Why homemade is better than a purchased option
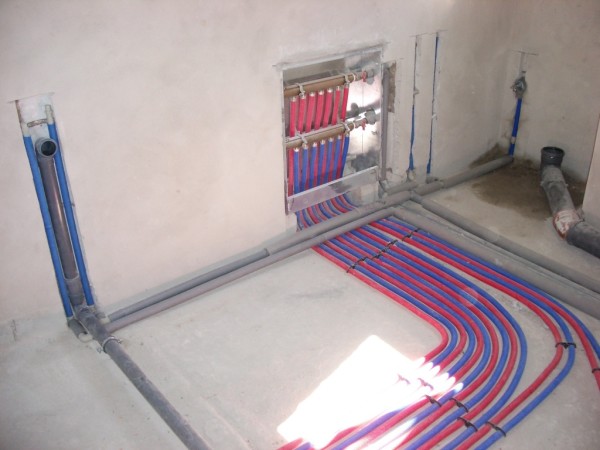
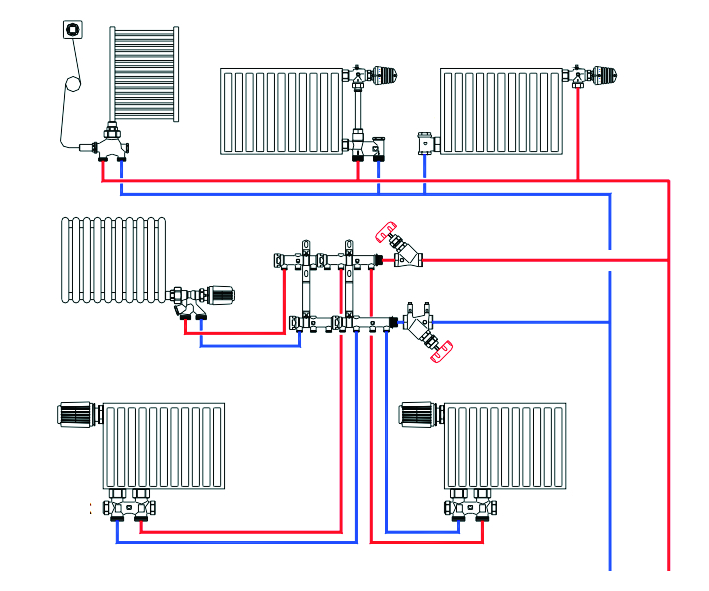
To establish the normal operation of autonomous heating in a house with a height of more than 1 floor is not an easy task even for a specialist. To do this, equip a special room and begin to dance from the stove. Directly behind the heating equipment, a collector for boiler wiring is mounted. Through it, pipes are routed through the floors. In a large house, one coolant distributor is not enough, so a collector is needed for each floor for additional wiring around the premises.
It is not easy to find equipment in the store that perfectly matches the tasks of your home. A do-it-yourself heating manifold, designed for the power of the boiler you use, the length of the circuits and the heated area of \u200b\u200bthe rooms and underfloor heating, will ensure comfortable living in the house in the winter. In addition, a self-made steel pipe collector will cost much less than a purchased one, especially if you need at least one of them per floor.
Collector heating
In collector heating, each device has its own independent supply. This makes it possible to regulate the temperature of a single radiator taken or completely exclude it from the circulation of the coolant (turn it off). The node of the system is precisely the collector, which looks like a comb. It includes the main supply and return lines, and secondary piping out. The collector water heating system can be either single- or double-circuit.
Pros:
- The ability to adjust the optimal parameters of the air in the room. That is, each heater in the circuit is controlled independently and centrally. If the room became hot for some reason (many guests came, an additional heat source appeared, etc.), the temperature in the radiator can be lowered without disturbing the microclimate in other rooms of the house. In general, different temperatures can be created in different rooms. This allows you to save on energy resources.
- Application in the installation of a system of pipelines of small diameters. Each branch that comes out of the collector lives one heater or a small group. It follows from this that the pressure in the pipelines is not very high (but acceptable). The small diameter of the pipelines determines the good aesthetics of the heating system. Its elements do not stick out and do not clutter up the room.
Minuses:
- High consumption of consumables during installation (in contrast to the serial connection of heaters in the heating system). The more complex the connection configuration of individual elements, the less savings.
- The collector assembly itself does not look aesthetically pleasing, cumbersome. So that he does not rush into the eyes, he needs to be hidden.
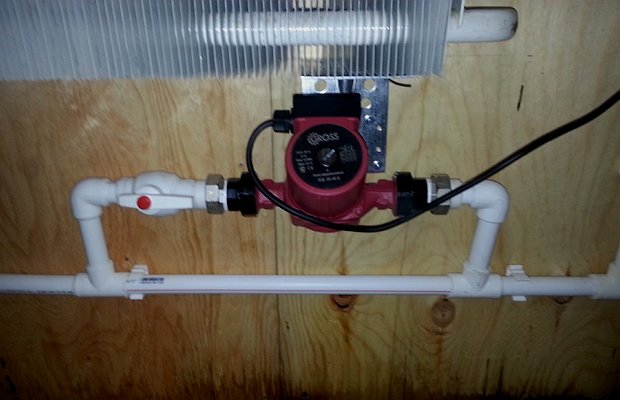
- In a collector heating system, installation of circulation pumps (on the supply and return) is indispensable. The force of gravity for the normal circulation of the coolant in the circuit is not enough. The purchase and installation of circulation pumps is also not a small additional cost.
- Energy dependence. Not only will circulation pumps hit the budget, but that's not all. An unscheduled power outage in the village can lead to a malfunction of the heating system, and in winter - freezing of the coolant inside the pipelines. This is all due to the fact that the pumps are powered by electricity.
- Experts do not recommend installing collector heating systems in city apartments.
Manufacturers offer many different models of collectors on the construction market. Among them there are devices with the maximum set of elements. Part of the coolant supply is equipped with flow meters. With these devices, you can control the flow of water in the circuit.This is done in order to balance the pressure in the system. Part of the coolant return is equipped with temperature sensors. With the help of these devices, the temperature in the heating radiators is regulated. The system allows you to automatically control the heating of each heater. Thermal sensors for the collector system can also be different. Often use brass elements with an inch passage. Thermal sensors have plugs on the return line. This allows, if necessary, to connect additional elements to the system.
There are people who make combs with their own hands. This is strongly not recommended. Combs must be mounted by qualified specialists who have sufficient knowledge and skills, and will perform the work in accordance with the current building codes and regulations. After installation of the system, hydraulic tests are carried out. Ignoring building codes and regulations during installation leads to negative consequences, up to system breaks and accidents.
The place for installing the collector is determined at the design stage of the heating system. If the house has several floors, each has a place for a collector block. Most often, a special niche is made in the wall for this, at a small height from the floor level, but so that small children or animals cannot get into it. The comb must be installed in a room with acceptable air humidity (pantry, corridor, etc.).
The device can be attached directly to the wall if it is mounted in a utility room or placed in a cabinet specially designated for this (meaning a metal box with a door).
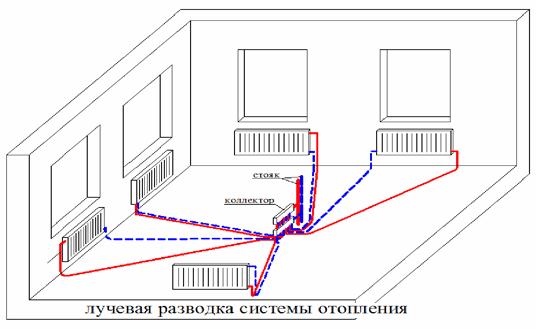
Radiant heating system optimal solution
Diagram of a radiant heating system.
Anyone who owns their own home naturally wants to organize an optimal system of good heating with their own hands. He must know for sure: the ideal heating system has not yet been invented, therefore it is necessary to choose what is most practical and has received positive approval. The heating system, nicknamed radiant, can be given preference. Its romantic-geometric name is quite understandable: every radiator has its own beam as a pipeline.
If the owner owns a cozy, not very massive house, consisting of two floors, then the scheme for constructing a heating system using collectors implies the presence of a collector on each floor. They are combined in a parallel way, then they put the boiler, then the expansion tank. This heating system is sometimes called a two-pipe system. And it is right. A pair of pipelines runs through all the rooms that need to be heated. One line of pipes is created for the direct movement of the fluid - the coolant, the other is responsible for the way back.
Most wanted models
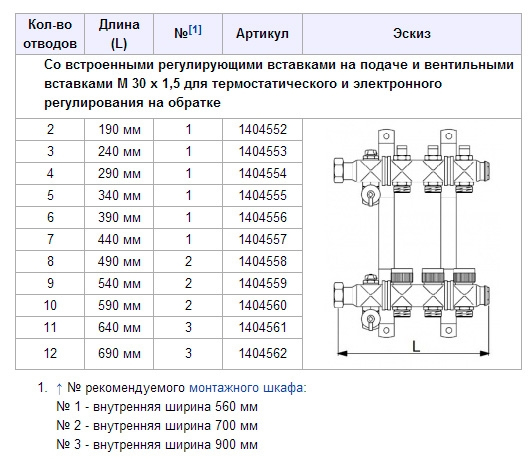
1. Oventrop Multidis SF.
The inch comb of heating is intended for the organization of heating by a water heat-insulated floor. Manufactured from high wear resistant tool steel. Main characteristics:
- allowable pressure in the circuit - 6 bar;
- coolant temperature - +70 °С.
The series is produced with M30x1.5 valve inserts, and can also be equipped with a flow meter for connecting circuits located in different rooms. Bonus from the manufacturer - soundproof mounting clamps. The number of simultaneously serviced branches is from 2 to 12. The price, respectively, is 5650-18800 rubles.
To work with high-temperature appliances, Oventrop suggests using the distribution manifold of the Multidis SH stainless steel heating system with a Mayevsky tap. The design already withstands 10 bar at + 95-100 ° C, the throughput of the comb is 1-4 l / min. However, for products with 2 circuits, the indicators are slightly weaker. The cost of Oventrop SH hydrodistributors fluctuates in the range of 2780-9980 rubles.
Plumbers: You'll pay up to 50% LESS for water with this faucet attachment
- HKV - brass manifold for underfloor heating. Holds a pressure of 6 bar in the range of + 80-95 ° С. Rehau version D is additionally equipped with a rotameter and a tap for filling the system.
- HLV is a heating distribution manifold designed for radiators, although its characteristics are identical to those of HKV. The only difference is in the configuration: there is already a Eurocone and the possibility of a threaded connection with pipes.
Also, the manufacturer Rehau offers to buy separate Rautitan combs with three exits for pipeline installation using compression sleeves.
Distribution collector of heating from steel with an anticorrosive covering. It works in systems with temperatures up to +110 °C at a pressure of 6 bar and hides in a special heat-insulating casing. The capacity of the comb channels is 3 m3/h. Here, the choice of designs is not too rich: only 3 to 7 circuits can be connected. The cost of such hydraulic distributors will be from 15,340 to 252,650 rubles.
Stainless steel manifolds are produced in an even more modest assortment - for 2 or 3 circuits. With the same characteristics, they can be purchased for 19670-24940 rubles. The most functional Meibes line is the RW series, which already comes with various connecting elements, thermostats and manual valves.
- F - a flow meter is built into the supply;
- BV - has quarter taps;
- C - provides for building a comb through a nipple connection.
Each Danfoss heating manifold allows a pressure in the system of 10 atm at the optimum temperature (+90 °C). The design of the brackets is interesting - they fix the paired combs with a slight offset relative to each other for more convenient maintenance. At the same time, all valves are equipped with plastic heads with printed markings, which allows you to set their position manually without the use of tools. The price of Danfoss models, depending on the number of connected circuits and additional options, varies between 5170 - 31,390.
The heating manifold can be selected for a euro cone with 1/2″ or 3/4″ outlets or with a metric threaded connection. Far combs withstand pressure up to 10 atm at temperatures not exceeding +100 °C. But the number of outlet pipes is small: from 2 to 4, but the price is the lowest of all the products considered in our review (730-1700 rubles for an unpaired distributor).
Selection Tips
Despite the seeming simplicity of the combs, they need to be selected based on several technical parameters at once:
1. Head in the system - this value determines what material the distribution manifold can be made of.
2. The throughput must be sufficient so that the connected heating circuits do not “starve” from a lack of coolant.
3. Energy consumption of the mixing unit - as a rule, it is determined by the total power of the circulation pumps.
4
The ability to add contours - this parameter should be paid attention only when it is planned to build additional objects in the future that need heating
The number of nozzles on the hydraulic distributor must correspond to the number of connected branches (heaters). In some cases, it is better to install several collectors, for example, in a two-story house - one block at each level. It is also allowed to install unpaired combs at different points: one on the supply, the other on the return.
Finally, experts and experienced installers in their reviews advise not to save on buying a good collector. In order for it to serve for a long time and not cause any special problems, the name on the box must be known.
Installation options for water heating systems
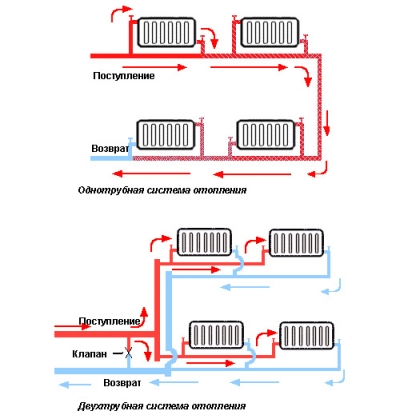
Single-pipe heating is more often used for private houses of a small area; for large areas, we recommend looking towards two-pipe systems.
What is the best way to lay pipes and connect radiators? If you have a small house, literally 2-3 rooms, you can save a little on material and lay a single-pipe system. Here, the coolant passes sequentially through all radiators, reaches the last battery and returns to the boiler through the return pipe. With this gasket, the bottom battery connection is used. The disadvantage is insufficient heating of the most distant rooms, since heat transfer in radiators leads to a decrease in the temperature of the coolant.
The problem with coolant cooling is solved by installing circulation pumps and jumpers / bypasses on each radiator (Leningrad scheme).
Two-pipe systems are more advanced. In them, a solid pipe is laid to the farthest radiator, from which taps are made to intermediate radiators. After passing through the radiators, the coolant is sent to the return pipe. This scheme allows you to ensure uniform heating of all rooms. and its main disadvantage is the increased complexity of installation.
If you choose between one-pipe and two-pipe systems, then we recommend stopping at the two-pipe version. It will provide uniform heating of rooms and will allow you to regulate the temperature by cutting off unnecessary radiators.
Pipe selection
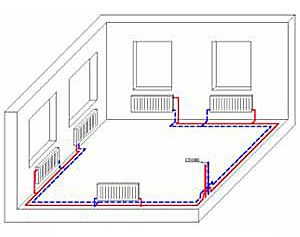
Individual heating. which is mounted according to the beam scheme, requires the correct selection of pipes. Communications must be flexible enough to avoid the installation of a large number of connections. Pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene are best suited for these purposes. Such products are sold in bays.
Polyethylene pipes that are suitable for a radiant heating system must have an airtight layer. When using conventional varieties, air enters the system. It leads to the development of corrosion of metal elements, the rapid failure of equipment.
¾ inch pipes are used to connect the collector to the boiler. Radiators can be connected to the comb with ½ inch communications. This is possible if a circulation pump is used in the system. Otherwise, the diameter of the pipes may be larger.
Why you need a distributor
The heating manifold is a simple device consisting of a pipe section with several branch pipes, to which all heating circuits are connected. With the help of a distribution comb, several consumers can be connected to the heat carrier at the same time:
- heating radiators in all rooms
- warm floor
- hot water boiler
- convectors and other devices
The main task that the heating distributor performs lies in the name itself - it evenly transfers heat from the heating boiler to all heating elements. At the same time, the device maintains the same temperature in all rooms.
All distribution manifolds are equipped with shut-off valves. It is installed either on the device itself or on a pipe that connects to the outlet.
In the event of an emergency (pipe breakage or water leakage at the joints), ball valves installed on the boiler manifold block the damaged circuit without turning off the entire heating system and keeping the heat in the house. In addition, with the help of such a tap, the temperature in individual rooms is regulated.
In private houses with more than one floor, collectors are installed on each floor, which allows you to turn off the heating in temporarily unused rooms, thereby saving fuel.
The distributor for heating consists of 2 combs arranged in parallel. One of them is installed at the outlet of the coolant from the heating boiler, and the return circuit of the system is supplied to the second.
Design features
Radiant heating, unlike tee heating, with which all owners of city apartments and old houses are familiar, does not provide for a series, but a parallel connection of batteries to a heating boiler.
In this case, a special collector cabinet is mounted, in which all the necessary control equipment and pumps are carefully installed. gauges, taps and so on.
The differences between the two installation schemes mentioned above are as follows:
- Tee wiring requires a much smaller number of pipes themselves, but when installing it, you need to use a lot of fittings: tees, spurs, couplings, and so on. This complicates the installation procedure. In addition, the sequential method of arranging the heating system is considered less reliable, since in this case there is a high probability of errors that will lead to depressurization, the formation of areas with different fluid pressures, and so on.
Tee pipe connection method
- Radiant heating distribution, despite the need to purchase a much larger number of pipes, uses only two connections for each radiator: at the junction with the collector and at the battery pipe.
As a result, you can safely wall up each "beam" of the heating network into the floor, without fear that it will leak at some junction. In addition, if a breakdown is detected, you can easily turn off the problem area without disturbing the circulation of the coolant through the heat exchange equipment installed in other rooms.
Beam diagram of the distribution of heating pipelines
It should be noted that one of the main disadvantages of radiant heating is its price. This is especially true for systems equipped with electrical equipment.
Note! As in the case of the tee system, the radial system provides for the organization of natural (gravitational) and forced (with the help of pumps) coolant current. Let's look at both types in more detail.
Let's look at both types in more detail.
Advantages and disadvantages of radiant heating systems
Positive sides
The main advantage of the beam scheme is ease of use.
Special equipment makes climate network management as ergonomic and convenient as possible:
- You can set the temperature of each heating radiator in the house without leaving the manifold cabinet. In addition, if necessary, you can completely shut off the water supply to any element of the system without disrupting the operation of the entire heating network.
- Each pair of pipes connects the collector to only one radiator. Therefore, small diameter pipelines can be used, which are easy to disguise under the floor covering. Among other things, this allows you to partially warm the floor surface.
Pipes of the radiant heating system are laid before the floor is poured
- Thanks to the use of special devices (the so-called hydraulic arrows - collectors with a large diameter), it is possible to form several heating zones in the house with different coolant temperatures.
In this case, a short circuit is organized between the supply and return pipes. Heated water constantly circulates in the hydraulic arrow, and its intake can be made at different distances (the temperature will also depend on this).
Negative sides
To complete the picture, it should be said about the disadvantages of using a radiant heating system.
It is because of them, despite all the advantages, it is not very common:
- Greatly increased consumption of supply and discharge pipes. The more spacious the house and the more complex the geometry of the rooms, the more details you will need. In addition, the complexity of installation increases, which cannot but affect the estimated cost of construction.
The radiant heating system requires the use of a huge number of pipes and collectors
- The need for hidden installation.If the traditional tee system can be mounted along the walls, then you cannot place a huge number of pipes this way. They must be hidden under the floor. You can wall up in the walls, but in this case, the consumption of material will increase even more.
- No joints. When designing pipelines, care must be taken to ensure that the pipe under the floor does not contain a single joint. In this place, gusts most often occur, and the cost of repairing the breakdown will be far from low and very laborious.
- If the system design provides for several circuits with different coolant temperatures, then each of them must be equipped with a circulation pump.
Collector scheme for heating a one-story house with forced circulation
Another type of wiring is collector. This is the most complex system, involving the use of a large number of different pipes and special distribution devices, which are called collectors. The principle of operation of a system with a collector circuit for heating a one-story house with forced circulation is that boiling water from the boiler goes to special collectors that serve as distributors between various radiators. Each battery is connected to it by two pipes. Such a system, while effective, cannot boast of being cheap. It can regulate the temperature not only on each circuit, but also on each battery, which allows you to create your own temperature regime in any room.
For the development and installation of a collector heating system, it is better to invite specialists
They make such a heating scheme for a one-story house with forced circulation, since naturally water cannot circulate efficiently through numerous pipes and collectors. The essence of this scheme is that directly near the boiler a centrifugal circulation pump crashes into the return pipe, which continuously pumps water using an impeller. Due to this, the system develops the pressure necessary to completely pump the entire line, heating all the batteries evenly. If you purchased an expensive wall-mounted automatic boiler, then it most likely already has a circulation pump installed, which is set to the optimum pressure for this boiler. If your boiler is simple, then when buying a centrifugal pump, you need to consult about its compatibility in terms of pressure generated with this boiler in order to avoid an emergency.
Collector heating system compiled by a specialist
The collector circuit is rarely used in two-story houses, since it, although effective, is very cumbersome. The wiring for two floors will be too complicated. That is why it is in demand only in the heating scheme of a one-story house with forced circulation.
Useful advice! To install a collector water heating system in your country private house, you need to take care of purchasing the required number of thermostats and shut-off valves. This will allow you to adjust the climate in the house in a semi-automatic mode.
Circulation pump for forced water recirculation in the heating system
Summarizing the above, it can be noted that the choice of the three existing types of water heating wiring should be carried out deliberately. In a small one-story house, only one pipe can be laid. This scheme is also called "Leningrad". If the area of \u200b\u200bthe house is significant or it is two-story, then it is better to make a two-pipe heating system with a return pipe. To create a modern and efficient heating system in the house, you can mount it according to the collector scheme. It will cost more, but it will also be much more effective.The main thing is that any created system always works well and reliably in any, even difficult, conditions. To do this, you need to build it according to all the rules and recommendations.
Types of water heating systems in a private house
There are several types of water heating for private houses. Here we mean standard heating systems with radiators, underfloor heating and baseboard heating. Individual types can be combined with each other, which allows you to achieve efficient heating. For example, ordinary radiators are mounted in bedrooms and living rooms, and heated floors are often laid in bathrooms and toilets - an excellent solution for those who cannot stand the cold and do not like cold tiles. Let's look at the individual types of heating and their benefits.
Radiator
Radiator heating systems are timeless classics. The principle of their operation is to transfer heat from the coolant through radiators installed in the premises. Such heating systems are installed in the vast majority of buildings for various purposes - in residential, industrial, administrative, utility and many others. They are relatively easy to install - just stretch the pipes and connect radiators to them.
Previously, water heating in a private house involved the installation of bulky cast-iron radiators. Over time, they were replaced by lighter and thinner steel radiators made of corrosion-resistant steel. Later, aluminum batteries were born - they are light, cheap and durable. For a private home, this is the most ideal battery option.
The main advantage of radiator systems is that for their laying it is not necessary to pour concrete screeds. All installation is reduced to the installation of the boiler and radiators with their subsequent connection. Radiators provide effective heating of the premises and do not violate the interior design, especially if they are modern multi-section aluminum batteries.
Warm floor
Water floor heating in a private house can work both in independent mode and in auxiliary mode. In independent mode, there is no need to lay pipes with radiators, and all floors emit heat. Thanks to this, children can play on such floors without fear, they will not be blown or see through. Are your feet constantly cold? Then you will definitely like always underfloor heating. In auxiliary mode, they work as an addition to radiator systems.
Underfloor heating systems are good in kitchens, bathrooms and toilets. where on the floor most often lies eternally cold tiles. Underfloor heating will help keep floors warm and comfortable. For example, in the bathroom you no longer have to stand barefoot on cold tiles. The same applies to the toilet. If you have a tiled floor in your kitchen, feel free to install underfloor heating systems here as well. Another place where a warm floor will become an attribute of comfort is a bedroom - you see, it’s not pleasant to get out from under a warm blanket and become heels on cold floors.
Underfloor heating is characterized by a low coolant temperature, not exceeding +55 degrees, which allows you to create economical heating systems. But the need to make concrete screeds and pass through walls and door frames is a significant disadvantage. It is best to consider the need to install the system at the stage of building a house.
Skirting
Modern heating systems, built on the basis of classic aluminum radiators, differ in that the heat from them spreads only upwards - due to natural convection. As a result, all warm air rises, and cold air enters in its place. There is nothing surprising in the fact that the legs of the household begin to freeze.The only plus is the lack of cold from the windows, as it is carried away by convection to the ceiling. But what about heating? Do not lower the radiators to the very floor?
Skirting heating systems become a way out of the situation. It uses small-sized radiators made of brass or aluminum. The coolant is supplied through plastic pipes of small diameter. The system is complemented by taps, air vents and other necessary accessories.
All this is placed in a special plastic plinth - the air that enters here heats up and heats the walls on top. Further, the room is warmed by infrared radiation from heated walls and floors. There are no drafts blowing on the floor in heated rooms. Here, not only the walls are heated, but also the floors themselves, making the rooms warm and comfortable.
The advantage of baseboard heating is that it can be laid at any stage, even after construction is completed. Disadvantages - the high cost of installation and a lot of requirements for the placement of skirting boards and other elements. Simultaneous installation of all types of the described systems is also allowed.
General requirements for the installation of beam wiring
With collector-beam wiring, the method of laying pipes in the floor in a screed is common, the thickness of which is 50-80 mm. Plywood is laid on top, covered with a finishing floor covering (parquet, linoleum). Such a thickness of the screed is quite sufficient for the free "embedding" of the intra-apartment (intra-house) radiant wiring of the heating system. It is possible to lay pipes outside along the walls under decorative plinths, which inevitably increases the length of the pipelines. There are known options for laying pipes for beam wiring in the space of a false (suspended) ceiling, in strobes.
Connecting radiators with a collector-beam scheme.
Metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene pipes (PEX-pipes) are used, laid in a corrugated pipe or in thermal insulation. PEX pipes have an undoubted advantage here. According to SNiP, only inextricable joints can be “embedded” in concrete. PEX-pipes are connected by means of tension fittings related to inextricable connections. Metal-plastic pipes use compression fittings with union nuts. To “monolichize” them means to violate the SNiP. Each detachable pipe connection must be accessible for maintenance (tightening).
Even without fittings, not every metal-plastic pipe is unambiguously suitable for laying in a floor screed. Manufacturers' products suffer from a serious defect: layers of aluminum and polyethylene delaminate under the influence of repeatedly changing coolant temperature. After all, metal and plastic have different coefficients of volumetric expansion. Therefore, the adhesive connecting them should be:
- internally strong (cohesive);
- adhesive to aluminum and polyethylene;
- flexible;
- elastic;
- heat resistant.
Not all adhesive compositions of even well-known European manufacturers of metal-plastic pipes satisfy these requirements, which delaminate over time, the inner layer of polyethylene in such a pipe “collapses”, reducing its cross section. The normal operation of the system is disrupted, and it is almost impossible to find the location of the malfunction - they usually “sin” for malfunctions of thermostats, pumps and other products with moving parts.
In the light of the foregoing, we recommend that readers pay attention to metal-plastic pipes from VALTEC, which uses an American adhesive from the DSM concern, which ensures the strength of the metal / plastic connection, adhesion and the complete absence of delaminations.
The principle of operation of the heating manifold
The heating manifold works according to the following principle - the liquid, entering the device, is more rationally distributed through the pipeline, but to complete the picture, let's take a closer look at this whole process.
- The heated liquid is directed from the boiler to the collector, entering the hot liquid reservoir.
- By means of a pump, the coolant is evenly distributed to each pipe branch.
Important! The heating manifold will not work without a pump, so installing the first automatically implies installing the second element
- After going through the entire cycle, the liquid returns to the tank, but for cold water and then is discharged back to the boiler.
For two-story private houses, it is recommended to use more than one heating collector, while the use of several installations does not interfere with each other, and does not affect the distribution of the coolant. Thus, if you do not need to use the shower, or you decide not to heat one of the rooms, it is enough to turn the shutter valve and make it impossible for the liquid to circulate through the pipes leading to them.
2 Types of structures for heating a house
Heating with water as a carrier has a very simple principle of operation, and its design consists of three main components: a heating element (boiler), a pipeline through which the liquid passes, and radiators. The latter heat up and give off heat to the environment. The coolant gradually cools down and, having passed a circle through the system, returns back to the boiler, and the cycle repeats again.
There are two ways to regulate the microclimate. The first is to set the boiler to the desired temperature, the second is to change the coolant flow in a particular radiator using a special tap. They are installed at the input of each battery. In addition, there is an automatic adjustment by means of a thermostat. If a two-pipe system is installed in the house, then a bypass must be installed in front of each tap or thermostat.
Bypass for heating system
Still systems are divided into natural and forced. In the first case, the heating functions independently of electricity, and the design itself is extremely simple. The liquid flows through the pipes due to the temperature difference without the help of any pump. Hot water has a lower density and weight, so it tends to rise, and when it cools, it compacts and returns to the heater. Minuses:
- a large number of pipes;
- the diameter of the pipeline must ensure natural circulation;
- it is impossible to use modern radiators with a small cross section.
In forced systems, the circulation of the coolant occurs due to the operation of the pump, and all excess liquid enters the expansion tank. A pressure gauge is provided to control the pressure. The advantages include a small coolant consumption. Also here you can install pipes of any diameter, including small ones. The system is highly efficient. There is only one drawback - the dependence of the pump on electricity.
Advantages and types of heating network at home with two mains
The main distinguishing feature of this system is the presence of two pipes:
- One of them transports the coolant from the heating boiler to heating devices, registers;
- The second line is needed to withdraw the cooled liquid and return it to the boiler.
Schematic diagram of the operation of a two-pipe heating system
The advantage that such a two-pipe system has is the uniform supply of coolant with the same temperature to all heating devices.
If a single-pipe line is used, then the coolant has to pass through all pipelines and heating devices in series - as a result, the batteries and radiators at the end of the circuit do not warm up well.
There is an opinion that a two-pipe system requires shaped costs in double volume (in comparison with a single-pipe system). But this is not entirely true: a single-pipe system requires the installation of pipes of large diameter, while in a two-pipe line, you can get by with products of a smaller diameter, respectively, and they will cost less. The same applies to the size of the fittings - the difference in cost is small.
The small size of the heating elements does not spoil the interior of the room, but if necessary, the pipeline can be mounted (and thus disguised) in building structures. You will get a closed piping system.
The location of pipes combined into a single heating network can be done in one of the following ways:
- Horizontal. Such a heating system is usually installed in low-rise buildings with a large length, for example, it can be a warehouse or a production workshop. The horizontal network is also most often installed in panel-frame buildings, i.e. where there are few or no piers at all and it is possible to install risers on the stairwell or in the corridor. A horizontal network implies a constant circulation of the coolant.
- Vertical. This method involves connecting heating devices to the main riser, installed vertically. The vertical system is used in multi-storey buildings, where each floor is connected separately. The horizontal two-pipe system will cost the homeowner less, but the vertical network almost does not form air jams, which simplifies its operation.