Work acceptance procedure
When accepting such work, first of all, the tests themselves are carried out, which can be:
- Hydraulic - only non-pressure drainage systems are exposed to them, whether it be sewage pipelines or storm sewers. the check is carried out in the areas between the wells by filling the system with process water. Tests are carried out in two stages - checking pipes and connections before backfilling the soil and checking the performance of the entire sewer after backfilling the soil. Tests are carried out by supplying water to wells or receiving grids for 30 minutes, during which the performance of the system is measured and the tightness of seams and joints is controlled. Tests can also be made on the ability of pipes and connections to withstand the maximum allowable pressure in the entire drain.
- Pneumatic - during such tests, the ability of the waste system to withstand the design pressure is checked, according to GOSTs or project documentation. For such a range of studies, specialized organizations are involved that have the necessary equipment and licenses, the process itself includes checking the pressure in the system or in its individual sections when air is supplied under pressure.
If during the experiments the entire system withstood the normative indicators of SNIP 3.05.04-85, then an act of acceptance of the work performed is drawn up, otherwise a defective statement and an act of troubleshooting the drain are drawn up.
During periodic control at enterprises that have pipelines for domestic and drinking purposes, external drain systems are also tested during disinfection or treatment with special reagents.
Testing basic principles
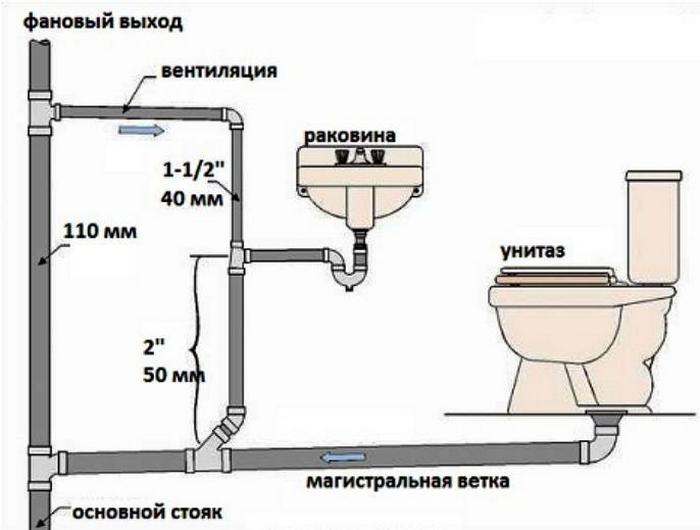
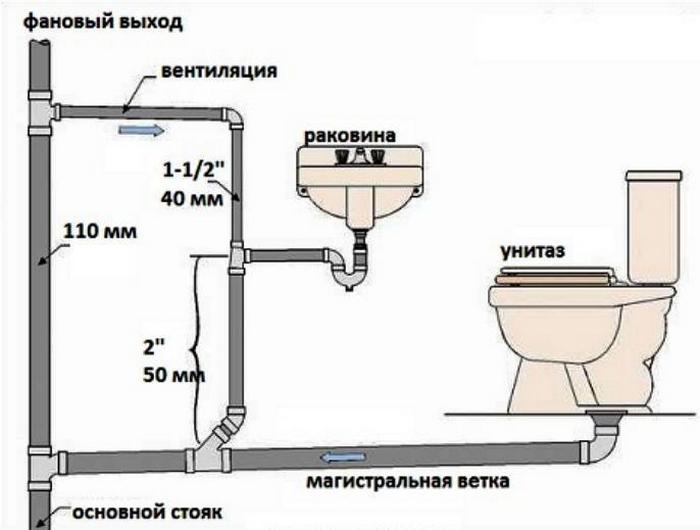
The internal system includes the following objects:
- All plumbing points and household appliances that drain water;
- All pipeline connected to the central manifold;
- Central sewer line.
The external system under test includes:
- A pipeline located outside the building for transporting wastewater to a place of accumulation or disposal;
- All revision and rotary wells;
- Storm channels.
In order for the testing to pass qualitatively and fully reflect the state and performance of sewer communications, it is necessary to adhere to the basic rules:
So, all plumbing points before work should be cleared of possible construction and natural debris;
It is worth checking all points for cracks, chips and other damage;
It is important to track the evenness of all straight sections of the network. There should be no deflections and bends;
All vertical risers must be checked with a plumb line;
To check the pipeline, you can use both the hydraulic method (strait method) and pneumatic (pumping the system with air);
Important: the strait of sewer communication can only be carried out if the air temperature around does not fall below +5 degrees
If the outdoor temperature is below the specified parameter, then the pneumatic testing method is used.
For each floor of the building, it is worth conducting a separate communication check. To do this, on all other floors, plugs are installed for revision.
After completion of the installation work of the internal sewage systems and drains, the installation organization must carry out their tests with the preparation of an act in accordance with Appendix "D" "Internal sanitary systems of the building" (updated version of SNiP 3.05.01-85).These tests shall be carried out by spilling water by simultaneously opening 75% of the sanitary appliances connected to the area to be tested. The “household” name of the act comes from the test method - an act on a sewer strait or an act on a sewer strait. However, the name of the act according to the regulatory documentation is as follows - act of testing internal sewage systems and drains
.
We figured out the correct name of the act and its purpose. Now let's take a closer look at the form of the act of testing internal sewage systems and drains and the method of filling it out.
First, fill in the name of the system on which the tests were carried out. We take the name of the system from the project documentation. For example, it can be "domestic sewerage K1".
Next, you need to fill in the name of the capital construction object. There is nothing complicated here. Information about the name is taken from the project documentation or building permit. After that, we enter data about the city in which the capital construction object is located and the date of the test.
The block in which data on the commission that conducted the tests is entered includes the following information: the name of the customer organizations, the general contractor, the installation (construction) organization, as well as the positions, initials and names of representatives of these organizations.
In paragraph 1 of the act of testing internal sewage systems and drains, data (name) on the design organization, design documentation code, drawing numbers are entered in accordance with which the installation work was performed.
In paragraph 2, we indicate the number of simultaneously open sanitary appliances and the time during which the tests were carried out. Sanitary appliances include bathtubs, washbasins, shower trays, drains, bidets, toilet bowls, toilet bowls, urinals, sinks, sinks, plums. During the tests, in accordance with at least 75% of the sanitary appliances connected to the tested area must be open at the same time.
Paragraph 3 of the sewer test report includes data on the defects identified during the tests. If no defects are found, then we put a record that during the inspection during the tests, no leaks were found through the walls of pipelines and joints.
Based on the results of the tests, a decision of the commission is made, which is recorded in the trailer of the act. As a rule, this is a template paragraph, which is only supplemented with data on the name of the tested system.
After completion of the tests, the act of the strait is signed by all members of the commission. Changing the form of the act and deviating from it is not allowed.
The quality of the installed sewerage in a country house and beyond is checked at all levels. First of all, all building codes and requirements must be observed. Then the installation is controlled. And at the end, tests are carried out and an act is drawn up for a sewerage strait, a sample of which can be found on the Internet.
Persons - members of the commission
As a separate item in the act of checking the external or internal sewerage, it is necessary to record all the data about the members of the commission. These are:
- Representatives from the client organization.
- Representatives from the general contractor. These persons are responsible for the correct installation of drains in case of non-compliance with technical and operational standards during a spill.
- Members of the design organization who were involved in the development of the communication under test project.
- A representative of a company or organization that was engaged in the study of the soil at the site for the installation of external or internal communications. This office is fully responsible for the inconsistency of the data obtained on the site in terms of environmental and climatic conditions for the construction of sewer communications.
So, in the paragraph of the test acceptance certificate, it is necessary to enter all the initials and surnames of the commission members with their signatures.
How to test the finished sewer system
The “household” name of the act comes from the test method - an act on a sewer strait or an act on a sewer strait. However, the name of the act, according to the regulatory documentation, is as follows - the act of testing internal sewage systems and drains.
Info
We figured out the correct name of the act and its purpose. Now let's take a closer look at the form of the act of testing internal sewage systems and drains and the method of filling it out
Attention
Next, you need to fill in the name of the capital construction object. There is nothing complicated here
Information about the name is taken from the project documentation or building permit.
Testing of external sewerage networks
Preliminary tests Acceptance tests Pneumatic tests Preliminary tests The hydrostatic pressure in the pipeline during its preliminary test should be created by filling the riser installed at its upper point with water, or by filling the upper well with water, if the latter is to be tested. In this case, the value of hydrostatic pressure at the top of the pipeline is determined by the magnitude of the excess of the water level in the riser or well above the pipeline rack or above the groundwater horizon, if the latter is located above the rack. The value of the hydrostatic pressure in the pipeline during its testing must be indicated in the working documentation. For pipelines laid from non-pressure concrete, reinforced concrete and ceramic pipes, this value, as a rule, should be equal to 0.04 MPa (0.4 kgf / cm2).
Testing the external network Testing the external sewage system is carried out mainly in a hydraulic way. Produced works:
- pipeline slope control;
- the pipeline is tested for tightness;
- examination of wells and other equipment.
The level of the slope of the external sewerage is checked by the level.
The check is carried out between the wells, in stages, each section is disconnected from the system using a plug. Test scheme for non-pressure systems::
- checking pipes for blockages and residues of construction debris, if necessary - flushing;
- spill test - a section of the system is filled with water, if no leaks are detected within 10 minutes - the test is passed.
Water is supplied to the pressure sewer under pressure. With the same pressure at the inlet and outlet of the pipe, the test is also considered passed.
The check includes:
- testing of the pipeline for tightness (carried out as described above. Pipe sections located between wells or other elements of the system are taken for verification);
- checking the level of the slope of the pipeline;
- testing of wells and other equipment;
- checking the performance of storm drains.
To check the level of pipe laying, which is necessary for a gravity sewer system, a level is used.
If pressure sewerage is being tested, then water must be supplied to the piping system under pressure specified by the design documents. The test of pressure sewer pipelines is considered successfully passed if the pressure in the flow to the network and at the outlet from it is the same.
Who is responsible for the health of the sewer
The composition of the commission conducting the inspection of the sewer network includes representatives of:
- the company that made up the . This organization is responsible for the correctness of the calculations and drawing up the drawings of the sewer network;
- organization that carried out research on the ground in which the installation of sewage was planned. This company is responsible for the correctness of the data relating to climatic conditions, the environmental situation, on the basis of which the system design was developed;
- companies involved in laying the sewer network are responsible for the quality of work and compliance with existing standards;
- customer organization. Controls all stages of construction. Responsible for the correctness of the inspection when commissioning the sewer network.
Each organization has its own area of responsibility, the boundaries of which are clearly defined. After the inspection, all members of the commission sign an act of testing the sewerage system.
In case of detection of errors or shortcomings, each company can be brought to criminal, disciplinary or administrative liability.
Testing basic principles
The internal system includes the following objects:
- All plumbing points and household appliances that drain water;
- All pipeline connected to the central manifold;
- Central sewer line.
The external system under test includes:
- A pipeline located outside the building for transporting wastewater to a place of accumulation or disposal;
- All revision and rotary wells;
- Storm channels.
In order for the testing to pass qualitatively and fully reflect the state and performance of sewer communications, it is necessary to adhere to the basic rules:
So, all plumbing points before work should be cleared of possible construction and natural debris;
It is worth checking all points for cracks, chips and other damage;
It is important to track the evenness of all straight sections of the network. There should be no deflections and bends;
All vertical risers must be checked with a plumb line;
To check the pipeline, you can use both the hydraulic method (strait method) and pneumatic (pumping the system with air);
Important: the strait of sewer communication can only be carried out if the air temperature around does not fall below +5 degrees
If the outdoor temperature is below the specified parameter, then the pneumatic testing method is used.
For each floor of the building, it is worth conducting a separate communication check. To do this, on all other floors, plugs are installed for revision.
During the test of the external sewerage by the strait method, the same document is drawn up as during the test of the internal sewage system. The form of the act itself is not a form of strict reporting and can be drawn up by the customer, contractor or subcontractor.
Also, during the experiments on the external water drainage system, one of the forms of SNiP 3.05.04-85 can be used, which is a general form of the acceptance document for the work performed during the installation or repair of sewage drainage.
Filling out the act point by point
- In paragraph 1
will contain details of the company that designed the drainage system. The name of the cipher on which all project documentation was compiled is also entered here. In addition, in the first paragraph of the document on testing the sewerage by the method of spilling internal and external communications, it is necessary to enter all the numbers of the drawings that were used during installation for each section of the drainage system. - Point 2
of the above test report must contain accurate information on the number of simultaneously open sanitary points and the period of time during which the tests were carried out using the full pressure strait method. Sanitary points according to SNiP include toilets, sinks, bathtubs, showers, bidets, urinals, plums, etc.
- Point 3
of the completed act is intended for records of possible violations in the system operation. That is, about the occurrence of leaks, stagnation, blockages, etc. If none was found at the time of checking the communication, then in paragraph 3 a record is made that no leaks and other unauthorized deviations in the operation of the sewer were detected at the time of the test. -
Last section
- this is a decision of the commission, which allows or does not allow putting the drain into operation, depending on the test result obtained.
If obvious shortcomings are found in the work of communication, indicating a negligent attitude of the contractor or all organizations related to his work, then the organization responsible for the shortcoming, according to the law, bears administrative, disciplinary or criminal liability (depending on the identified defect).
The specifics of drawing up a test report
Regardless of the type and method of verification, the document must contain the following items:
The header of the document, where the date of compilation and the city in which the document is drawn up and signed should be indicated. The indication of the city is mandatory, since the signing of the act may take place outside the settlement where the installation or repair of the water drainage system was carried out.
Also in this part of the document, the name of the organizations and the full name of the leaders should be indicated, as in the charter of the organizations that carried out control, testing and technical or architectural supervision over the progress of the work.
Also in this paragraph there should be references to the design marks and coordinates of the sewage system, according to the master plan or special sections of the construction project.
Document header template
After the heading of the document, there is an extract from the technical conditions according to which the experiments were carried out. This section contains calculation formulas, a list of necessary test equipment, conditions and procedures for carrying out work.
When filling out this paragraph, the data taken from the measuring instruments during the research are used. If the act itself does not contain this section, then there should be a link to the test report, which describes the process in detail and all calculations are made. All results can be summarized for convenience in a single table.

Sample filling section of measurements and calculations
The last item is the decision of the commission, which indicates the result of the tests and the conclusion that the drain system is ready to be accepted into operation. In case of non-compliance, the reason is indicated and links are given to defective statements and acts for correction and revision.
In the event that the pipeline has passed all the tests, the full data of all members of the acceptance committee and their signatures are indicated, after which this document becomes the basis for drawing up an act of disagreement or a statement of work performed, according to the conclusion of the expert committee.
An important condition for the preparation of this document is the procedure for empowering members of the commission, for which the necessary orders of managers must be created. Also important are the attestation documents of all members of this commission, confirming the qualifications of the participants to conduct research or monitor the progress of their conduct.
Methods for testing sections of internal sewerage
- testing network pipes for strength, and their connections for tightness;
- compliance of the location of the installed devices and elements of the outlet pipeline with the design documentation;
- correct installation of plumbing fixtures in relation to the floor surface (the distance from the floor to the upper edge of the receiver of each plumbing fixture is prescribed in the above-mentioned SNiP);
- the presence of a slope of horizontal sections of the pipe and the degree of verticality of the risers.
The test of pipes and connections for tightness in a gravity system, regardless of the material of manufacture of the pipeline and fittings, is carried out by the spill method. The essence of the technique is that part of the main pipeline (lounger) is fenced off in a certain area from the rest of the system. This is done with special plugs through the revision holes. The separated section is checked by filling with water through the nozzles of plumbing fixtures
According to SNiP, the results of the spill deserve attention if the pipeline was filled with the participation of at least ¾ (or 75%) of all devices connected in this isolated section.Testing the pipeline by the spill method is considered positive if the connections, after filling the system, did not give the slightest leak within 10-15 minutes (depending on the volume of the area filled with water)
According to the regulatory documentation, the strait, that is, the test of the sewer system by filling it with water, is informative when the air t˚ is above 5˚. If the temperature is lower, a pneumatic leak test of pipes and connections is carried out (with compressed air). The integrity of the riser is also determined by air, sometimes - the outer sections of the pipeline. Let us apply the pneumatic testing method in assessing the performance of a pressurized sewerage system, when wastewater is forced out, under pressure created by pumping equipment.
The location of the installed plumbing fixtures and its compliance with the design documentation is determined visually. The standing height of the receiver of each device, the correct connection of the toilet drain, washbasin siphons, bathroom sinks, etc. are objectively assessed and reflected in the act. Visually assess the condition of the plumbing fixtures themselves. They must be free of visible contamination and mechanical damage.
The correctness of the slope of the pipes inside and outside the building is controlled using a bubble building level. If the slope of the lounger of the internal sewerage network is allowed at least 1 cm per linear meter, then outside this figure must be increased to 2 cm per meter.
The installation position of the riser (this data is also reflected in the final act) is checked with a plumb line. A deviation from the vertical by 3˚ is allowed. A water tightness test of the riser is also carried out. The pressure in this case should be about 0.8 MPa.
Download Sample
After the installation of the sewer system, before proceeding to the finishing work inside and backfilling the trenches from the outside, the drainage network must be tested to make sure that the nodes, pipelines and their connections are tight. Checking the external system and the internal network is carried out in various ways, regulated by the fundamental document of the builders - SNiP. How the tightness of pipes and sewer connections is tested by spillage, filling, and other methods, and what data is entered, if necessary, in the inspection report, you will learn by reading the article.
The entire sewerage system in each building is divided into an internal sewerage network and an external sewerage system. The internal sewer wiring includes the following nodes to be checked:
- plumbing fixtures and places of their connection with outlet pipes;
- local sections of a horizontal pipeline with pipes flowing into it from plumbing fixtures;
- sewerage risers;
- outgoing pipe.
In the outer part of the sewer system, sections of the pipeline (between cleaning, auxiliary equipment) are tested for tightness, as well as:
- operability of wells, tightness and slope of the pipeline;
- condition of treatment or storage facilities (reservoirs);
- storm sewer.