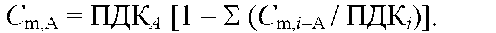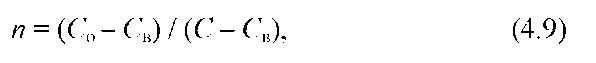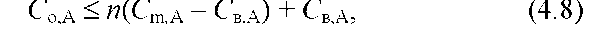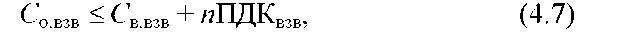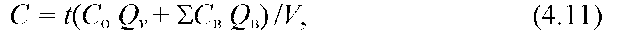chemical pollution
Output of surface wastewater with impurities
The quantitative and qualitative composition of all contaminants is diverse. But all chemical pollution can be divided into two groups:
- The first includes pollution containing inorganic impurities. These include effluents from sulfate, soda plants, processing plants. In their composition, they contain large quantities of heavy metal ions, alkalis and acids. They change the quality of the water.
- The second group includes effluents from oil refineries, petrochemical plants, organic synthesis enterprises, coke production. Wastewater contains a large amount of phenols, aldehydes, resins, ammonia, and petroleum products. Their harmful effect lies in the fact that the organoleptic characteristics of water deteriorate, the oxygen content in it decreases, and the biochemical need for it increases.
Currently, the main pollutant of water bodies is oil and oil products. When they get into the water, they create a film on its surface, heavy fractions settle to the bottom. Taste, color, viscosity, surface tension changes. Water acquires toxic properties and poses a threat to humans and animals.
Wastewater from petrochemical plants contains phenol. When it enters water bodies, the biological processes occurring in them are sharply reduced, the process of water self-purification is disrupted. There is a smell of carbolic acid in the water.
Pulp and paper industry enterprises have a detrimental effect on the life of water bodies. The wood pulp is oxidized, there is a significant consumption of oxygen and, as a result, fry and adult fish die. Insoluble substances and fibers worsen the physical and chemical properties of water. Mole alloys have a harmful effect on water bodies. Tannins are released from the bark and rotting wood into the water. The resin absorbs oxygen, which leads to the death of fish. In addition, mole alloys clog rivers and clog their bottoms. In this case, the fish are deprived of spawning grounds and feeding places.
Determination of permissible concentrations of pollutants in the wastewater of the enterprise
Permissible concentrations (DC) of pollutants in wastewater from enterprises are determined based on the following conditions:
1. DC of a pollutant in the sewer network (at the outlet of the enterprise) is accepted according to Appendix 1 to the Rules for the acceptance of wastewater from enterprises into municipal and departmental sewerage systems in settlements of Ukraine.
2. DC of a pollutant in biological treatment facilities (at the entrance to these facilities) is determined by the formula:
, g/m3
where — DC of the pollutant in the aerotank, g/m3 (accepted according to Annex 2 to the Rules for the acceptance of wastewater from enterprises into municipal and departmental sewerage systems of settlements in Ukraine or according to the project of urban treatment facilities);
— average daily wastewater consumption at the inlet to the treatment plant, m3/day (equal to 500,000 m3/day);
— average daily consumption of wastewater from enterprises that may contain this pollution, m3/day (equal to 200000 m3/day, for chromium6+, chromium3+ and cadmium it is 100000 m3/day, for sulfides 50000 m3/day).
— concentration of a pollutant in domestic wastewater, g/m3.
3. The limits for the discharge of pollutants into the reservoir, which are set for Vodokanals by the bodies of the Ministry of Energy and Resources of Ukraine in permits for special water use.The DC of a specific pollution by the value of the total limit for its discharge into a reservoir is calculated by the formula:
,g/m3,
where , t/year - part of the limit, which falls on the domestic wastewater of the settlement;
365 is the number of days in a year;
Qhb is the average daily consumption of household wastewater in a given city, m3/day (equal to 300,000 m3/day);
— average daily consumption of wastewater from enterprises that may contain this pollution, m3/day (equal to 200,000 m3/day);
TOR - coefficient of efficiency of removal of this pollution at urban wastewater treatment plants (accepted according to Appendix 2 to the Rules for the acceptance of wastewater from enterprises into municipal and departmental sewerage systems of settlements in Ukraine or according to the project of urban wastewater treatment plants);
, t/year
where Qcommon — annual amount of wastewater;
MPCwaters — MPC of a pollutant in a reservoir for drinking and domestic water use, g/m3 (accepted according to Table 1 of SanPiN No. 4630-88) .
Of these three values, the smallest is set as DC.
The results of the DC calculation are shown in Table 4.4
Table 4.4 DC of pollutants in wastewater from the enterprise
|
Name of pollutant |
Cst |
DC1 |
WITHi |
DC2 |
MPC |
LPV |
KO |
TOR |
DC3 |
DCR |
|
pH |
6,5-9,0 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
6,5-9,0 |
|
|
suspended solids |
500 |
— |
— |
30,75 |
— |
— |
0,95 |
360 |
360 |
|
|
BOD5 |
350 |
— |
— |
6 |
— |
— |
0,95 |
435 |
435 |
|
|
Oil products |
20 |
10 |
24,25 |
0,3 |
org |
4 |
0,85 |
4,16 |
4,46 |
|
|
Fats |
50 |
50 |
5 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
5 |
|
|
sulfates |
400 |
500 |
800 |
500 |
org |
4 |
— |
775 |
400 |
|
|
chlorides |
350 |
350 |
500 |
350 |
org |
4 |
— |
482,5 |
350 |
|
|
surfactant |
— |
20 |
42,5 |
0,5 |
org |
4 |
080 |
0,5 |
0,5 |
|
|
Iron |
— |
2,5 |
3,25 |
0,3 |
org |
3 |
0,50 |
0,3 |
0,3 |
|
|
Copper |
— |
0,5 |
1,25 |
0,1 |
org |
3 |
0,40 |
0,408 |
0,408 |
|
|
Zinc |
— |
1,0 |
2,5 |
1,0 |
common |
3 |
0,30 |
3,5 |
2,5 |
|
|
Nickel |
— |
0,5 |
1,25 |
0,1 |
s-t |
3 |
0,50 |
0,49 |
0,49 |
|
|
Cadmium |
— |
0,01 |
0,05 |
0,001 |
s-t |
2 |
0,80 |
0,019 |
0,019 |
|
|
Chrome6+ |
— |
2,5 |
7,5 |
0,5 |
s-t |
3 |
0,50 |
3,92 |
3,92 |
|
|
Chrome3+ |
— |
0,1 |
0,5 |
0,05 |
s-t |
3 |
0,50 |
0,39 |
0,39 |
|
|
Ammonia nitrogen |
— |
30 |
45 |
1,0 |
s-t |
3 |
0,60 |
1,0 |
1,0 |
|
|
Nitrites |
— |
3,3 |
8,25 |
3,3 |
s-t |
2 |
— |
8,09 |
8,09 |
|
|
Nitrates |
— |
45 |
45 |
45 |
s-t |
3 |
— |
110,25 |
45 |
|
|
Phosphates |
— |
10 |
10 |
3,5 |
common |
4 |
20 |
3,5 |
3,5 |
|
|
Sulfides |
1,5 |
1,0 |
2,5 |
common |
3 |
— |
1,5 |
|||
|
Fluorides |
— |
— |
— |
1,5 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
1,5 |
We will assess the quality of wastewater according to the calculated allowable concentration. The results of the evaluation in table. 4.5
Table 4.5 Evaluation of wastewater quality according to the calculated DC
|
No. p / p |
Name of indicator |
Concentration, mg/l |
Grade |
|||
|
Permissible |
Actual |
|||||
|
KK-7A |
KK-19 |
K-19 |
||||
|
1 |
pH |
6,5-9,0 |
6,8-7,87 |
6,5-7,21 |
7,1-8,9 |
+ |
|
2 |
suspended solids |
360 |
350,0 |
322,3 |
154,0 |
+ |
|
3 |
BOD5 |
435 |
112,0 |
85,4 |
359,2 |
+ |
|
4 |
Oil and oil products |
4,46 |
4,3 |
1,98 |
4,0 |
+ |
|
5 |
Fats |
5,0 |
50,0 |
2,5 |
1,0 |
— |
|
6 |
sulfates |
400 |
206,0 |
288,0 |
365,0 |
+ |
|
7 |
chlorides |
350 |
231,0 |
208,0 |
322,0 |
+ |
|
8 |
surfactant |
0,5 |
0,194 |
0,11 |
0,18 |
+ |
|
9 |
Iron |
0,3 |
0,01 |
0,25 |
0,07 |
+ |
|
10 |
Copper |
0,408 |
0,02 |
0,005 |
0,005 |
+ |
|
11 |
Zinc |
2,5 |
0,05 |
0,002 |
0,004 |
+ |
|
12 |
Nickel |
0,49 |
0,2 |
0,08 |
0,09 |
+ |
|
13 |
Cadmium |
0,019 |
0,01 |
0,009 |
0,009 |
+ |
|
14 |
Chrome 3+ |
3,92 |
0,02 |
0,01 |
0,01 |
+ |
|
15 |
Chrome6+ |
0,39 |
0,002 |
0,002 |
0,002 |
+ |
|
16 |
Ammonia nitrogen |
1,0 |
0,9 |
0,7 |
0,02 |
+ |
|
17 |
Nitrites |
8,09 |
0,04 |
1,7 |
2,64 |
+ |
|
18 |
Nitrates |
45 |
0,95 |
4,24 |
12,65 |
+ |
|
19 |
Phosphates |
3,5 |
3,1 |
2,55 |
1,8 |
+ |
|
20 |
Sulfides |
1,5 |
1,5 |
1,2 |
1,5 |
+ |
|
21 |
Fluorides |
1,5 |
0,16 |
0,9 |
1,1 |
+ |
According to the calculation of permissible concentrations, the wastewater of the enterprise does not correspond to the following indicators: fats.
Indicators of water pollution by organic substances
Indicators of organic water pollution reveal direct signs of source contamination and indirect ones. Direct biological indicators reflect the number of microorganisms and parasites, the total microbial number. Determination of faecal water pollution by the coli index also refers to methods for identifying direct signs of biogenic pollution.
Fecal pollution is typical for water bodies located near agricultural land. Signs of faecal contamination are changes in oxidizability, an increase in the concentration of ammonium nitrogen, etc. An increased level of ammonium nitrogen is an indicator of fresh fecal contamination, which is an epidemiological threat.
Drinking water in the regions will become better
The Ministry of Natural Resources is systematically working to treat industrial wastewater. According to the head of the department, Dmitry Kobylkin, the problem of human pollution of water bodies is exhausting itself, but the level of anthropogenic impact is still high.
Mr. Kobylkin noted that the volume of untreated sewage entering drinking water sources annually is approximately 30%. Since 2012, the state has implemented 64 investment projects for wastewater treatment. About 58 billion rubles were allocated for all this. Despite the fact that the final objectives were achieved, the discharge of polluted waters was noticeably reduced, in general, the situation continues to be quite tense.
Important! Under the patronage of the Ministry of Natural Resources, the federal program "Clean Water" is being carried out, designed for 2019-2024. Subsidies were provided to all regions to support the project to improve the quality of water supply
They should be used to combat anthropogenic pollution of water bodies.
In order to qualify for public funds, the regions will have to complete several basic steps:
- Assessment of the state of water supply facilities, identification of problematic points. At this stage, it is necessary to identify the sources of polluted water, develop specific plans and programs to correct the situation. It is also required to determine the protection of water bodies from pollution.
- Approval of the program for the construction and reconstruction of drinking water supply facilities. Projects must fully comply with all current legal regulations.
- Sending an application to the Ministry of Construction for a subsidy.
It is extremely difficult to assess the effectiveness of the program. According to Maxim Yegorov, who is the Deputy Minister of Construction and Housing and Utilities, only the number of the population provided with high-quality drinking water can become a key assessment. Given the fact that the problem is gradually being corrected, the effectiveness of the Clean Water program is quite high.
Interesting: Payment for environmental pollution has become too high: what does human activity lead to?
Most of the water quality improvement programs in recent years have been implemented at the expense of regional budgets. As the head of the State Duma Committee on Natural Resources, Nikolai Nikolaev, noted, most of the ongoing initiatives had a positive effect. However, with the support of the state at the federal level, more ambitious results can be achieved. 147 billion rubles were allocated for the reconstruction of the centralized water supply system in cities and the installation of water pipes in rural areas.
Mr. Nikolaev expressed confidence that the state should control not the amount of allocated funds for a particular project, but how much water will become of high quality.
Increase in fines for water pollution up to 2 times
In recent years, the state has faced the need to introduce an environmental responsibility policy for legal entities and organizations responsible for ignoring water use rules. This can be done only through the introduction of new sanctions for violations in this industry.
Since April 26, a project aimed at toughening responsibility for violating the rules for the protection of water bodies has acquired legal legitimacy. This initiative was developed by the Legislative Assembly of St. Petersburg.
One of the authors of the project was the deputy Nadezhda Tikhonova. Presenting the initiative at the plenary session, she noted that the existing maximum fine for polluting water bodies does not exceed 50,000 rubles. At the same time, the punishment for air pollution is 180-250 thousand rubles, for violations in the field of protection of subsoil and hydro-mineral resources - 300-500 thousand rubles. The existing spread is too large. To correct this situation, the Legislative Assembly of St. Petersburg submitted amendments to the existing standards.

According to Ms. Tikhonova, the amendments to the Code of Administrative Violations will eliminate the disproportion in sanctions for air, water and subsoil pollution. If earlier organizations were fined for air pollution in the amount of 250 thousand rubles, and water - 20-50 thousand rubles, now the penalties will be approximately equal.
The adopted draft provides for the introduction of several types of liability:
- for officials who allowed pollution of water bodies or other harmful phenomena, the fine will be 20-30 thousand rubles (previously it did not exceed 2 thousand rubles);
- for legal entities that have allowed pollution of water bodies with sewage - 80-100 thousand rubles (against 10-20 thousand rubles before);
- illegal extraction of sand, gravel, clay and peat will cost legal entities 100-120 thousand rubles (previously 20-30 thousand rubles), officials and officials - 30-40 thousand rubles (against 3 thousand rubles before);
- violation of the requirements for the protection of water bodies, entailing the danger of clogging, depletion or pollution of water bodies with waste will cost organizations 150-300 thousand rubles (30-40 thousand rubles before the adoption of amendments), for officials penalties will increase from 4 thousand rubles to level of 50-80 thousand rubles.
The maximum allowable amount of sanctions for ignoring the rules of water use from April 26 is 120 thousand rubles. If it is proved that pollution has affected specially protected objects, tourist areas, places of mass recreation, glaciers and water bodies with healing natural resources, the fine will increase to 300 thousand rubles. A similar punishment is provided for the discharge of industrial waste, the disposal of hazardous substances. Recall that before the adoption of the new law, the fine for such actions was a maximum of 50 thousand rubles.
"Criminal Code of the Russian Federation" dated 06/13/1996 N 63-FZ (as amended on 05/29/2019) of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation Article 250. Water pollution regulates the amount of punishment and fines for pollution of water bodies.
The increase in fines also affected the violation of water use rules in fishing, mining and peat extraction. Also, new sanctions are provided for legal entities that ignore the established rules in the construction and operation of oil pipelines and other industrial facilities at water bodies.
Important! The change in environmental responsibility policy affected only legal entities and officials. For individuals, penalties have not changed
Wastewater Treatment Methods
Wastewater treatment methods are divided into:
- Mechanical;
- Chemical;
- Physical and chemical;
- biological;
- Thermal.
All methods of wastewater treatment can be divided into destructive and recuperative. The latter provide for the extraction of valuable substances from wastewater for their further processing. In destructive methods, all substances that pollute wastewater are destroyed. And the products of their destruction are removed from the water in the form of sediment or gases.
The following wastewater treatment methods are distinguished:
- Purification from emulsified and suspended impurities. To do this, coarse impurities are separated by settling, filtration and straining, flotation and centrifugal settling. Finely dispersed substances are separated by flocculation, electroflotation and electrocoagulation;
- Purification of impurities dissolved in wastewater. For this, ion exchange, distillation, reverse osmosis, freezing, electrodialysis, cleaning methods using chemical reagents are used;
- Cleaning from organic impurities;
- Regenerative methods: rectification, clarification, ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis.
- Destructive: vapor-phase, liquid-phase, electrochemical, radiation oxidation;
- Purification of gases: reagent methods, heating, blowing.
In practice, three methods are used to treat all wastewater. The first one has been used for a long time and is considered the most economical. Wastewater is discharged into large streams, where it is diluted, aerated and neutralized in a natural way. At present, this method has shown to be ineffective.
The second method is to remove organic matter and solid contaminants through mechanical, biological and chemical treatment. Most often, this method is used in municipal wastewater treatment plants.
The third method involves reducing the volume of wastewater by changing technological processes.
Despite the fact that many enterprises are trying to make their cycles closed, the most radical solution to the problem of wastewater treatment is the construction of the most modern treatment facilities. In such structures, mechanical cleaning is provided at the first stage. A sieve or grate is installed on the path of the flow of effluents, with the help of which suspended particles and floating objects are captured. Sand and other inorganic substances settle in sand traps.Oil traps and grease traps catch oil products and fats. The flaky particles are captured after settling them with the help of chemical coagulants.
Error message
Text…
Ways to solve the problem of water pollution

 Stages of wastewater treatment
Stages of wastewater treatment
The main source of water pollution is human activity. Ways to solve the problem lie in the field of wastewater treatment, preventing the ingress of pollutants into water bodies and soil. In order to completely solve the problem of water pollution, an integrated approach must be applied.
Plays a role and work on the reduction of harmful emissions into the atmosphere, and personal culture of water use. Since the problem is global, joint efforts of all countries are needed.
Industrial and domestic wastewater treatment
Polluted effluents from industrial enterprises end up in rivers. Sewers lead to reservoirs. Not everywhere use full-fledged wastewater treatment. Organic residues are less dangerous to nature than chemicals. But biological discharges pose a danger to cities located downstream of the river.
In order to avoid pollution of water bodies with wastewater, new treatment technologies are being developed and implemented. Wastewater treatment plants are called "aeration stations", although aeration at them is far from the only process.

 Biotreatment of wastewater is carried out with the addition of bacteria
Biotreatment of wastewater is carried out with the addition of bacteria
Stages of wastewater treatment:
-
mechanical cleaning.
Drains pass through grates, sand traps, grease traps, primary clarifiers, filters and septic tanks. -
Biological cleaning.
Activated sludge, which is a combination of bacteria and protozoa, removes organic matter. -
Physico-chemical stage.
Needed to remove dissolved substances and suspended particles. Includes aeration, flotation, centrifugation and other methods. -
Disinfection of treated wastewater.
For disinfection, ultraviolet irradiation, ozonation, treatment with chlorine and its compounds are used.
Disinfection of natural waters using chemical reagents
A popular way to destroy unwanted microorganisms is to add oxidizing agents to the water. For this purpose, chlorine, chlorine dioxide, ozone, sodium hypochlorite are often used. An insufficient amount of the reagent will not have the desired effect, and an excess will harm health.
Pumping contaminated water into special tanks
For pumping heavily polluted water, surface and deep drainage pumps are used. The liquid is pumped out in such cases:
- at breaks of sewer pipes;
- removal of water from basements and cellars;
- cleaning of polluted reservoirs;
- drainage of puddles after rains, floods and pipe breaks;
- pumping out cesspools.
Hazardous liquids that cannot be purified are stored in tanks. These liquids include water contaminated with radioactive elements. Reinforced concrete and metal tanks are located on the surface, underground or buried. They have a complex system of protection against leakage and damage during earthquakes.
The state is concerned about the problem of clean drinking water
Despite the common belief that the quality of water directly depends on the presence of sources of pollution, in reality this is not entirely true. Great importance is also given to the condition of air and soil. The main sources of water pollution continue to be unauthorized dumps located near water use facilities. It is with them that the state is actively fighting within the framework of the Ecology project.

After the introduction of the so-called "garbage reform" in Russia, the task of the state was to get rid of unauthorized garbage dumps. For this, a strategy is being implemented, according to which by 2024 about 60% of all waste will be recycled rather than landfilled.
The state intends to pay special attention to the adjacent areas to Lake Baikal and the lower reaches of the Volga.New treatment facilities will appear here in the near future, existing landfills and landfills will be eliminated
This will help prevent key causes of water pollution.
Interesting: The law on water protection zones, which implies the introduction of fines for parking a car within the boundaries of a water protection zone, was adopted with discontent. People still don't understand how a car standing by a body of water on the ground can pollute the soil. This indicates the need for detailed information of the population about environmental pollution by anthropogenic factors.
It is worth noting that the quality of water also depends on the state of the atmosphere. This is due to the fact that initially dangerous compounds enter the air, after which they fall out in the form of rain. The State Duma is preparing to consider a project on the introduction of penalties for enterprises that have distorted data on emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere.
Important! From July 1, a new article will appear in the Code of Administrative Violations, establishing punishment for violation of the requirements for equipping sources of hazardous emissions with special treatment complexes and facilities. Since January 2019, a law has been in force in Russia on the creation of automatic control systems for the level of pollutant emissions
The legislator requires that such control systems be installed at all hazardous industrial facilities. Data collection is entrusted to a specialized State register, the operator of which is Rosprirodnadzor
Since January 2019, a law has been in force in Russia on the creation of automatic control systems for the level of pollutant emissions. The legislator requires that such control systems be installed at all hazardous industrial facilities. Data collection is entrusted to a specialized State register, the operator of which is Rosprirodnadzor.
In accordance with this law, the state establishes the following liability measures:
- for non-fulfillment or untimely fulfillment of the requirements for equipping pollution sources with control systems for legal entities, the fine will be 100-200 thousand rubles. For officials - 20-40 thousand rubles;
- failure to provide up-to-date data for entering into the register will cost legal entities 50-100 thousand rubles, officials - 10-20 thousand rubles;
- for deliberate distortion of data, the fine will be 100-200 thousand rubles (for organizations) and 15-30 thousand rubles (for officials).
In accordance with the new requirements, citizens engaged in entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity will incur a similar punishment with legal entities. For individuals, the system of sanctions will remain unchanged.
Regulation of wastewater release
The permissible degree of pollution of wastewater and their discharged amount depend on the capabilities of the reservoir where they are discharged, and on the sanitary requirements for the water of this reservoir. This quantity is determined by calculations in accordance with the technological regulations.
where Covvz — allowable concentration of suspended particles in wastewater; Svvv - their concentration in the reservoir before the discharge of wastewater; MPCvzv — the maximum allowable concentration of suspended solids in the reservoir; n is the multiplicity of dilution of wastewater in the reservoir.
Calculation of the composition of wastewater by the concentration of harmful substances:
Calculation of the wastewater dilution ratio:
where CO,a is the permissible concentration of harmful substance A; WITHVA the concentration of harmful substance A in the water of the reservoir before the discharge of wastewater; n is the dilution factor; Cm A is the maximum allowable concentration of harmful substance A in the presence of other i-th harmful substances of the same limiting indicator of harmfulness,
where Co is the concentration of pollutants in wastewater; Cv and C are the concentration of pollutants in the reservoir before and after the discharge of wastewater into it.
Calculation of dilution ratio for reservoirs with directional flow:
where Qe - the volume of water consumed by the reservoir; Qv — the volume of wastewater discharged; m is the mixing coefficient, showing the proportion of water in the reservoir, spent on mixing.
Under the condition of complete mixing of wastewater, the concentration of impurities in the reservoir C at an arbitrary point in time is equal to:
Calculation of the allowable composition of wastewater based on the concentration of suspended solids Cv vzv is carried out according to the formula PDS = Q^ Cst:
where V is the volume of the reservoir; t = V / (Qv + - Qn) - the period of complete water exchange in the reservoir; Q P - loss of clean water of the reservoir, for example, during evaporation.
Sewage treatment. Purification is the destruction or removal of contaminants from water. Disinfection is the destruction of pathogenic organisms in wastewater.
For wastewater treatment, the following methods are used: hydromechanical, physicochemical, chemical, electrochemical, thermal, biochemical methods. The specific method of their purification depends on the amount of water, on the type and concentration of pollutants in them.
To separate insoluble impurities, in addition to settling facilities, hydrocyclones, centrifuges, filters, flotation units are used.
Physical and chemical cleaning methods: coagulation, oxidation, sorption, ion exchange, extraction, membrane methods. They allow you to remove heavy metal ions, dissolved salts, acids, alkalis, biogenic compounds.
Biochemical methods are used to decompose organic matter, since some microorganisms are able to consume wastewater organic matter for nutrition. Cleaning is carried out using aerotanks, biofilters, oxygen tanks; biological ponds and fields.
The possibilities of wastewater treatment by different methods are illustrated in Table 4.3.
Table 4.3 Degree of treatment of industrial wastewater
|
Cleaning methods |
Purification degree,% |
|
|
for insoluble substances |
according to BODP |
|
|
Hydromechanical |
60-90 |
30-40 |
|
Chemical |
80-90 |
40-50 |
|
Physico-chemical |
90 |
50-75 |
|
Biological |
90 |
80-90 |
BODP biological need for oxygen.
How to determine the degree of pollution
To determine the chemical composition of the water source and identify deviations from the norm, experiments are carried out that show the degree of water pollution and help find a solution for its purification. Water is sampled and tested in the laboratory. The degree of pollution is determined by a number of indicators:
- color;
- oxidizability;
- the presence of Escherichia coli;
- the presence of heavy metals and other substances hazardous to health;
- the number of microorganisms, the ingress of pathogenic bacteria;
- degree of turbidity;
- smell, etc.
A number of plants are bioindicators of water pollution. The presence of duckweed in a water source indicates the purity of the water.
Why determine the degree of water pollution
Environmental pollution is becoming global. There is a reduction in drinking sources. Industrial enterprises discharge a significant amount of chemicals into the environment, some of the substances penetrate into lakes and rivers. The problem of ecology is the pollution of underground reservoirs - the main source of water suitable for consumption. Determination of the composition of water sources is required to assess the quality and compliance of drinking water with established standards.
In Africa, South America and Asia, contamination of drinking water is a potential hazard. Contamination of water bodies is the cause of the epidemiological threat. In case of disease outbreaks, analysis of water sources is required. Determining the degree of biological contamination of water helps prevent the spread of infection.
Sample analysis is carried out to determine the suitability of a water reservoir for irrigation. The analysis determines the measures needed to treat wastewater. Also, the study of water bodies is required to identify the degree of impact of industrial enterprises on the environment.