Freezing point of water
The freezing process takes place when cooled down to zero degrees on the Celsius scale. This does not apply to all water. Molecules attach themselves to impurities, which are particles of dust, salt, etc. Therefore, pure or distilled water, without the presence of these very impurities, under the influence of low temperatures in the Celsius column, can remain in a liquid state longer than ordinary water.
It is also interesting that while other substances decrease in volume when freezing, water, on the contrary, increases. This is because the distance between the molecules expands during the transition to the solid state. Despite the fact that the volume increases, the mass does not increase when freezing, and weighs as much as warm water.
Many people wonder why water does not freeze under a thick layer of ice. Any physicist will answer that under a layer of ice, water does not freeze, since the surface of the ice serves as a heat insulator.

Why does hot water freeze faster than cold water?
It is known that hot or warm water freezes faster than cold water. Unbelievable but true. This discovery was made by Erasto Mpemba. He conducted experiments using the frozen mass, and found that if the mass is warm, then it will freeze faster. The reason for this, as studies have shown, is the high heat transfer of hot and warm water.

Are the freezing point of water and altitude related?
As you know, pressure changes at altitude, so the temperature of the transition to the solid state of all aqueous solutions at altitude differs from the temperature on a normal surface.
Examples of temperature changes at altitude:
- altitude 500 m - the freezing point of water is not zero ° C, as under normal conditions, but in the presence of already one ° C;
- height 1500 m - crystallization occurs in the presence of about three ° C, etc.

How pressure affects the process of water crystallization
If you understand the relationship between pressure and crystallization of water, then everything is quite simple.
Interesting! The higher the pressure, the lower the rate of transformation of water into ice crystals, and the higher the boiling point!
That's the whole secret, and if you think logically, then with a decrease in pressure, all indicators go in the opposite direction. Therefore, it is difficult to cook something in the mountains, since the temperature at which water boils does not reach one hundred degrees Celsius. Conversely, ice melts even at low temperatures.
Crystallization temperature of aqueous solutions
Water is a good solvent and therefore easily combines with other substances. The resulting solutions, of course, will freeze under different conditions. Consider a couple of options for temperature criteria for freezing different solutions based on water.
Water and alcohol. With a large amount of alcohol in the water, the freezing process will begin in the presence of very low temperatures. For example, at a ratio of 60% water to 40% alcohol, crystallization will begin in the presence of minus 22.5 ° C.
Water and salt. The temperature at which freezing occurs is directly related to the degree of salinity of the water. The principle is that the more salt in the water, the lower the crystallization temperature. How seawater freezes is directly related to the salt content.
Water and soda. The crystallization temperature of the solution is 44 percent, plus 7°C.
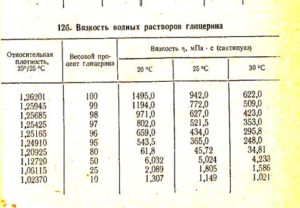
Water and glycerin, at a ratio of 80% to 20%, where 80 is glycerin, and 20 is water, the presence of -20 ° C is required to freeze the solution.
All temperature values fluctuate depending on the degree of concentration of foreign solutions or other substances in the water.
Measuring the viscosity of liquids with an Ostwald viscometer
In order to determine the viscosity coefficient ηhis of the investigated liquid using an Ostwald capillary viscometer (Fig. 6), it is necessary to know:
- η0 is the viscosity of water,
- t0 is the time of water flow between marks a and b,
- tx is the time of flow of the investigated liquid between marks a and b,
- ρ0 is the density of water,
- ρx is the density of the investigated liquid.
Rice. 6. Ostwald capillary viscometer (a, b, d - marks limiting the liquid level, c - capillary).
The viscosity of the investigated liquid is determined by the formula (9).
Work order
Task 1. Determine the viscosity of solutions with different concentrations.
-
Pour water into the leg of the viscometer that does not have a capillary (Fig. 6) up to the mark d.
-
With a pear, suck the liquid through the capillary to mark a. After removing the pear, close the hole of the left knee of the viscometer (with a hand, a cork, a swab, etc.) (see Fig. 6). Prepare and turn on the stopwatch, opening the hole of the left knee, and turn it off when mark b flows, thus determining t0 - the time of water flow between marks a and b.
-
Repeat measurements 4-5 times, find the average time.
-
Do steps 1-3 for all test liquids.
-
Calculate the viscosity coefficients of the studied liquids using formula (9).
-
Enter the data in table 1.
Table 1
| № | Concentration, % | t1 | t2 | t3 | t4 | t5 | | |
| 1 | ||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||
| 6 |
Task 2. Determine the concentration of an unknown solution.
-
Plot Viscosity Ratio vs Solution Concentration
-
Knowing the viscosity of the unknown solution, determine its concentration from the graph.
Table 2
Density of water at different temperatures
| ρ, kg/m3 | t, 0C | ρ, kg/m3 | t, 0C |
| 999,13 | 15 | 998,02 | 21 |
| 998,97 | 16 | 997,80 | 22 |
| 998,80 | 17 | 997,57 | 23 |
| 998,43 | 19 | 997,32 | 24 |
| 998,23 | 20 | 997,07 | 25 |
Table 3
Viscosity of water at different temperatures
| η, Pa.s | t, 0C | η, Pa.s | t, 0C |
| 0,00114 | 15 | 0,00098 | 21 |
| 0,00111 | 16 | 0,00096 | 22 |
| 0,00108 | 17 | 0,00093 | 23 |
| 0,00103 | 19 | 0,00091 | 24 |
| 0,00100 | 20 | 0,00089 | 25 |
Table 4
Density of glycerin solutions of various concentrations
| WITH, % | ρ, kg/m3 | WITH, % | ρ, kg/m3 |
| 5 | 1012,5 | 45 | 1112,5 |
| 10 | 1025,0 | 50 | 1125,0 |
| 15 | 1037,5 | 55 | 1137,5 |
| 20 | 1042,5 | 60 | 1150,0 |
| 25 | 1052,5 | 65 | 1162,5 |
| 30 | 1075,0 | 70 | 1175,0 |
| 35 | 1087,5 | 75 | 1187,5 |
| 40 | 1100,0 | 80 | 1200,0 |
Independent work on the topic:
– solution of situational problems;
- listening to abstracts
Final control of knowledge:
– solving problems for tickets;
– responses to final control tickets;
- summarizing.
Homework to understand the topic of the lesson
Control questions on the topic of the lesson:
1. What is the viscosity of a liquid called?
2. What kind of fluid flow is called laminar? Turbulent?
3. What characterizes the Reynolds formula?
4. Write Newton's formula and explain the physical meaning of the quantities included in it?
5. What is the coefficient of dynamic viscosity? In what units is it measured?
6. What fluids are called Newtonian? What determines their viscosity coefficient?
7. What liquids are called non-Newtonian? What determines their viscosity coefficient?
8. Write the Poiseuille formula, explain the physical meaning of the quantities included in it.
9. What methods are used to determine the viscosity of a liquid?
10. Tell about the rheological properties of blood and other biological fluids, about the use of rheological analyzes in medicine.
11. What does the velocity gradient show? Show graphically.
12. What phenomenon is called internal friction?
Test tasks on the topic:
IS THE APPLICATION OF GLYCERIN IN HEATING JUSTIFIED?
Quite high requirements are imposed on the coolant for heating systems. It must be fire and explosion-proof, provide good thermal performance, and also not contain additives prohibited for use. Ethylene glycol or propylene glycol is used as the basis for the production of high-quality heat transfer fluid, which also ensures environmental friendliness.
Recently, glycerin-based antifreeze coolants have appeared on the market. This product is promoted mainly by small, little-known firms on the antifreeze market. The question arises: glycerin and coolant - is their union appropriate?
And, indeed, the first antifreezes that appeared in our country in the twenties of the last century were made on the basis of glycerin. Their weaknesses were insufficient fluidity and extremely high viscosity, which the pumps could not handle. They tried to solve the problem with the help of alcohol, including methyl alcohol. However, along with the improvement in fluidity, many problems appeared. The fact is that methanol is a strong psychotropic poison.As a result, the behavior of drivers who involuntarily sniffed such antifreeze sometimes defied any logic and posed a danger to the health and life of others. In addition, methyl alcohol has a low boiling point and when it evaporates, the viscosity of the product immediately increases. The problem was resolved only when ethylene glycol became the basis of the coolant. And by the end of the thirties, the beginning of the forties, ethylene glycol antifreezes almost completely replaced glycerin-methanol ones.
In addition, glycerin is thermally unstable, decomposes during prolonged heating, with the formation of a poisonous volatile substance - acrolein, which has a sharp unpleasant odor that causes tearing. Decomposition products are toxic, and precipitating increase the corrosive activity of the coolant. As a result, the requirements for seals and parts made of non-polar rubbers and plastics are increasing. In addition to high viscosity, glycerin also foams strongly, which leads to airing of the system and poor heat dissipation.
Manufacturers of glycerin coolants are trying to compensate for all the above disadvantages by adding various additives, including aliphatic alcohols - methanol, ethanol, propanol. These alcohols can significantly reduce the viscosity or density of the antifreeze coolant. But they boil already at temperatures above 65 degrees, which leads to a deterioration in the thermal performance of the coolant. These alcohols are capable of dissolving rubber and polymers, and are also prone to cavitation and strong evaporation. In addition, methanol is a strong poison and is forbidden for use in the production of antifreeze liquids.
Ensuring the quality of glycerin coolants, especially with methanol, requires the addition of expensive additive packages to the mixture. And although the cost of glycerin is now lower than the cost of glycols, the additive package for making quality glycerin heat transfer fluids is more expensive than the additive package for antifreeze based on ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. And if the cost of glycerin antifreeze on the market is lower than that of glycol, it means that the manufacturer simply saved on quality and did not add the necessary expensive additives to the product!
So the choice is up to the buyer: either a reliable and proven coolant based on glycols, or a glycerin "pig in a poke".
The choice of our company, like most of the leading manufacturers of antifreezes, is fundamentally unambiguous - glycerin cannot be used in its pure form, but mixed with methanol is dangerous and criminal!
The main argument confirming our position on this issue is that in any important and large facility, the use of glycerin in heating and cooling systems is NOT ALLOWED by existing standards!
MEG
Ethylene glycol is a product of ethylene oxide hydration in the presence of sulfuric or phosphoric acid. Refers to polyhydric alcohols. Does not freeze at low temperatures and lowers the freezing point of water. Capable of absorbing water from the air.
It is sold in metal and plastic barrels, up to 227 liters. As well as plastic cubes 1000l.
It is necessary to store the substance in a sealed container made of aluminum or steel with anti-corrosion protection in a closed warehouse without heating. The shelf life for the highest grade is 12 months, for the first grade - 3 years from the date of production.
Name of indicator Norm
Appearance, odor Clear, colorless liquid with an oily texture. Without smell.
Soluble in water, alcohols, toluene, benzene
Density 1.112 g/cm?.
Melting point 12.9 degrees Celsius
Boiling point 197.3 degrees Celsius
Application
Due to its ability to reduce the freezing point, monoethylene glycol is used in the production of antifreeze and brake fluid for cars, as well as in the manufacture of cellophane and polyurethane. To a lesser extent, it is used in the production of inks and printing inks.
Hazard Class
Refers to combustible substances. Self-ignition occurs at a temperature of 380 degrees, a flash of vapor when heated to 120 degrees. Toxic. Ingestion is not allowed. Vapors are less harmful.
Glycerol
Chemical formula: HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH
International name: Glycerine
CAS NO: 56-81-5
Qualification: Imp. "h", GOST 6259-75
Appearance: clear, odorless liquid
Packing: 25 kg cans, 250 kg drums, 1500 cubes
Storage conditions: in a ventilated dry room at a low temperature
Synonyms: 1,2,3-trioxypropane
We offer Glycerin in cans, barrels, cubes at competitive prices.
| Specification | |
| Molecular weight | 92.10 |
| Basic substance, not less than | 99.5% (actual 99.8%) |
| Ash content, no more | 0.01% (actually less than 0.1%) |
| Water content, no more | 0.5% (in fact 0.1%) |
| Content of chlorides, no more | 0,001 % |
| Sulfate content, no more | 0,002 % |
| Heavy metals, no more | 0.0005% (actually less than 0.00005%) |
| Chlorine compounds (as CL), no more | 0,003 % |
| Arsenic, no more | 0.00015% (actual less than 0.00001%) |
| Color (APHA), no more | 20 (actually less than 10) |
Glycerin is a colorless, hygroscopic, viscous, odorless, sweet-tasting liquid. Miscible in any ratio with water, ethanol, methanol, acetone, insoluble in chloroform and ether. When glycerol is mixed with water, heat is released and contraction occurs (volume reduction). When glycerol interacts with hydrohalic acids or phosphorus halides, mono- or dihalohydrins are formed; with inorganic and carboxylic acids - complete and incomplete esters, with dehydration - acrolein. Glycerol can be oxidized, and depending on the conditions and nature of the oxidizing agent, glyceraldehyde, glyceric acid, tartronic acid, dihydroxyacetone, mesoxalic acid can be obtained. Glycerin is found in natural fats and oils as mixed triglycerides of carboxylic acids.
Application Glycerin is widely used • in the pharmaceutical industry, for example for the production of nitroglycerin, medicinal ointments; • in the food industry, for example in the production of liqueurs, confectionery; • in the cosmetics industry, in the manufacture of perfumes and cosmetics; • in the production of glyptal resins; • as a softener for fabrics, leather, paper; • as a component of emulsifiers, antifreezes, lubricants, shoe polishes, soaps and adhesives, • as a raw material in the production of polyalcohols, which are used in various foams. • as a plasticizer for cellophane, etc.
At what temperature does water freeze in heating pipes in a residential building
If the temperature in the house remains -10 for several days, and there is water in the pipes, then it can freeze, which will lead to rupture of the pipes. Many have probably seen modern heating batteries with a water drain function. Almost all modern batteries are equipped with the ability to drain water. This is done so that in the event of an emergency, when the temperature in the house is -10, the water does not freeze and does not tear the pipes. If the situation has come to this, we sympathize with you very much, most likely you will have to change the batteries, since during the freezing of water, microcracks have probably occurred that make the further operation of these batteries dangerous.
Why can water freeze in pipes? If during the heating season, just when the batteries are filled with water, a breakdown occurs and the water is cooled down, and the temperature drops rapidly outside, this can lead to freezing of the pipes.
We have already answered the question at what temperature water freezes, as an experiment, take a small glass, fill it halfway with water and put it in the freezer for several hours, two hours are enough for the water to partially turn into ice.
Water is one of the most essential substances on our planet. It has a lot of properties that make it, to some extent, unique. One of the most famous properties that even a small child knows about is the freezing of water.It is known that 0 degrees Celsius is the crystallization temperature of water. But not everything is so simple. We will consider some of the subtleties of this process further.

Density of glycerin solution at 25
The arithmetic mean of the densities of alcohol and glycerol.
209.4. 1.047. 25.265.0. 1.060. ... See what is the Density of aqueous solutions of glycerin in other dictionaries E236 File Formic acid.svg Structural formula of formic acid Formic acid methanoic acid is the first ...
What is the density of glycerin at 17 degrees Celsius?
8
Density at 25 C, g cm. ... A solution of glycerin at a concentration of 25% or more does not expose microbial contamination; in more dilute solutions, microorganisms multiply well in it.
3,14
Which liquid has a higher density, glycerin or alcohol? explain
Ssss
TK-April on the site throughout Russia. Concentration, density and refractive index of solutions of glycerol 15 С. … 1.0594. 1.3633. 25.1.0620.
Calculate the molar mass of both substances. For alcohol, it is less (92 g / mol versus 46 g / mol for alcohol), and the density is correspondingly lower. When it comes to ethyl alcohol.
What is the point of such questions? Information is found in search engines
The arithmetic mean of the densities of the components of the mixture.
Determine what mass of glycerol with a density of 1.26 g ml should be taken to prepare an aqueous solution c.42. ... 111 g of phthalic anhydride and 46 g of glycerin with a density of 28 V are placed in a glass beaker with a capacity of 0.25 l.
How to calculate the density and viscosity of a liquid containing water, alcohol and glycerin?
For this, rheometers are sold. you don't have to count anything. just freeze.
triethylene glycol. propylene glycol. Glycerol. … propylene glycol 40%. -25 C. ... The density of aqueous solutions of ethylene glycol at various temperatures.
You need to know the percentage of all components of the mixture (at least!)
No way. Is, look for data received by someone.
Please help, will a piece of ice float in gasoline, kerosene, glycerin? why?
It will be in glycerin, it doesn’t float in whiskey - the density is about the same as gasoline
It also increases the density of the finished solution and improves the quality of the bubbles. ... Glycerin solution 25g bottleTula Pharmaceutical Factory LLC. … Sodium tetraborate solution in glycerin vial 20% 30g, Samara FF, Samara Russia.
Ice is less dense than oil, so it will be.
Compare the density of ice with the density of these liquids. if the density of ice is less, then it will float; if it is more, it will sink.
Do not know. depends on which piece. if there is enough air in the ice to keep it on the surface, it will float, and if not, then it will not. try it yourself. kerosene is cheap.
Depending on what temperature this ice is cooled to
The boiling point of aqueous solutions of glycerin decreases with a decrease in the concentration of glycerol with a content of 5% water, the boiling point is 160-161, its density is 1.26362 g cm3. … 25 25 C . ZnCl2.
I have never seen ice floating in the gas tank and canister. And he certainly is))). So he's probably at the bottom. I saw glycerin only in a vial and in heat))).
Oyoy!
X amount of diluted glycerol, g A density of distilled glycerol, g ml ... Solutions of glycerol at a concentration of 25% and above are not subject to microbial contamination, more dilute solutions are ...
Will a piece of ice float in gasoline, kerosene, glycerin?
Find out the density and that's it!
Density of aqueous solutions of alcohols. Densities of aqueous solutions g cm3 at 20 C are given for the following substances: ethanol, 1-propanol, 2-propanol, ethylene glycol, glycerol, D-mannitol.
Yes)))
If the density of the ice is less than the density of the liquid, then the ice will float
What is the density of glycerin at a temperature of 24 gr. WITH?
Glycerin Degrees Celsius020406080100120140169180Density g/cm3126712591250123812241208118811631126
For a temperature of 24 degrees = determine by interpolation between 20 and 40 degrees
Calculate the boiling point of an 8% solution of glycerol C3H6O3 in acetone. The answer is 57.7oC. 4.A solution, 100 ml of which contains 2.3 g ... Take the density of the solution equal to one. Answer 608 Pa. Ticket 14 25 1. How many grams of BaCl2 2H2O ...
Questions on Chemistry))) And Physics. Which liquid is denser than water and also conducts electricity but not metal?
Glycerin, ethylene glycols, formamides, butyrolactone, almost all acids, amines. and much more.
Sulfuric acid concentration, % by mass. Density at 25 C, g cm. ... 25.60-0.1950 0.000 8 - relative humidity,% - refractive index of an aqueous solution of glycerol at 25 C for line D sodium - solution temperature, C ...