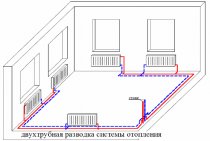
silicate plasters
The third type of decorative coatings for facades - silicate plaster can be called universal in all respects. At the same time, its particular efficiency was noted when using facades made of foam and aerated concrete blocks. However, those who are used to relying on expert advice can safely entrust the facade and walls of their house (whatever material they are built from) to silicate plasters.
Due to the presence of liquid glass (sodium silicate) and other additives, these plasters are excellent defenders of the facade walls of houses located near highways.
One of the main advantages of this coating is its wide range of colors and excellent durability. Thus, adherents of constancy - this is your choice. Note that the supporters of change are impressed by silicate plasters with the opportunity to experiment not only with color, but also with all possible and impossible textures.
Design features of fireproof facades
Limitations associated with facade insulation with extruded polystyrene foam. According to GOST 30244-94, thermal insulation in the form of polystyrene foam boards has a degree of flammability (P-G4). Ignition of the material begins at a temperature of 220-380 °C, self-ignition - 460-480 °C. The same class of fire hazard as part of facade systems is provided for polystyrene foam. In addition to rapid ignition, the situation is complicated by the release of combustible gases provoking rapid and intense combustion. To reduce the fire hazard, fire cuts are provided in the facade systems. The main purpose of the cut-offs is to stop the spread of fire between floors and along the outer walls.
The system of wet insulation of the facade must comply with the established GOSTs regarding the maximum load and resistance to tearing. The thickness of the plaster over the polystyrene boards must be at least 4-7 mm. In practice, this layer is often equal to 1-1.5 mm, which is a gross violation of fire safety requirements for facade systems. Decorative polymer plasters already when heated to 240-260 ° C lose their strength characteristics. Therefore, it is not recommended to use polymer plasters on polystyrene and foam boards. Fire-retardant plaster for the facade must withstand temperatures close to 1000 ° C. The destruction of the protective layer leads to an increase in the intensity of combustion, due to the fueling of the flame by the gases released. Thanks to the cuts on the wet facade, it is possible to stop the fire or, at least, reduce the spread rate. Be sure to frame window and door openings with non-combustible heat-insulating materials.
Facing facades with ventilated structures also has its own limitations and rules, primarily associated with greater flammability. The high class of fire hazard of the facade aluminum subsystem is due to the fact that there are voids between the finishing layer of the material and the thermal insulation, which provoke an increased upward movement of air masses. As a result, air draft provokes the rapid spread of fire. Modern thermal insulation makes it possible to do without these combustible materials. If a decision is made to use wind and hydro protection, it is imperative to make fire cut-offs in a ventilated facade
It is especially important to provide for cuts when using combustible insulation and cladding.
Hinged facade systems made of porcelain stoneware belong to the NG class. The weak point of the design is in the profile system, which is used for installation
Low-quality guides are already deformed at a temperature of 280-300 ° C, which leads to the collapse of the installed porcelain stoneware from the facade of the building. Another difficulty is that at a certain temperature, the plates begin to crack.
Fire safety requirements for ventilated facades require that inexpensive ACPs (aluminum composite panels) be abandoned. The ignition temperature of the material is 120 degrees. Cheap composite panels based on polyethylene are classified as hazard class G4. According to the PPB, they are prohibited from being used for high-rise buildings. The fire safety of hinged facade systems is checked in accordance with GOST 341251-2003.
Translucent facade systems generally tolerate high temperatures and surface heating well. The weak point of the translucent structure is the profile guides used, and the glass fixing sealants. Facade glazing is applicable for industrial and office buildings, provided that sealing compounds with high thermal stability are used.
Depending on the main purpose, the permissible fire hazard class of facades can vary from K0 to K3. The use of combustible materials, as well as errors in design decisions, lead to an increase in the coefficient to unacceptable values.
17. Thin-layer plaster, mesh plastering, rustication between slabs
Thin-layer plaster. Thin-layer plaster is applied only on stone, brick, concrete, reinforced concrete, cinder-concrete and other stone-like surfaces. On wooden, straw, reed and fiberboard surfaces, the thickness of the plaster must be at least 20 mm, regardless of the type of plaster.
With a coating thickness of up to 7 mm, a plastic solution is prepared and applied in one layer at a time, carefully leveling. With a coating thickness of 10 mm, the solution is applied in two layers: spray and primer. Before applying the solution, the surfaces are moistened with water. If thin-layer plaster is of high quality, beacons are arranged.
Plastering on mesh surfaces. Mesh surfaces prepared for plastering are painted with a creamy cement mortar or cement paste. Staining is repeated two or three times in 4-8 hours with a slight pressure on the brush. Sometimes a creamy solution is sprayed over the grid with a spatula from a falcon. The spray is applied in two to three doses two to three hours after each application. The solution covers the grid with a thin layer, giving it the necessary rigidity, and it stops vibrating. Then plastering is carried out in the usual way. The solution is often smeared with the back of the spatula.
The cement mortar is prepared in the following sequence. First, a dry mixture of cement and sand is made, fibrous additives are added there and everything is thoroughly mixed, then water is poured. Cement-lime mortars are prepared first, like cement mortars. After that, the lime dough is diluted with water, mixed and lime thick milk is obtained, on which the mixture is closed.
After the mesh cells are smeared or closed with a solution, a day later they begin to apply the solution in the usual way - by throwing or spreading.
If plastering is carried out along beacons, then after closing the cells of the grid with a solution and setting it (in a day or later), they begin to hang, make marks and beacons, which are plastered in the usual way. Lighthouses are best arranged in the same way as on concrete surfaces, using a rule with a level. Often lighthouses arrange it this way. First, nails are frozen into the solution, the surface is checked on them and marks are made on the nails, to which the rule is attached, and a solution is applied under it.After applying the soil, gypsum beacons are cut down, their installation sites are cleaned of gypsum, moistened with water, sprayed and covered with a solution, which is then leveled. After that, cover and grout are performed.
Finishing rustication between floor slabs. Before finishing, it is necessary to prepare the seams. They are cleaned with a steel brush or cut with a chisel. Then the gap between the plates is filled with tow, compacted, but in such a way that it does not reach the front surface by 15-20 mm.
The seams between the floor slabs are covered flush with the slabs with mortar, leveled and rubbed. To make sedimentary cracks between the plates less noticeable, a small semicircle is arranged along the mortar - rust. This whole process is called rustication.
There are two ways to finish rustication. The first is that the rust is cut through with a rustication over a rubbed, slightly seized mortar (Fig. 47, a). The second method is that the rust is pulled out over a fresh, unset solution, using the simplest template for this purpose (Fig. 47, b). It is made from a board of the desired width, cut at an angle of 45 ° on one side.
In order for the rustication to be rectilinear, they are performed according to the rule, which is attached to the ceiling with the help of two or three thin rails 10-15 cm long more than the height of the room (Fig. 47, c). Reiki are placed obliquely on the floor and first they press the ends of the rule with them, and then the middle of the rule with an additional rail. At the same time, the slats are slightly bent, springy and firmly press the rule to the ceiling. Rustovka is carried out according to the rule, cutting through the rust. If the rust is not clean enough, it is corrected with a trowel. Sometimes, rust is carried out with a trowel with a rail nailed to its canvas in the form of rust, after wetting everything with water. From this, the rust becomes cleaner.
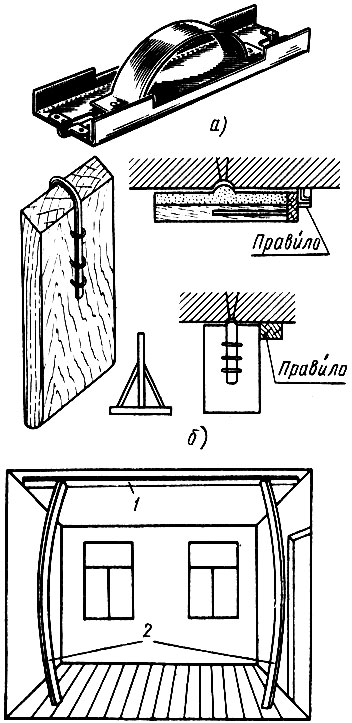
Pulling out the rusts with a template is performed in several steps, the solution is applied in thin layers. After cutting through the rust or pulling, the rules are removed and stripping and grouting are performed. Rust should be strictly against the seam or gap between the plates.
Steel elliptical bottoms in Samara at samara.sngexp.ru/catalog/dnishcha-i-zaglushki.
Types of facade plaster
Plaster mixtures are used both for leveling walls and for decorative finishes. They can have a different composition and differ in their characteristics:
- Mineral plaster is sold as a dry mix and is one of the most inexpensive types. The basis of the mixture is cement, to which various substances can be added to reduce water absorption, the development of fungi, and improve adhesion. The solution is easy to apply and has a high vapor permeability. When the house shrinks, such a coating may become cracked due to a lack of elasticity.
- Silicate plaster - durable, elastic, vapor-permeable, protects walls from moisture, does not attract dust.
- Acrylic plaster is more durable (up to 25 years) and elastic. Forms a layer that does not allow moisture to pass through, therefore it is not combined with all materials. Can be applied over foam insulation. It is not recommended to apply it near busy highways, as it tends to be polluted by dust.
- Silicone plaster is a modern coating with high elasticity, vapor permeability and antistatic properties. It has a long service life, is resistant to atmospheric influences, precipitation, aggressive environments. Sold ready for use.

Facade plaster for outdoor use
Thanks to modern brick, many buildings can be given five points for appearance. Wooden houses have always been and will be beautiful. However, in addition to these building materials, there are many others. They are no less practical and can be more attractive in terms of cost. All of them have one thing in common - they all (or almost all) require additional finishing, such as whitewashing or staining. However, its most popular and effective type is plastering.
The reason here is not only the desire to raise the aesthetic appeal, not only to "play with color", not only to improve the performance of the wall and foundation material, but also to protect the house, its walls and foundation.
Let's try to make out: facade plaster, in its properties, main characteristics and determine the optimality for finishing the house with your own hands.
Facade plaster - combination of types
Acrylic facade plasters
is a product of modernity. The complex formula of the main substance, combined with a whole set of components, gave them excellent performance in terms of vapor permeability, elasticity and resistance to temperature extremes.
Facade plaster bark beetle
On a note
The use of acrylic plasters minimizes the formation of mold. This is especially true in regions and places with high humidity. It should be added that acrylic facade plasters are among the most unloved environments for ants and other insects.
In aesthetic terms, it is acrylic that can give you fantasies in the form of imitations of "lamb" or "bark beetle".
It is also important that this type of plaster is sold ready-made and no additional manipulations are required for use.
SPECIFICATIONS
Facade decorative plaster is used both for internal and external works, it is applied on a prepared base with a reinforcing layer. Facade decorative plaster gives the facade of the building a finished look. Resistant to weathering, has high crack resistance and impact resistance.
Cement thin-layer plaster HAGAst Außenputz Fs-415 white
PURPOSE
Plastering walls and finishing facades of buildings and structures.
Alignment of ceilings and walls in wet rooms (including the walls of swimming pools).
Cosmetic repair of damaged concrete or plastered bases.
Substrates: brick, concrete, cement or gypsum plaster.
PREPARATION OF THE SUBSTRATE FOR PLASTERING
The substrate must be dry, strong, solid and must not shrink or warp. Pollution, dust, stains from oil products, oils and fats of various origins, peeling plaster or other coatings with poor adhesion to the substrate are removed. Protruding pieces of mortar, concrete or other irregularities are removed. Before applying the cement plaster, gypsum-containing and highly porous substrates are treated with a primer.
PREPARATION OF PLASTER MIXTURE
5.0-6.0 l of clean water is poured into the container (t 15-20°C). 2/3 bag of dry mixture is poured out, mixed, the remaining amount of the mixture is poured out and mixed again until a homogeneous consistency is formed. The plaster mortar mixture is kneaded mechanically using an electric drill with a nozzle (at 400 - 600 rpm). The resulting mixture of facade plaster is kept for 2-3 minutes, then mixed again. At 20°C, the prepared mortar mixture of cement facade plaster retains its working consistency for at least 4 hours.
APPLICATION OF PLASTER MIXTURE
The plaster mixture is applied to the wall with a metal spatula and a trowel. The plaster applied to the wall is aligned with the beacons with a metal rule. The permissible thickness of the plaster layer in one working pass is 5-30 mm.The application of the next plaster layer is allowed only after the previous layer of plaster has completely dried. After the plaster starts to dry, it is carefully sanded with sandpaper or other abrasive material.
Note: The ambient temperature during the plastering work should be in the range from +5°С to +35°С. During drying, the plaster must be protected from high temperatures and direct sunlight. If there are expansion joints on the base, then when applying the plaster, it is also necessary to make expansion joints, repeating their geometry and then filling them with polyurethane sealant.
TOOL CLEANING
Hands, tools and containers are cleaned with warm water immediately after using the plaster mixture.
PACKAGING AND SHELF LIFE
HAGAst Außenputz Fs 415 cement thin-layer plaster is supplied in three-layer paper bags with a polyethylene liner of 25 kg.
Technical characteristics of the plaster mixture HAGAst Außenputz Fs 415:
Application temperature range, ° С — from +5 to +35
Moisture content of the dry mix, %, not more than — 0.1
Maximum aggregate fraction, mm - 0.63
Water consumption for mixing, l / kg - 0.22 - 0.2 4
Mortar mixture consumption: kg/sq.m per 1 mm layer thickness - 1.5
Open time, min – 20
Life time, h, at 0 ° С not less than - 3
Compressive strength after 28 days, MPa, not less than — 12
Adhesion after 28 days, not less than 0.7
Frost resistance, cycles, not less — 50
Fire-retardant materials and compositions for facades
- Mineral insulation with NG class - able to withstand temperatures up to 1000 ° C. GOST allows the use of mineral insulation for the facades of high-rise buildings. If foam plastic is used in facade systems, it is mandatory to make vertical and interfloor cut-offs from mineral thermal insulation.
- Clinker facade thermal panels. Unlike composite materials based on polyethylene, clinker thermal panels do not burn and do not emit harmful fumes. When installing clinker systems, special fasteners are used for fire protection, where one steel profile is taken for each aluminum guide profile.
- Refractory plasters - do not eliminate the need for cuts, but allow you to slightly increase the fire resistance of the material.
- Fireproof tapes. The cut-off on the facade with different finishing systems can be made with tape material. Alternatively, the junction of a non-combustible and combustible facade system should be surrounded by cuts.
- Paints and pastes. The SNIP standards for fire protection of wooden facades provide for the mandatory manufacture of fire protection with an increase in fire resistance up to R 180. If additional insulation is carried out, NG class mineral wools are used.
- Fire belts in the insulation system of ventilated facades should be thought out taking into account the presence of combustible materials. Instead of waterproofing, you can use mineral insulation with a cached layer.
- To avoid the collapse of composite materials, the number of clamps is increased. The test method - by fire, showed that this measure allows, even with strong heating of the surface, to prevent cracked porcelain stoneware slabs from falling down.
After completion of the work, a fire inspection of the facade system is carried out. The effectiveness of fire protection, compliance of finishing materials with the requirements are checked. A decision is made to put the building into operation.
Fire-retardant treatment of facade structures
- Special varnishes and protective paints are applied to plaster facades. One of the beautiful and at the same time reliable solutions is decorative facade plaster, resistant to fire safety.
- Facade cladding made of wood is treated with varnishes and two-component compositions. The tree may require the use of additional biosecurity.Facade varnish for wood allows you to preserve the texture and appearance of natural material. At the same time, GOST requires the manufacture of cuts on wooden facades.
- AKP. The fire safety of ventilated wooden facades requires the treatment of aluminum rails with special compounds that increase fire resistance. For other types of materials, this norm is advisory in nature.
Types of facade plaster and their features
External work on the facade of the house is carried out using the following types of building and decorative mixtures:
- mineral compounds. They are based on cement, sand and additional polymeric substances that are used to improve the performance of the solution. The main advantages are high strength, reasonable cost, high vapor permeability, environmental friendliness. The disadvantages include insufficient resistance to deformation, under their influence, the coating cracks.
- Acrylic plaster mixes. Based on acrylic resin and synthetic binders. The advantages of this facade material include good resistance to temperature extremes, elasticity, protection against fungi and mold, vapor permeability, resistance to UV radiation. We also note a large selection of texture solutions - bark beetle, mosaic, pebble. The disadvantage is that it gets dirty quickly, therefore it requires constant maintenance in operation.
- Silicate-silicone plaster. The material combines the advantages of silicone and silicate compounds, is characterized by high elasticity, vapor permeability, low water absorption and resistance to fungi. The solution is recommended to be used as a finishing coating for thermal insulation systems of facades with mineral wool and polystyrene foam boards. Apply the plaster material on brick or concrete walls with a stainless steel float, which is placed at an angle of 60 degrees. The texture of the coating is formed with a plastic grater, which is held parallel to the surface to be treated.
- Silicone-based decorative plasters have maximum durability, high strength and resistance to mechanical stress - the facade of the house is protected from cracks. In addition, the coating has self-cleaning properties - it repels dirt and dust, has elasticity and good vapor permeability. The main disadvantage is the high cost.
The technology of applying thin-layer plaster
But here a reasonable question may immediately arise: how immediately? Even without installing beacons? But after all, according to the generally accepted technology of plastering, it can be applied immediately to walls, ceilings and partitions only when their deviations from the correct position in height are no more than 1:100 for the surface inside buildings, and in width and length no more than 1:200 to the side of buildings .
Of course, to perform such work requires greater accuracy of brickwork, but it is achievable. At least, not only in the middle of the last century, but even today, there are masons who are distinguished by the high quality of their work, which subsequently does not need to be repeatedly forged and covered over.
Plastering technology
The classic technology used for plastering facades involves the application of three layers. Consider the sequence of actions in detail:
- To apply the solution as accurately as possible on the walls of the house with your own hands, you can install beacons. To do this, at a distance of about 25 cm from the edge of the wall, a thick solution prepared in advance is applied pointwise (with a diameter of 5-15 cm), in increments of 50 cm.
- The lighthouse (metal guide) is sunk into the solution. With the help of the rule and the level, a vertical arrangement is achieved. The plaster protruding above the lighthouse is smoothed with a spatula.
- When the solution has hardened, the gaps formed under the lighthouse are filled with a solution.
- The second beacon is located on the other side of the wall (the optimal distance between the beacons is 1.7-1.8 m).
- For walls longer than 2 m, intermediate beacons are added (it is convenient to align them with a stretched cord).
- To apply the first layer of plaster (spray), the cement mortar is diluted with water to a semi-liquid consistency. The solution is thrown onto the wall with a ladle. The surface should be as rough as possible for better adhesion of the layers. Waiting for the layer to dry.
- Dilute the solution to a consistency resembling thick sour cream. You can do it yourself with a spatula or use an electric drill with a special nozzle.
- The solution is thrown onto a section of the wall of the house between two lighthouses 40-60 cm high.
- The trapezoid rule with a narrow side is applied to the beacons from below and gradually lifted, moving from side to side. Excess plaster is removed, the surface remains smooth. Waiting for the layer to dry.
- In conclusion, a decorative layer (coating) is applied. After it dries, if desired, staining can be done.
Decorative plaster
To create a decorative texture, thin-layer plasters on various bases are used. For do-it-yourself application, you will need a spatula and a stainless steel grater. When using a dry mix, you should not knead a large amount of mortar at once, since setting occurs quite quickly.
After 15-20 minutes, you can already start creating an invoice. To do this, you need a plastic grater or a special roller. Depending on the direction of movement of the grater, you can get a different pattern. The thickness of the grooves depends on the grain fraction, which is indicated on the package.
One of the most popular types of exterior decoration of houses can be safely called the plastering of facades. With the help of dry and ready-to-use mixtures on a different basis, you can create a reliable, durable coating for a house with an unusual texture. Having studied the application technique, you can do it yourself.
Properties of decorative exterior finishing of facades with plaster
Plastering the facade
The main purpose of the facade finishing plaster is to create an attractive design and protect it from all kinds of external influences that can contribute to destruction. This is ensured by the technology of applying facade decorative plaster and the fact that it has such properties that are advantageous over other similar coatings:
- It does not lose its qualities under the influence of wind, precipitation and ultraviolet radiation, in fact, it is a kind of facade protection.
- Shows resistance to temperature extremes and climatic features.
- Has high compressive strength.
- It is endowed with the ability to "breathe", that is, to pass air and steam out. This helps to maintain the original surface structure of the building.
- Improves the thermal insulation of interior spaces.
- It is an excellent sound insulator, preventing street noise from entering the house.
- Provides an opportunity for the implementation of a variety of design projects with a wide choice of colors.
- The technology of applying facade decorative plaster is very simple and easy. It does not require complex preparation of the base.
- All work can be carried out on their own, without involving specialists.
- Large selection of textures and colors.
- Cost advantage compared to other finishing materials. The price of each type of decorative plaster depends on the structure and the ingredients in its composition.
This informative and useful article talks about the features and benefits of using thin-layer plaster in construction and repair.
© Build-Chemi.ru. Copyrighted
Subsection: Special plasters
Technologies
Sgraffito technique - a step towards the perfection of your interior
Recently, very often, colored decorative plaster has been used as a finish, which is perfect for finishing the facades of buildings and various elements of architecture.
Silk plaster - a highlight in interior design
Many designers have recently often used silk plasters for wall decoration. What are they? Let's figure out what their beauty and zest?
Plaster: types, purpose, work technique
Plaster is a material intended for construction work. The technology for applying plaster is similar to the technology for putties with a slight difference - plaster is not polished with abrasive materials
Plastering surfaces by machine - advantages
Wall plastering is one of the important stages of finishing a room. For small volumes of work, plaster is applied manually, and for objects larger than 300 m2, machine application of plaster is required.
How to make 90 degree corners when plastering walls? The master reveals his secret
Do you know how to correctly set beacons and plaster walls? It's great. Do you get 90 degree angles? Check your finished walls with a square
Surface preparation for plastering
Plastering is considered the main work of leveling the surface, and is also a preparation for the next stage of repair. The plastering technology itself also needs a preparatory stage.
Plastering works. (stages)
As a rule, after all the preparatory manipulations with the surface, the plaster work itself has three main stages
Marble plaster: types, advantages, technology of use
One of the most popular ways to finish walls is the use of marble plaster, which, due to its appearance, is able to perfectly imitate natural stone, which creates a special feeling of comfort and wealth in such a room.
Machine plaster MP 75
Machine application plaster MP 75 is a highly adhesive, universal dry plaster mix based on gypsum and polymer additives.
Plastering wooden walls
Plaster is a material for finishing walls, ceilings, partitions and other surfaces.
news
Reliable protection for builders
By supporting the development of a work culture in various professional areas, the company…
SAINT-GOBAIN BEGINS PRODUCTION OF GYPROC "OPTIMA" AND GYPROC "STRONG"
In May 2017, two new products became available on the Russian market at once…
WEBER continues to localize the production of building materials
In May 2016, at the Saint-Gobain plant in Arzamas, Nizhny Novgorod Region…
The production of new cement plaster was launched at the Novosibirsk plant "Hercules-Siberia"
According to the press service of the Novosibirsk company "Hercules-Siberia", in ...
LKZ Raduga presents professional decorative materials ARCOBALENO
A new product on the Moscow market of paints and varnishes from LKZ Raduga, meet!
Acrylic…
Tizol announced the start of the development of a unique fire-retardant plaster
According to information provided by the press service of Tizol OJSC, located ...
Rainbow paint. Plaster in assortment
During the construction season, we restyled the label and expanded the assortment…
Bergauf presented a new specialized thermal plaster
The Bergauf company recently presented its next development. Received…