To ensure the safe operation of the electrical wiring of modern apartments, residual current devices (RCDs) or differential automata are increasingly being chosen today. The use of each of them ensures the early shutdown of the section of the electrical circuit in which there are insulation violations. In addition, with the correct organization of automatic protection of the electrical network using such devices, reliable disconnection of consumers in the event of overloads or short circuits is ensured. At the same time, the main difference between an RCD and a difavtomat is the need to install and use an additional circuit breaker with such a device.
It should be noted that for the correct functioning of the protection against high differential currents, it is necessary to have a three-wire single-phase system, which includes a ground wire. Such a wiring system is now ubiquitous in new buildings, but is extremely rare in old buildings.
To answer the question of how an RCD differs from a difavtomat and which device is more preferable to choose for use in your apartment, you need to familiarize yourself with their main technical characteristics, principles of operation, as well as design and operation features.
RCD application
Residual current device is used for switching in a network supplying groups of consumers with the flow of currents acting under normal operating conditions.
The main task of the RCD is to turn off a section of the electrical system if a differential current occurs in it that exceeds the allowable value.
The occurrence of leakage current is explained by the presence of some insulation resistance of the wiring and electrical consumers. Since this resistance cannot be infinitely large, the so-called normal leakage current will always flow through it, the value of which must be within certain allowable limits.
In order to better imagine what undesirable processes occurring in the power grid it protects difavtomat or RCD, consider the following schemes.
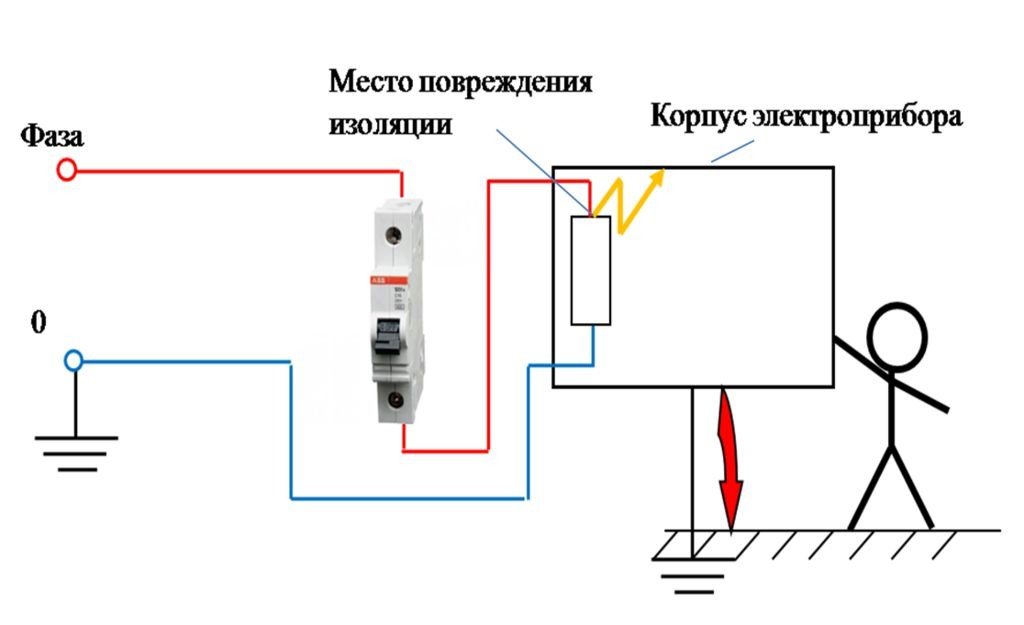
The first of them shows a case of electric shock to a person, which occurs as a result of touching an ungrounded body of an electrical appliance with broken insulation. In this circuit, there is a circuit breaker that disconnects its contacts in the event of an overload or short circuit, but such protection does not work when a phase is shorted to earth.
The second figure shows the leakage current path when the insulation of the grounded housing of the electrical appliance is broken. Since the resistance of human skin is much higher than the resistance of the ground loop, in this case, electric shock does not occur. However, the metal parts of the housing have a certain potential with respect to ground.
The danger of such a situation lies in the fact that when using conventional circuit breakers, in the event of a significant decrease in the insulation resistance of electrical appliances, the consumer is not automatically disconnected from the network.
The flow of leakage current causes heating of the ground connections to the case, which increases their resistance. In turn, air humidity, the condition of a person's skin, the material of shoes and the floor in the room, as well as many additional factors affect the value of the resistance of the body-man-ground circuit. If we take into account the peculiarities of the operation of electrical appliances in places with high humidity (kitchen or bathroom), then the risk of electric shock remains quite high.
In addition, the flow of current through the broken insulation causes it to heat up and further destruction. In certain cases, this may cause a fire.
The principle of operation of the RCD is based on the constant measurement of the magnitude of the differential current. While it lies within the permissible limits, no action occurs, but as soon as this value exceeds the permissible value, the RCD disconnects consumers from the mains.
The nominal values of leakage currents, which are designed for most modern devices of residual current, are 30 and 100 mA. The increase in differential currents can be caused by various reasons, the most common of which is the deterioration of the insulation between the grounded housing of the electrical appliance and the phase wire of the electrical network. Large leakage currents appear in cases where violations were made during the installation of electrical wiring associated with incorrect connection of the neutral and ground wires.
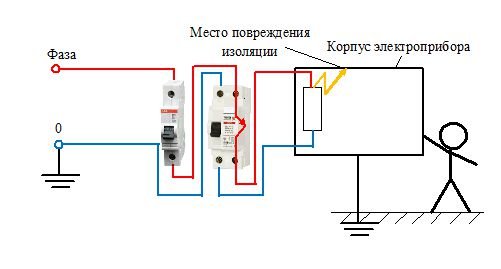
The third diagram shows an electrical circuit in which, in addition to the circuit breaker, an RCD is used. In the event of a leakage current, the value of which exceeds the nominal value, the automation breaks the circuit.
If you use such protection in electrical networks, the consumers of which do not have grounding, then for its operation it is necessary to create a closed circuit between the metal case of the device and the ground. As a rule, such a circuit closes if a person touches the body of the electrical installation.
Thus, the use of RCDs allows you to open the electrical circuit in the following cases:
- If a person touches an ungrounded body of an electrical installation, which has become energized due to insulation damage.
- If a leakage current occurs through the ground loop due to a violation of the insulation of live parts, the value of such a current must exceed the allowable value.
- In case of erroneous connection of the neutral and ground wires in the electrical installation.
- When the neutral wire is broken.
RCD connection
It should be noted that the RCD does not provide protection for short-circuit and overload currents. Therefore, such devices must be connected together with a circuit breaker, the permissible current of which must be less than the same value for the RCD. Such a power supply circuit for an electrical consumer is shown in the third figure.
As can be seen from the diagram, the phase wire is connected to the corresponding contact of the device through a circuit breaker. The neutral wire must also be connected to the consumer through the RCD.
If you choose to use three-phase protection devices, they are connected in the same way: three phase and neutral wires are inserted into the connectors that are marked accordingly.
In order to check the operability of the RCD, just press the TEST button located on its body. A working device will then immediately turn off. However, some models are not equipped with such a button. You can check their performance by creating an artificial circuit between the phase wire and the protective ground, in this case, a leakage current immediately occurs, to which the RCD reacts. You can make such a circuit using any metal object, but it is better to choose a cartridge with a light bulb.
The test current leakage method is the most reliable, since it allows not only to check the operability of the RCD, but also to assess the correctness of its connection.
To monitor the health of the RCD, it is impossible to close the phase and neutral wires together, since this will cause the circuit breaker to operate as a result of a short circuit.
Residual current device selection
When choosing an RCD for your apartment, you should pay attention to its following characteristics:
- Rated current.This value is selected based on the total power of consumers connected to the section of the electrical network, at the input of which an RCD is installed. In any case, the rated current of the device cannot be greater than that of the circuit breaker.
- Rated voltage. There are no problems with the choice of this value; in single-phase networks, devices for 230 V are used, in three-phase networks - for 400 V.
- Manufacturer. With a certain degree of distrust, you need to treat the products of Chinese companies. In the relay protection and automation market, brands such as Legrand, Schneider Electric and EATON have proven themselves well. One of the commonly used single-phase RCDs is VAD2. As for domestic manufacturers of such devices, it is quite safe to choose them, since in many cases these products are not inferior to Western counterparts, while being much cheaper.
Differential machine
A difavtomat is a device that combines an RCD and an ordinary circuit breaker.
The characteristics of each model are applied to its case in the form of a special marking. The main ones are:
- Rated current and type of time characteristic, eg C63. This means that the rated current is 63 A. The time-current characteristic is the dependence of the disconnection time of the circuit breaker contacts on the current flowing through them. For circuit breakers used in power supply systems of various objects, these characteristics are different. In apartments and residential buildings, automatic machines with a C-type characteristic are used.
- Leakage current (0.03 A, 0.1 A) at which that part of the circuit breaker that responds to the magnitude of the differential current operates.
- Rated voltage (230 or 400 V).
- Type of machine (for operation with alternating or rectified direct current).
- Principal connection diagram.
To answer the question of how to distinguish an RCD from a difavtomat, just look at their appearance. Although at first glance the differences are not very noticeable, but for a knowledgeable person they are, as they say, obvious:
- The type of time-current characteristic is not indicated on the RCD.
- The difavtomat in the circuit diagram applied to its body has two additional switches, indicating thermal and electromagnetic releases.
- The name of the device (VD or RCBO).
A residual current controlled circuit breaker has the following advantages:
- When installing a difavtomat there is no need to install any additional protective equipment.
- Almost all such devices are equipped with a special indication that allows you to accurately determine what caused the device to work: from the appearance of a large leakage current, short circuit or overload.
Answering the question posed, what is the difference between an RCD and a difavtomat, the following should be taken into account. Judging by the quantity and quality of the functions performed, there is not much difference in which device to choose: difavtomat or RCD. At the same time, the cost of a combined device is even higher than the total price of an RCD and an ordinary machine. In addition, if one of the separate devices fails, it can be repaired or replaced without removing the second one, this is much cheaper than repairing a difavtomat.