Product characteristics
During installation, two types of fittings can be used:
- with threaded fasteners;
- collet.
The material used for their manufacture is stainless steel, various alloys (bronze, brass), technopolymers.
Fittings for any pneumatic systems are used in devices, the principle of which is based on the use of compressed air energy. In order to ensure complete tightness of the system and prevent loss of power in operating equipment, reliable pneumatic tubes and fittings are required.
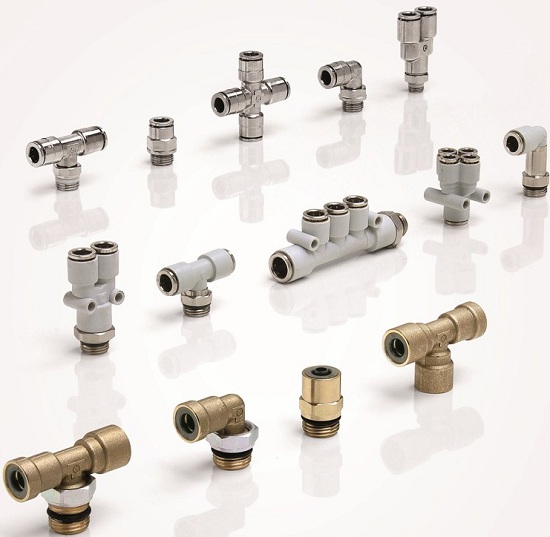
Metal and polymer collet pneumatic fittings
Today, industrial enterprises specializing in the production and supply of pneumatic tubes and fittings offer a wide range of this type of product.
There are two main types of such products:
- Fittings, the purpose of which is to control the flow of compressed air (gas). They can change the physical characteristics of substances passing through the system in such devices as air throttles, silencers, consumption (flow) regulators, etc.
- Push-in fittings that require a minimum amount of time to install (dismantling) and are mainly used to connect separate parts of a system consisting of many tubes.
Application area
Pneumatic tubing as well as fittings are essential for control and reliable sealing in a variety of pneumatic systems. They are also installed in systems for transporting (pumping) air that has previously been filtered.
Using push-in fittings to connect the compressor
Their use is also possible in plumbing systems, when it is necessary to create an absolutely tight connection.
In the latter case, special attention should be paid to the material from which the connectors are made, since the integrity of the entire system (its tightness) will depend on their wear resistance under various operating conditions. MV pneumatic fittings are used in systems that work with filtered air
Such connectors withstand internal pressure up to 12 bar, and do not lose their performance at temperatures from -10 to +70ºC
MV pneumatic fittings are used in systems that work with filtered air. These connectors withstand internal pressure up to 12 bar, and do not lose their performance at temperatures from -10 to +70ºC.
The material for the manufacture of such fittings is high-tech plastic, and the connection types are threaded or quick-release collets.
The plastic that is used in the manufacture of such products consists of an acetal polymer, with its properties far superior to the functional features of a conventional polymer or metal.
For such models, resistance to corrosion is inherent, they have a high level of rigidity. Produced in various standard diameters.
Polymer air fittings are widely used in industry, where they can be installed in systems for the preparation, transportation, processing of compressed air or other gaseous substances.
Connecting pipes to the pneumatic system using push-in fittings
The main devices on which such connectors are often used are regulators, pneumatic valves, pneumatic cylinders, filters, microfilters, lubricators and other similar mechanisms.
Connection types
All pneumatic fittings can be divided into threaded parts and collets.
Threaded fittings are installed on systems for controlling the air environment, changing its performance. Threaded fittings are detachable connections, but are installed where frequent dismantling is not provided, for example, on control panels.
Collet fittings provide a reliable, tight connection of pneumatic system parts with frequent dismantling.This does not mean that push-in fittings are not used for mounting stationary systems, but their distinguishing feature is that these elements allow you to quickly dismantle the connection if necessary.
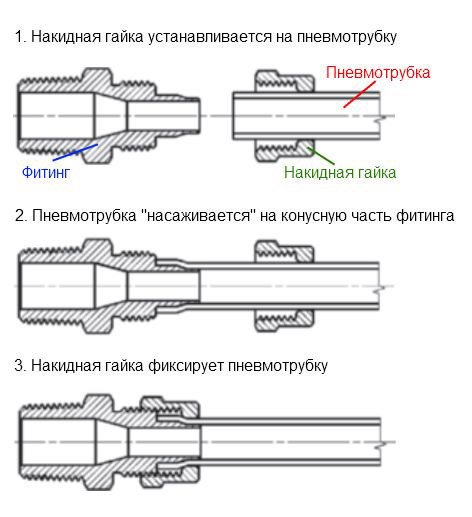
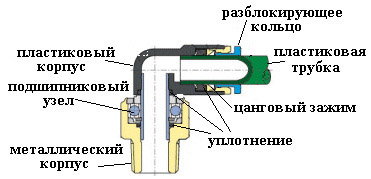
The mechanism of action of the collet connection is simple. The fitting consists of a body with a fitting, a union ferrule and a lock nut. High tightness is ensured by compression of the elastic material of the air tube.
Mounting scheme:
- the locknut and compression ring are removed from the fitting and put on the gas pipe in the same order;
- the tube is put on the fitting of the pneumatic fitting;
- a crimp ring is brought to the junction;
- fix the connection with a nut, which creates clamping pressure on the tube with the fitting;
- the locknut is not tightened to the end, leaving 1 - 1.5 threads of thread.
By purpose and configuration, the following pneumatic fittings are distinguished:
- rotary - corner fittings with external, internal thread or collet;
- connecting - coupling parts for connecting homogeneous pipelines or tubes of different materials, which can be threaded, collet, flanged;
- transitional - pneumatic fittings for switching to a different diameter, with different types of threads;
- bends - tees, cross-shaped connecting elements for tapping or redirecting the flow;
- plugs;
- nipple fittings;
- stop valve.
A variety of assortment of pneumatic fittings allows you to choose the right part in each case.
Materials used for the manufacture of pneumatic fittings
Fittings for pneumatics can be made from a wide variety of materials, the choice of a particular model depends on the characteristics of the line itself and its operating conditions.
Fittings for pneumatic systems
Most often on sale you can find fittings from such materials:
- Various types of steel (including stainless).
- Copper and alloys based on it (bronze, brass). Manufacturers offer elements with various types of coating - nickel plating, chromium plating, application of polymeric materials, Teflon.
- Composite materials.
- Various types of polymers. The most widely used fittings for pneumatic systems are made of PVC, polypropylene, polyethylene, polyamide, polyurethane, acetal polymers.
As already mentioned, the intended operating conditions play a large role in the choice of fitting material. So for systems used in the medical or chemical industry, materials are needed that do not affect the transported medium. In addition, such fittings must be resistant to aggressive chemicals. Therefore, fittings made of stainless steel or polymeric materials are most often used in such systems.
If we talk about the cost of connecting elements, then metal fittings have a higher price, but they also have better technical characteristics, so their use is advisable for making permanent high-strength joints. For the installation of lines from HDPE pipes that will operate at significant pressure, it is best to use brass threaded fittings for compressed air, plastic models have slightly worse characteristics.
A significant part of the fittings are elements of dissimilar materials. So transitions from metal to plastic and vice versa are in great demand, they allow you to include various shut-off valves, valves, taps in the system. For these purposes, it is desirable to use quick-release modifications of fittings that are mounted without special devices using ordinary keys.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pneumatic fittings are designed for mounting only detachable connections based on thread or compression pressure (collet).Both types of fittings provide reliable sealing of the system. The choice of one or another type of connection depends not so much on reliability considerations, but on the purpose and operation features of the node.
Advantages of pneumatic fittings:
- parts allow you to connect pipes with a diameter of 8 mm;
- they can be used in the installation of plumbing systems, creating reliable connections;
- make it possible to operate systems in the temperature range from -10 to +70 degrees, with an internal pressure of compressed gas up to 12-15 atm .;
- are made of special alloys and polymers resistant to aggressive environments;
- they provide a high degree of sealing of the system even after repeated dismantling.
The disadvantages of pneumatic fittings include their higher cost compared to conventional fittings and the limitation in the use of collet connections.
Material of manufacture and main types of connectors
All types of air fittings can be made of polyamide (nylon and rilsan), teflon, polyethylene, polyurethane. Nickel-plated steel, copper, stainless alloys are often used in production. Brass air fittings can be used provided there is no exposure to aggressive media.
Connectors, which are designed for the hermetic device of pneumatic systems, are divided into the following types:
- straight;
- corner;
- tees;
- splitters;
- adapters.
Metal, plastic and bronze collet fittings for pneumatic systems (tees, couplings, bends, splitters)
The following types are most in demand in the application:
- ruff, which has an external and internal thread;
- adapter for connecting tubes of different diameters;
- corner with internal or external thread;
- combined angle (external and internal thread);
- tees with internal or external thread;
- combined tees;
- T and Y shaped tees with different thread arrangement;
- cruciform connections;
- transitional couplings;
- external threaded adapters;
- plugs;
- hose connectors;
- quick fittings;
In combination with pneumatic fittings, special tubes are used:
- Polyurethane. They are resistant to mechanical stress (twisting, squeezing, bending). With physical impact, they quickly recover in their original form. Not subject to hydrolysis, resistant to oils, ozone, microorganisms, different types of fuel. The only drawback is that they are affected by acids.
- Polyamide (rilsan). They are very flexible and durable at the same time. Do not lose their properties at temperatures from -10 to +70ºC. With firmness transfer influence of alkali, gas, fuel, engine oil.
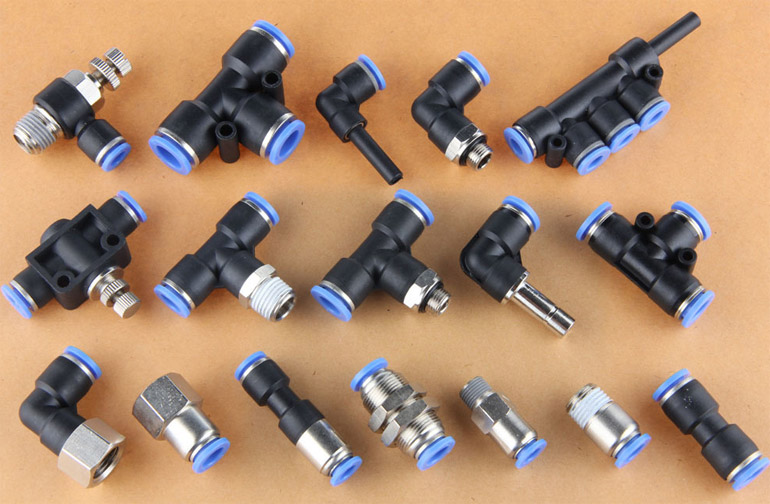
A wide range of types of polyurethane pipes for connecting pneumatic systems
Installation of push-in fittings
An example of connecting two metal-plastic pneumatic tubes using a collet-type pneumatic fitting:
- Cut two tubes to the required length with special scissors.
- Calibrate the tube opening with a calibrator.
- Chamfer the inner surface of the tube with a chamfer.
- Check the presence and quality of the dielectric gasket and two sealing rubber rings on the fitting shank.
- Slide the union nut and then the collet onto the first tube.
- Insert the fitting shank into the tube opening until it stops.
- Screw the union nut onto the fitting body by hand.
- Repeat steps 5, 6 and 7 for the second tube.
- Tighten the union nuts on the fitting body with a ring wrench, leaving 1-1.5 threads free.
- Installation completed.
Collet pneumatic parts (fittings) are designed for strong connections without leakage of air or other working media in pneumatic systems.
A wide range of products makes it possible to choose a wide variety of manufacturing materials and allows the use of collet pneumatic fittings in various equipment,ensuring reliability of fastening and tightness of connection.
What are pneumatic fittings made of?
Materials for the manufacture of pneumatic fittings are distinguished by increased reliability, resistance to corrosion.
Manufacturers offer pneumatic fittings made of high-strength alloys or polymers:
- stainless steel - for systems that operate in chemically aggressive environments, in medical instruments and systems;
- alloys with an anti-corrosion coating that ensure a reliable connection for a long time: from brass or copper, as well as nickel-plated bronze or brass products or chrome-plated steel;
- copper;
- polymers - polyurethane, polyethylene, polyamide, polypropylene, polyvinyl chloride and acetal polymer (material with increased strength);
- combined pneumatic fittings, which are made of metal in combination with polymer inserts.
The production of a large number of air fittings from different materials is due to the need to select them depending on the specific operating environment of the system.
- For example, in medicine, there are more stringent requirements for connecting parts, since human life and health depend on their quality.
- In the chemical industry, where aggressive media are transported, fittings are made of inert materials.
- Polymer fittings are indispensable for large-scale industries with a neutral environment, medium operating parameters of systems, where the price of the product is decisive. They are much cheaper than metal counterparts, provide proper rigidity in systems for supplying or processing compressed air and other gases.