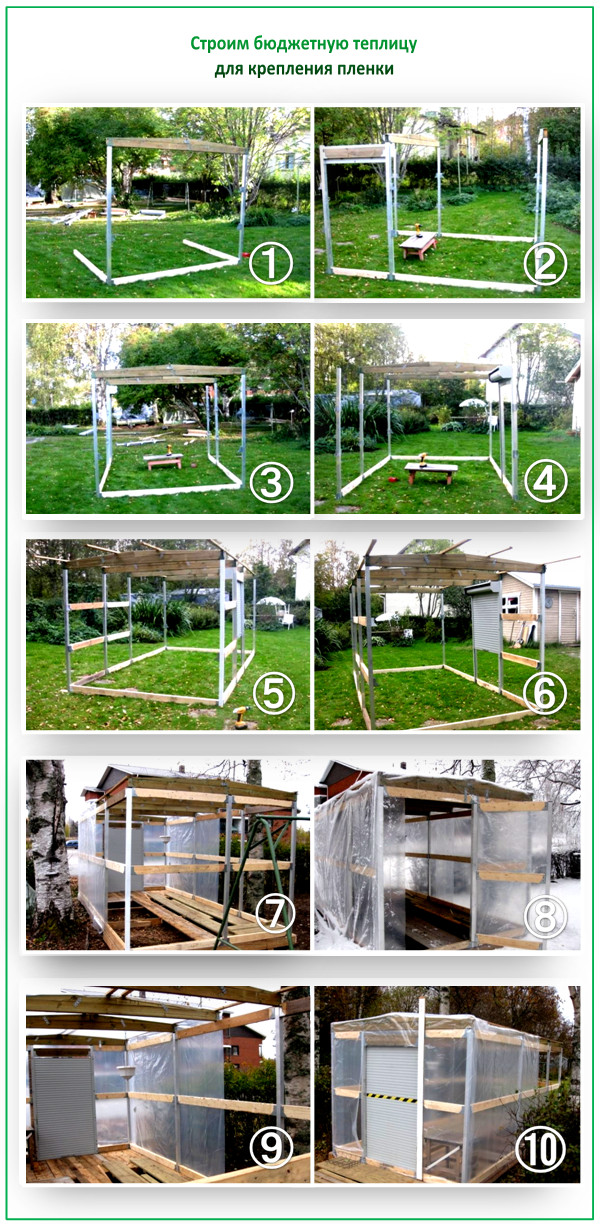
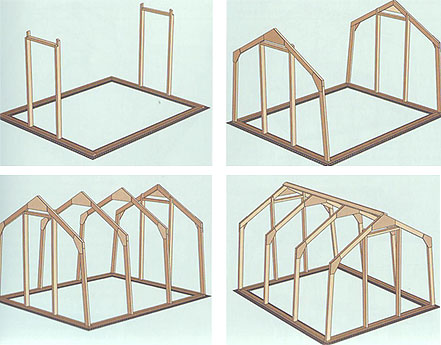
We build a budget version of the film construction
The wooden frame is ideally suited for the film - it does not heat up, and therefore does not heat it either. But today such greenhouses are being successfully built from other materials.
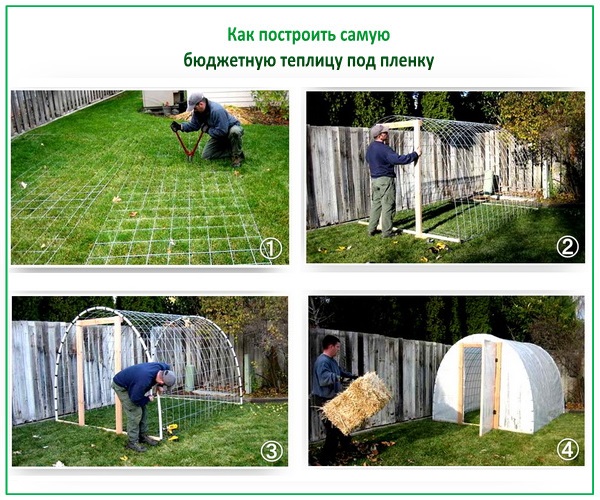
Option # 1 - arched greenhouse under the film
Let's go straight to the order of work:
- Step 1. We make the foundation. To do this, we attach anchors to the vertical arches and dig them into the ground. These are 40-centimeter pipe sections, to the end of which a tee is welded. It just keeps the greenhouse from wind loads. And to the other end we cook a cross, to one of the side exits of which we attach a piece of pipe of 80 cm - which is equal to the distance between the arches, and it is no longer necessary to cover it with a film. After that, finally, we weld the entire structure in one line.
- Step 2. Install the greenhouse. To do this, we dig a groove, and put the lower harness horizontally in it. After digging, we weld the arches - for this, we vertically weld a piece of pipe 5.5 m into the cross, and the other end of the pipe to the opposite side of the strapping. It turns out the arch.
- Step 3. Strengthen. At this stage, we mount longitudinal power elements - these are boards 10 cm wide and 25 mm thick. Soak all wooden parts with an antiseptic three times before installation.
- Step 4. We complete the ridge of the greenhouse. To do this, you will need help - one person will hold the wooden plank inside the greenhouse, and the other will screw it from the outside through the pipe with self-tapping screws for rigidity. In the same way, everything is attached from the outside - the whole structure is quite rigid and durable.
- Step 5. Install windows and doors. You can make them from wooden bars 50x50 mm. What design they will already be depends on what exactly you will grow in the greenhouse, and what kind of ventilation you need.
- Step 6. We process a tree. The lower bar of the end harness, which is in contact with the ground, is additionally impregnated with mining or antiseptic resins from the store - so that it does not rot in the ground.
- Step 7. We cover the greenhouse with a film and cover with earth those remnants of it that were on the ground.
After all this, we take care of how to reduce the overheating of the film in those places where it comes into contact with the frame. On hot days, the metal can heat up to +70°C!
Option # 2 - mesh frame greenhouse
A greenhouse that is durable and ideal for covering with a film can also be made from a conventional mesh frame. To do this, purchase a metal mesh with large cells in a building materials store. Take the one where the wire is thinner and lighter, then it can be easily bent and conveniently fastened.
But make all the necessary dimensions in advance - in such a greenhouse the plants should be good and free, consider the height of the structure. Also put the mesh on the floor - this is what will hold the entire frame of the greenhouse, and it is thanks to this that your greenhouse will be portable. By the way, take the grid there harder.
Make the doors to such a greenhouse the same as to any ordinary one - from rails, boards and bars, or simply tighten it with a film. And you will add structural rigidity with a flexible plastic pipe, the ends of which need to be stuck into the ground.
That's all - it remains only to cover the greenhouse with a strong plastic film. Minimum time, minimum cost, minimum effort - and a lightweight portable greenhouse is ready!
How to build greenhouses with multilayer film
Two layers of film will withstand a short-term frost without any problems - but if you are heating the greenhouse, this is not a problem at all.
And here is how the greenhouses are covered with three layers of film (which is especially important for the northern regions): the second layer is inside the frame, and between the two layers there is from 7 to 10 cm. in the center it turned out about 2 m, and on the sides - 1 m 20 cm.3 meters should remain between the crossbars, and take a film of the same width. Nail it with strips of conveyor belt. So inside the greenhouse, as it were, another one turns out, and between the films themselves there are two whole air layers. Summer residents call such designs "thermos" - they are so warm and comfortable for plants. But in the spring you can safely remove the third layer - it is not needed yet.
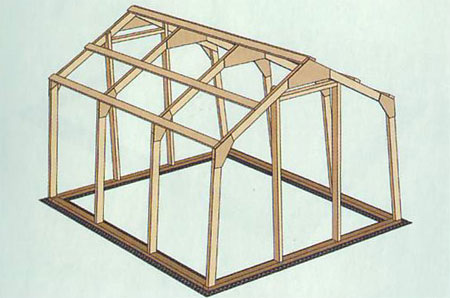
Option 1. Greenhouse with a wooden frame
What materials are needed
To put such a polycarbonate greenhouse on the site with your own hands, you will need the following materials:
|
material name |
section mm. |
length m. |
number of pcs. |
|
board section |
20x100mm |
3.7m |
8 pieces |
|
board section |
25x305mm |
3.7m |
2 pieces |
|
board section |
25x305mm |
3.05m |
2 pieces |
|
board section |
25x150mm |
3.048m |
1 piece |
|
board section |
50x100mm |
3.05m |
10 pieces |
|
board section |
50x100mm |
3.07m |
2 pieces |
|
board section |
50x100mm |
4.9m |
2 pieces |
|
bar section |
100x100mm |
4.9m |
2 pieces |
Additionally you will need:
- polycarbonate - panels with dimensions: 1600x2600mm - 2 pieces for end walls, 6 panels 1265x1585mm for roofing and 6 plates 1265x1690mm for walls;
- plywood - size 12x1220x2440mm, 1 sheet 8-12 mm thick;
- construction nails or screws;
- door hinges - two pairs;
- door handles and locks;
- soft or steel sheet for roofing;
- roofing steel cornice;
- wood preservative.
Directly for cutting panels, you need a construction knife with good blades and a steel ruler, preferably at least 1 meter long. As well as the following tools: measuring tape, hammer, circular saw, square, screwdriver, level and piece of cord.
Foundation installation
Do the installation of a polycarbonate greenhouse on a high-quality strong foundation. For this type of greenhouse, you can dig a strip pit yourself in a section with a depth and width of a shovel bayonet. Thanks to this, the floor in the greenhouse will be dry.
Install the foundation on a beam (sometimes called a half-beam) with a section of 50x100mm. Fold up the frame. Tie the bars together in half a tree and lay them on the waterproofing. Be sure to thoroughly soak them with an antiseptic and cover with mastic from rubber-bitumen mass.
Immediately orient the foundation to the cardinal points so that the installed greenhouse is well lit by the sun.
How to assemble a polycarbonate greenhouse support
The support for the ridge beam in the greenhouse are doorways. Place racks and crossbars on the end walls.
Assemble frames on level ground. It’s good if you have a conductor available - a special construction site with stops, in which it will be convenient to position, mark, cut and assemble parts. Attach the rafter beams to the wall with plywood brackets. Install the frames on the door frame.
It is necessary that the ridge corners of the frames lie strictly in a straight horizontal line. You can check this by pulling the cord between the extreme frames. They must be vertical. After that, install two skating boards.
To fix the frame, special beams are installed, with which the greenhouse frames are connected into one common structure. Runs (beams) are made along a horizontal line and at the same distance from each other.
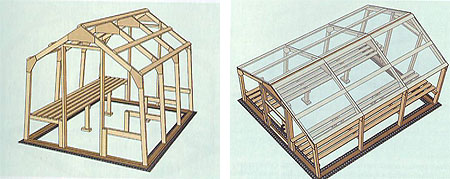
Attachment of internal equipment
The next stage in the installation of a greenhouse made of cellular polycarbonate is the installation of internal equipment. Almost everything is known about the installation of beds on the ground, so we will consider the option of installing boxes with plantings on long benches.
Install the benches on the support frames. Attach them to the wall beams of the greenhouse frames, and make supports from bricks or timber. Align the corners of the support frames with a cord and level. Screw or nail the slats onto the supports from above - to form a working surface.
Door setting
Next - install the doors in the opening. Take the door of a conventional frame structure on door hinges.In the middle of the door frame between the crossbars, install an inch-thick piece of board, which will act as a reinforcing joint. You can also put a doorknob on it.
Polycarbonate cladding
The installation of a polycarbonate greenhouse ends directly with paneling. The polycarbonate panel consists of two sheets interconnected by longitudinal ribs of the same material. Cut it with a construction knife along the ruler, without making much effort so as not to break it.
Screw the finished panels cut to the desired size to the greenhouse frames. We recommend using pan head screws with press washers for this. Due to the increased surface area and reduced height, this type of head is particularly suitable for clamping sheet materials. To make everything even more accurate, fasten the screws through a lining made of metal or plastic. Cover the panels facing the ridge with special elements made of roofing material or steel. After that, your greenhouse is ready.
What is better for a greenhouse fabric, polycarbonate or film
What coating should be used to finish greenhouses so that the plants are in ideal conditions for germination and development? What to choose: woven or non-woven material? This is the question that gardeners ask themselves when they get up before the construction of greenhouses and hotbeds. The choice of canvases for today is huge and it depends on various factors, for example, on cost, characteristics, or on external data.
Types of coverage and their characteristics:
- Silicate glass has excellent light transmission, as well as an unlimited service life, but it has a high cost, weight and material is very fragile, which makes it less popular. For greenhouses, glass with a thickness of 4 mm should be used.
- Cellular polycarbonate is much stronger than the previous material, and it is also resistant to various temperature extremes, ultraviolet radiation. It is elastic and can be finished with a variety of configuration designs. The thickness of polycarbonate is 6-16mm. In terms of service life, it is the most durable, since the canvas can be used for up to 20 years.
- Polyethylene film is the most affordable material and is an excellent way to shelter plants from rain and wind. Unfortunately, the canvas is not durable and can be deformed at the slightest mechanical impact. The film is purchased, as a rule, for one season.
- Acrylic canvases are a rarity for vegetable gardens, but the material has excellent strength and elasticity. There is no limitation on service life.
- PVC sheets are an innovation in covering greenhouses and small greenhouses. Such a canvas has excellent resistance to mechanical stress, temperature changes, as well as harmful UV rays.
- Non-woven covering material can be used up to 6 seasons, it perfectly passes moisture and prevents the penetration of the harmful rays of the sun.
Under such a fabric, the plants will be in an optimal microclimate, which means it will be an ideal option for growing a rich and high-quality crop.
Cellular polycarbonate is the leader in sales of the modern market
Why do most summer residents still prefer cellular polycarbonate? It's all about durability - you only need to build such a structure once, and you won't have to think about repairs anymore. It remains only to grow and enjoy the harvest.
Cellular polycarbonate is indeed much warmer than window panes - even with a thickness of only 8 mm, it already retains heat inside the greenhouse twice as well, and a thickness of 16 mm is comparable to triple glazing. For modern greenhouses, the material is sold exactly cellular - i.e. with cellular structure. It consists of an upper and lower layer, between which there are stiffening ribs.The sun's rays settle on the bottom and top sheet, but penetrate inside in different directions - scattering, which is especially good for the growth of the future crop. Manufacturers also claim that it delays the "hard" ultraviolet rays - exactly those that act destructively on plants, but the "useful" ones completely miss. Therefore, in such constructions, you can even sunbathe safely, without fear of getting burned - this will not happen.
According to its chemical structure, it is a polycondensation of diphenylolpropane with carbonic acid. And all derivatives of the latter are called carbonates - that's where the famous name comes from.
For the installation of polycarbonate, special aluminum fastening systems, profiles and other structures that can be ordered are traditionally used. But many summer residents are confused by the question of how to fix polycarbonate - is it really possible to do without branded thermal washers or is it more rational to use self-tapping screws for profiled sheet? Should the sheets overlap or use a special profile to connect them? To answer this question, let's look at the coefficient of thermal expansion - 0.068 mm from each meter per 1 degree. At first glance, this seems insignificant - but with a temperature drop from -20, as in Russia in winter to +30 in summer, a six-meter sheet will change in size by exactly 34 mm, and this is already quite noticeable. And the self-tapping screw, which is always in place due to the almost complete absence of thermal expansion in the metal, will simply “break” an oval hole in the material. At the same time, branded washers with a diameter of more than 30 mm completely seal the holes and are designed for any thermal deformations that are invisible to the eye.
Just pay attention when buying plastic thermal washers that they are too fragile after two years - due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation
And, finally, polycarbonate has high impact resistance - it perfectly tolerates strong hail and even a thrown stone will not particularly harm it. That is why the manufacturer generously gives a guarantee for such covering material for all 10 years. And sheets can be bent, unlike glass - and therefore such different structures are built from them today. A real outlet for landscape designers!
Related article: Which polycarbonate is better for a greenhouse - learning to choose
Greenhouse nonwoven fabric
Non-woven covering material has a lot of advantages, which is why it is so popular today.
Advantages:
- It is able to pass moisture, the rays of the sun, however, there is a certain stabilizer in the canvas, which is a component of the raw material from which a material is created that can prevent the penetration of harmful UV rays. It is the harmful rays that cause indelible harm to plants.
- Greenhouses made of covering fabric slowly heat up and cool down for a long time, respectively, inside the structure the temperature is maintained at an optimal level throughout the day.
- Under such material, the soil cannot dry out, even in dry weather, and during heavy rains, excess moisture is absorbed into the greenhouse cover.
- Removing and stretching the canvas is not difficult and does not take too much time. Due to the high strength of the material, it cannot be torn even under strong mechanical stress.
The average service life of nonwoven fabric is 3-6 years.
Assembling the greenhouse Dachnaya-Optima
Finally, consider the assembly of the reinforced greenhouse "Dachnaya-Optima" from the company "Volya".


Prices for the greenhouse "Dachnaya-Optima"
greenhouse dacha optima
Step 1. In pairs, collect the upper arcs (4c), connecting them with each other with runs (2). Attach the horizontal ties (9) and end top ties (5) to the arcs of the ties.

 Stages of assembly of arcs
Stages of assembly of arcs
Step 2. Attach runs (2) to the just assembled arcs.
 Purlin fastening
Purlin fastening
Step 3Then, on one side of the partially assembled frame, attach the lower arcs (4n) to the upper arcs (4c), and then the runs (2) to them.
 Fastening of the lower arcs and runs
Fastening of the lower arcs and runs
Step 4 Repeat step 3 on the other side of the frame.
 The same actions must be performed with the second side of the frame.
The same actions must be performed with the second side of the frame.
Step 5. Now attach the parts that are needed to fix the greenhouse if it is installed in the ground, and not on the foundation. These are racks (1) and supports (3). They will help the greenhouse stay in the ground.
 Fastening parts for installing the greenhouse in the ground
Fastening parts for installing the greenhouse in the ground
Step 6. Pull the wire bandage into the free hole of the support (3).
Step 7. Install the bottom end ties (6, 6k), as well as the doorway pillars, upper and lower (7 and 8).
Step 8. Now, inside the partially assembled frame, on each supporting arc, install the side struts (10), which are obtained by assembling from two identical parts. Install the side strut spacer (part 11) with one end at the junction of the side struts (10), and with the other end on the supporting arch. Connect the tie-rods to the side struts with stiffeners (18).
 Scheme of installation of side struts
Scheme of installation of side struts
 Installation of side struts
Installation of side struts
Step 9 Assemble the end doors from the parts: vertical door (12), horizontal door (13), diagonal door (14), diagonal door trim (15). Collect vents from horizontal vents (19) and vertical vents (20).
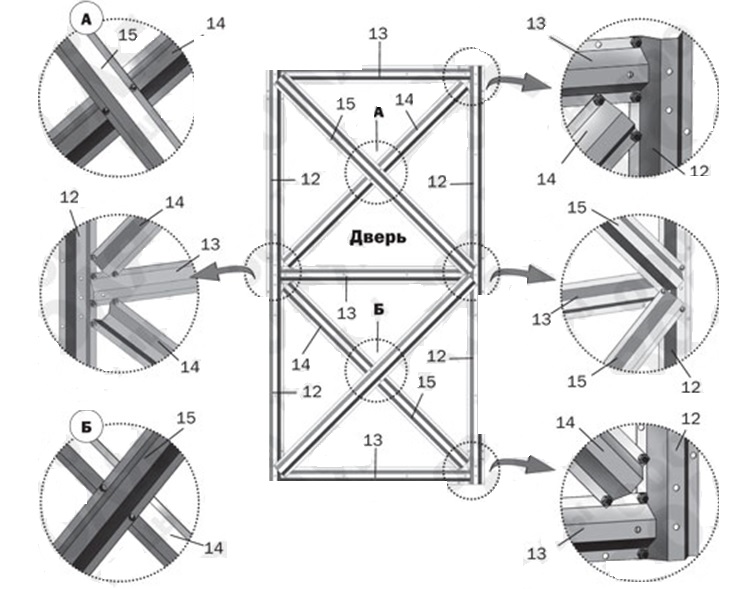
 Window assembly scheme
Window assembly scheme
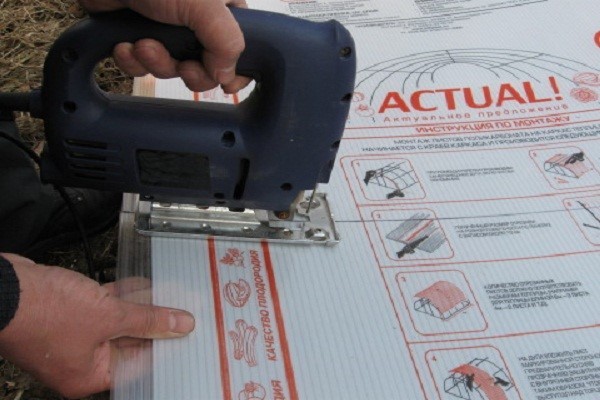
Step 10. Start cutting polycarbonate. To do this, cut a piece 1950 mm long from one of the sheets of covering material. Attach it to the end of the greenhouse and mark the template along the upper and lower arcs (4c and 4n), remembering to leave an allowance. Align the edge of the sheet along the edge of the doorway pillars, upper and lower (7 and 8), and the upper edge of the material should be 3 cm higher than the lower edge of the end top tie (5). Cut out the resulting piece. Mark the rest of the sheet, as in the figure.
 Polycarbonate sheet cutting scheme
Polycarbonate sheet cutting scheme
 Cutting polycarbonate for the end part of the structure
Cutting polycarbonate for the end part of the structure

Step 11. At the ends, install the corners for attaching the cover.
Step 12. Cut pieces of the ridge panel cover in place from the remnants of the covering material.
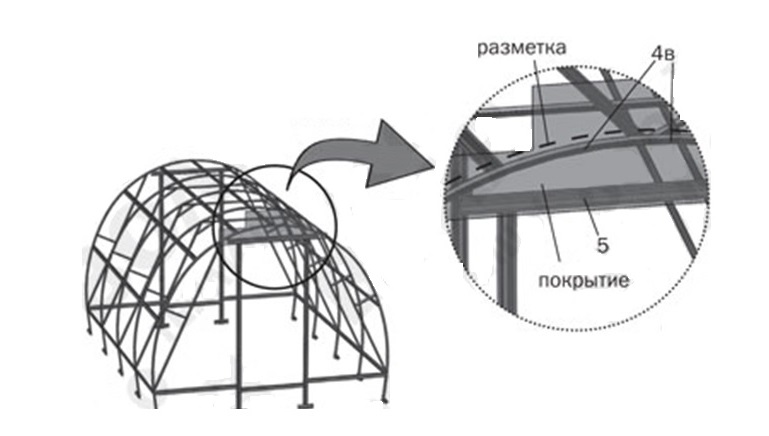
Step 13. Install the side parts of the end, as in the figure. Fasten the cover with screws and washers, holding it, along the details: the end lower screed (6k), along the edge of the doorway pillars, upper and lower (7 and 8), as well as at the corners. Trim the material along the arcs and attach the sealing profile.
 Coating fixing
Coating fixing
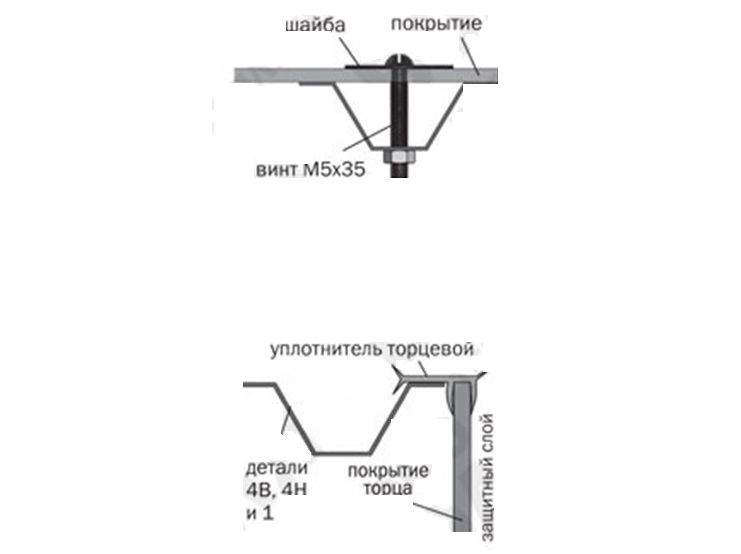
Step 14 Strengthen the polycarbonate with washers on the window and door, making an allowance on one side. Install the sealing profile along the door contour. Loops install over polycarbonate.
 polycarbonate door trim
polycarbonate door trim
Step 15. Attach the end plate (16) to the end cover, fasten it to the end top tie (5) through the cover.
 End plate fastening scheme
End plate fastening scheme
 Location of attachment points
Location of attachment points
Step 16. Do not forget to correctly install the vents and doors on the ends along with the seals.
 Scheme of installation of doors and windows
Scheme of installation of doors and windows
Step 17. Install the washers and hooks on the end.
Step 18. Attach the tubular doorway reinforcements.
 Mounting of tubular amplifiers
Mounting of tubular amplifiers
Step 19 Sheathe the greenhouse with polycarbonate. Don't forget to leave visors over the ends. Install a wire band (6) along the arc of the frame, starting from the middle of each sheet. It is pulled together with the lower bandage with the help of corners and screws.
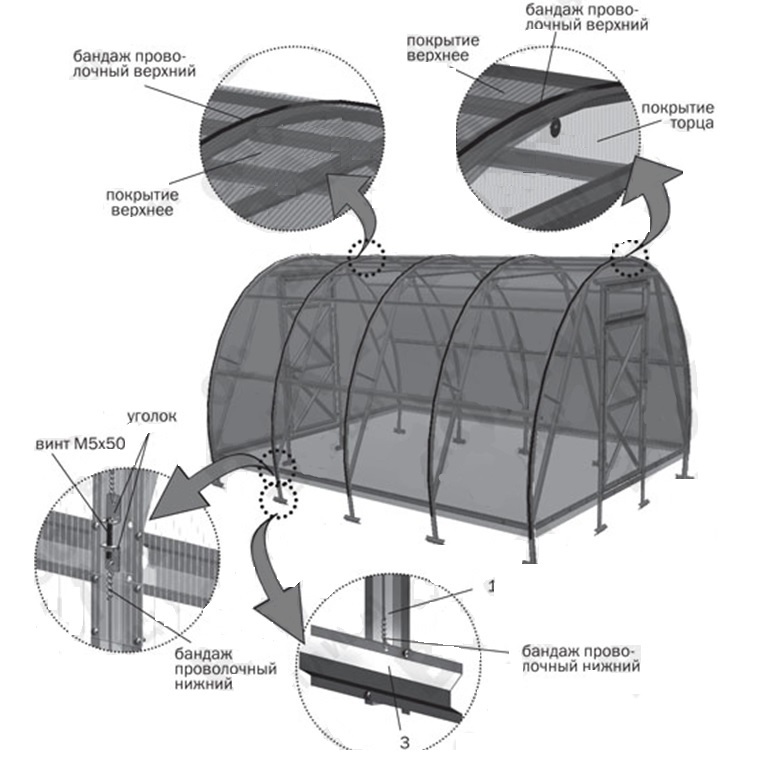
Step 20 Attach the polycarbonate to the purlins (2).
 Fastening polycarbonate on the girders of the structure
Fastening polycarbonate on the girders of the structure

Video - Demonstration of the strength of the greenhouse "Dachnaya-Optima"
Now you know everything about reinforced greenhouses and you can safely choose the one that you like the most.The main thing is to correctly assemble the structure, since the service life will also depend on the accuracy of installation and the correct installation of the structure.
Design features of reinforced greenhouses
Above, we talked about the fact that there are reinforced greenhouses and ordinary ones. Let us consider in more detail what are the main differences between these two types of structures.
- The material from which the frame is made. A reinforced greenhouse, as a rule, has a frame made of metal with a thickness of at least 1.2 mm, and often thicker.
- Arc structure. In reinforced greenhouses, the arcs, as a rule, are double. That is, a thinner arc is welded to each bearing part from the inside. It also gives additional strength to the frame.
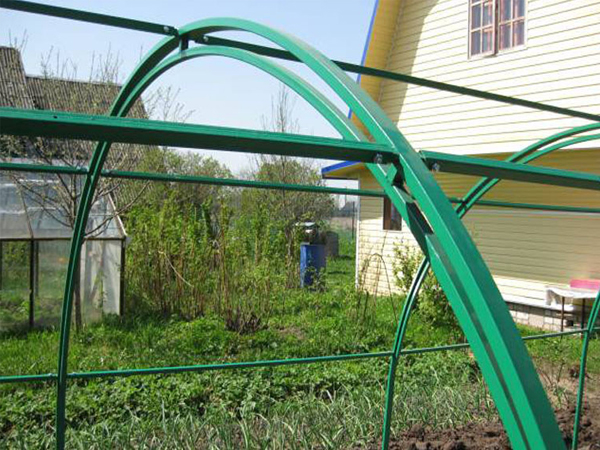

The presence of transverse and longitudinal ties (lintels). Additional ties, especially located in the upper part of the greenhouse, allow the frame to become stronger and more reliable.
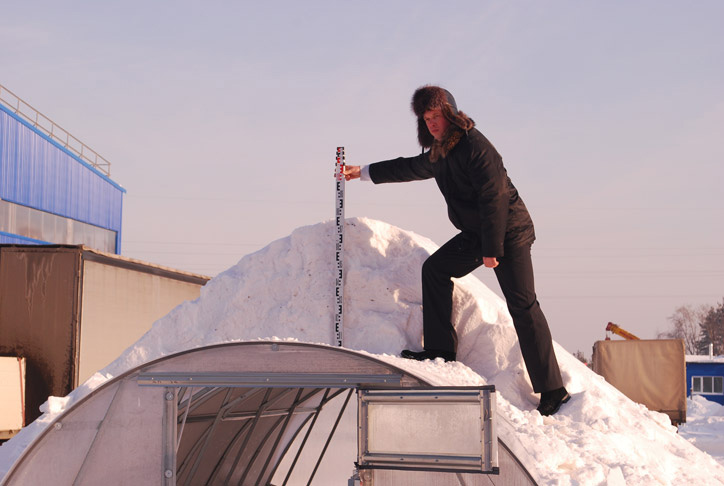
The presence of a horizontal guide at the arched greenhouse. This do, located on the roof under its very ridge, strengthens the weakest point of the structure - the upper part of the arch. As experts note, if snow falls on a greenhouse of this shape, then it will be held precisely in the area of \u200b\u200bthe ridge.
Distance between arcs. The smaller the gaps between the supporting arcs, the more evenly the load is distributed on the frame and the covering of the greenhouse. With a strong snow load, it is easier to cope with the greenhouse that has a step between the arcs of about 40-60 cm.
 The smaller the distance between the arcs, the more evenly the load is distributed
The smaller the distance between the arcs, the more evenly the load is distributed
Thickness and density of polycarbonate. The coating of a reinforced greenhouse cannot be thin - polycarbonate with a sheet thickness of less than 4 mm is completely unsuitable for this category of structures.
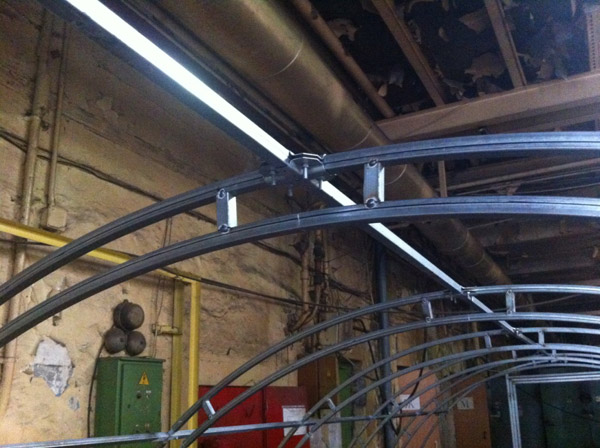
Availability of special connectors. Parts of some models of reinforced greenhouses are interconnected using cross connectors, which provide a stronger connection at the nodes between the elements.
 An example of the use of cross-connectors ("crabs")
An example of the use of cross-connectors ("crabs")
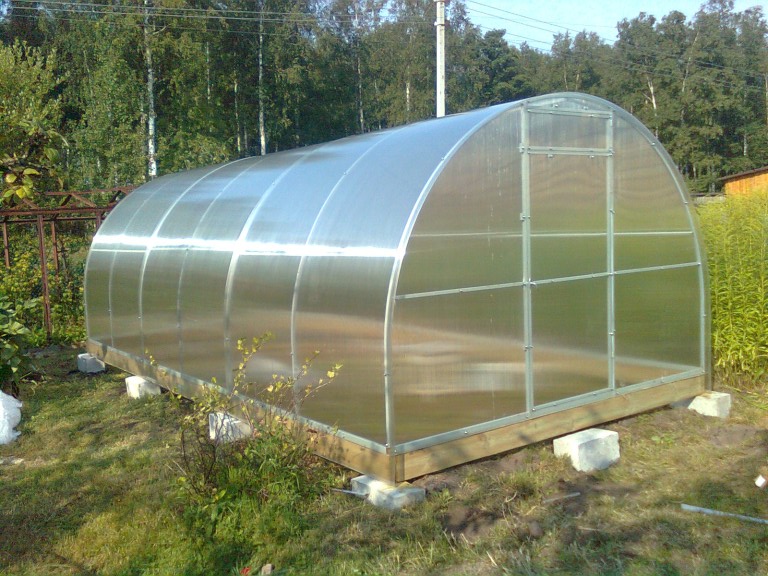
Arc section. The thickness of each arch must be at least 20 mm. Otherwise, the frame based on such elements cannot be called reinforced and even simply durable. With heavy snowfalls, a greenhouse on such a basis will easily collapse - a thin profile will collapse or break.

 Greenhouse made of solid arcs with a welded end
Greenhouse made of solid arcs with a welded end
As you can see, it is not so difficult to distinguish a reinforced greenhouse from a standard one.
The main thing is to pay attention to its device and immediately identify the main features of a solid and reliable design.
Based on the foregoing, we can highlight the main advantages of reinforced greenhouses:
- long service life;
- reliability;
- resistance to strong snow and wind loads.
Reinforced greenhouses have some disadvantages. The main disadvantage is the high price. Since the production costs of reinforced greenhouses are higher, their cost in comparison with standard structures will be very high. They are also much heavier than their lightweight ones, so this design is best placed on the foundation, especially on soft subsidence soils.

Summary
We have tried to cover the range of covering materials as fully as possible:
- from the most common and budget;
- to recently appeared on the market and, accordingly, more expensive.
We talked about the advantages of each of the coatings and did not forget to point out minor disadvantages.
Even watermelons can be grown in a greenhouse - the main thing is to choose the right covering material
The traditional video in this article contains some more useful tips from an experienced owner on the right choice and use of covering material.
Share: Nikolay Published: 11.06.2014
What other types of coverage are there?
Photo of polycarbonate for greenhouses and greenhouses
Small greenhouses are not advisable to cover with glass. It is a fragile and heavy material.It transmits ultraviolet light, which can be detrimental to plants.
In addition, glass greenhouses are difficult to install and there are problems with sealing. Imperfect glass was replaced by a better material - polycarbonate.
It has become relatively recent to use it as a coating for a greenhouse. It is cellular and monolithic.
Its popularity is growing every year faster and faster.
The properties of modern greenhouse polycarbonate, due to which it has replaced glass, are as follows:
- Durability - does not crack or break;
- Convenient for transportation - can be rolled up;
- Passes the ultraviolet necessary for plants;
- Plastic and non-flammable;
- Environmentally friendly;
- durable;
- Light;
- Not afraid of hail and wind.
The instructions for assembling a polycarbonate greenhouse tell you what tool it can be cut with and how to ensure sealing. Often stationary greenhouses are made in summer cottages. Previously, they were covered with glass or film, but with the advent of polycarbonate, there is a desire to replace the old coating with a new one.
This is quite possible and does not present any difficulties. On an old strong frame of any shape, it is easy to mount sheets of the desired size.
How to cover an old greenhouse with polycarbonate correctly:
- Calculate the amount of material, buy it with a margin;
- Prepare the necessary tools, it is easily cut with an ordinary knife;
- Self-tapping screws for fastening and rubber bands and profiles for sealing.
Polycarbonate sheets are attached to the greenhouse frame with thermal washers - this is a plastic washer on a leg, the length of which is equal to the thickness of the panel. They provide reliable installation.
Moreover, modern thermal washers have rubber gaskets, which prevents moisture and dirt from penetrating inside the greenhouse.
Thermal washer
A large selection of different materials will help you decide how to cover the greenhouse. The main thing is to create all conditions for the growth and development of plants.
Dome greenhouses
Another very beautiful shape that a greenhouse can have is a dome. And if the English one is something classic and stylish, then the domed greenhouse is just a modern and even somewhat “space” building. It is perfect for those who love new design styles such as high-tech.
 dome greenhouse
dome greenhouse
 Geodome and relaxation area in one bottle
Geodome and relaxation area in one bottle
A domed greenhouse (or geo-dome) is similar to a sphere consisting of segments that resemble honeycombs. Or rather, not even a ball, but a hemisphere standing on the ground. The window segments that make up the greenhouse can be triangular or hexagonal. The design strongly resembles a gazebo and looks like something cosmic, but at the same time very interesting, therefore it is often able to decorate a summer cottage itself.
 Amazing space interpretation of a domed greenhouse
Amazing space interpretation of a domed greenhouse
The frame of the dome greenhouse can be made of plastic, wood, metal. At the same time, it can be covered with film, glass and polycarbonate.
Such a greenhouse, in addition to beauty, has a lot of advantages:
- well lit from within;
- very reliable and not afraid of either winds or snowfalls;
- retains heat well;
- it is easier to create an optimal microclimate for plants in it;
- if the greenhouse is of sufficient size, then it is very convenient to work in it - the side walls do not press and do not interfere.
 Polycarbonate dome greenhouse
Polycarbonate dome greenhouse
If you like modern styles, then a domed greenhouse is definitely your option. Interestingly, the larger the design in size, the easier and faster it is to create.
Film for greenhouse
Film is one of the most common types of coating for greenhouses. It can be bought at any store and in every market. And it is inexpensive. But it becomes unusable literally in one season, and in places of attachment to the frame, the film wears out even faster. However, film greenhouses are quite practical.
The film scatters light well, which favorably affects the growth of crops.The significant disadvantages of this covering material include the fact that condensation forms on its inner side, which leads to surface contamination and the spread of diseases among greenhouse crops.