Thread sealing with FUM tape.
The abbreviation FUM stands for fluoroplastic sealing material. FUM withstands temperatures from -200º C to 240º C and pressure up to 30 atmospheres. Therefore, it can be used both in heating systems and in water supply networks. FUM is suitable for non-freezing coolants and other aggressive environments. To seal threads on gas pipes, a special gas FUM tape is used (it is thicker than water). This sealing method is very simple, I personally prefer to seal the thread with FUM tape, but this is a matter of skill and taste. I bring to your attention the following video on this issue:
Main technical properties of the sealing tape
Video
The FUM tape has the following characteristics:
- Reduced coefficient of friction. The fluoroplastic seal, in addition to plasticity, is slippery, which simplifies fitting fittings.
- Thermal stability, allowing to withstand temperatures up to 260 degrees without destruction and loss of sealing properties. In addition, fluoroplastics are very efficient dielectrics.
- Strength and plasticity. Seals made of this material work stably at pressures up to 10 MPa, and are able to withstand short-term loads up to 42 MPa, for example, those that occur during hydraulic shocks in pipeline systems. The service life of a seal made of FUM tape (fumka) is determined at 13 years. Decomposes faster when exposed to light, but this is not for our case, you just need to take this factor into account when organizing the storage of the material.
- chemical passivity. Not subject to destruction under the influence of acids and alkalis, which is determined by the uniform distribution of fluorine atoms over the surface of the product. Solvents capable of destroying this sealant have not yet been invented. Resistant to decay processes.
How to use FUM tape for gas and plumbing pipes correctly, we will consider in more detail.
What happens if there is no shut-off fitting in the system
To cut off stray currents in pipelines, a special dielectric insert is used. It cuts into the area between the tap and the connection to the gas-consuming device. Or in the area between the gearbox and the gas meter. What happens if there is no such insertion? Believe me, no good. Firstly, your or a neighbor's stove, column or boiler may suffer from a stray current or turn into a source of one. As a result, there is a risk of losing their performance, due to the defeat of the "smart" filling, assembled on the basis of capricious chips that react even to minor power surges.
Secondly, a spark can occur in the pipeline - a source of fire. Moreover, cases of spontaneous combustion of the eyeliner are not so rare. And if this fact is not discovered in time, the case may end in a big catastrophe. The detonation of the gas-air mixture can destroy even an apartment building. Thirdly, the user may be electrocuted. If the potential of the stray charge is significant, and this happens during a thunderstorm or a power failure, then we can not talk about an unpleasant “bite”, but about a full-fledged injury with difficult to predict consequences.
Therefore, in the set of rules SP 42-101-2003, regulating the construction of gas distribution systems, there is a special clause (6.4), stipulating the mandatory presence of a dielectric insert, used even in polyethylene pipelines. And modern industry produces several types of such cutters.
How does a breakdown occur in the gas network
Natural gas is supplied to homes and other premises through metal pipes laid underground in urban areas or above its surface in the private sector. Metal corrodes when exposed to moisture. Applying a positive electrical potential helps to reduce the degree of corrosion.
According to the safety regulations, a dielectric coupling is installed on the pipe at the entrance to the house. In this way, the indoor gas riser is protected, provided that the coupling is installed correctly and is in good condition. But the deaf grounding of the pipe in the basement of the house can break due to corrosion.
Further, in a house or apartment, suppose the stove is connected to the riser through a rubber hose with a metal braid. If suddenly the insulation of the electrical wire in the plate is broken, the current will go through the hose braid. Depending on the strength of the current, the time of heating and breakdown of the hose will be short or long, but a breakdown will certainly occur.
Sometimes residents of the house arrange grounding on the gas pipe.
Possible fire due to a gas leak in the apartment. Everything can do without victims, but with material losses. After such an event, the question of why a dielectric coupling for gas is needed will no longer be hypothetical for residents.
Dielectric insert for gas
The dielectric insert for gas is designed to prevent leakage currents from flowing through the gas pipeline when an electric potential occurs on the body of a grounded electrified gas appliance (stove, oven, boiler, boiler, etc.), protects the electric ignition system, timers, backlight.
The insert protects the electronic parts of gas appliances and meters from failure during emergencies associated with the ingress of electric current into the gas main due to malfunctions in the electrical part of gas appliances, as well as in case of illegal grounding of electrical appliances on gas steel pipes.
The dielectric insert is a one-piece connection and is installed between the gas cock and the gas supply. The metal parts of the insert fused into the dielectric do not touch each other, which makes it impossible for leakage currents to pass through the insert. The insulating insert has an inner surface completely covered with a dielectric, which excludes the contact of each of the metal parts of the insert with the gas passing inside the insulator.
Technical data and characteristics:
- Threaded metal parts of the insert are made of brass grade LS-59-1
- Electrical insulator: yellow polyamide (according to GOST 14202-69)
- Rated pressure: PN 0.6 MPa.
- Operating temperature: -60°C to +100°C.
- Nominal diameter: DN15 or DN20.
- Inner passage diameter: 11.5 mm or 15.0 mm.
- Options for threaded connecting fittings: nipple/nipple, nipple-nut.
- The size of the pipe thread of the connecting fittings is 1/2″ or 3/4″.
- The insert withstands a test voltage of 3750V by applying 50Hz alternating current to metal parts for at least 6 seconds.
- Electrical resistance at 1000V: more than 5MΩ.
- Category of resistance to burning PV-0 according to GOST 28157-89.
Rules for installing dielectric inserts
- Installation, reinstallation and repair of gas equipment must be carried out by specialists of the gas service in accordance with DBN V.2.5-20-2001 "Gas supply of residential buildings"
- Mount the dielectric insert between the gas cock and the gas hose. The recommended tightening torque is 25 N/m. Insert tightening torque: 50 N/m.
- The dielectric insert for gas does not require verification and maintenance during operation.
- It is forbidden to dismantle/mount the insert without first shutting off the gas supply valve.
The dielectric insert for gas complies with TU U 28.7-31940558-007-2005 "Brass connecting parts with cylindrical thread for pipelines" and the requirements of technical documentation
How to connect HDPE pipes types of connections fittings, couplings, welding and their features
The relevance of the question of how to properly connect HDPE pipes is explained by the fact that such products made from low-pressure polyethylene are actively used in modern construction, as well as for repair work. The installation of such pipes, which can be used to transport various media, can be carried out even by those who have never encountered the need to perform such a procedure before.
The device of a summer irrigation water supply system from HDPE pipes
Scopes of pipes from polyethylene of low pressure
Due to their unique characteristics, HDPE pipes are widely used not only in capital construction, but also in domestic conditions. The most common areas of application for such pipes are:
- installation of pipelines used for water supply of building structures for various purposes;
- arrangement of sewer systems;
- protection of electrical cable systems;
- formation of a waterproofing layer for elements of heating mains;
- protection of communication cables when they are laid in open ground;
- ensuring the normal functioning of artesian wells;
- formation of concrete structures during the construction of monolithic building structures;
- installation of irrigation systems for greenhouse facilities.
HDPE pipes are color-coded depending on the purpose
The high popularity of such products is also due to the fact that the connection of HDPE pipes can be performed using various technologies, each of which ensures its reliability and tightness.
Connection methods
How to connect HDPE pipes? To begin with, you should study the features of this technological operation. To date, many methods have been developed that allow reliable connection of pipes made of this material. All compounds obtained using such methods can be divided into two types:
- one-piece (created by welding);
- detachable (formed using special connecting parts - fittings).
Removal of HDPE pipe using a threaded tee
Most often, when using pipes made of HDPE, detachable connections are used. This is due to the following advantages of compounds of this type.
- There is no need to purchase special welding equipment or involve specialists whose services are not cheap.
- Connections of this type can be made even in places where the use of welding is not possible. In particular, metal fittings are used in cases where the connection of pipes made of HDPE must be made under water.
- Connections of pipes made of HDPE are carried out very quickly, which does not in the least affect their reliability.
Types of fittings for connecting HDPE pipes
Household gas leaks, their detection and liquidation
Gas contamination of any room can occur due to gas leakage:
- from connections of gas pipelines, gas fittings and equipment, as well as through their leaks;
- from taps (latches) accidentally left open unattended;
- in case of rupture of any welded joint on the gas pipeline, both directly at the place of gas consumption, and in the adjacent underground section, from where gas can enter the room at the points of entry of gas pipelines;
– in the case of gas combustion with poor draft and poor regulation of the combustion process, as well as with poor ventilation of the room, without good removal of products of incomplete combustion.
Detection of gas leaks from internal gas pipelines is carried out by washing threaded, welded and flanged joints. The use of open fire for these purposes is strictly prohibited. A sign of a gas leak in this case is the presence of bubbles of soap solution.
When lathering, a solution of soap (powder) is used in the proportion of 35 g per 1 liter of water at an outside temperature above 0 ° C, and at low outside temperatures, glycerin is added to the soap emulsion solution, respectively, in the amount of 450 g per 515 g of water or ethyl alcohol in amount of 560 g per 450 g of water.
The detected gas leak from the gas pipeline is eliminated:
– replacement of hemp packing in threaded connections;
– change of gaskets or tightening of bolts in flange connections;
- welding of a defective seam on a gas pipeline.
Identification and liquidation of places of gas leakage from external and underground gas pipelines by the emergency service of the operational organization of the gas economy.
All of these works are carried out after disconnecting the repaired section of the gas pipeline from the existing network by closing shut-off valves or valves with the installation of plugs after them.
The gas pressure in the disconnected section of the gas pipeline is reduced to zero before repair, and the remaining gas is removed to the outside through a “candle” or a rubber hose.
Upon completion of the repair of the gas pipeline section, the plug on the shut-off valves is removed and the repaired gas pipeline is purged with gas until the air is completely expelled. At the same time, the density of all connections of the gas pipeline and installed fittings is checked with a soapy solution.
A somewhat different way is to eliminate gas leaks behind the hydraulic fracturing pressure regulator. In this case, two gas fitters in hose gas masks should enter the hydraulic fracturing room, and the third should be on duty outside the entrance. One of the mechanics gradually opens the valve on the bypass gas pipeline and brings the pressure downstream of the regulator to a value slightly greater than the upper limit of adjustment. Another locksmith closes the valves before the filter and behind the regulator, and then installs a plug between the flanges of these valves and the devices to be switched off. The pressure regulator is dismantled for repair, and the hydraulic fracturing room is thoroughly ventilated and checked for the absence of gas with a portable gas analyzer PGF-2M. In the absence of gas in the room, work on the repair of the regulator is already carried out without a gas mask.
In a similar way, gas leakage is eliminated through leaks in the safety valve, filter and gas volumetric meter installed in the hydraulic fracturing.
Until the gas leak is eliminated, it is prohibited:
– turn on and off conventional electric lighting;
- use electrical appliances (tiles, bells, etc.);
- smoking, lighting matches and lighters;
- bring open fire (torch, lantern "bat") and use it to find gas leaks.
Requirements for gas fittings
Connections for gas pipelines must be sealed (any leakage of gaseous fuel can lead to poisoning and serious accidents). All elements of the gas supply system must be resistant to pressure surges and withstand an ultimate load of up to 2.3 MPa.
Special requirements are placed on corrosion resistance. The outer surface of the pipe must be protected from rust, while this requirement is not imposed on the inner surface due to the fact that metal oxidation does not occur as a result of exposure to natural gas, therefore, the inner walls of the pipe do not corrode.
Gas most often requires parts with a diameter not exceeding half an inch, with the exception of only boilers with high power. The size of the section of products for completing gas pipelines is regulated and determined by the technical conditions for the gas supply of the facility.
Flange connection of gas pipes
 Flange connection is the most common type of detachable pipe connection.
Flange connection is the most common type of detachable pipe connection.
Due to the simplicity of design, ease of disassembly and assembly. But at the same time, there is a high cost of work and a low reliability of the connection compared to welded.
And if the pressure of the transported medium changes, then a gas leak may occur.
The flange connection consists of:
- from 2 flanges;
- fasteners - studs, bolts, nuts;
- O-ring or gasket.
Most often used technical rubber gaskets, asbestos cardboard or sheet paronite.
Gas pipes can be metal or plastic
During their installation, special attention should be paid to sealing pipe joints. The sealing of gas pipes must be carried out especially carefully.
If you use sealants that are not intended for this purpose, then in the future you may encounter gas leaks that can lead to an explosion. Sealing of threaded connections is carried out using sealants, as well as sealants.
Solvent based sealants
This gas pipe sealant is a drying paste. Often a solvent-based sealant is used in conjunction with flax. Before connecting the pipes, the thread is coated with a sealant. After a certain time, the composition solidifies in the threaded gap and prevents gas leaks from occurring. Such sealants have one serious drawback - if it is required to fix a large threaded gap, then it should be borne in mind that in this case the sealant will shrink. Also, such connections need regular tightening.
Linen winder
Winding for gas pipes is used for sealing pipes together with red lead on drying oil. Red lead can be replaced with iron lead. If only linen winding is used during the installation of pipes, then the risk of corrosion of threaded connections in this case will increase. Linen winding is quite inexpensive and provides high fixation strength and adhesion. Sealing pipes with winding is carried out as follows:
1. From the outside, several notches can be applied to the thread. Thanks to the notches, the winding will not slip off. Notches are applied to the thread with a file.
2. Then you need to remove several fibers from the linen tow and twist a thin rope out of them.
3. This linen rope is wound around the thread, starting from its edge.
4. As soon as all the recesses of the thread are filled, red lead on drying oil is applied on top of the winding.
5. Then the connection must be carefully twisted, smoothing the protruding flax fibers.
Use for sealing pipes FUM tape

- low quality of sealing those joints that are subjected to vibration;
- insufficiently high quality sealing of threaded connections exceeding ¾ inch in diameter.
FUM tape should be wound on a clean and dry connection, like linen thread.
Universal sealing thread

- affordable cost;
- ease of use;
— high quality sealing of gas pipes;
- high bonding strength.
Before winding the universal sealing tape on the thread, it is imperative to make notches on it. Also, this sealing tape is not recommended for sealing large diameter gas pipes.
Any threaded connection in heating or water supply requires the use of various sealing agents. Without them, the threaded connection simply starts to leak, which causes various unpleasant consequences. In this article, I will tell you about the different methods of thread sealing and their applicability in different working conditions. Let's start from simple to complex.
How to install the clutch act carefully
Clause 6.4 of the set of rules SP 42-101-2003 indicates that MD and HP must be mounted between the gas distribution valve and the consumer device, due to this, the following sequence of actions is applied during the installation of dielectric cut-offs:
- We close the valve on the iron pipe supplying gas to the stove, boiler or column. At the same time, it is better to leave the burners of the devices open so that the gas in the supply burns out.
- Holding the valve body with the first Swedish key, carefully twist the supply nut with a spare key - an elastic pipeline (hose) connecting the shut-off assembly with a section of the gas inlet pipe of the boiler, stove or column. The use of a pair of keys in this case in the first place, because the supply nut can “stick” to a fitting or a piece of valve pipe and transfer torque to it, after that gas will pour into the room, and it will be possible to close its supply only with a street reducer valve.
- We screw the FUM coupling (polymer sealant) onto the free ends and twist it into the gas pipeline valve with our hands. Then we take the same two keys and, holding the valve body, screw the coupling to the end. Try not to overdo it at this step, because too much force will deform the valve body and leak gas.
- We screw on the free end of the coupling the nut for supplying to the device that consumes gas, controlling our own force and holding the connector with one of the Swedish keys.
- Next, the impermeability of the resulting joint should be analyzed. To do this, you need to purchase a shaving brush and, after carefully lathering it, process all the joints of the valve, coupling and supply. Then you open the valve and observe the foam at the joints. If you do not see bubbles, the joints are screwed in tightly, and your gas pipeline is ready for non-hazardous operation.
If soap bubbles are found at the joints, it is necessary to close the gas supply valve and carefully tighten the coupling or supply nut. If this does not help, you will need to disassemble the entire connection and add a few turns of the FUM to the ends of the coupling.
Important: the use of matches or lighters instead of soap suds when testing the tightness of the joints is absolutely prohibited. You may not have time to react and turn off the gas, causing a serious fire
And with a strong leak, you can be fussed - the sight of a flaming valve unbalances even the most cold-blooded professionals. Due to this, soap suds is considered to be the optimal impermeability tester.
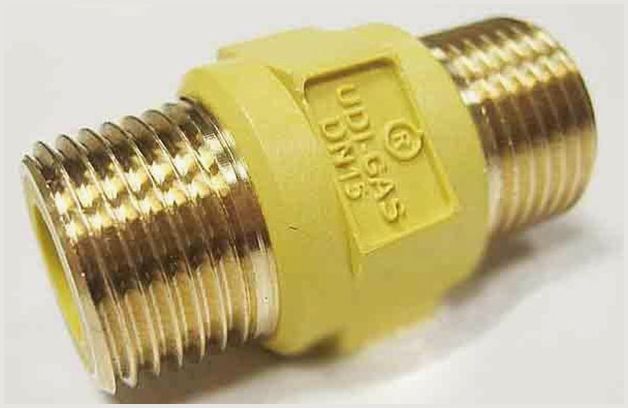
Dielectric couplings
Dielectric couplings
The company "Santim" sells insulating sleeves of its own brand STM GAZ of various configurations and diameters. All products are manufactured on modern equipment and passed the control of laboratory testing centers. The dielectric inserts (couplings) offered by us meet the requirements of Russian regulatory documents.
The purpose of the insulating sleeve
Dielectric insert for gas - a non-separable fitting with threaded ends, which is an insulating obstacle to the passage of stray currents through gas pipelines. The coupling is installed in the area between the shut-off valves and consumer equipment with electronic "stuffing" (boiler, meter, stove, fireplace, etc.).
The cause of stray currents can be both the ground loop located next to the gas pipeline, and the pipeline itself, which is loaded with a weak electrical potential to prevent corrosion. The absence of an insulating insert in the home line can not only damage the electronics of the equipment, but also cause an accident, since the devices themselves become dangerous sources.
The design of the dielectric coupling
The insulating sleeve is a structure of two interconnected fittings using an insert made of a non-combustible composite material - glass-filled polyamide.The non-separable coupling guarantees no gas leakage during operation.
The polyamide insulating insert is characterized by high strength and chemical inertness. For the manufacture of threaded metal parts of the coupling, brass of the LS-59-1 brand is used, which is not subject to corrosion processes.
The dielectric insert is available in two versions: fittings on both sides or instead of one of them there is a nut. The Santim company offers insulating couplings with ¾ and ½ ″ connecting threads, with a conditional internal passage of 15 and 20 mm.
- All STM dielectrics are designed for operation with operating pressure up to 0.6 MPa.
- Ambient temperature - from -20 to +80 °C.
- The insulating sleeves are capable of withstanding voltages up to 3.75 kV for 6 seconds.
- The electrical resistance of the polyamide insert is 5 MΩ.
Insulating sleeves are mandatory for installation in accordance with SP 42-101-2003 "General provisions for the design of gas distribution systems" (clause 6.4).
Our offer
To purchase dielectric inserts, specify the required number of items and send a request to our managers for invoicing, indicating contact information. You can quickly place an order using our price list by downloading it on the "Prices" page. A flexible pricing system when making bulk purchases will allow you to get significant discounts.
We sell STM insulating sleeves both in large wholesale and in small lots (for an amount of at least 10,000 rubles). The Santim company delivers goods to all regions of the Russian Federation from warehouses in Moscow, Novosibirsk and Yekaterinburg with the help of leading transport companies. You can get more detailed information about the technical characteristics of insulating inserts from our specialists by contacting them by phone numbers listed on the "Contacts" page.
How to fix a gas leak from a gas cylinder with your own hands
How to fix a gas leak from a high pressure gas cylinder valve or from a system attached to a cylinder?
Situation example. You filled the cylinder at the station, arrived home, connected the reducer, as well as the sleeves, tightened the hex of the reducer on the cylinder, opened the cylinder valve - and you understand that the gas is poisoning somewhere in the upper part of the flywheel. If the cylinder is filled with, for example, carbon dioxide, you will immediately feel an extraneous smell.
Attention! We warn you that the repair of cylinders should be carried out by specially trained and certified specialists! We strongly do not recommend that you carry out independent repairs of high-pressure cylinders, unskilled intervention can lead to tragedy. When carrying out the repair work described below, you are responsible for the manipulations carried out.
It happens that you need to work, but there is a small malfunction that is quite acceptable to fix on your own.
So, in order to eliminate the breakdown described above, it is necessary to do the following (valid only for the valve type VK-94 and its modifications):
To start, take a 27mm wrench and try to tighten the nut shown in the photo clockwise. In most cases this helps.
If, when you try to open the flywheel, the gas begins to poison from its upper part again, it is necessary to unscrew it counterclockwise until it stops, the leak should stop.
If the previous manipulation did not help, then the following must be done (valid only for the VK-94 valve, the procedure should be carried out only with skill):
Unscrew the nut under the flywheel counterclockwise and remove it from the cylinder.
Then use a 10mm wrench to unscrew the nut located at the top of the flywheel.
Remove the stem from the nut - a stuffing box is installed inside it.
If the cylinder is not the first freshness (and those in our country are 90%), then the gasket will be in the appropriate, “shabby” condition.To eliminate the leak, you need to make the same new gasket from fluoroplast (GOST 15180-86) or paronite (GOST 481-80). You can try to make a gasket from a plastic canister, but this is short-lived and ineffective. The inner hole of the gasket should be no more than 8.5 mm in size, the outer one, respectively, according to the size of the inner diameter of the nut. The stem after replacing the gasket should sit in a tight fit, you will need an additional tool to hammer it (hammer, flat part of the adjustable wrench, etc., etc.) and thus put it back in place. Then the flywheel is installed back and screwed with a nut.
Note. The flywheel nut is not tightened all the way, but so that the spring is tensioned, but not clamped. Otherwise, the flywheel will not rotate.
Install the assembly back on the cylinder and tighten the nut clockwise with a 27 mm wrench not to the stop (with a force of 5-7 kg).
Note. Similar procedures can be performed only with the VK-94 valve and its modifications.
The valve type VKB cannot be disassembled. If there is gas in the cylinder, even residual pressure, it is strictly forbidden to open the nut. Because apart from it, the pressure in the cylinder does not hold anything! SUCH CYLINDER CAN ONLY BE REPAIRED EMPTY.
There is a small control hole on the back side of the VKB type valve. In the event of a breakdown of the diaphragms that are inside the valve, gas begins to flow from this hole. If gas does not come out of this hole when the gearbox is screwed on and the valve is opened, then the valve is in good condition and it is allowed to work.
VKB is usually installed on helium cylinders, as a rule, VK-94 is installed on all other gases.
If the cylinder is expired and needs to be inspected or replaced, pay attention to the following things:
The cylinder wall should not have dents, rotting shells with a depth of more than 1 mm;
Pay attention to the date of manufacture of the cylinder, the passport must be read on it;
Pay attention to the valve, it should not be beaten off (so that it can be unscrewed).
How to fix a gas leak yourself
Of all the possible breakdowns in engineering networks, a gas leak is the most dangerous malfunction, so the slightest problems in the gas supply must be eliminated immediately. Of course, it is better to entrust the repair of gas equipment to specialists, but in some cases you have to solve problems yourself. Most often, gas leakage occurs at the joints. With a simple tool and some accessories, most of us are quite capable of fixing such a breakdown on our own. To do this, you will need: a gas key, a soap solution, a flexible gas supply, paranitic gaskets or a fum tape. The first sign of a gas leak is the appearance of a characteristic smell in the room. It will require step-by-step actions to eliminate it, sometimes it is necessary to replace only flexible metal hoses, and sometimes more serious intervention is required.
Step 1.
The exact location of the leak must be determined. To do this, all existing gas appliances and connections must be checked. It is very simple to do this: all joints of pipes, piping, ball valves must be covered with soapy water. If there is a leak, air bubbles will appear in the weak spot. The procedure for checking a gas column or boiler is somewhat different. First you need to turn off the gas supply and ventilate the room well. Then open the valve and turn on the burner. If the flame that appears is larger than usual, this means that the leak is in the combustion chamber, and the gas appliance needs to be repaired. It is necessary to repair gas equipment in specialized service centers.
Step 2
Having determined the cause and location of the leak, you can begin to eliminate it. To do this, the gas supply valve is closed, after which the problematic connection is untwisted and repacked.If the cause of the leak is in the gas line, it must be replaced, as the lines cannot be repaired. When installing, it must not be twisted so as not to disable it. To do this, you will need an additional wrench that holds the hose itself while another wrench tightens the union nut.
Step 3
After the cause of the leak has been eliminated, the entire system must be checked for leaks again. To do this, it is necessary to reapply the soapy solution to all connections, and if no more leaks are found, a control test of the gas appliances can be performed. If the devices work stably and there is no smell of gas, then the system is tight and fully operational.
Some Helpful Tips
In case of failure of gas appliances, contact a certified service center. Most likely, in this case, the repair will be cheaper. If the smell of gas is heard in the room, even if not very sharp, in no case should you use matches or household lighters. It is necessary to immediately turn off the gas supply, ventilate the room well and take steps to eliminate the gas leak. If you need to replace the gas supply, you can’t save money, but it’s better to choose a quality sample from well-known manufacturers. A high-quality gas supply must have individual packaging and a passport.
Varieties of dielectric cut-off couplings and bushings
The product range of stray current cutters for gas distribution systems is usually divided into two groups, which include:
Is it worth it to install a variable ignition timing? HBO 2. HBO 4
- Dielectric couplings (MD) are special connectors with threaded ends installed between the gas pipeline and the blue fuel-consuming device.
- Dielectric bushings (VD) - non-conductive liners, placed in the place of collapsible interface of gas pipeline components.
For its part, the assortment of couplings is divided into 4 standard sizes, based on the diameters of the threaded part: ?, ?, 1, 1?. A similar set allows you to cover all types of pipeline fittings used in gas pipelines, because the diameters are less than ? inches and more inches and a quarter in such systems are not used. Moreover, the nomenclature of couplings can be divided according to the design features of this connector, highlighting 3 groups: MD thread/thread, MD thread/nut, MD nut/nut. After all, the thread of this connector can be cut both from the outside and in the middle of the end part.
Dielectric couplings are mandatory for gas appliance hoses
The range of dielectric bushings is divided only based on their geometric dimensions - according to the diameter of the liner. In this case, we are dealing with 11 standard sizes and diameters from 8 to 27 millimeters. At the same time, both couplings and bushings have the same strength margin. The working pressure of one and the other types of cut-offs is 0.6 MPa (about 6 atmospheres), and the maximum is 50 MPa (493 atmospheres). In both cases, an almost non-combustible polymer material is used as a dielectric - polyamide, which has a high resistance (about 5 million ohms).
Application of anaerobic sealant.
- Operating temperature for which the sealant is intended.
- The maximum thread diameter that can be sealed with this sealant.
- Effort is needed for disassembly - there are sealants with light, medium and high disassembly forces. High break force sealants are used for large thread diameters (2.5 inches or more). Before disassembly, such a connection must be heated.
Instructions for using anaerobic sealants are given below in the video:
Anaerobic sealants are used in water supply systems, heating systems and gas pipelines. The operating temperature range usually lies between -60º and 150º C.Sealants are resistant to aggressive media and can be used together with non-freezing heat transfer fluids.
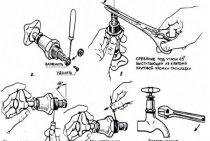
Thread sealing with flax and paste.
This method is perhaps the oldest of all. Here, linen strands are used as a sealing material, which are lubricated with a special paste for ease of subsequent disassembly. This is a rather time consuming and difficult way for a beginner in plumbing, but if you want, you can try. In order to understand how to wind linen strands on threads correctly, I suggest you watch the following video:
This method is also suitable for water supply and, to a limited extent, for heating (the operating temperature should not exceed 90º C), but it is impossible to seal plastic threads with it (as with HDPE fittings). When wet, linen gets wet and expands, and the plastic fitting may burst. Also, not recommended
use flaxseal in heating systems filled with low-freezing liquid.