External inspection of boilers under steam.
Outer
inspection of boilers complete with equipment,
equipment, service mechanisms
and heat exchangers, systems
and pipelines produced under steam
at operating pressure and if possible
combined with test in action
ship mechanisms.
At
inspection to ensure that the
condition of all water-indicating devices
(water gauge glasses, test taps,
remote water level indicators
etc.) and in good working order
upper and lower blowing of the boiler.
Must
to check the condition of the equipment,
the correct operation of the drives, the absence
passages of steam, water and fuel in glands,
flanges and other connections.
Safety
valves must be tested in operation
for actuation. The valves must be
adjusted to the following pressures:
pressure
valve opening
R
open
≤ 1.05 R
slave
for R
slave
≤ 10 kgf/cm
2
;
R
open
≤ 1.03 R
slave
for R
slave
> 10 kgf/cm
2
;
Maximum
allowable operating pressure
safety valve R
max
≤ 1.1 R
slave.
Safety
superheater valves must be
adjusted to work with
some ahead of boiler houses
valves.
Must
be tested in operation manual drives
rupture of safety valves.
At
positive results of external
inspection and verification in operation one of
boiler safety valves
must be sealed by the inspector.
If
check of safety valves
on waste-burning boilers in the parking lot
appears to be possible due to
the need for long-term work of the main
engine or feed failure
steam from the auxiliary boiler,
running on fuel, then check
adjustments and sealing
safety valves can be
produced by the shipowner on a voyage with
execution of the relevant act.
At
certification should be
the operation of automatic
regulation of the boiler plant.
At
this should make sure that the alarm,
protection and interlocks are working
fail-safe and work in a timely manner,
especially when the water level drops.
in the boiler below the permissible level, upon termination
air supply to the furnace, when extinguishing
torches in the furnace and in other cases,
provided by the automation system.
Should
also check the operation of the boiler room
settings when changing from automatic
to manual control and vice versa.
If
on external examination will be found
defects, the cause of which is not
can be established by this inspection,
the inspector may require
internal audit or
hydraulic test.
Hydraulic testing of pipelines of heating systems
Hydraulic testing of the heating system is a prerequisite for ensuring comfortable conditions in a private house. Over time, heating elements wear out and fail, testing the heating system helps prevent damage during the heating season.
Before installing heating elements and pipelines, a hydraulic calculation of the heating system is carried out, taking into account the material and internal diameter of pipes, the diameter of fittings and fittings, pipe wall thickness and other technical parameters. With incorrect calculations, the efficiency of the system can be significantly reduced, and the period of operation can be reduced several times.
Consider how the diameter of the pipeline of the heating system is calculated and the diameter of the pipes is determined depending on the nominal load on a single section.
Calculation of the section of the heating pipe
D = √354∙(0.86∙Q:∆t):V
where D
- diameter of the heating pipe, cm;
Q
- load on the calculated section of the system, kW;
∆t
– temperature difference between the falling and return pipes, ᵒС;
V
is the speed of movement of the coolant, m/s.
This calculation allows you to determine the average diameter of the pipe of the heating system. Professional calculations of the heating system use significantly more data. In this case, not only the size of an individual pipe is determined, but also the diameters of the narrowed sections, the distance between the pipelines, and so on.
Why is hydraulic testing of a heating system necessary?
Each individual heating system has its own operating pressure, which determines the degree of heating of the room, the quality of the circulation of the coolant, and the level of heat loss. The choice of working pressure is influenced by a number of factors, including the type of building, the number of storeys, the quality of the line, and so on.
While the coolant moves through the pipelines, various hydraulic processes occur, which lead to pressure drops in the system, called water hammer. It is these loads that usually cause the accelerated destruction of the heating system, therefore hydraulic tests are carried out at a pressure 40% higher than the nominal one.
Hydraulic testing of pipelines of heating systems is carried out after performing the following work:
- checking valves, serviceability of valves of shut-off type;
- strengthening the tightness of the system by means of additional glands (if necessary);
- restoration of pipeline insulation layers, replacement of worn materials;
- cutting off the house from the general system with the help of a blind plug.
When carrying out pressure testing, as well as for further filling the system with coolant, a drain-type valve is used, which is installed on the return.
6 RECOMMENDED MEASURING EQUIPMENT
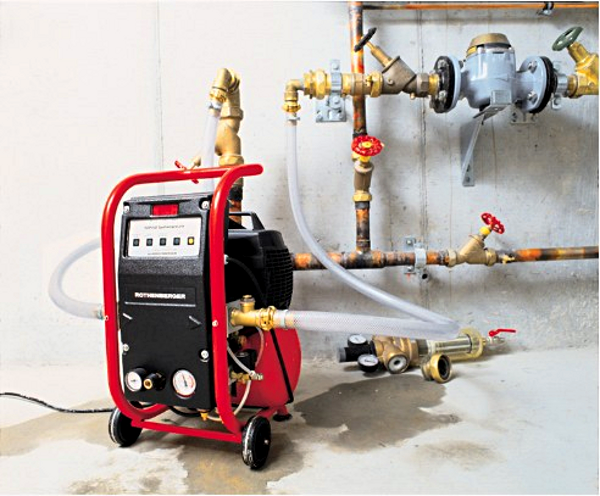
When testing heat networks for hydraulic losses, it is necessary to simultaneously measure and record a large number of parameters, mainly pressures and flow rates of network water.
Therefore, great attention should be paid to the choice of measuring equipment and the organization of the measurement process.
Registration of the measured parameters can be carried out by recording them by observers in the appropriate tables, as well as automatically - by recording on various intermediate information carriers.
Currently, a wide range of measuring and recording equipment of domestic and foreign production is being produced that meets the requirements given in the section.
For visual recording of pressure, exemplary deformation pressure gauges (MO type) of an accuracy class of 0.4 and higher can be used, and with significant pressure changes along the length of the network, accurate measurement deformation pressure gauges (MTI type) with an accuracy class of at least 0.6 can also be used.
For automatic registration, electric pressure transducers of the MT100 type manufactured by Manometr, METRAN-43 of the Metran concern or ZOND-10 transducers manufactured by NPP Hydrogazpribor with an accuracy class of 0.25 and higher can be used. When these instruments are equipped with secondary indicating equipment of the appropriate accuracy class, they can also be used for visual recording of pressure measurements.
Flow measurements can be made by standard flow meters at the heat source and subscriber inputs as part of heat supply and consumption metering units, provided that they have the required accuracy class, are metrologically certified and installed in accordance with technical requirements.
Flow measurements can also be made using portable ultrasonic flow meters of domestic and foreign production, subject to the rules for their installation. These devices are equipped with indicating digital devices and have outputs of normalized current signals, which allows them to be used both for automatic and visual registration of measurement results. Portable flowmeters from KRONHE, PORTAFLOW flowmeters from various manufacturers, portable flowmeters from PANAMETRICS, as well as domestic flowmeters from VZLET can be used for testing.
Automatic registration of the measured parameters to improve the accuracy of measurements, it is advisable to carry out in digital form. To do this, the computing units of heat meters can be used, provided they comply with the requirements for the frequency of registration of the measured parameters.
Currently, a large number of different specialized controllers are produced for converting and storing measurement information, however, they are designed to process a large number of measurement channels for a long time with a fixed frequency of polling sensors and are mainly used for large information and measurement complexes. Therefore, their application for hydraulic loss testing, as a rule, requires some refinement.
A ready-made independent device of this type, applicable in the field, is the data storage device SQUIRREL 1003 from GRANT. It has the necessary service capabilities with sufficient storage capacity.
Measurements of network water temperatures can be made with any thermometer that provides an accuracy of at least 1.0 °C.
The results of the control pressure testing of the gas pipeline
A positive result of the work performed is a stable pressure in the gas communication section. In this case, the repair team must remove the hoses connecting the duct to the gas pipeline. During these actions, it is necessary to check that all shut-off valves on the air supply to the gas pipeline are closed. Next, plugs are installed on the pipes supplying air to the gas pipeline.

In the event of a pressure drop in the communication during pneumatic pressure testing, its result will be negative, and the launch of the gas pipeline will be delayed until appropriate measures are taken. A subsequent survey of the test site will be required to identify non-conformities with their further elimination. Then, the gas pipeline must be re-checked.
The results of the work carried out are recorded in a special journal and recorded in the outfits of the working team. Before starting the system, it must remain air pressure.
At enterprises with gas supply, in addition to the act of acceptance and delivery of gas facilities, the following documents must be available:
- an order to appoint a person responsible for the organization's gas facilities;
- instructions for the operation of communications, equipment and apparatus of the organization's gas facilities;
- instruction on labor protection during operation and repair work on gas pipelines and gas equipment.

Company video PROMSTROY
Watch other videos
Hydro tests are needed to establish the actual hydro readings of a new line and equip points or transform these values when used. During this approbation, p, waste is simultaneously transformed together with t of the coolant in certain segments of the heating network. According to the measurement values p in the delivery and return pipelines, the actual piezometric mode is built, and the counting mode p is set according to the liquid flow rates in places. By comparison, the discrepancies of the specific and counting piezometric modes are formed.
Thermal tests are needed to find out the real waste of heat in the lines and compare them with calculated and normalized readings. The need for this testing is dictated by the usual defeat of thermal insulation, its change in separate places, and, moreover, by the transformation of buildings. During approbation, the flow rates and t of the coolant are replaced at the base and at the end of the investigated part of the supply and return pipelines.
Testing for the highest temperature of the heat carrier is carried out to revise the practicality of buildings, the performance of correctors, the displacement of risers, to identify real stresses and distortions of more loaded parts of the heating line.
Also, heating mains are tested for strength and impermeability. They are performed both on separate segments and on the general line in general. When performing these tests, client devices must be exactly turned off, their testing is also carried out separately.
- Testing can be carried out on water and steam heating lines for heat consumption.
- Testing of water heating lines for hydroflow.
Act of pressure testing of the heating system
This document displays the following information:
- What kind of crimping method was used;
- The project in accordance with which the circuit was installed;
- The date of the check, the address of its conduct, as well as the names of the citizens who sign the act. Basically, this is the owner of the house, representatives of the repair and maintenance organization and heating networks;
- How were the identified problems resolved?
- Check results;
- Are there signs of leakage or reliability of threaded and welded joints. In addition, it is indicated whether there are drops on the surface of fittings and pipes.
Regulatory rules for hydropneumatic testing
The rules for carrying out such work are determined by regulatory documents - SNiP (building regulations).
These standards regulate certain technological schemes and instructions, taking into account the specifics of the work in terms of compliance with safety regulations, and also determine the equipment for pressure testing the heating system.
Some of them extend from the front to the rear vertically throughout the car and take up all the windows, preventing head bumps and crystals from entering the cabin. In some models, additional airbags are also available in the following area on the injury scale: leg area. To minimize damage to occupants, most airbags have begun to include a system that allows them to deploy more or less intensity depending on the severity of the crash. Thus, the rapid expansion of the bag does not allow harm with minor impacts.
Hydraulic tests should be preceded by flushing and preparation of the main pipeline of the heating system. Flushing is carried out in various ways and aims to remove scale and deposits of their various salts and other chemical compounds from the inner walls of pipes in the system. For this, a compressor is used.
What is pressure testing of a heating and water supply system
It should not be forgotten that the airbag is an addition to the seat belt and does not replace it in any way. This cushion can prevent injury in very low speed crashes, but if we don't wear a belt it doesn't help in heavy collisions.
Air conditioning Increases comfort while driving, cools the air entering the passenger compartment and dries and filters the air. Its most famous mission is to maintain a stable temperature inside the vehicle using a refrigeration circuit. He bases his work on the fact that a liquid evaporates by increasing its temperature or decreasing the pressure it is subjected to, a process in which heat is absorbed.The closed circuit is used with a gaseous refrigerant having a low boiling point.
The composition of deposits on the walls of pipes of heating systems (in descending order):
- divalent iron oxide;
- magnesium oxide;
- calcium oxide;
- copper oxide;
- zinc oxide;
- trivalent sulfur oxide.
What is the practical meaning of such washing? During operation, the heating efficiency is significantly reduced due to deposits and deposits on the pipes.
The passage diameter of the pipes due to deposits and scale is almost halved. All this leads to breakdowns and violations of proper operation. Due to scale and deposits, the quality of water circulation is reduced.
Its action is based on Faraday's Law: a coil of wire that moves inside a magnetic field is charged by electrical energy. Thus, the generator consists of a magnetic part called a rotor that rotates inside the housing. To ensure that the generator always moves at high speed, it is attached to the engine with a series of pulleys and belts. Some competition vehicles use special permanent magnet generators that provide higher rotational speeds and weigh less than usual.
Such a high temperature will fall into both the tap and the batteries.
For safety reasons during the test period hot water will be turned off
all consumers connected to the district heating system. will also heating off
schools, preschool institutions, health care institutions. During the tests for 5 - 6 hours, high temperature water will circulate in the heating systems of residential buildings.
Residents in whose apartments polypropylene pipes are installed should not worry, because even when a coolant at an elevated temperature is supplied to the internal system of the house, a displacement of network water from the supply and return pipelines must be provided, and the coolant will enter the heating system with a temperature of no higher than 95 degrees, and this is in accordance with the regulations.
It is also noted that sometimes during testing, management organizations arbitrarily turn off central heating systems in residential buildings, in addition to the safety-required shutdown of hot water supply. This is contrary to the test program and may adversely affect their conduct, causing an increase in pressure in pipelines and causing damage.
IMPORTANT: The leaders of the management company, HOA, housing cooperative need to complete the entire range of technical and organizational measures to prepare for temperature tests.
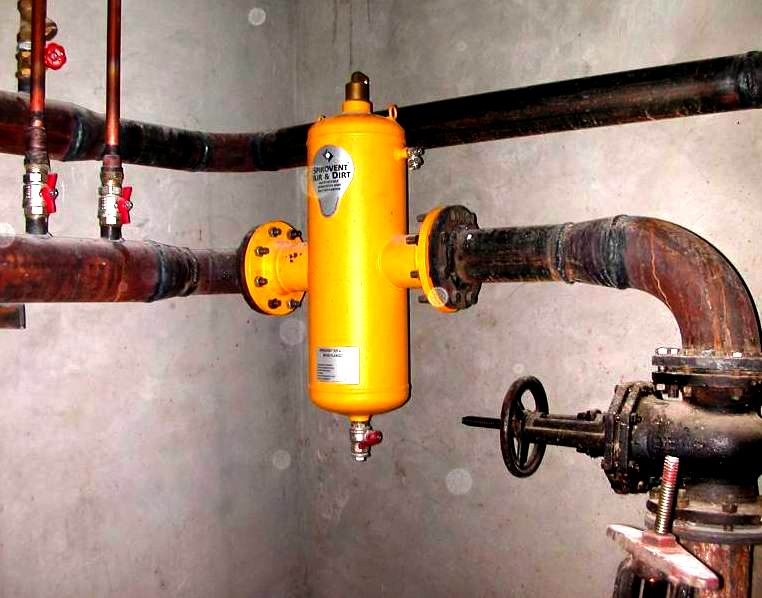
What is an air separator
Air separators or their other name - air collectors for heating systems are designed to remove air from the coolant that circulates in the circuit. It is used for systems of any type, in underfloor heating systems and in. Water is passed through a separator to remove dissolved gases and various contaminants that adversely affect the system and contaminate various valves. The air separator makes the question - how to properly remove air from the heating system, absolutely irrelevant. But to increase the reliability and durability of the system, a separator and manual or automatic air vents are installed in the heating system of a house or enterprise.
Air separators have many useful properties that improve heating circuits:
Therefore, the answer to the popular question - how to bleed air from the heating system, is simplified. There will be so little air in the system that its scanty remnants can be easily removed manually. For this, Mayevsky cranes and automatic air vents are used. There is a fundamental difference between manual and automatic air vents. The Mayevsky crane removes, for example, air congestion that has accumulated at the top points.
The separator extracts the air dissolved in the water and removes it.

Flushing period for heating systems
Temporary scheduled shutdown of the heating network does not imply a drain on the resource from the radiators.
This is due to the following reasons:
- the deposits will dry out, harden;
- after refilling, leaks will occur in the connecting areas.
Therefore, experts recommend draining water from the heating system of an apartment building only in summer, after the end of the cold period. The spent resource is discharged into the sewer through the drain valve. To speed up the flow of water, it is necessary to open the air locks on the radiators of the upper floors. The risers are cleaned first with cold, then heated water, while the liquid coming out of the pipes will carry mud, lime suspensions with it.
At the end of the procedure, the boiler is filled with water with the addition of chemicals that slow down the slagging of the heating circuit. The level of liquid in communications should not rise above the control mark of the safety tank.
When and for what gas facilities do you need control pressure testing?
Pressurization with air or inert gas is carried out:
- for gas control points (GRP) and gas control units (GRU) after they have been installed;
- for internal and external gas pipelines, tanks, apparatus and equipment before connecting them to existing communications;
- for pipes and gas equipment after repair or replacement.
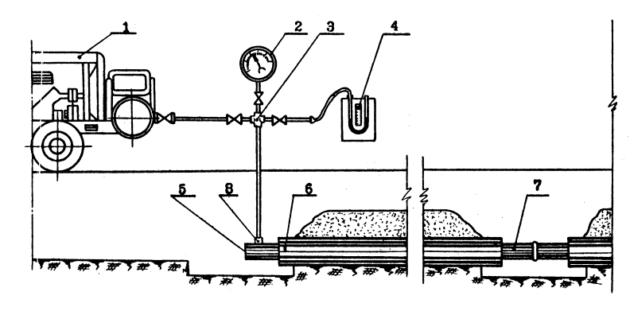
When the indicator of excess air pressure in the embedded pipeline is not lower than 100 kPa, control pressure testing can be omitted.
A control check with an inert gas or air of external communications is carried out at a pressure of 20 kPa, while this value should not fall by more than 0.1 kPa within an hour. This procedure should be applied to the internal gas pipes of industrial shops, rural enterprises, public buildings and boiler houses, as well as the apparatus and equipment of hydraulic fracturing and gas distribution units, only under a pressure of 10 kPa, with an allowable loss per hour of 0.6 kPa.
A control check with air at a pressure of 30 kPa for 60 minutes must be carried out for containers with liquefied gas. The health check is considered passed if the pressure readings on the pressure gauges have not decreased.
Heating wiring options
Working mechanism for all hydraulic systems
as the masters say, PiterRem is about the same; it involves heating the coolant in the boiler (heat generator), from where the coolant enters a closed chain of pipes and heaters laid throughout the house. Water is usually used as the heat carrier; much less often other liquids are used for these purposes - the so-called "antifreeze", special anti-freeze liquids. Passing through all the heating devices of the chain, water or another coolant gives off heat to each of them, after which it returns to the boiler, and then the whole process is repeated.
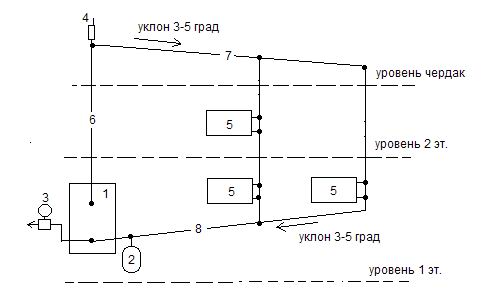
Diagrams of hydraulic heating systems
differ not only in their engineering features, but also in the principles of operation. According to the nature of the movement of the coolant, they are divided into systems with natural and forced circulation. The former are used in small houses (50-150 m²), the latter in traditional construction (250 m² and more).
-
natural circulation
- water is heated in the boiler and rises through the supply vertical pipeline. As the water cools, it becomes heavier, its density increases, and completing the circle, the less warm water that gave off heat returns to the boiler through the return pipeline. Such a system is able to work without electricity, but it looks “not very” in the interior of the house and “eats” more fuel.
-
forced circulation
- the coolant moves with the help of a circulation pump, which allows the use of pipes of smaller diameters and does not observe slopes. The circulation pump only helps the coolant overcome the resistance of the pipelines. A system with forced circulation is more comfortable, the heat in such a system can be controlled. The quality of such a heating system is higher, but uninterrupted power supply is required here.
Permissible test pressure during pressure testing of water heating
Many developers are interested in under what pressure it is necessary to check the heating system. In accordance with the requirements of SNiP presented above, during pressure testing, a pressure higher than the working one by 1.5 times is allowed
, but should not be less than 0.6 MPa.

In private houses equipped with autonomous heating, it does not rise above 2 atmospheres, and it is adjusted artificially: if there is excess pressure
, then the relief valve immediately turns on. Whereas in public and multi-apartment buildings, the working pressure is much higher than these values: five-story buildings - about 3-6 atmospheres, and tall buildings - about 7-10.
What precautions should be taken
First of all, you need to be careful when handling heating appliances. To avoid emergency situations during the test period, hot water taps should be kept closed.
If the shut-off valves that turn off hot water are faulty in the heating point of a residential building, and hot water actually continues to flow into the house, we recommend that you be careful when using water, establish increased control and exclude small children from access to mixing devices.
There are 4 types of heat network tests:
-
For strength and tightness
(crimping
). It is carried out at the manufacturing stage before applying insulation. When used annually. -
at design temperature
. Carried out: in order to check the operation of expansion joints and fix their working position, to determine the integrity of fixed supports (1r. in 2 years). Tests are carried out during the manufacture of networks before applying insulation. -
hydraulic
. They are carried out in order to determine: the actual consumption of water by consumers, the actual hydraulic characteristics of the pipeline and the identification of areas with increased hydraulic resistance (1 time in 3-4 years). -
Thermal testing
. To determine the actual heat loss (1 time in 3-4 years). Tests are carried out according to the following dependence:
Q \u003d cG (t 1 - t 2) £ Q norms \u003d q l *l,
where q l - heat losses of 1 m of the pipeline, are determined according to SNiP "Thermal insulation of pipelines and equipment".
Heat losses are determined by the temperature at the end of the section.
Strength and tightness tests.
There are 2 types of tests:
-
hydraulic
. -
Pneumatic
. Checked at t n
Hydraulic tests.
Devices: 2 manometers (working and control) class above 1.5%, manometer diameter not less than 160mm, scale 4/3 of the test pressure.
Order of conduct:
- Shut off the test area with plugs. Replace gland compensators with plugs or inserts. Open all bypass lines and valves if they cannot be replaced with plugs.
- The test pressure is set = 1.25R slave, but not more than the working pressure of the pipeline P y. Exposure 10 minutes.
- The pressure is reduced to the working pressure, at which the inspection is carried out. Leaks are monitored by: pressure drop on the pressure gauge, obvious leaks, characteristic noise, fogging of the pipe. At the same time, the position of the pipelines on the supports is controlled.
Pneumatic tests
it is forbidden to carry out for: Above-ground pipelines; When combined with laying with other communications.
When testing, it is forbidden to test cast iron fittings. It is allowed to test ductile iron fittings at low pressures.
Devices: 2 pressure gauges, pressure source - compressor.
- Filling at a rate of 0.3 MPa/hour.
- Visual inspection at pressure P ≤ 0.3P tested. , but not more than 0.3 MPa. R isp \u003d 1.25R work.
- The pressure rises to P tested, but not more than 0.3 MPa. Exposure 30 min.
- Reduction of pressure to P slave, inspection. Leaks are determined by signs: a decrease in pressure on pressure gauges, noise, bubbling of a soap solution.
Safety precautions:
- during the inspection it is forbidden to go down into the trench;
- do not get exposed to the air stream.
Design Temperature Tests
Thermal networks with d ≥100mm are tested. At the same time, the design temperature in the supply pipeline and in the return must not exceed 100 0 С. The design temperature is maintained for 30 minutes, while the increase and decrease in temperature should not exceed 30 0 С/hour. This type of test is carried out after pressure testing of networks and elimination of gusts.
Tests to determine thermal and hydraulic losses
This test is carried out on a circulation circuit consisting of supply and return lines and a jumper between them, all branch subscribers are disconnected. In this case, the decrease in temperature along the movement along the ring is caused only by the heat losses of the pipelines. The test time is 2t to + (10-12 hours), t to - the time of run of the temperature wave along the ring. Temperature wave - an increase in temperature by 10-20 0 C above the test temperature along the entire length of the temperature ring, is established by observers and the temperature change is recorded.
The test for hydraulic losses is carried out in two modes: at maximum flow and 80% of the maximum. For each of the modes, at least 15 readings should be taken with an interval of 5 minutes.
Why and when to conduct hydraulic tests
Hydraulic testing is a type of non-destructive testing that is carried out to check the strength and tightness of pipeline systems. All operating equipment is exposed to them at different stages of operation.
In general, there are three cases in which testing must be mandatory
regardless of the purpose of the pipeline:
- after the completion of the production process for the production of equipment or parts of the pipeline system;
- after completion of the installation work of the pipeline;
- during the operation of the equipment.
Hydraulic testing is an important procedure that confirms or disproves the reliability of a pressure system in operation. This is necessary to prevent accidents on highways and preserve the health of citizens.
A procedure is being carried out for hydraulic testing of pipelines in extreme conditions. The pressure under which it passes is called test pressure. It exceeds the usual working pressure by 1.25-1.5 times.
Features of hydraulic tests
Test pressure is supplied to the pipeline system smoothly and slowly so as not to provoke water hammer and the formation of accidents. The pressure value is determined not by eye, but by a special formula, but in practice, as a rule, it is 25% more than the working pressure.
The force of water supply is controlled on pressure gauges and measurement channels.According to SNiP, jumps in indicators are allowed, since it is possible to quickly measure the temperature of the liquid in the pipeline vessel. When filling it, it is imperative to monitor the accumulation of gas in different parts of the system.
This possibility should be ruled out at an early stage.
After filling the pipeline, the so-called holding time begins - the period during which the equipment under test is under increased pressure
It is important to ensure that it is at the same level during exposure. After its completion, the pressure is minimized to a working state.
Personnel serving it must wait in a safe place, as checking the functionality of the system can be explosive. After the end of the process, the results obtained are evaluated according to SNiP. The pipeline is inspected for metal explosions, deformations.