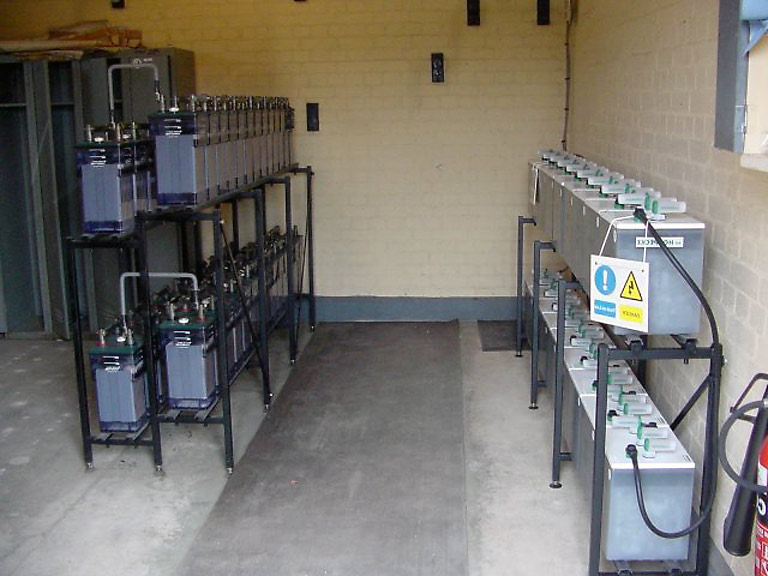
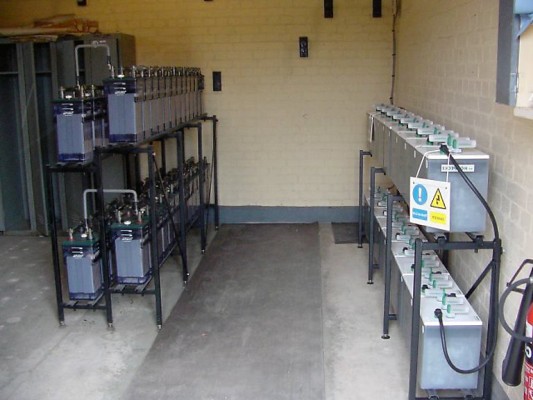
What is special about battery room ventilation
The specifics of the operation of battery stations is that during operation, heat and a certain amount of harmful and toxic components are released into the surrounding air. When a certain concentration of these chemical elements and substances is reached, workers may be poisoned by their vapors, the occurrence of respiratory diseases and the creation of an explosive situation.
Ventilation of battery rooms provides for several varieties and design schemes, including the use of main and additional sources of air exchange in the building, in accordance with the standards provided for by the building code.
The correct arrangement of the air exchange system in the battery station will exclude the formation of excessive accumulation of harmful substances (lead dust, caustic potassium, arsenic hydrogen, caustic sodium) and make the work of workers safe from the point of view of harm to their health and life.
Types of local fixtures
As auxiliary elements, installation is practiced as part of a common network of devices that ensure the elimination of harmful substances at the place of their occurrence.
These designs include:
- Open fixtures, which include racks, side suction, overturned exhaust hoods.
- Closed structures provide sealing of the space where toxic components are released; among these devices, special shelters, fume hoods, and battery boxes are the most well-known.
Despite the fact that local devices do not replace fans, their use significantly reduces the concentration of harmful substances in the battery room.
Ventilation device diagrams
The construction of ventilation involves the use of one of the following schemes, the choice of which is made depending on the capacity of the equipment, the volume of the room and other factors.
- With longitudinal supply, it provides for the horizontal movement of the volume of air masses along the structure. This option is characterized by ease of implementation, uniform air distribution and air exchange within the norms stipulated by snip.
- The transverse type is characterized by lower efficiency and has a number of disadvantages. The main ones include insufficiently active air circulation as a result of the close location of the openings for supplying fresh air and the air duct for removing exhaust air masses.
- The device, which provides for the bottom supply and removal in the upper part, allows you to effectively eliminate the hydrogen that collects at the ceiling. On the other hand, during the construction of channels on opposite walls, air circulation is ensured, which excludes the excess concentration of electrolyte vapors and the creation of dangerous conditions for the health and life of workers.
Finally
Planning and organization of ventilation systems for battery rooms should take into account a number of specific conditions and requirements of construction and design documentation. The most rational version of the device is the location of the inlet and outlet openings of the system on opposite sides using elements of local air exchange.
Fire safety battery
Batteries must be placed correctly, i.e. completely isolated from gas, water and sparks. The reason for this is the risk factors:
- the release of hydrogen by batteries, which forms a combustible mixture in the air;
- the acidity of sulfuric acid, which is part of lead-acid batteries;
- the toxicity of sulfuric acid and lead, which are found in many batteries.
If a fire breaks out in the rooms where the batteries are stored, it will be very violent, with explosions and the release of toxic, poisonous fumes, which is why the fire safety of batteries is so important.
Fire safety of battery rooms
The necessary safety of batteries is determined according to a special instruction developed on the basis of:
- Technical regulation 123-F3;
- PPR RF 390;
- VPPB No. 01-04-98;
- PUE;
- PTEEP.
According to the instructions, the following rules must be followed on all batteries:
- On the doors there should be inscriptions: "Battery", "Flammable", "Do not enter with fire", "Smoking is prohibited" or appropriate prohibitory signs.
- Rooms for storing, charging, repairing batteries should be separated from each other by non-combustible partitions.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the serviceability of seals and devices for self-closing vestibule locks.
- The supply and exhaust ventilation must be able to be blocked in order to stop the charging current when the ventilation is turned off.
- Wiring is carried out in specially processed tires, the terminals must be copper or lead-plated.
- If batteries are to be connected or disconnected, the charging current must be switched off.
- Batteries must be repaired in rooms separate from those where they are stored.
- Accumulators for storing acid batteries are painted with acid-resistant paint, alkaline - with bituminous.
- Glasses in battery windows are made matte or painted white with a special paint.
- If it is necessary to carry out soldering work in the charging room, stop charging the batteries and ventilate the room for at least 20 minutes.
- There must be a lock on the doors.
- Prohibited in batteries:
- smoking;
- storage of acids or alkalis;
- storage of overalls;
- installation in the same room of acid and alkaline batteries.
Failure to comply with the instructions is a direct path to disciplinary, administrative or even criminal liability.
Responsibility for the compliance of the accumulator with all the requirements of the industrial safety is borne by the head of the power supply, appointed by order of the head.
Battery fire fighting equipment
To ensure readiness to extinguish a fire and prevent the development of a fire, batteries provide:
- fire alarm,
- manual or
- autonomous fire extinguishers.
The premises must always have:
- improvised means - a container with sand, a shovel, an ax, etc .;
- carbon dioxide OT;
- powder OT.
Effective and reliable means are self-triggering devices based on capturing an increase in temperature by a sensitive sensor. Exceeding the critical level is a signal for self-spraying of the powder and eliminating the fire.
To accurately determine the number and type of fire extinguishers, it is necessary to make a calculation, during which to find out the category of the room in terms of explosion and fire hazard. Further, the battery is equipped with PT facilities in accordance with the PUE.
System classification
The classification of ventilation systems distinguishes them according to the following criteria:
1. Purpose:
- supply;
- exhaust;
2. Operating principle:
- natural;
- artificial (mechanical);
- combined;
3. Scope:
- general exchange;
- localizing;
- combined.
If everything is obvious with the appointment from the name, then the principle and scope require some explanation. Natural ventilation provides air supply due to its difference in density outside and inside the room, while artificial ventilation implies the presence of special devices (fans, ejectors, etc.) for the purposes of air exchange.
Combining them with each other is possible, but in this case, not in all combinations.If a natural air inflow is allowed with a mechanical exhaust, then with an artificial inflow, the exhaust must necessarily be artificial, in order to avoid the entry of polluted air into other rooms, due to the creation of excess pressure in the accumulator.
When choosing artificial exhaust ventilation, it should be taken into account that, due to the specifics of the chemical composition of the air, the fans must be of intrinsically safe design, and the devices that control their launch must be located in another room. Backup fans should also be included in the composition, starting work automatically in the event of a shutdown of the main ones. In addition, it is necessary to back up the mechanical system with natural ventilation. The volume of air exchange per hour must be at least two times, with a mechanical system, and at least once, with a natural one.
To increase the efficiency of ventilation in general, in volume, so-called local suctions can be additionally used - devices that help remove harmful substances directly from the sources of their release. They are of two types:
1. Closed:
- fume hoods;
- battery boxes;
- special shelters;
2. Open:
- airborne;
- overturned exhaust umbrellas;
- slotted (racks).
As the name suggests, the former enclose the space with the batteries on all sides and have doors or covers for maintenance, as well as separate air ducts for the exhaust. The scope of their application is limited to stations that are not too large in terms of the number of batteries. Open devices have a short range. Careful consideration should be given to their location, taking into account that, while effectively removing harmful substances, they do not interfere with the work of employees.
In any case, one localized ventilation (local suctions), as a rule, is not enough, since hydrogen will inevitably accumulate under the ceiling of the room. The general exchange system must provide at least one air exchange per hour. Exhaust air ducts (general and local) with combined ventilation can be combined.
Requirements for a space for charging electric forklifts
Nowadays, most enterprises are trying to operate warehouse equipment that runs on an electric motor.
Forklifts powered by electricity are more cost-effective, economical, compact, environmentally friendly, but despite all the advantages, it is impossible to do without the organization of the charging process and maintenance of their batteries.
correct organization of a room for charging the batteries of a loader contributes to the fact that the equipment will last longer.
During operation, the electric forklift does not emit harmful substances, which makes it the most popular in enclosed spaces.
But still, during recharging, the battery emits sulfuric acid vapors and hydrogen, which becomes explosive at a certain concentration; therefore, we need to properly organize a special charging room its batteries.
Forklift battery charging room requirements
Batteries are charged in a room with natural and forced-air ventilation in an explosion-proof design. Supply and exhaust ventilation must be separate from the general ventilation system.
Heating of the accumulator charging room should be carried out by calorific heaters located outside the heated room.
The heat supply must be through the ventilation duct. Heat appliances must not allow sparks to occur. The walls and ceiling are painted with paint resistant to alkalis and acids.
To organize a room intended for charging batteries, it will be necessary to make the necessary calculations: calculation of air exchange and calculation of the amount of vapor emitted.Ideally, it is better to entrust the calculations to a specialist technologist.
Personnel for work in the battery charging rooms must be instructed and specially trained. On the doors of the room there should be explanatory signs with the inscriptions: “battery”, “no smoking”, etc.
Buildings in which battery charging rooms are located must have II level of fire resistance and comply with all fire safety requirements. Usually, for charging gel batteries, fire safety requirements are less stringent.
Our company manufactures a range of devices for charging batteries of all types of forklifts, electric carts, reach trucks.
All products manufactured by our company are made according to high technologies, which contributes to uninterrupted operation for a long time.
How to properly charge a forklift battery
One of the most expensive parts of an electric forklift is the battery, so its maintenance and charging must be given the utmost attention. Proper handling of the battery can save the life of the battery and even extend its life cycle, while inept handling, incomplete charging reduce the operating period by 1.5-2 times
Proper handling of the battery can save the life of the battery and even extend its life cycle, while inept handling, incomplete charging reduce the operating period by 1.5-2 times.
It is worth thinking about these indicators, given that the battery sometimes costs more than one hundred thousand.
Features of proper battery charging
How to properly charge the battery so that it lasts a long time? There are certain rules:
- The battery must be charged exactly up to 100%. Insufficient charge leads to loss of resource.
- Connect the battery to the charger only when the charge level drops below 20%. We do not recommend working until you are completely exhausted, because. in this case, hydraulics and traction are lost.
- The battery should be charged no more than once a day. With frequent or incomplete charging, the battery stops accumulating and holding a 100% charge. Moreover, the resource is reduced quite quickly, leading to new costs.
- Periodically it is necessary to carry out an equalizing charge. This procedure allows you to correct some deviations in performance that appear during battery operation. The frequency of equalizing recharging depends on the age of the battery. Old units are charged in this way every 5 charges, new ones - every 10.
- Keep an eye on the charge level indicator yourself. Many batteries are automatically disconnected from the network when fully discharged, and this adversely affects their lifespan and quality of operation.
- Do not be lazy to carry out regular maintenance of equipment. Periodic maintenance will extend the battery life and save you money on buying a new one.
Air exchange schemes
The efficiency of air exchange depends not only on the principle of its operation, but also on the layout of the supply and exhaust openings. The most common today is such an installation of a ventilation system, when the supply air flows move at a height of 1.5 - 1.7 m from the floor, along the room and exit at the ceiling and at the floor on the opposite side of the inflow. Thanks to this scheme of air flow, there are no stagnant zones in the room. In practice, it looks like this:
- On opposite walls are two air ducts, with closely spaced openings. The inlet is located at the level of a person's breathing from one end of the battery shop, and the exhaust, in the upper part from the other end of the room. Air currents, as it were, “shoot through” it, leaving no pockets with poisoned air masses.
- The scheme is also widely used when the air flows go across, but it is not so effective due to the proximity of the supply and exhaust air ducts.
- Another common scheme in battery shops is when the vents are located on one wall. The supply air flow is supplied to the lower part of the room, at a height of 40 cm from the floor, and the hood takes polluted air masses from its upper part. This scheme is very effective in small rooms used for battery rooms.

Consumption depends on:
- The type of batteries used.
- their modes of operation.
- Their quantities.
- Battery charging method.
- From the selected air circulation scheme.
It is very important that the calculations are made correctly, and as a result, such equipment was chosen that will ensure the effective removal of polluted air with its minimum consumption.
Basic installation rules
The ventilation system for battery storage and charging areas includes air intakes and air ejection devices, an autonomous cleaning and filtration system, as well as heaters for heating air masses. In addition, air ducts, mechanical air extraction equipment and air distribution devices must be included.
Installation of industrial ventilation in such workshops is carried out according to strictly defined rules:
- Separate ventilation systems are installed for different types of batteries.
- During installation, a series connection scheme of the main exhaust fan with charging equipment is used. When the fan stops, the charger will automatically stop working.
- When installing the ventilation system, an autonomous air outlet is used. It is strictly forbidden to connect it to a ventilation shaft common with the enterprise.
- When installing natural ventilation as a backup, the ventilation ducts must be without valves and blocking equipment. It is allowed to install a fire-retardant damper in the ventilation shaft for ventilation.
- All ventilation equipment must be located in a separate workshop, and to ensure fire safety, it must be made in an explosion-proof design.
Requirements for air exchange systems
- The main requirement for such systems is the effective removal of harmful substances in the air masses.
- The system must be supply and exhaust. The hood should be carried out both from the upper part of the room and from its lower part (70% of the air masses should be removed at the top, and 30% near the floor).
- The exhaust ventilation device must provide at least two air exchanges in the battery shop.
Types of ventilation
Ventilation systems for battery rooms can be both supply and exhaust. In addition, according to the principle of action, they are:
- Natural.
- Incentive or mechanical.
- Combined.
Even in places of charging and storing batteries, general ventilation or local (local) ventilation can be equipped. General exchange - removes polluted air masses from the entire room, and local - from places of direct pollution.
The use of any particular system must be justified by calculations of the required air exchange.
The natural ventilation system in battery shops, as the main one, is practically not used due to its low efficiency. This type is necessarily made a backup in the event of a stop or failure of the mechanical ventilation system.
Fire safety requirements for battery rooms
According to the Intersectoral Labor Protection Rules for the Operation of Industrial Vehicles, the charging room must have the following compartments:
Charging room list:
- charging;
- repair;
- aggregate;
- acid;
- alkaline.
Banners should be hung on the common entrance door of the battery rooms, “Do not enter! Fire hazardous work is underway”, “Smoking is prohibited”.
Features of battery rooms
The repair department is equipped with lifting mechanisms. All equipment in the compartment is explosion-proof. In the alkaline compartment there is always a cabinet with a hood for charging and storing batteries.
Attention! Electrolyte preparation and charging of devices in the same room is prohibited. The dimensions of the charging room should allow you to freely charge the battery
The dimensions of the charging room should allow you to freely charge the battery.
All chargers and other equipment are placed in a separate room, limited by a fire wall from the charging compartment.
Opened terminal and plug substances must only be used in this compartment.
Attention! All rooms with a chemically active background must be equipped with general ventilation with explosion protection. For example, such rooms include - electrolytic, workshop, chemical warehouse
For example, such rooms include - electrolytic, workshop, warehouse of chemicals.
It is necessary to provide automatic blocking of the current for charging the devices when the ventilation is turned off.
To illuminate the charging and alkaline compartments, lamps of increased reliability against explosion are used. The repair department is equipped with the same equipment with a mains voltage of not more than 42 V.
All charging rooms must be equipped with fire extinguishing equipment!
If it is planned to serve only 10 batteries in the room, then only the repair compartment and the electrolyte preparation department can be included in its structure. If the company has less than 200 vehicles, then the electrolyte department is not required.
In order to maintain safety in the charging rooms, the following list of accessories must be available:
- in the charging compartment for acid batteries there should be: a sink with water, a towel, soap, cotton wool, containers with a 5-10% solution of baking soda.
- the charging compartment of alkaline batteries is equipped with a washbasin with water, a towel, soap, cotton wool, containers with a 5-10% solution of baking soda and a 2-3% solution of boric acid.
When organizing compartments for battery rooms, our company recommends taking into account the Intersectoral Rules for Labor Protection in the Operation of Industrial Vehicles, POT RO 14000-005-98. Position. High risk work. Organization of the event (approved by the Ministry of Economy of the Russian Federation on February 19, 1998) and other legislative documents in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
The 4AKB-YUG company is engaged in equipping all types of battery rooms with equipment of its own production.
We also independently develop and manufacture mobile battery workshops. We manufacture and sell cabinets and racks for placing, storing and charging batteries.
In addition to the standard products presented in the catalog of the company, we can make models to order of any overall dimensions, colors, as well as any type of execution.
Fire safety requirements for battery rooms - Fire safety
Fire safety shows the state of protection from fire - uncontrolled combustion that can cause enormous damage and threaten human life.
When a production or storage building is being designed, the fire safety category of the premises is immediately determined. It is calculated on the basis of the "Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements".
This is necessary for the installation of fire safety measures at this facility. The category is a classification characteristic that determines the possibility of a fire or explosion. There are 5 categories.
Application area
4.4.1. This chapter of the Rules applies to stationary installations of acid batteries.
The regulations do not apply to special purpose battery installations.
4.4.2. Accumulator battery rooms in which batteries are charged at a voltage of more than 2.3 V per cell are classified as explosive class B-Ia (see also 4.4.29 and 4.4.30).
The premises of rechargeable batteries operating in the mode of constant recharging and charging with a voltage of up to 2.3 V per cell are explosive only during the periods of battery formation and charging after their repair with a voltage of more than 2.3 V per cell. Under normal operating conditions with voltages up to 2.3 V per cell, these rooms are non-explosive.
Battery ventilation
March 10, 2009
Ventilation of the accumulator should be forced-air and exhaust; exhaust openings - ensure the removal of 1/3 of the exhaust air from the upper zone and 2/3 of the air from the lower; exhaust fans - explosion-proof. Premises equipped with acid accumulators must have ventilation providing the maximum permissible concentration of sulfuric acid mist of 1 mg/m3 at a level of 1.5 m from the floor; rooms equipped with alkaline batteries - ventilation that provides at least two air exchanges per hour and the concentration of hydrogen in the air is not more than 0.7% by volume.
Stationary batteries must be installed in a room specially designed for them with an entrance through a vestibule, the dimensions of which allow either of the doors to be opened or closed when the other is closed. The door from the battery room to the vestibule and the door from the vestibule to the production room must open outward, and both doors must always be tightly closed so that gases and electrolyte mist do not penetrate from the battery room into the production room. The door of the battery room must have a self-locking lock that can be freely unlocked from the inside without a key, and there are signs on the door with the inscriptions: “Battery”, “Do not enter with fire”, “Smoking is prohibited”.
From the “Safety Rules…”:
8.2.19. Accumulator and acid rooms should be equipped with stationary forced supply and exhaust ventilation with a mechanical drive.
In addition, for ventilation of accumulator and acid rooms, natural exhaust ventilation must be equipped, which provides at least one air exchange per hour.
In the vestibule of the accumulator, air support must be provided.
8.2.19. Ventilation is equipped separately for acid and alkaline batteries.
The switches for the ventilation systems of the battery should be located outside, at the entrance to the room.
It is necessary to provide for the interlocked switching on of the charging rectifier with the battery exhaust ventilation system and its automatic shutdown when the fan is not working.
8.2.21. On automatic telephone exchanges with a capacity of 500 numbers inclusive, in battery rooms equipped with closed and sealed batteries, natural ventilation is allowed in the amount of two air exchanges per hour.
8.2.22. The inclusion of battery and acid ventilation in the chimneys or the general ventilation system of the building is prohibited.
Gas release must be carried out through a shaft that rises above the roof of the building by at least 1.5 m. The shaft must be protected from atmospheric precipitation.
8.2.23. Ventilation equipment of exhaust systems should be located in an isolated room and provided in an explosion-proof design.
Ventilation equipment of supply systems can be provided in the usual version, provided that a self-closing return damper is installed in the area behind the fan at the point where air exits the ventilation chamber.
8.2.24. The suction of gases should be carried out both from the upper and lower parts of the room and from the side opposite to the inflow of fresh air.
If the ceiling has protruding structures or slopes, air extraction must be provided from each compartment, respectively, or the upper part of the space under the ceiling.
8.2.25. The distance from the upper edge of the upper ventilation holes to the ceiling should be no more than 100 mm, and from the bottom edge of the lower ventilation holes to the floor - no more than 300 mm.
The air flow from the ventilation ducts should not be directed directly to the surface of the battery electrolyte.
Metal ventilation ducts must not be placed under batteries.
8.2.26. The ventilation of the battery room should provide a temperature not higher than 25 ° C, the maximum allowable concentration of sulfuric acid aerosol 1 mg / m3 at a level of 1.5 m from the floor, the amount of hydrogen is not more than 0.7% by volume.
General requirements for battery ventilation
- Orientation to the maximum level of fire safety: after all, one of the key elements of the battery "exhaust" is combustible hydrogen gas. Therefore, smoking, the use of open flames near the intake or outlet is not allowed in the most categorical way. The minimum height of the exhaust riser above the roof level is 1.5 meters. And on the sockets of the supply and exhaust systems, a number of fine-mesh nets are mounted to trap sparks.
- Conscious rejection of the secondary use of supply air from other industrial premises, as well as the recirculation of the flow. Ventilation of the battery storage room involves the use of only outside air, purified from water, organic and mineral dust, as an inflow.
- Air intake into the exhaust duct not only at the ceiling level, but also at the floor level. The maximum removal of the lattice from the plane of the attic or interfloor ceiling is 10 centimeters. The height of the air intake grille above the floor level is 30-100 centimeters.
- Conscious rejection of the complex configuration of the duct network. Preference for direct-flow branch lines, inside which there will be no "pockets" for the accumulation of combustible hydrogen.
The design of the air exchange system in battery rooms
Battery shop
- Ventilation and heating of accumulator rooms are focused on the maximum level of fire safety. Therefore, these engineering systems will have to be separated from similar communications serving other production and functional areas of the building in which the battery room is located.
- It is allowed to use schemes of the following type: mechanical exhaust and natural inflow or mechanical inflow and exhaust. The use of a scheme with mechanical inflow and natural exhaust is unacceptable.
- In addition to the main exhaust system, slot-hole or side exhausts, exhaust hoods or cabinets should be installed in the battery room. These elements will have to be placed above each stand-alone battery, or rack (rack) with batteries. Moreover, all local suctions will have to be connected to the central exhaust riser using separate channels.
- The pressure equipment used must not generate sparks, even accidentally. This also applies to pressure units, and lighting fixtures.
- All pressure units must be duplicated by redundant units with the same characteristics. The connection of the backup fan is controlled by the status monitoring unit of the main pressure unit.