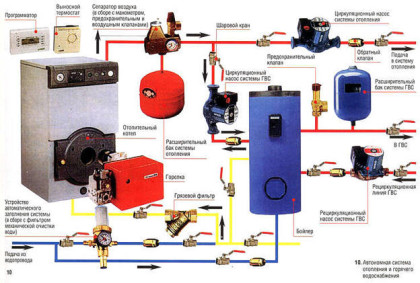
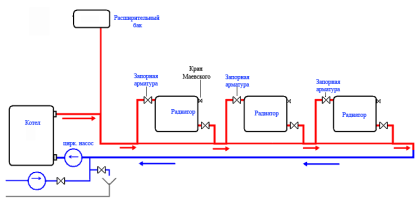
How to plan a forced circulation system
First you need to decide on the power of the boiler. This can be done again according to average numbers: 1 kW of boiler power is taken per 10 m 2 of area. If the ceilings are higher than 2.5m, a multiplying factor of 1.2 is required. It is also necessary to increase the power when located in the northern regions. These norms are for central Russia. If the house is located to the north, add another 30-50%. A margin is also required if the house is poorly insulated, because it is necessary to compensate for heat losses that escape through the walls / floor / ceiling. So in this case, you need to take more powerful equipment.
You also need to decide on the type of water treatment for domestic needs. If the boiler will heat it, the boiler power should also be increased for this - add 30-50% to the calculated boiler power. Read more about how to determine the power of the boiler for heating read here.
When calculating the heating system at home, you need to decide on the power. boiler
Then we proceed to calculate the number of radiators: at least one for each window, plus one radiator for the bathroom/toilet. In the northern regions, to save heat, radiators installed in the corridor / vestibule, which work as thermal curtains, performed well.
When calculating the number of radiators, they proceed from the rule: for each window - one radiator
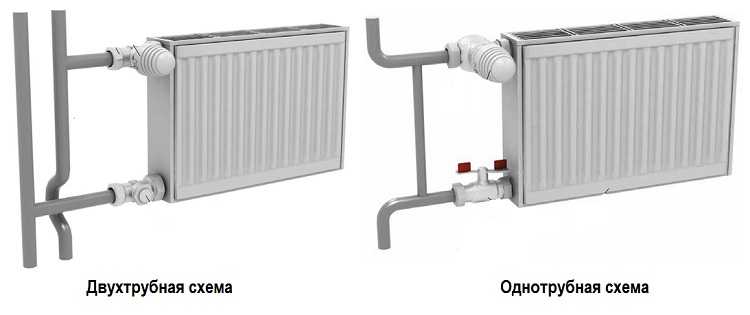
After you have decided on the number of radiators, you need to calculate the number of sections in each. In the general case, they are calculated based on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room: there are norms. Knowing the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, divide it by the norm and get the number of sections. But this is again an average approach. Here it is also necessary to take into account the type of wiring and the location of the radiator in the heating circuit. For example, one-pipe wiring. It is characterized by the fact that radiators located closer to the boiler receive a hotter coolant and heat up to higher temperatures. The farther the radiator is located, the colder the coolant washes it. Therefore, to compensate and equalize the position in the distant radiators, the number of sections is increased or they are installed with a larger area (height and power).
They do the same with two-pipe wiring, although the difference is not so obvious there: a coolant with the same temperature is supplied to the inlet of each radiator, just for those located closer to the boiler, the flow rate through the radiator is higher than for distant ones. To equalize the flows, thermostatic valves are installed on each radiator.
To regulate the heat transfer of the radiator and compensate for the system, thermostatic valves are installed.
But in a two-pipe heating scheme there is an option with a Tichelman loop. Such a heating scheme is initially compensated (if the radiators are installed the same). But it requires more pipes even compared to a conventional two-pipe.
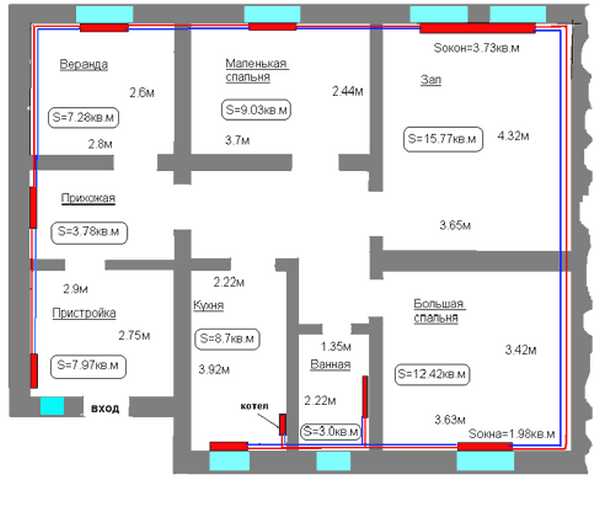
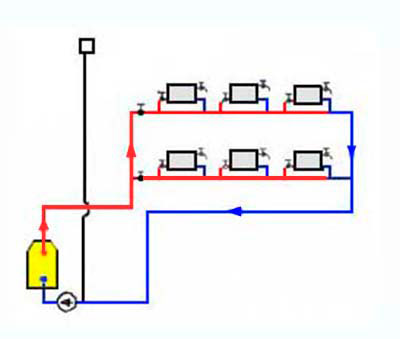
Scheme of a system with forced circulation. The house is two-storey. Two-pipe system with bottom supply, dead-end flow pattern of the coolant
We decided on the number, composition of radiators, type of wiring. It is necessary to determine the type and diameters of pipes and the type of system. What are the pipes for heating and the features of their use are described here.
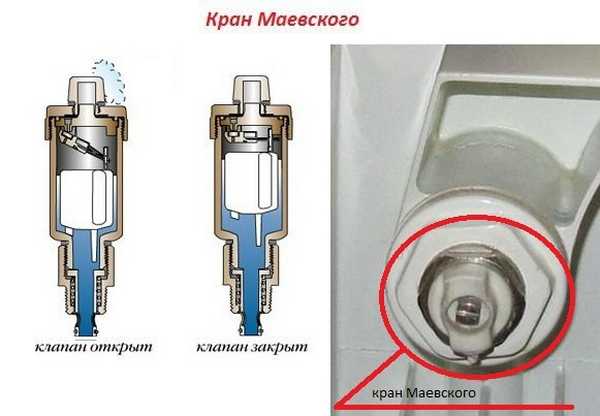
To bleed air from the system, a Mayevsky crane is installed on the radiators
When installing the system yourself, after the radiators are assembled and the pipes are connected, the entire system must be flushed. And only then connect the pump and boiler. In systems with solid fuel boilers, a safety group is required, which includes a pressure gauge, an air outlet valve and a blast valve, which is set to the operating pressure in the system and, if it is exceeded, automatically fires.
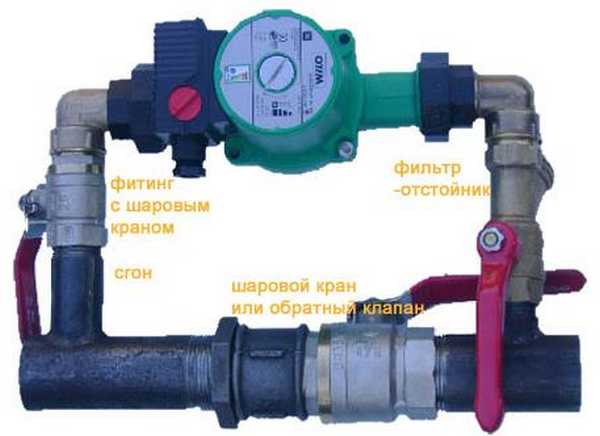
A filter must be installed at the feed line boiler inlet to protect the circuit and equipment from abrasive or contaminant particles.
The selection of a pump and expansion tank is irrelevant if you plan to install a wall-mounted gas boiler. Most models have a built-in expansion tank and pump.Then all that remains is to navigate by the volume of the system with which this modification can work. Based on this, select the diameters of the pipes and the area / power of the batteries.
How to choose a heating pump
Best suited for installation are special low-noise centrifugal-type circulation pumps with straight blades. They do not create excessively high pressure, but push the coolant, accelerating its movement (the working pressure of an individual heating system with forced circulation is 1-1.5 atm, the maximum is 2 atm). Some models of pumps have a built-in electric drive. Such devices can be installed directly into the pipe, they are also called "wet", and there are devices of the "dry" type. They differ only in the rules of installation.
When installing any type of circulation pump, an installation with a bypass and two ball valves is desirable, which allows the pump to be removed for repair / replacement without shutting down the system.
It is better to connect the pump with a bypass - so that it can be repaired / replaced without destroying the system
The installation of a circulation pump allows you to adjust the speed of the coolant moving through the pipes. The more actively the coolant moves, the more heat it carries, which means that the room heats up faster. After the set temperature is reached (either the degree of heating of the coolant or the air in the room is monitored, depending on the capabilities of the boiler and / or settings), the task changes - it is required to maintain the set temperature and the flow rate decreases.
For a forced circulation heating system, it is not enough to determine the type of pump
It is important to calculate its performance. To do this, first of all, you need to know the heat loss of the premises / buildings that will be heated
They are determined based on losses in the coldest week. In Russia, they are normalized and installed by public utilities. They recommend using the following values:
- for one- and two-story houses, losses at the lowest seasonal temperature of -25 ° C are 173 W / m 2. at -30 ° C, losses are 177 W / m 2;
- multi-storey buildings lose from 97 W / m 2 to 101 W / m 2.
Based on certain heat losses (denoted by Q), you can find the pump power using the formula:
c is the specific heat capacity of the coolant (1.16 for water or another value from the accompanying documents for antifreeze);
Dt is the temperature difference between supply and return. This parameter depends on the type of system and is: 20 o C for conventional systems, 10 o C for low-temperature systems and 5 o C for underfloor heating systems.
The resulting value must be converted into performance, for which it must be divided by the density of the coolant at operating temperature.
In principle, when choosing the pump power for forced circulation of heating, it is possible to be guided by averaged norms:
- with systems that heat an area up to 250 m 2. use units with a capacity of 3.5 m 3 / h and a head pressure of 0.4 atm;
- for an area from 250m 2 to 350m 2, a power of 4-4.5m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.6 atm are required;
- pumps with a capacity of 11 m 3 / h and a pressure of 0.8 atm are installed in heating systems for an area from 350 m2 to 800 m2.
But you need to take into account that the worse the house is insulated, the greater the power of the equipment (boiler and pump) may be required and vice versa - in a well-insulated house, half of the indicated values \u200b\u200bmay be required. These data are average. The same can be said about the pressure created by the pump: the narrower the pipes and the rougher their inner surface (the higher the hydraulic resistance of the system), the higher the pressure should be. Full calculation is a complex and dreary process, which takes into account many parameters:
The power of the boiler depends on the area of the heated room and heat loss.
- resistance of pipes and fittings (read how to choose the diameter of heating pipes here);
- pipeline length and coolant density;
- number, area and type of windows and doors;
- the material from which the walls are made, their insulation;
- wall thickness and insulation;
- the presence / absence of a basement, basement, attic, as well as the degree of their insulation;
- type of roof, composition of the roofing cake, etc.
In general, heat engineering calculation is one of the most difficult in the field. So if you want to know exactly what power you need a pump in the system, order a calculation from a specialist. If not, choose based on average data, adjusting them in one direction or another, depending on your situation. It is only necessary to take into account that at an insufficiently high speed of movement of the coolant, the system is very noisy. Therefore, in this case, it is better to take a more powerful device - the power consumption is small, and the system will be more efficient.
Local automatic temperature stabilization
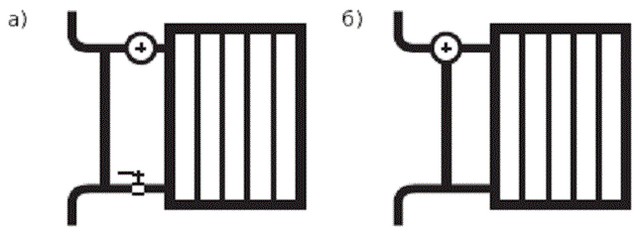
One-pipe adjustable radiator assembly with a through (a) or three-way (b) thermostatic valve on the top connection.
The adjustable radiator assembly of vertical single-pipe heating can be made with a through-flow (Fig.a) or three-way (Fig.b) thermostatic valve (thermostat). The piping unit branches the coolant into two flows: through the device and through the bypass. The diameters of the thermostat valve plunger and the opening for the passage of liquid are made to the maximum. The thermostat does not clog when the coolant is contaminated and ensures its free flow (when fully opened). Unauthorized replacement of the radiator, accompanied by the removal of the thermostat, does not lead to an imbalance of the entire heating system, as in the two-pipe version.
If the room air temperature exceeds the set temperature, the valve will close (go to the minimum mode), directing the liquid along the bypass past the radiator. Closing (minimum opening) of the valves of all thermostats in this riser increases the proportion of coolant passing through the bypasses from 80% to 90%, while simultaneously reducing the flow through the radiators, i.e. without changing the total cost.
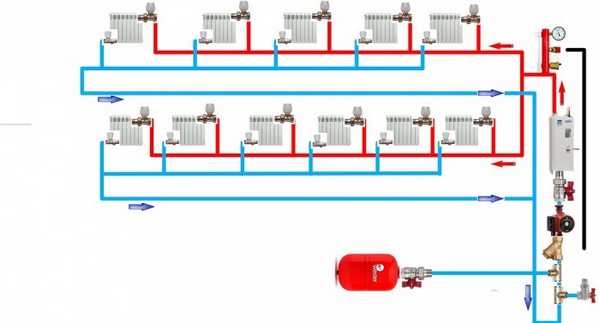
Elements and principle of operation of the system
One-pipe system, which is also called Leningradskaya. is a closed loop. In this circuit, both the supply and return pipelines are combined. The system is filled with antifreeze or tap water. For the latter, a separate pipeline with shutoff valves is provided. To drain the coolant, there must be a separate pipe with a valve leading to the sewer. It is desirable to equip the system replenishment unit with a filter.
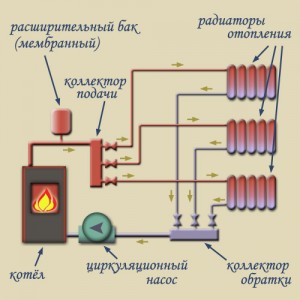
The main elements of the heating system
The coolant heated in the boiler coil enters the pipeline, passes through the risers and radiators, gives off energy, cools down, flows through the pump, which pumps the flow moving into the boiler. To prevent emergency situations, the system has a tank of a closed (membrane) or open type. Regardless of the type of tank, installation is carried out on the upper technical floor of the building (or the attic of the house).
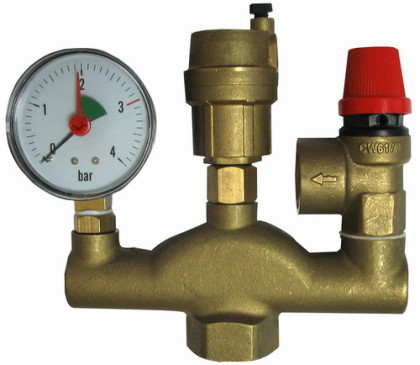
Also, the system must have a security group (sometimes called a security block). The device includes the following elements:
- air vent;
- safety valve;
- pressure gauge and thermometer (can be combined in a single housing).
In the event of an emergency situation associated with excessively high pressure, the safety team will equalize it and prevent equipment breakdowns and rupture of pipelines. With the help of the device it is easy to regulate the temperature and pressure in the heating system. Sometimes devices that are part of the safety group are mounted separately on the supply pipeline, cutting a safety valve above the level of the boiler equipment, but more often a single safety unit is connected to the heating system, reducing installation time.
Manometer and thermometer in one housing
Security group. Photo
Radiators in a single-pipe system can be connected in several ways - in parallel, diagonally, with bypasses, etc. At the installation stage, it is recommended to install temperature controllers on each radiator. In addition, to bleed air and prevent the formation of air locks, it is worth installing Mayevsky taps on each radiator or purchasing radiators with already installed taps.
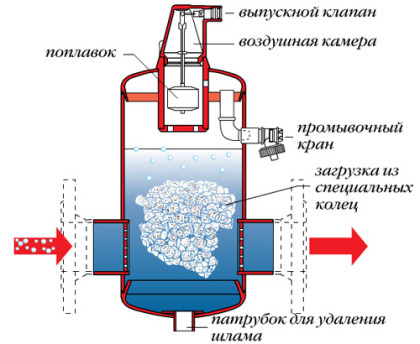
Air separator - an analogue of the Mayevsky valve
Separately about the pump and its choice
In systems with natural circulation, pipes of increased diameter are used, which is necessary to overcome hydraulic resistance by the coolant flow. The hydraulic pump, on the other hand, "pushes" the coolant, allowing it to overcome resistance even in pipes of small diameter.
In everyday life, pumps with a power of up to 100 watts are usually used. This device drives the flow through itself, increasing its speed, but without changing the existing volume. To select a pump, you must correctly determine the amount of required pressure.
To calculate, you need to know the power of the heater. This indicator is equal to the amount of water that passes through the boiler (flow).
Power (kW) = Flow (l/min)
If the boiler power is 50 kW, then the flow rate will be 50 liters per minute. Through a radiator with a power of 5 kW per minute passes 5 liters of water. The same principle is used for all sections of the chain.
where L is the length of the circulation ring.
That is, for every ten meters of the system, 0.6 kW of power is required. For a section of 50 m, a pump with a power of 3 kW is required. For a segment of 100 m - 6 kW. The table below shows the recommended pipe diameters, when choosing a pipe with a diameter less than necessary, it is recommended to purchase a pump with increased power and pressure.
Table 1. The ratio of the diameter of the pipeline and the flow rate of the coolant
The system may have not one pump, but two. In the event of a breakdown of one pump, the second (backup) will help prevent interruption in the operation of the entire heating system.
Pumping equipment should be mounted on a site with a cooled coolant, since the high temperatures of the liquid that passes through the equipment leads to a decrease in the service life of bearings, stuffing box, rotor.
In private houses, "wet" type circulation pumps without a throttle are often used. The pump body is usually cast iron, and the rotor is steel or made of durable plastic. Such models do not need lubrication and other maintenance for two decades. The coolant plays the role of lubrication and cooling.
Pipe selection
The cross section of the pipes is one of the decisive factors for circulation: the diameter of the pipes should not be as large as possible, but it should not interfere with the flow of water. As a rule, 100 W / m2 is needed to heat a private house. Then, for heating 25 m2, 2500 W is required, i.e. 2.5 kW. A certain pipe diameter corresponds to its own thermal load. Three main categories:
- ½ inch diameter - thermal equivalent of 5.5 kW;
- diameter ¾ inch - thermal equivalent 14.6 kW;
- diameter 1 inch - thermal equivalent of 29.3 kW.
In this case, to heat a one-story house of 25 m2, you need to use the smallest pipes with a diameter of ½ inch. The materials from which the pipes are made can be different: high-quality steel, pipes made of polypropylene are also popular.
Reasons for the lack of water circulation
Often, users of one- or two-story houses are faced with a situation where the heaters begin to work less efficiently. If there is no circulation in the heating system, there may be reasons for this.
The lack of circulation in the heating system can be caused by:
- system contamination. Batteries must be periodically flushed, otherwise the structure may become clogged over the entire diameter.If this happens, you will have to change the pipes.
- The pipe diameter is too small. And the smaller the diameter of the pipes, the greater the hydraulic resistance. This can also be the reason that there is no circulation in the heating radiator, or it is, but very weak.
- Airing the heater. To solve this problem, Mayevsky cranes are installed.
Very often, in heat supply systems with natural circulation, wet-type pumps with a power of up to 40-60 W are installed. You can read more about the operation of heat pumps for heating here. This is one of the options for improving the circulation of water in the heating system of the house. In addition, pumps can help save up to 25% on costs.
- How to pour water into an open and closed heating system?
- Popular Russian-made outdoor gas boiler
- How to correctly bleed air from a heating radiator?
- Expansion tank for closed heating: device and principle of operation
- Gas double-circuit wall-mounted boiler Navien: error codes in case of malfunction
Recommended reading
Steam heating: advantages and installation methods Infrared home heating: pros and cons Independent and dependent heating system: advantages and disadvantages Autonomous heating of an apartment and a private house
2016–2017 — Leading heating portal. All rights reserved and protected by law
Copying site materials is prohibited. Any copyright infringement entails legal liability. Contacts
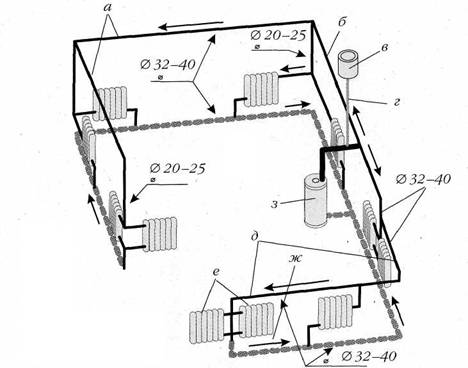
Types of single-pipe system wiring
In a single-pipe system, there is no separation between a direct and a return pipe. The radiators are connected in series, and the coolant, passing through them, gradually cools down and returns to the boiler. This feature makes the system economical and simple, but requires setting the temperature regime and correctly calculating the power of the radiators.
A simplified version of a one-pipe system is only suitable for a small one-story house. In this case, the pipe passes through all the radiators directly, without temperature control valves. As a result, the first batteries along the coolant turn out to be much hotter than the last ones.
For extended systems, this wiring is not suitable. after all, the cooling of the coolant will be significant. For them, they use the Leningradka single-pipe system, in which the common pipe has adjustable outlets for each radiator. As a result, the coolant in the main pipe is more evenly distributed throughout all rooms. The layout of a single-pipe system in multi-storey buildings is divided into horizontal and vertical.
Horizontal wiring
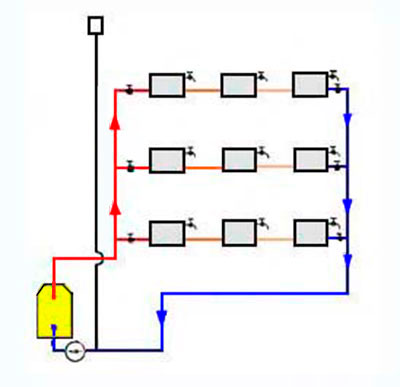
They are combined into a return line riser and fed back to the boiler or boiler. Temperature control taps are located on each floor, and Mayevsky taps are on each radiator. Horizontal wiring can be performed both by flow and by the Leningradka system.
Vertical wiring
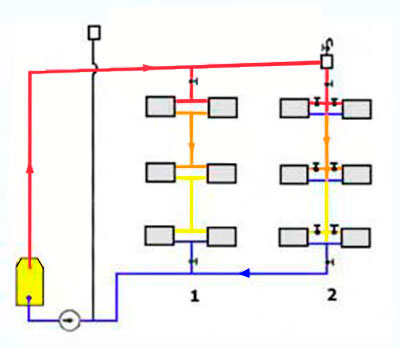
The choice of wiring system for a private house depends mainly on its layout. With a large area of \u200b\u200beach floor and a small number of storeys of the house, it is better to choose vertical wiring, so you can achieve a more even temperature in each room. If the area is small, it is better to choose horizontal wiring, as it is easier to adjust.In addition, with a horizontal type of wiring, you do not have to make extra holes in the ceilings.
Video: one-pipe heating system
Scheme of a single-pipe heating system
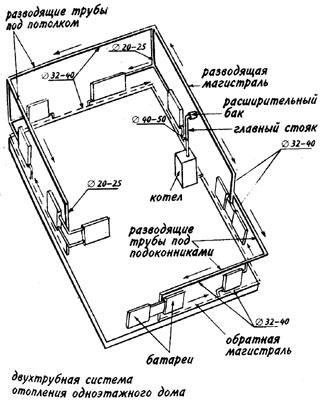
One-pipe heating scheme for a one-story house
Of course, all design and subsequent work always depends on what financial possibilities the owner of the project has.
As for technical equipment, at the moment there are all kinds of options on the market that are suitable for people with different income levels.
A circulation pump, if of course it is possible to install it, will increase the efficiency and effectiveness of the entire system. But it is not a mandatory device if your building has a small area.
If you are going to build a small country house or a cottage, also not large, then you can live without such a pump.
Be aware that if you want your home to have natural circulation, then you need to install the main pipe with a slope of half a centimeter.
The heating system consisting of one pipe includes:
- Piping wiring.
- Expansion tank. (Read how to calculate a heating tank)
- Boiler for heating.
- Wiring.
They can be of different types:
- radiant;
- Star-shaped;
- Collector.
Know that the heating system of a one-story house does its job very quickly, so it functions very simply. The main thing is to decide on the materials of which it will consist, and then already make fairly simple calculations regarding the heat loss that the house may experience in the future.
The water that is heated from the boiler enters the heating devices through the pipeline and supply lines to it. After it enters the radiators, they take away all its heat. Further, according to the same scheme, he returns back. An expansion tank is located at the highest point of such a heating system.
At the moment of movement through the pipeline, the transmission itself takes place directly, it is carried out through the walls of pipes and devices. At the moment, a single-pipe heating system is considered the most economical of all existing ones.
But such a heating system has a small drawback. It lies in the fact that the temperature at all points of the system is completely different. In the radiator located at the very end of the installation, the water will always be much colder than in the one located next to the boiler.
Watch the video on the example of the Leningradka system:
In addition, another disadvantage is that in order to shut off one of the batteries, you will have to turn off the entire heating network as a whole.
Scheme of a two-pipe heating system
Two-pipe heating scheme for a one-story house
A house no higher than one floor can be heated with a double-circuit design.
This is very convenient, because in this heating option the house will be warm all the time and will be supplied with hot water.
Single-circuit systems can be found quite often, for example, the first is used for heating, the second for hot water supply.
The most important thing in designing your future housing is to find the optimal balance between costs and heat losses, this is the most important thing. In addition, you should also take into account the power characteristics of the boiler and the efficiency with which the radiator battery will carry out its work.
In addition, you should also take into account the power characteristics of the boiler and the efficiency with which the radiator battery will carry out its work.
As an example, you can watch the video (above) on the relevant topic, then everything will immediately fall into place, and you will know what to expect from your heating system.
open type
The principle of operation is the same as that of the closed version.But in this case, excess coolant is forced out into an open-type tank, which is mounted under the ceiling of the room or in the attic.
An open tank is a tank with a leaky lid, which is supplied with an emergency overflow - a pipe brought outside the attic to the street or connected to the sewer.
The disadvantages of an open system include the constant supply of oxygen to the coolant, which accelerates the corrosion of the metal from which the circuit elements are made. Airing of the pipeline also occurs - to avoid this, radiators are mounted at a slight slope and automatic air vents - Mayevsky cranes - are mounted in the upper part.
In addition, the liquid from the open tank evaporates and it is necessary to add water regularly so that the open system can function normally. Water is poured into the tank manually from a bucket, or a water pipe with a valve is brought in.
The advantages of open-type tanks are affordable cost and the ability to make a tank of the required dimensions with your own hands.
Heating schemes for wooden residential buildings
It should be noted that the heating scheme in a wooden house is not easy. Of course, you can use electric, air and oven options. But most users opt for water heating systems.
A house made of wood has a high heat capacity, so more heat energy is needed to warm it up.

Heating scheme for a two-story residential building
A heating system with natural circulation of a two-story house is being implemented in two-pipe and one-pipe systems. They have one principle - a pipe rises from the boiler to the maximum height, and then the coolant is distributed over the heating structures. The difference lies in the following: in a two-pipe heating system, water that has already cooled down is collected in another pipe, which is connected to the return inlet of the heat boiler. As for the one-pipe system, a pipeline from the outlet of the last battery goes to the boiler return inlet. A two-pipe heating scheme with natural circulation is the most suitable option for houses with two floors.
A two-pipe system differs from a single-pipe system only in the order in which the heating elements are connected. Before each battery, it is recommended to put an adjusting tank. To ensure normal water circulation in a two-story house, there is always enough distance between the center of the boiler and the upper point of the supply pipeline. Therefore, the storage tank for heating can be equipped not in the attic of the room, but on the second floor.
Heating scheme of a one-story residential building
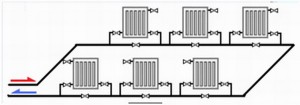
In the private sector, a horizontal heating system is widely used, which is classified into dead-end and associated water movement systems. With a dead-end system, each of the batteries is located further from the boiler. Such a system can be easily unbalanced. Therefore, they set it up for a very long time. It should be noted that the associated heating system, the scheme of which involves a greater consumption of pipes compared to a dead-end one, is used mainly in simple heat supply systems.
When choosing a passing system, it must be taken into account that the circulation rings must be the same.
All radiators in the system work as one. Today, flexible hoses are very often used for home heating. They are used to connect heaters to the heating system.