All right, let's build a house
Published on 01.12.2013

It is necessary to have accurate information in order to correctly determine the type of foundation and the depth of its laying. In the process of choosing the type of foundation, one of the important factors is the level of occurrence of groundwater (GWL) - the first aquifer below ground level. It is no secret that, in addition to atmospheric precipitation, water bodies are also sources of groundwater.
Therefore, special attention should be paid to this indicator in places where they are located close to the construction site.
It should be understood that the higher the groundwater level, the lower the bearing capacity of the soil.
However, even with a low GWL, you need to pay attention to the composition of the soil, since it can be dry, but have a low bearing capacity, for example, sandy dusty soils
The high level of groundwater occurrence imposes significant restrictions on the arrangement of house foundations. First of all, this prevents the construction of underground facilities (basement, basement, etc.), as there is a constant threat of flooding. Additional costs for high-quality waterproofing and drainage will be required. The depth of the foundation in this case must be chosen depending on the depth of soil freezing on the site, since a high level of groundwater significantly reduces the bearing capacity of the soil.
The low level of groundwater does not affect the choice of the foundation of the house. In this case, they are guided by the type of soil and its bearing capacity.
Approximately high and low levels of groundwater occurrence are considered at a mark of 2 m from the earth's surface: more than this - low GWL, less than 2 m - high GWL. However, often groundwater is located underground in waves. Therefore, on the same plot of land in different places there may be a different level of groundwater. This must be taken into account when designing the foundation. For flat areas, the GWL is, as a rule, evenly distributed.
There are several ways to independently determine the level of groundwater, as well as indirect signs - lush and lush vegetation is one of these signals about the proximity of groundwater. Since the groundwater level depends on the season, it is most accurately determined in the spring, when the soil is saturated with precipitation.

If there are wells, wells near the site, then first of all it is them that should be checked, since they are filled with ground water. The water level in the well will be the desired groundwater level.

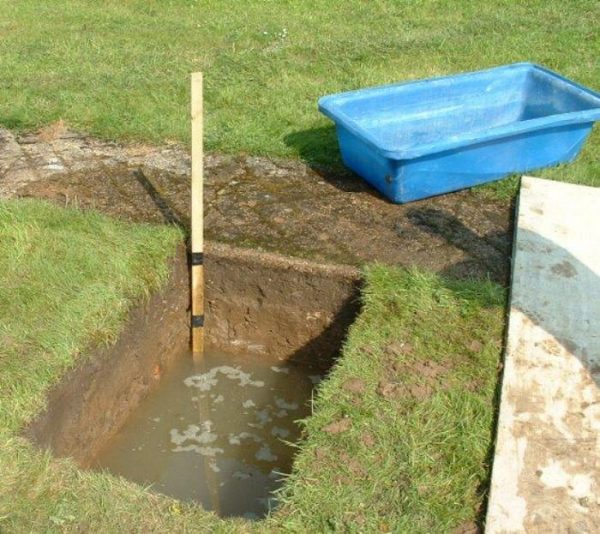
If this is not possible, then it is necessary to drill in places where the GWL is determined, wells of small diameter and a depth of 2–2.5 meters. This can be done with an ordinary garden drill (manual or mechanical). For some time (about a day), observations of such wells will prompt the level of groundwater. If at the end of the day the bottom of the well remains dry, then the GWL is considered low and vice versa. If water accumulates in the well, then it is necessary to measure this level, it will be the level of groundwater at this point.
Knowledge of the GWL on the land plot for the construction of a house will also be useful in the process of arranging wells, water wells, drainage systems, decorative ponds, etc.
It is extremely important to have reliable information, therefore, although there are folk methods for determining this indicator, accurate data can only be obtained with the help of engineering intelligence
Tip: Do not skimp on engineering surveys - conducting them once for a particular site, the data obtained will be useful more than once and can save significant funds in the future.
Ventilation device
Proper ventilation is half the guarantee of the safety of the contents of the cellar.It will not allow the products to deteriorate, but at the same time it will not freeze and will maintain the required level of humidity.
Usually, the simplest and cheapest type is installed - ventilation from pipes, which can be done in two ways:
The first method is the installation of two pipes placed at different ends of the cellar at different levels.
The opening of the supply pipe is installed at a height of 50-60 cm from the floor, and the exhaust pipe - under the very ceiling. This is necessary for better air circulation, according to the simple laws of convection, familiar to everyone in the course of physics in high school.
To regulate the temperature, you can equip the pipes with dampers, and the diameter of the pipes will directly affect the quality of air exchange, it cannot be less than twelve centimeters.
The second method is suitable only for small cellars with an area of 6-8 square meters and consists in installing one two-channel square pipe 15 * 15 cm, divided inside into 2 channels.
Such a pipe can also regulate temperature and humidity by a valve and by moving it up or down.
The problem of how to make a cellar if there is groundwater nearby is actually not so difficult, it just requires a little more cost for moisture-resistant materials and calculations for proper construction.
Another related video:
If you are not greedy and lazy, you can put a cellar on almost any site, and you do not need to have special construction or geological skills.
Other ways to determine
One of the easiest ways is to contact the land management service, where they can provide specific data, or at least topographic maps, by which you can determine the highs and lows. By the way, in this regard, you can make independent observations. Take a look around and evaluate whether the area is on a hill or in a lowland. The lower the level, the more likely it is that groundwater will be close.

In the case when there is a well nearby, then the level can be approximately estimated from it. To do this, just look into the middle, lower the measuring cord to the water mirror, then measure the distance. But the value will be approximate if the source is filled with an underground river, which can slightly raise this value due to the current. Also, this will not talk about the saturation of the soil specifically in your area.
Drainage and lowering of the groundwater level
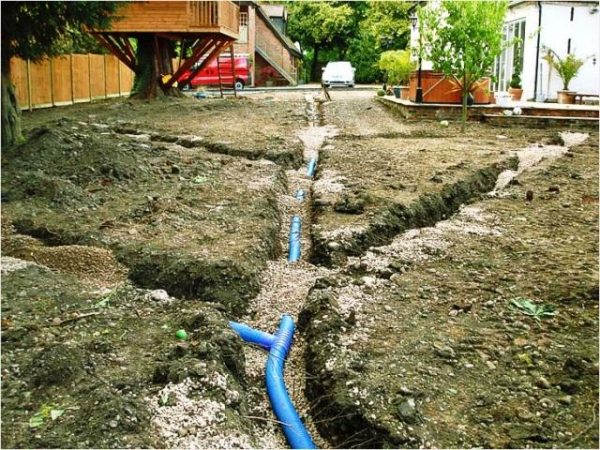
When arranging excavations located below the groundwater level, it is necessary to drain the water-saturated soil and ensure its development under normal conditions. In addition, it is necessary to prevent the ingress of groundwater into pits, trenches and workings during the period of work in them.
An effective technological method for solving such problems is the pumping of groundwater. Ditches and trenches with a small influx of groundwater are developed using open drainage, and if the inflow of water is significant and the thickness of the water-saturated layer to be developed is large, then before the start of work, the groundwater level is artificially lowered using various methods of closed drainage, called dewatering.
Open drainage is used to pump flowing water directly from pits or trenches with pumps. With open drainage, groundwater seeps through the slopes and the bottom of the pit and is directed along dug drainage ditches or trays to pits specially arranged in the lower part of the pit, called sumps, from where water is pumped out by diaphragm or centrifugal pumps of appropriate capacity. Pumps are selected depending on the debit (inflow) of water, and the debit itself is calculated according to the formulas for the steady movement of groundwater.
Drainage ditches are arranged with a bottom width of 0.3 ... 0.6 m and a depth of 1 ... 2 m with a slope of 0.01 ... 0.02 m towards the pits.The pits themselves in stable soils are fixed in the form of a wooden log house without a bottom, and in slipping soils with a sheet pile wall.
Open drainage is a simple and affordable way to deal with groundwater, but has a serious technological drawback. Ascending flows of groundwater flowing through the walls and bottom of pits and trenches liquefy the soil and bring small particles out of it to the surface. As a result of such washing out, this method has a number of significant disadvantages:
Level detection
There are several ways to determine the level of groundwater. But there is a general rule: measurements should be taken in early spring, immediately after the snow melts, because during this period the groundwater is at its maximum.
The simplest, but at the same time the most accurate and effective way is to determine it by the water level in the wells located next to the site. Water in the depths of the well comes only from groundwater, therefore, by the distance from the top of the well to the water surface, you can accurately determine how far they are from the surface. For a more accurate picture, it is better to perform such measurements not in one, but in 2-3 wells.
The second method, which is often used in the construction of private houses, especially if there are no dug wells nearby, is drilling test wells. With this method, an ordinary garden drill is used as a working tool. With this drill, 3-4 test wells are drilled along the perimeter of the construction site to a depth of 2-2.5 m. If water does not appear in these wells for 1-2 days, this means that it is deep enough, during construction it can not fear.
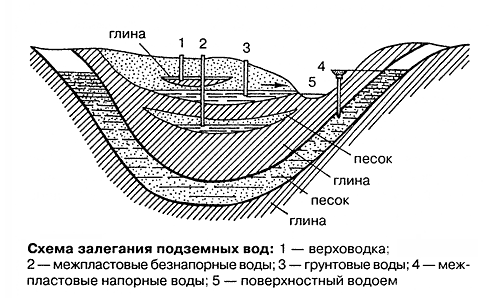
Scheme of the main types of groundwater.
There are also old ways. For example, a piece of wool should be washed well and dried. Then you need to take this scrap, a raw chicken egg (necessarily freshly laid, still warm) and a clay pot.
In the place chosen on the site, you need to carefully remove the sod, put wool on the bottom of the formed hole, put an egg on the wool and cover them with an inverted clay pot. From above, the pot must be carefully covered with a piece of removed turf.
This kind of indicator will show the results the next morning, as soon as the sun rises.
It is necessary to remove the sod, carefully remove the pot and pay attention to the dew formed under it. If there is dew not only on the wool, but also on the egg, then you can be sure that the water in this place is not very deep.
If the dew has formed only on the wool, but not on the egg, then it is at a decent depth. If, as a result, both the wool and the egg remain dry, then the water in this place is very deep, if there is any.
It is possible to determine that groundwater is close without carrying out earthworks on the site. It is enough just to examine it carefully. If during a drought thick green-emerald grass or a lot of moss grows on your site, and in the evenings you constantly see fogs over your site, although there is no river or lake near the site, then it is highly likely that the waters are high.
You can also decide on the plants growing on the site. If hemlock, nettle, horse sorrel, foxglove, sedge, reeds predominate among them, then from the ground surface to the water it is probably no more than 3 m. And if wormwood or licorice predominate, then you will not find moisture in less than 4-5 m.
So, there are many ways to determine the depth of groundwater. Not all of them are equally accurate, but you can use them to get a general idea of \u200b\u200bthe aquifers in your area. If you want to know the exact picture, then order a special geological survey of your site. After all, an accurate map of groundwater can only be drawn up with the help of well drilling performed by professionals.
Drilling method
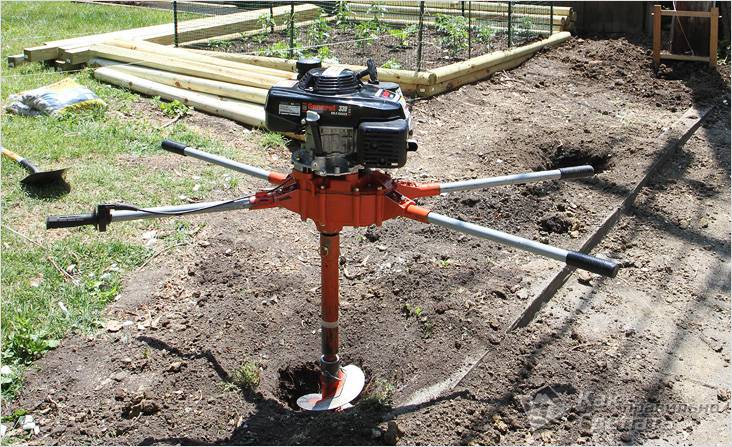

One of the modern and simple ways to determine the level of occurrence of perched water is carried out using a conventional hand drill. The fact is that if the reservoir is deeper than 2 meters, then there is nothing to worry about and you can safely carry out construction. A garden drill machine perfectly breaks through such a distance. For work you will need:
- spoon drill;
- metal or other straight rod;
- roulette.
With everything you need, a small well is drilled
It is important to go deeper than 2 meters. When performing work, it will be necessary to remove the soil in a timely manner so that it does not crumble
After reaching the required depth, cover the hole and leave it in this state for a day. The rod is marked with a tape measure. You can choose the step that is convenient for you personally. It sinks to the bottom, is removed and a visual assessment of the liquid is made. These actions should be repeated for several days. If the indicators do not change, then the value can be considered constant.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=6fEh5sKPTp8
Working with Wellpoints
Forced lowering of the water level is the arrangement of a drainage system, pipe wells and / or wells, wellpoints. Industrial dewatering of the pit uses wellpoints - wellpoints of light type (LIU), ejector dewatering units (EVU), well systems and chains (CC), deep pumping equipment for dewatering, and vacuum dewatering units (UVV). This equipment is folded into a scheme for extracting water from the soil of a trench or pit using a chain of boreholes with water receivers made up of pipes and connected to a drainage well, pumping equipment and pipe outlet.
Methods and technology of dewatering, as well as the choice of equipment (wellpoints or ejectors) depend on the depth of excavation, geological and hydraulic conditions of the soil in the pit, and many other indicators.
To implement artificial dewatering of construction sites, a condition is necessary under which k ≥ 1-2 meters per day. A smaller coefficient slows down the movement of groundwater, therefore, in such cases, open drainage, vacuuming or electric osmosis is used.
The technology in which wellpoints are used is a chain of wells located close to each other, in which tubular water receivers of small diameter are built - wellpoints. These wellpoints are connected to a common circuit, which is connected to the suction manifold and pump. In order to forcefully lower the groundwater level by 4-6 meters, in light soil (sand or sandy loam), LIU is used - light wellpoint installations.
LIA can be single-row (for dewatering in pits up to 450 cm wide), double-row (to ensure dewatering in pits more than 450 cm wide), as well as multi-tiered (up to three tiers), which, if necessary, will equip to lower the groundwater level to a depth of ≥ 5 meters .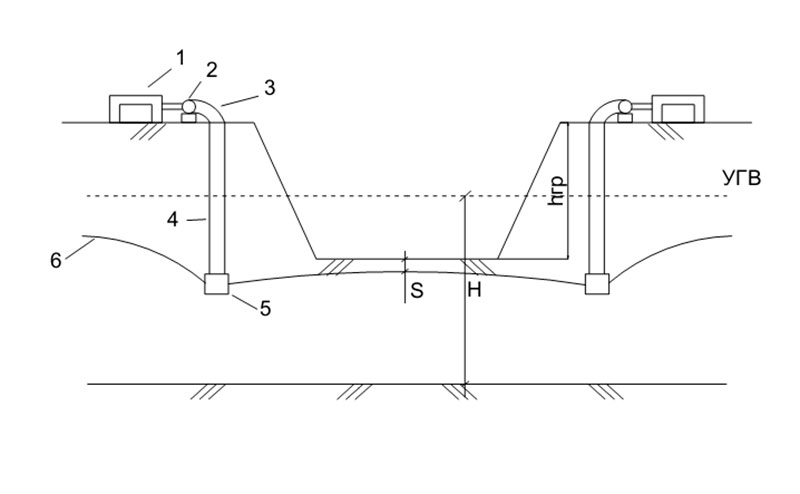
The figure shows a standard drainage scheme for LIA. Distance S must be at least 50 cm.
- Surface centrifugal pump;
- Collector for collecting groundwater;
- Corrugated rubberized hose;
- Overfilter pipeline;
- Actually the filter;
- depression curve.
With multi-tiered dewatering, the first step is to activate the upper tier of wellpoints, which serves as protection for the soil, after which you can open a pit or trench on the first ledge. Next, the lower tier of the LIA is installed, and the pit is deepened again. Thus, it is possible to build up the tiers to the required depth of the trench or pit. Previous LIA circuits can be turned off and even disassembled after the next tier is put into operation. Such a decrease in GWL is useful in the construction of facilities on poorly permeable soils, provided that a more water-saturated soil layer lies under them.
The ejector technology of dewatering is used in parallel with wellpoint installations, and allows using water jet pumps to lower the groundwater level to 15-20 meters, provided that the filtration coefficient k at the site is ≤ 0.5-1 meters per day. Under the action of pumping equipment, groundwater is fed into a special circulation tank for subsequent pumping from the construction site. In addition to pumping, some water can be removed through the sewer system, and some of it is fed back to the pump to ensure its safe operation.
If it is necessary to carry out dewatering at the construction site, then the ejector method is best used during erosion of the upper layers of the soil. The initial stage is the drilling of wells for the installation of wellpoints. This method can be used both in industrial and individual construction. The difference is only in the number of mounted devices and wells. The technology works most effectively at depths of 10-15 meters.
What is it
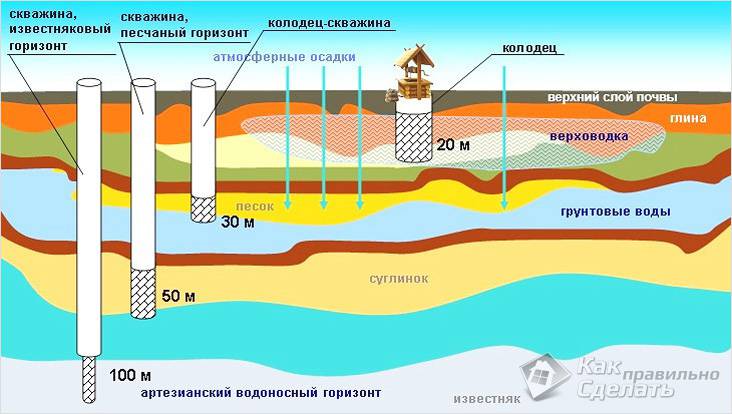
Groundwater is the topmost layer of liquid that occurs in the earth. Sources are rivers or lakes that may be nearby. Another filler is precipitation in the form of rain and snow. The level may fluctuate at different times of the year. For example, in the summer, with a severe drought, the GWL drops to a minimum, which causes wells and streams to dry up. Their proximity to the surface may impose such restrictions during construction:
- inability to organize a basement or cellar;
- the impossibility of building an outdoor toilet;
- difficulties in choosing the type and size of the foundation;
- restriction on the use of certain building materials;
- growth of mold in the house;
- the complexity of laying communications in the ground;
- high degree of soil heaving.
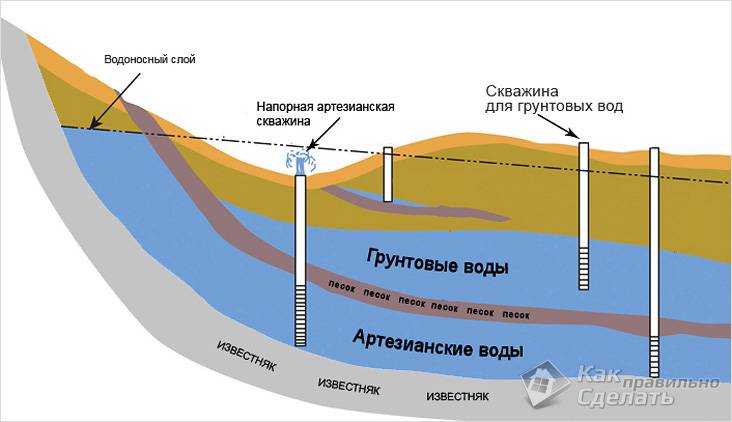
According to the level of distribution, 3 main types of aquifers are distinguished:
- Verkhovodka. May reach to less than 2 m from the surface. It is most often observed in areas where clay and loam predominate in the composition of the soil.
- Interlayer. Consists of perched water and other waters that have been purified through a natural filter. Usually does not have pressure.
- Artesian. It is very similar to the previous one, but is able to independently rise to the surface, due to the presence of internal pressure.
The latter species is quite rare, but can become a source of clean drinking water without the need to lift it with deep pumps.
Groundwater control

If it so happened that the situation in your area has changed dramatically and for some reason groundwater has begun to rise closer to the surface, there are several ways to help partially alleviate the situation:
- Organizing a hedge. To do this, you need to choose plants that are very fond of moisture and have a wide crown, which will contribute to a sufficient level of evaporation. For example, you can use wild rose, hawthorn, spirea, willow, sea buckthorn, elderberry. By organizing a small garden, you can significantly reduce the level of flooding.
- Open drainage system Open drainage system. A trench is dug around the perimeter of the site. Its depth must be at least 70 cm. In some cases, you will need to go deeper. Everything will depend on what level the top water is at. The bottom is rammed and covered with sand, which is also well compacted. Its layer should reach at least 10 cm. Small gravel is laid in the same layer. Excess moisture will go into this drain. You can take it out as far as possible from the territory. The disadvantage of this solution is the need for constant cleaning of the channels so that they do not become swamped.
- Closed drainage system.The trenches are prepared in the same way as described for the previous case, but it will take up to 1.5–2 m to go deeper. Geotextiles are laid on the sand and gravel cushion. Holes are made in a plastic or other pipe with a diameter of 200 mm or more to make it perforated. The pipes are lowered into the trench and again covered with geotextile. From above, everything is covered with soil.
- The well will help to some extent to solve the difficulty. To do this, it will be necessary to select the lowest point on the site and dig a well of the maximum possible depth. All water will be collected there.
- Wellpoint installation Well filter installation. It is a commercial product. This is a pipe with a wellpoint at the end. It is connected to a vacuum manifold and a pump. Water is pumped out automatically.
- Forced release. For these purposes, several wells are drilled in certain places to the aquifer. Centrifugal pumps are installed in the middle, which pump liquid to the surface. Then it is discharged into the sewer or drainage system.
- Vacuum installation. It is used in cases where the permeability of the soil is low. Tanks are installed on the surface. A rarefied pressure is created in them, which causes the water to rise in them. Withdrawal is carried out as in the previous case.

When raising groundwater, it is important to take care to protect sources of clean drinking water. For wells, a caisson installation is used
Land works are being carried out to the lower level of the water-resistant layer. A design is installed that will cut off the ingress of unwanted liquid inside. For wells, the method of external and internal waterproofing is used. A trench is dug around the perimeter and the rings are processed with a special compound.
Now you know the main methods using which you can roughly determine the level of groundwater. If they are at a depth of less than 2.5 meters, then construction on such a site is undesirable.
Deep drainage
When organizing deep dewatering, centrifugal-type deep pumps are necessary - for pumping groundwater from the calculated points of the aquifer in the soil. As in the previous cases, wells are being drilled to install tubular wellpoints. The difference between the technology is that the filter and the soil are in constant contact, in addition, when groundwater is pumped out by a deep pump, a depression funnel appears, in which the soil is also drained. Deep technology is necessary when creating a dewatering at depths of 20 meters or more, therefore it is used only in the construction or repair of industrial facilities.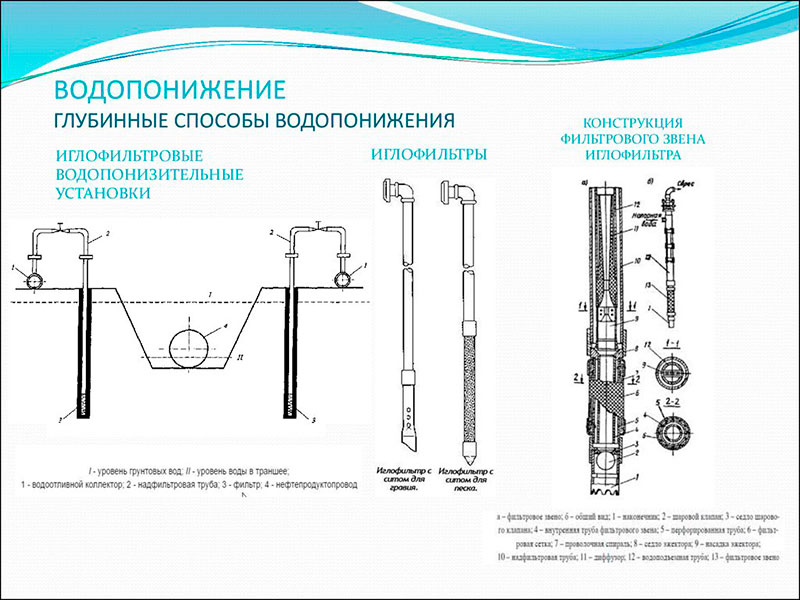
Plants

Plants serve as a good natural indicator of the depth of the top layer of groundwater.
In order to use this method, it is important that the site has been fallow for some time. This period will enable vegetation to find its niche.
You should pay attention to:
- Reeds. If it is on the territory allocated for development, then, most likely, the reservoir is located at a depth of 1 to 3 m.
- Cattail. It is a tall marsh grass. Often used for weaving various utensils. This view indicates that the liquid is about 1 m.
- Wormwood is a representative of Compositae. If it grows rapidly, then the limits of the aquifer are from 3 to 5 m. Construction can be freely carried out on such a site.
- Licorice is able to start up the root system to a depth of 5 m. Usually it indicates that the upper water threshold can reach 1.5 meters.
- Blackberries, raspberries - top water can reach 60 cm in a particular area.
- Gooseberries, currants and sea buckthorn are indicators of perched water at a level of 1 m from the surface.
- If apple and pear trees have been growing on the site for more than a year, then you can be calm: the water is at a level of 2 or more meters. The fact is that otherwise such trees do not withstand a longer stay with a lower occurrence of the water layer. With the growth of the root system, there is a greater consumption of oxygen, which is not enough, and the plant simply withers.
- For cherries and plums, water at a level of more than 1.5 meters will be required.
In the case where the site was cleared before the purchase, then you can ask around with the old-timers regarding the vegetation and their experience in construction work.
Concept in geology
As a geological concept, the groundwater level is a conditional line, below which the rock is saturated with water to the limit. After rain or snowmelt, a large amount of water goes underground through the pores in the ground. The level at which this water stops, since below all the pores are already filled with it, and is the level of groundwater in its purest form.
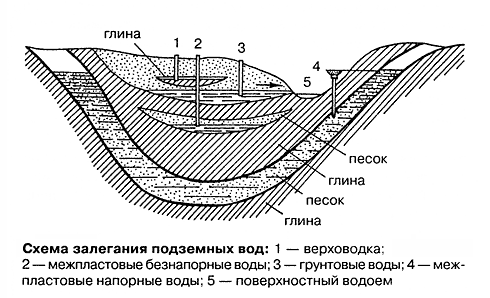
Scheme of occurrence of underground waters.
The depth of this level largely depends on the terrain, as well as on the presence of a river or lake near it. In mountainous areas, the depth of groundwater can exceed a depth of 100 m, while in swampy lowland areas it can become 1-2 m, and in some places only a few centimeters from the surface.
The lowest groundwater level is usually observed in winter.
It is in winter that the minimum amount of water enters the ground. Frozen ground becomes impervious to precipitation. And the precipitation itself falls in the vast majority in the form of snow, which does not melt until the spring heat.
Scheme of groundwater movement.
Aside from the scientific definition, the water table is the layer of water that is closest to the surface of the earth and is separated from the lower aquifers by a layer of rock or clay soil that prevents this water from seeping deeper.
It is clear that such a definition is inaccurate, since geology distinguishes three types of groundwater:
- perched water, the depth of which is 2-3 m from the surface and which tends to disappear in winter and in dry weather;
- unconfined groundwater is a layer of water that lies underground above the first impervious layer. The level of such waters depends entirely on precipitation and remains relatively stable, since there is no pressure in this layer of water;
- artesian water is a layer of water that is located between two water-resistant layers. If you break through the upper water-resistant layer, then the water from this layer under pressure will rise up. Water from this aquifer is used to equip artesian wells.
But since it is groundwater that gives builders the most trouble when arranging pits for foundations and basements, it is precisely this layer that determines the level of groundwater. Therefore, for practical work, such a definition of GWL is quite suitable.
Rules for planting trees and shrubs
When planting trees and shrubs in soil with a high water level, there are some nuances, subject to which a good harvest can be expected.
Firstly, not all cultures will take root on swampy soils. For them, shrubs that love acidic soils are best suited: blueberries, lingonberries, blueberries, currants, raspberries and others. Also, planting moisture-loving trees can be a good way out of this situation. These include willow, birch, mountain ash, plum, peach, cherry. Apple trees should be planted on a dwarf scion, due to the fact that their roots lie no deeper than 60 centimeters. But grapes or apricots are not suitable for such garden plots.
Secondly, the way of planting is different.
To begin with, with the help of a dug hole with a depth of 1 to 2 meters, they find out how close the water came.If its level is not higher than 60-70 centimeters, then this soil is suitable for planting fruit trees.
At the second stage, the pit is expanded to 1-1.5 meters, and the depth is reduced to 30-40 centimeters. The main task when planting is to make the roots grow not in depth, but in width. This can be achieved with a sheet of metal, slate, or thick boards laid at the bottom of the pit. One option is to concrete the bottom.
After that, a layer of drainage is laid in the pit. It can be large stones or broken bricks. Next, fertile soil is poured so that a hill is formed, the height of which varies from half a meter to a meter (depending on the culture of the tree). It is in this hill that the seedling is buried. The last step is to make the crate necessary to ensure that the landing hill is not washed away by rains.
Further care is no different from caring for normally planted fruit trees and shrubs.
How to lower and divert high groundwater
An open drawdown is the easiest way to divert water from a site. First, a pit is dug, and if moisture begins to flow from the walls and bottom, it is accumulated in the drainage ditches, and then pumped out. The option is working, but the massive withdrawal of groundwater leads to subsidence of the soil, therefore, before applying it, a specialist consultation is required.
In areas prone to swamping, drainage installations are actively used. To divert water, a trench is laid around the site, where groundwater will gradually come out. Then it is pumped out and taken out. It is more difficult and expensive to organize pipe drainage. For him, special polymer pipes with perforated walls are buried in ditches throughout the site. They need to be laid at a slope of several degrees so that the water flows by gravity into the prepared water collectors. In addition to pipes, sand traps and manholes will have to be installed for convenient maintenance of the system.
The most expensive way to get rid of groundwater is to use wellpoints. Pipes are buried vertically into the ground and are brought out to a depth of 5-20 meters with the help of pumps, depending on the type of installation. The specific method of lowering the GWL depends on the type of soil and the filtration coefficient (water flow rate).
What is ground water
Groundwater is water located not far from the surface, on the first aquifer, in the first aquifer.
Types of water in soils
The shallow depth of occurrence explains the strong seasonal fluctuations in the groundwater level. During periods rich in precipitation, the level rises, and hot weather, on the contrary, lowers the level.
Groundwater sources:
- Precipitation;
- Melting snow;
- Flood waters are closely located from rivers and lakes.
There are two types:
- Verkhovodka. Water that can be found almost under the surface, at a depth of 0.3-3 m. Verkhovodka is found in the ground in “spots”. In dry periods, it may disappear altogether, but returns with rains.
- Non-pressure ground water. They are found at a depth of 1-5 m. They do not disappear like perched water, but the level may fluctuate.
Before construction, it is imperative to find out the level of groundwater. The damage due to an incorrect assessment of this factor may be too great.
High groundwater makes the soil plastic and seriously reduces its bearing capacity. Which can lead to cracks in the foundation, walls, and collapse of part of the structure.
Water in the ground at a negative temperature freezes into ice. Which leads to such an effect as "frost heaving": uneven swelling of the soil under the foundation. Which can also lead to cracks and collapse.
High groundwater puts a lot of pressure on the foundation and basement structure. Which requires more effective waterproofing than usual.Otherwise, water will break into the basement, concrete structures will get wet (at negative temperatures, wet concrete cracks and peels off), fungus and mold will develop.