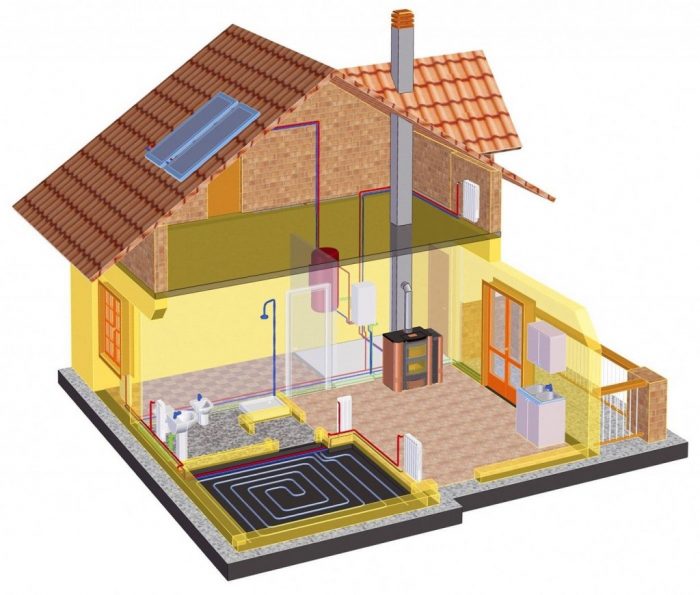
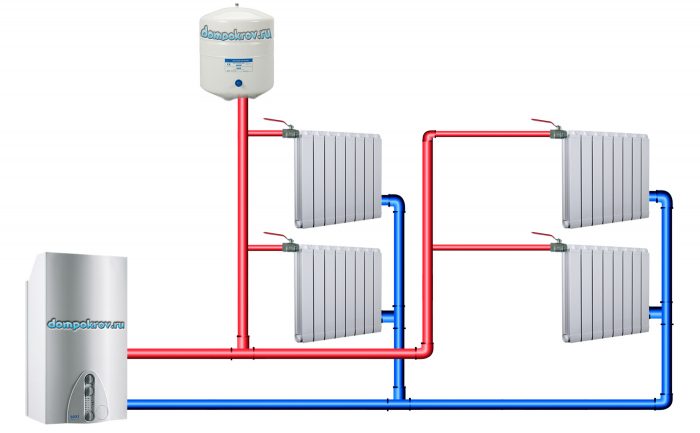
Vertical single pipe heating system
Vertical single-pipe water systems began to be used from the beginning of the 50s, and became widespread in the construction of residential multi-storey buildings. They can be performed with top and bottom wiring, as well as with “inverted” circulation. Heating devices can be connected to the riser from one (one-sided connection) or from two (two-sided connection) sides.
The connection of a particular device to the riser can be flow-through and with bypass sections (bypasses).
Vertical single-pipe heating systems are recommended for use in systems with a dead-end scheme for the movement of the coolant in the pipelines.
Water temperature and pressure in the heating system
To determine the temperature index, standards are used taking into account seasonal climatic features.
Standard options:
- at 0 outside the window, the supply to the radiators is +40 C .. +45 C, in the return line at least 35 C;
- at -20 - supply to radiators +67 C .. +77 C, in the return line - at least 53 C;
- at -40 - supply to heating devices of the maximum allowable values.
The pressure in the central heating system is also determined individually. If the structures are of the natural circulation type, then the pressure may be slightly higher than the static one. For one-story buildings with forced circulation, the working pressure should be in the range of 1.5-2.5 bar, with an increase in the number of storeys, the pressure must be increased so that the coolant circulates in normal mode. So, for five-story buildings, the pressure is 4 bar, for 9-story buildings - 7 bar, in high-rise buildings up to 10 bar.
Heating appliances
Obviously, the device of the heating system should include not only a heat source, but also heating devices. Which batteries are better for the economical homeowner?
To begin with, let's think about the conditions under which the radiator will have to work in an autonomous system.
The operating temperature is usually in the range of 50 - 80 degrees. Working pressure does not exceed 2.5 atmospheres. Water hammer is excluded - unless, of course, you fill the circuit by opening the valve abruptly and to failure.
If so, you can safely opt for aluminum sectional radiators - beautiful, cheap and with excellent heat dissipation.
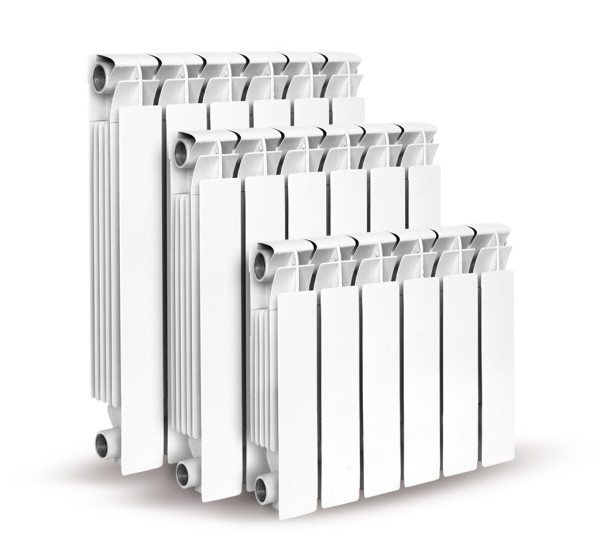
Aluminum sectional radiators.
As we have already found out, extreme pressure and high temperature are not expected in an autonomous circuit. If so, you can save on pipes: we will choose inexpensive, lightweight and durable polypropylene.
Since this material has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, we will have to:
- Select pipes with reinforcement. A layer of aluminum foil will noticeably reduce the heat elongation.
- Provide long straight sections of filling with compensators - ring or U-shaped bends.
The photo clearly shows the U-shaped compensators.
How to conduct heating yourself using polypropylene?
A low-temperature soldering iron is used to weld pipes with fittings. The melted surfaces are fixed in the working position and after 10 - 40 seconds (depending on the size) become a single whole.
An important point: aluminum foil must be removed from the welding field by stripping (shaver). It will weaken the connection, and in the future it can cause pipe delamination.
Cleaning polypropylene with a manual shaver.
What pipe diameters should be chosen?
- For filling a small (no more than 150 m2 per floor) house - with an outer diameter of 25 mm.
- For connections to radiators - with a diameter of 20 mm.
Additional elements
How is a closed-type heating system arranged?
In addition to the boiler, pipes and batteries, it has:
- The circulation pump that sets the coolant in motion.
- Jumper with cold water to fill the system with water.
- Dumps at the lowest points of the circuit, allowing it to be completely drained.
- Expansion tank. It compensates for the increase in the volume of the coolant with an increase in temperature.
- A safety valve that operates when the tank is overfilled and the pressure rises above the calculated one.
- Pressure gauge or thermomanometer for monitoring system parameters.
- Automatic air vent.
However: the pump, air vent, safety valve and (sometimes) expansion tank are often mounted in the boiler body, effectively turning it into a mini-boiler room. Before you go shopping, read the documentation.
The device of a modern gas boiler.
In addition, the following can be optionally installed:
- Cut-off individual heaters and sections of the valve circuit.
- Mud tank in front of the pump.
- Throttles or thermostats that regulate the temperature of radiators.
- At the upper points of the contour - additional air vents.
How to conduct heating in a one-story house yourself? According to the author, the best solution would be Leningradka - single-pipe wiring around the perimeter of the floor with radiators connected in parallel to the main bottling. It is absolutely trouble-free and eliminates the stoppage of circulation in some part of the circuit due to airing.
How to conduct heating on two floors?
There are two options here.
- Two rings (one per floor) with a throttle that limits the patency of the shorter of the circuits.
Leningradka variant for two floors.
- Two-pipe scheme with bottling on the ground floor and in the attic and risers connecting them with heating appliances.
How to connect radiators correctly?
For short (no more than 7 sections) heaters, the traditional side connection will be optimal. Longer batteries are best connected diagonally or from bottom to bottom.
Variants of water heating at home
In private and multi-apartment buildings, heating can be radiator (collector), baseboard or in the form of a warm floor. Each system has its own characteristics and benefits.
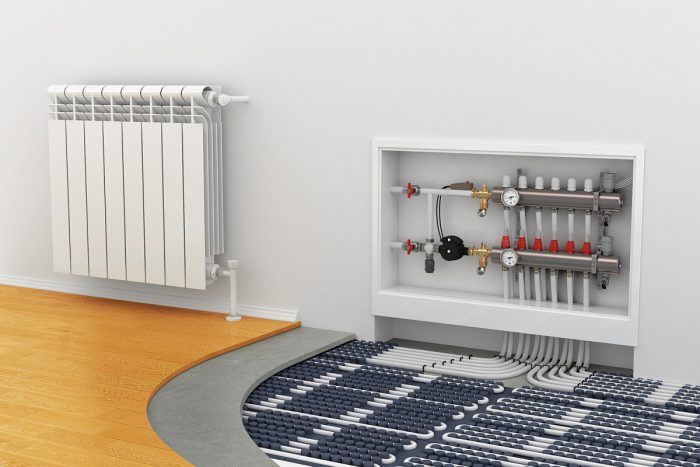
Warm floor
The design is a heating of the room from the floor, it is used in any type of room, suitable for rooms with any level of humidity, as well as for placement in open spaces (balcony, loggia, veranda). Features - the use of pipelines with a high degree of thermal conductivity, flexibility, strength.
The design is laid out under the screed, the advantages include:
- efficiency when using different floor finishes;
- a noticeable reduction in heat costs (up to 50%);
- low cost of construction and the ability to do it yourself;
- application in the combined circuit of the heating system.
An autonomous water floor does not depend on electricity in any way if it is powered by a gas boiler, so the owner may not be afraid of power outages, plus the threat of a short circuit or fire is minimized.
Baseboard heating
A warm plinth is a heating element that repeats the shape of a building analogue. The principle of operation of the device, located around the perimeter of the room, is similar to conventional radiators. The heating of the pipes inside the case occurs evenly, then the warm air rises up the walls, the room warms up on all planes: wall, floor.
The advantages of the system include:
- Formation of a comfortable temperature. Active circulation of air flows is excluded, which explains the softer and gradual heating of the room. In addition, it is possible to insulate the junction of the floor and the wall where mold appears - this is especially true for private houses.
- Easy installation. All structural units are sold ready-made. The arrangement can be single-, double-row, different in power.
The downside is the location.Placement along the walls along the bottom and the entire perimeter makes it necessary to abandon the usual order of furniture arrangement (near the wall).
Radiator heating
The classic scheme with batteries and pipelines. Radiators are connected with tees, which are mounted in the areas of connection with risers, pipes. The principle of the circuit is the connection sequence. You can make a beam design, which increases the possibility of heating.
The advantages include: ease of installation, efficiency and a variety of choice of schemes. Radiator heating can be combined with other types, equipped on the basis of one-, two-pipe schemes, and become an addition to the perimeter (tee) structure.
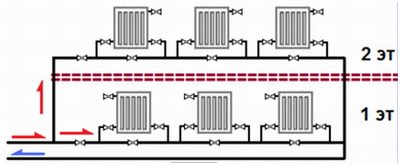
Vertical single pipe systems with bottom wiring
Such systems are carried out with U-shaped (scheme a) and T-shaped (scheme b) risers. They can be used in residential buildings with and without attics, standing up to 3 or more floors.
In the first figure (U-shaped riser), radiators 1 and 6 are connected to the riser in a flow pattern. Batteries 2 and 5 are connected through a bypass, offset from the axis of the riser. Heaters 3 and 4 have axial closing (bypass) sections. It should be noted that the flow of water into the devices is better when using offset (from the axis of the risers) bypass sections (approx. 2 and 5), and at the same time, the temperature expansion of the risers is compensated. Usually, the system uses one (sometimes two) connection options.
Heaters in flow-through (approx. 1 and 6) one-pipe systems on the lower floors should have more sections compared to appliances on the upper floors.
The diagrams also show various options for installing valves to disconnect devices from the system.
In U-shaped systems, the coolant rises in one riser and immediately gives off heat in the radiators. Therefore, in the second riser, the water temperature will be lower and more sections will be required to obtain the required heat transfer.
In a riser with a T-shaped wiring, the water first rises, after which it is distributed over two return risers, and therefore the decrease in the temperature of the coolant will be more uniform.
Heat source
How to heat a room located at a considerable distance from the nearest heating main? Obviously, this requires an autonomous source of heat - a water boiler.
When choosing the type of boiler, you should pay attention to two of its properties:
- Profitability. The lower the price of a kilowatt of thermal energy, the lower the operating costs.
- Autonomy of work. Ideally, heating equipment should not require attention to itself.
Let's make the corresponding ratings, and then compare the positions of boilers of different types.
economy
It seems that the table does not require any comments. Main gas leads in terms of low cost of heating by a huge margin.
autonomy
But according to this parameter, the estimates will be very different from the previous rating.
- The undisputed leader is electricity. The electric boiler does not require any maintenance in one form or another, nor the removal of combustion products. The owner only needs to set the temperature of the coolant or, in the presence of an external thermostat, the air temperature in the room.
The electric boiler does not require monitoring and maintenance.
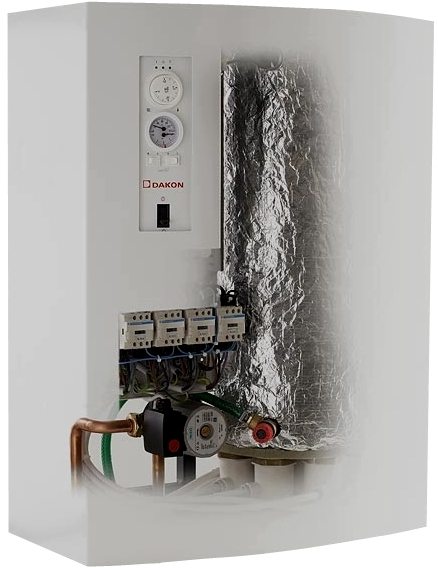
- In second place in terms of ease of use is gas. The device of heating systems with a gas boiler also allows them to work offline for an unlimited time, maintaining the set temperature. The owner will only have to additionally attend to the installation of the air duct leading to the street.
To clarify: we are talking about boilers with electronic ignition. Piezo ignition makes the boiler non-volatile, but it has to be manually ignited (in particular, when the igniter is off).
Wall-mounted gas boiler with electronic ignition.
- The use of diesel fuel also allows the system to work autonomously for a long time; however, the massive container with the solarium and the noise of the burner, which differs little from the noise of the aircraft on takeoff, make the use of this heat source less comfortable.
- Pellet boilers with a hopper and automatic fuel supply provide a slightly lower level of automation: the hopper has to be periodically loaded, and the hopper will not save you from cleaning the ash pan.
- Finally, solid fuel boilers require the most attention. Coal and firewood have to be loaded every few hours. The use of gas generators, top combustion boilers and heat accumulators change the picture for the better, but not so radically.
The conclusions are quite obvious - if you have the opportunity to use the main gas, you can not look for other options for implementing heating.
When choosing a gas boiler, you should pay attention to a couple more characteristics.
- If interruptions in the supply of electricity are not systematic, our choice is a product with forced draft and electronic ignition.
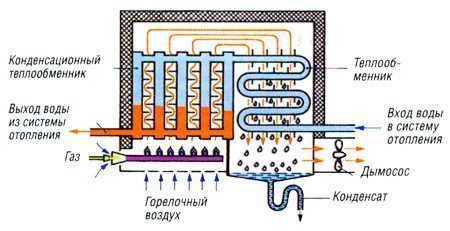
- Condensing boilers are more economical than convection boilers by 9-11%. They utilize not only the heat of combustion of gas, but also the energy released during the condensation of combustion products.
Scheme of operation of a condensing boiler.
Water system characteristics
Depending on the main method of heat transfer, convective and radiant heating are distinguished:
- convective. It implies maintaining the temperature of the indoor air at a higher level than the radiation in the room. The radiation temperature is understood as the average heat of all surfaces facing the room, calculated relative to the person who is in the center of the room.
- Radiant. It is characterized by an excess of the radiation type temperature relative to the air temperature. Radiant heating at a slightly lower room temperature is considered optimal for human well-being. For example, in civil buildings it is better to set climate systems at +18..+20 C instead of +22..+24 C.
Scheme of the device system of a private house
One-, two-pipe water heating of a country house, a mansion differs.
Single-pipe is considered simple and inexpensive, and also available for do-it-yourself installation. The scheme is a pipeline for transferring the coolant, to which all the radiators of the building are connected. The heat carrier goes through a full circle and returns to the boiler for heating, then the heat transportation cycle is repeated. The practical scheme has one drawback: in radiators located at the furthest distance from the boiler, the temperature regime will be reduced, but this is an advantage for people who cannot stand the heat.
The two-pipe scheme is characterized by increased complexity for self-assembly. It provides for the removal of a pair of pipes from the boiler at once, and one serves to supply hot coolant to the radiators, the second - to return the cooled liquid to the boiler. The advantage is that radiators with a two-pipe design can be arranged not in series, but in an order convenient for the owner of the house.
To make the quality of work high, experts advise mounting a distribution manifold. The unit is needed to regulate the flow of fluid to each radiator and control the temperature of the room.
There is also a bifilar heating system. It is a combination of one-, two-pipe schemes. The circuit is divided into identical parts, equipped with radiators, risers, branches. The ends are connected in order by one pipe: first, the elements of the first, and then the second end. The liquid is transported in opposite directions with different levels of heating, which explains the maintenance of the same temperature throughout the heating system.
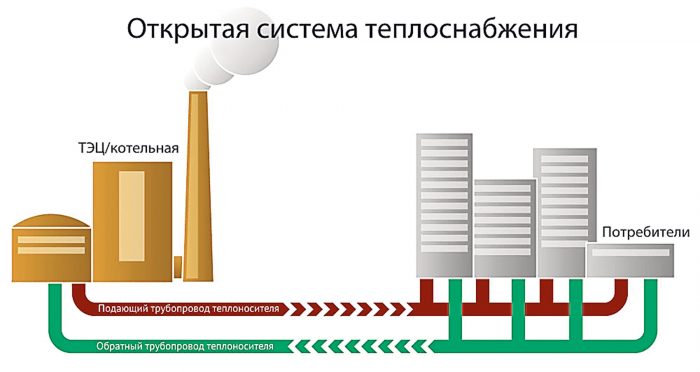
Scheme of the device system of an apartment building
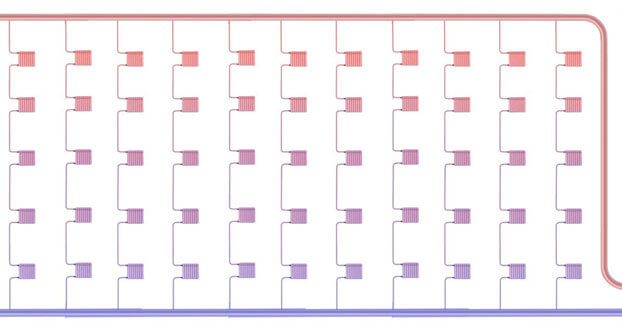
Projects of heating systems powered by a central station are always developed individually, taking into account the housing stock. Typical wiring is one-pipe systems, where there is a heating riser, to which radiators located in each apartment are mounted in parallel.There could be many risers, they are connected in parallel to the supply line, so they end up in approximately the same hydraulic conditions.
The advantages of the design are that even if one battery is disconnected in the event of a leak, the heating of other apartments does not change, which is achieved by using a bypass. And the presence of a balancing valve on batteries makes it possible to reduce the temperature in the room.
Components of a water heating system
The design consists of the following components:
- heat generator (furnace, boiler);
- pipelines;
- radiators;
- circulation pump;
- expansion tank.
If the circulation is natural, then the pump is not used, transportation is carried out due to the natural physical properties of the liquid.
How to decorate heating pipes
Heating pipes are such an element of the interior that performs a very useful function, but does not look particularly attractive. Often the pipes in the house are rather “rough”, they take up extra space and give the impression of some kind of incompleteness.
In new houses, the heating system is located so that it is not visible, all this is calculated in advance. However, those who live in old houses have a hard time, because before they did not think about the design of the room. The owners of these houses and apartments have to decorate the heating pipes if they want to make their home cozy and beautiful. In fact, disguising pipes is not as difficult as it seems to some. Moreover, after such a “make-up”, a new, full-fledged element of apartment decor will appear in place of an unattractive heating system, creating a beautiful view. The pipes themselves, of course, will also remain, but they will not be visible.
Antifreeze in the heating system
Filling the heating system with antifreeze is only recommended in certain cases, such as during particularly severe winters. A special aqueous solution of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol and other glycol-based formulations is used; solutions of inorganic salts.
It is considered an advantage to maintain the integrity of the entire structure, for example, if the house is used only in the warm season, and it is not possible to drain the water for the winter. Antifreeze will reduce the risk of rupture of the pipeline, radiators, boiler.
The use of antifreeze also has disadvantages - a reduced heat capacity with respect to water, so you will have to choose and install powerful radiators, high viscosity, and fluidity. It is unacceptable to use galvanized pipes, as antifreeze can change its chemical properties and lose its qualities.
How the heating system is filled
Before you start filling the heating system with water, you need to determine the volume. It is calculated according to the formula: sum up the volume of the boiler, expansion tank, radiators and pipes. The useful volume is indicated in the technical documentation.
Action algorithm:
- Start from the bottom point. The top point must be open.
- Connect the electric pump. Pump water through a faucet. It is better to open the crane only half way to exclude the possibility of water hammer.
- The filling of the system is evidenced by gurgling and the noise of water movement. You need to finish when liquid flows from the upper open point.
- Now you should bleed the air from the connected consumption devices, boiler, expansion tank, batteries, boilers. Bleeding is carried out using taps, valves, which the units are equipped with.
It remains to attach the hose to the top point, lower it into a container of water, turn on the pump and fill the system until water flows out of the hose without air bubbles. If necessary, loop the system, drive the coolant several more times to ensure high-quality degassing.
The last step is to pump air behind the expander membrane to ensure the correct pressure level.This is necessary for the functionality of the circulation pump - it will have to be turned on for testing (without heating).
Piping in a multi-storey building
As a rule, in multi-storey buildings, a single-pipe wiring diagram with top or bottom filling is used. The location of the forward and return pipes can vary depending on many factors, including even the region where the building is located. For example, the heating scheme in a five-story building will be structurally different from heating in three-story buildings.
When designing a heating system, all these factors are taken into account, and the most successful scheme is created that allows you to bring all the parameters to the maximum. The project may involve various options for pouring the coolant: from the bottom up or vice versa. In individual houses, universal risers are installed, which ensure the rotation of the movement of the coolant.
What is a water heating system
Water heating is considered to be heating by means of a liquid heat carrier (water or water-based antifreeze). Heat transfer is carried out through pipelines, convectors, radiators, collectors and a boiler. The main difference between a water system and a steam system is the stability of the aggregate state of the liquid. This property explains the lower temperature of the coolant and the safety of the water system in relation to other types of heating.
Advantages and disadvantages of the water system
In addition to simplicity and reliability, experts note the following advantages:
- uniform distribution of warm air in all rooms;
- when installing one heating boiler, it becomes possible to control processes from one point;
- equipment can be hidden under the decor, leaving only radiators visible - the underfloor heating system completely solves the problems of concealed installation;
- the maximum temperature of the coolant is not more than +95 C, the surface of the radiators is not more than +65 C - this minimizes the risk of burns when touching the elements for a short time.
An additional plus in the softness of the heat supplied is that the temperature rises gradually. For private houses, the advantage of the water system is that the carrier cools down slowly, which means that a comfortable temperature in the room will be maintained even after the heating is turned off.
There are also cons:
- Leakage risk. You can level the problem by using plastic rather than steel pipes.
- Freezing water. The situation occurs if the water in the system is not drained for the winter.
There are more pluses, which explains the popularity of structures in private and apartment buildings.
Classification of water heating systems
The classification of heating systems is based on a number of features:
- According to the design temperature in the supply line: below +70 C - low temperature, +70..+100 C - medium temperature, from +100 C - high temperature.
- According to the type of location of the supply / return line: with an upper wiring when the supply pipe is located above the heater (OP), from the bottom - if the supply and return pipes are laid below the OP.
- According to the location of the pipes connecting the radiators: vertical with a riser and connecting pipes laid out vertically, and horizontal - with a horizontal layout of pipes.
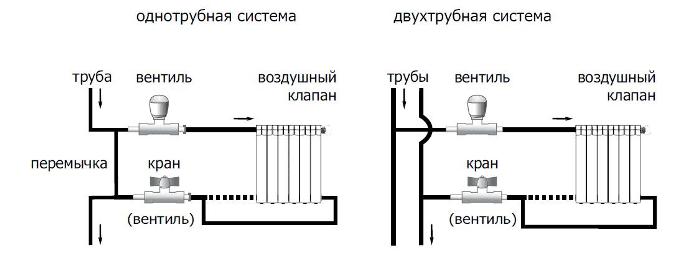
- According to the connecting scheme of pipelines and radiators: two-pipe with parallel connection of batteries, one-pipe with serial connection.
- According to the type of water direction in the supply and return lines: dead-end - with oncoming traffic, passing - with the coincidence of the directions of fluid flow.
The method of circulation of the flow is taken into account: natural is called gravitational, with the use of the power of pumps - forced.
Features of work on the replacement of pipes, risers and heating radiators
Dismantling of heating risers
Riser replacement
Since the modernization of heating may affect the systems of other apartments, it is necessary to notify the housing office about the upcoming work. Their worker must shut off the riser in case there is water in the system. When the replacement of pipes is not emergency, it must be carried out during the non-heating season.
Before changing heating pipes, you need to negotiate with neighbors from below and above, because if sections of old pipes remain in the ceilings, there will be a chance of leakage.
Dismantling steps:
- The housing office employee must close the risers and drain the water from them.
- The riser with the help of a grinder is cut off from the side of the upper and lower floors.
- Since the new riser pipes are plastic, a thread is made on the riser pipe, it is lubricated, sealed with fum tape. Then a coupling is screwed on that connects the plastic and steel pipes.
Installation of heating radiators
The best for central heating are bimetallic or modern cast-iron radiators - they have a large enough flow for water, so they are extremely rarely clogged.
Types of radiators
Battery Installation Features:
- First, the marking of the installation sites of radiators is done.
- Brackets must be used to install radiators.
- The installation of the battery must be carried out exclusively in level, since in the event of a skew, air can collect in it, and it will not work well.
- As a rule, radiators are installed under the window so that cold air does not penetrate into the room.
- The distance between the radiator and the wall should be about 5 cm, the gap to the floor - a maximum of 12 cm, to the window sill - 10 cm.
When pipes and radiators are replaced, they must be equipped with shut-off valves. This is necessary so that in the event of a radiator leak, this area can be blocked, and this does not affect the functioning of the entire heating system.
Connecting pipes to radiators
Heating system diagrams
- One-pipe system, where only hot water flows through the risers. For risers with such a system, pipes with a diameter of 32 or 25 mm are used. For pipes supplying coolant to radiators, a diameter of 20 mm can be used.
- A two-pipe system, where hot water is supplied through one pipe (“direct”), and is discharged through the second (“return”). With such a system, the diameter of the pipes is selected depending on the number of radiators: when there are 8 or more batteries, pipes with a diameter of 32 mm are used, when there are fewer batteries, 20 mm. For the riser system, a pipe diameter of 32 mm is also used.
When it is necessary to replace the heating pipes, it is important not to choose the diameter of the pipes going to the radiators less than those that were installed earlier. Installation of pipes to radiators:
Installation of pipes to radiators:
- With a single-pipe system, a Mayevsky crane is located in the upper part of the radiator, which is necessary for air discharge. Plug the bottom hole. The surface must be cleaned of paint before installing plugs. Then they mount the heating taps using a special key - preferably with union nuts. When to change heating pipes, the pipeline suitable for the radiator is mounted after its installation.
- With a two-pipe system, strobes are made for pipes in the floor, the pipes are sheathed with insulation and laid in strobes. The pipes that go to the radiators are similarly removed into the walls.
Heating pipes built into the walls
Final stage:
- connecting pipes to risers;
- when replacing heating risers, it is necessary to install a jumper (when the taps on the battery are closed, in the absence of a jumper, the entire heating riser will not work);
- the assembled system must be checked for leaks by testing at a pressure of 1.5 times the normal pressure.
With the correct replacement of the heating system in the apartment, the problem of heat and leakage will be solved for at least 20 years.
Heat supply of a multi-storey building
Distribution unit for heating an apartment building
The distribution of heating in a multi-storey building is important for the operational parameters of the system. However, in addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of heat supply
An important of them is the method of supplying hot water - centralized or autonomous.
In overwhelming cases, they make a connection to the central heating system. This allows you to reduce the current costs in the estimate for heating a multi-storey building. But in practice, the level of quality of such services remains extremely low. Therefore, if there is a choice, preference is given to autonomous heating of a multi-storey building.
Autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
autonomous heating of a multi-storey building
In modern multi-storey residential buildings, it is possible to organize an independent heat supply system. It can be of two types - apartment or common house. In the first case, an autonomous heating system of a multi-storey building is carried out in each apartment separately. To do this, they make an independent wiring of pipelines and install a boiler (most often a gas one). General house implies the installation of a boiler room, to which special requirements are imposed.
The principle of its organization is no different from a similar scheme for a private country house. However, there are a number of important points to consider:
- Installation of several heating boilers. One or more of them must necessarily perform a duplicate function. In case of failure of one boiler, another must replace it;
- Installation of a two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building, as the most efficient;
- Drawing up a schedule for scheduled maintenance and preventive maintenance. This is especially true for heating heating equipment and security groups.
Taking into account the peculiarities of the heating scheme of a particular multi-storey building, it is necessary to organize an apartment heat metering system. To do this, for each incoming branch pipe from the central riser, you need to install energy meters. That is why the Leningrad heating system of a multi-storey building is not suitable for reducing current costs.
Centralized heating of a multi-storey building
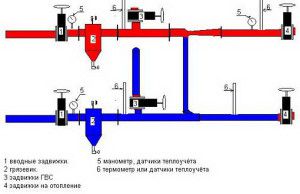
Scheme of the elevator node
How can the heating layout in an apartment building change when it is connected to the central heating supply? The main element of this system is the elevator unit, which performs the functions of normalizing the coolant parameters to acceptable values.
The total length of the central heating mains is quite large. Therefore, in the heating point, such parameters of the coolant are created so that heat losses are minimal. To do this, increase the pressure to 20 atm. which leads to an increase in the temperature of hot water up to +120°C. However, given the characteristics of the heating system in an apartment building, the supply of hot water with such characteristics to consumers is not allowed. To normalize the parameters of the coolant, an elevator assembly is installed.
It can be calculated for both two-pipe and single-pipe heating systems of a multi-storey building. Its main functions are:
- Reducing pressure with an elevator. A special cone valve regulates the amount of coolant inflow into the distribution system;
- Lowering the temperature level to + 90-85 ° С. For this purpose, a mixing unit for hot and cooled water is designed;
- Coolant filtration and oxygen reduction.
In addition, the elevator unit performs the main balancing of the single-pipe heating system in the house. To do this, it provides shut-off and control valves, which in automatic or semi-automatic mode regulates pressure and temperature.
You also need to consider that the estimate for centralized heating of a multi-storey building will differ from the autonomous one. The table shows the comparative characteristics of these systems.