What is important to consider when buying
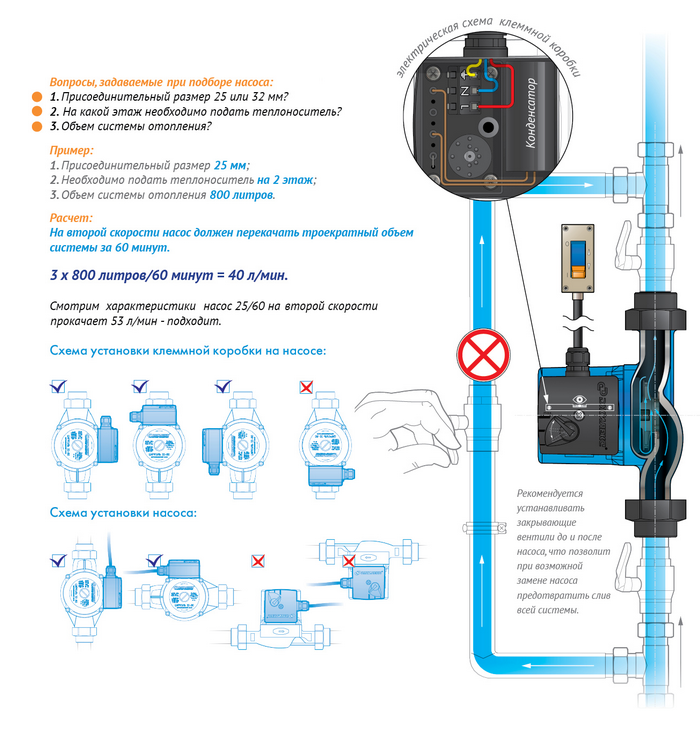
The basis of choice is power and pressure. To determine them, it is necessary to take into account: the hydraulic parameters of the heating system, the climatic conditions of the area and the construction features of the building. The calculation is quite complicated and requires the participation of a specialist. If this is not possible, then it is better to purchase self-regulating models and follow the tips:
- power (Q) can be taken depending on the heated area. For example, if the area does not exceed 350 m2, you should take the unit with Q = 2 m3/h;
- the pressure is determined by the length of the system (for every 10 m of its length, it accounts for 0.6 m).
It is also important to consider the type of coolant, operating temperature and fluid viscosity, energy consumption, its reliability and service life.
Installation
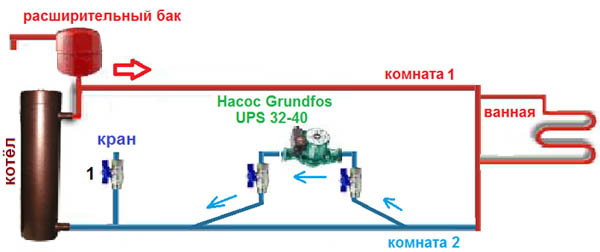
Installation of modern models of circulation pumps is allowed both on the supply and on the return (“return”) pipeline. But many experts argue that in the latter case, the equipment wears out less. Installed in a straight section with laminar flow in front of the boiler
It is very important to choose a place with a free approach to facilitate insertion and further maintenance. There are a number of other rules that should be followed during installation:
- standard models are installed strictly horizontally, otherwise productivity is reduced;
- shaftless pumps are mounted according to the manufacturer's recommendations;
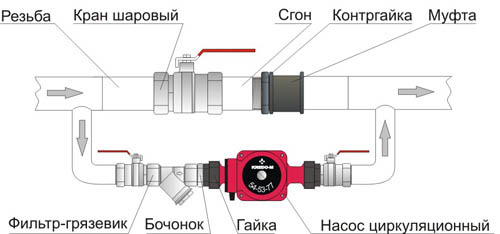
- a coarse filter should be placed in front of the unit to protect the mechanism from solid particles;
- ball valves are located on both sides in order to dismantle it in the event of a breakdown without draining the liquid from the system;
- make a bypass (bypass line) with a shut-off valve. It allows, if necessary, to ensure the movement of fluid bypassing the pump;
- install an automatic or manual gas outlet valve, if it is not provided for in the design.
Numerous reviews of circulation heating pumps indicate that they provide real savings and additional comfort only when installed correctly. Therefore, it is better to entrust the installation to professionals. To avoid unpleasant surprises and ensure stable operation, it is advisable to use an uninterruptible power supply.
Popular manufacturers
High reliability and exceptional quality are distinguished by Halm pumps for heating systems. In addition, thanks to the introduction of innovative developments, they function well at a mains voltage of 160–260 V. If the shaft is suddenly blocked, the engine goes into standby mode. The products of another German manufacturer, Wilo, stand out for their low energy consumption (A-class energy efficiency). There are models with an LCD display, which indicates the current parameters.
The Danish company Grundfos, winner of the Energy + Award 2008 for energy saving technologies, offers a wide range of pumps that are controlled by one button and have an Autodapt function to adjust pressure drops, according to the current needs of the machine. Italian pumps Dab for air conditioning and heating systems are characterized by a significant level of protection against corrosion. They have proven themselves well in private construction and when working in the central heating system. Models are available with a robust aluminum housing and polymer impeller. For most of them, the choice of one of six operating modes is carried out by simply pressing a button.
The Unipump brand offers a wide range of circulation pumps for small autonomous and large heating systems. Models are developed in accordance with the needs of the domestic market. A distinctive feature is high quality at an affordable price.
Main settings
| Manufacturer | A type | Power, W | Max. head, m | Productivity, m3/h | Prices, rubles |
| Halm | HUP 25-4.0 U 130 | 40-70 | 3,9 | 3,4 | 3150 — 3420 |
| HUP 25-6.0 E 180 | 40-95 | 5,7 | 4,3 | 6 630 — 7 000 | |
| HUP 50-11.0 U 280 M | 330-1100 | 12,3 | 31,7 | 27 500 — 36 900 | |
| Wilo | Yonos PICO model 25/1-8 | 4-75 | 4 | 2,5 | 9300 — 9410 |
| Wilo Star-RS type 15/4 | 28 / 38/ 48 | 4 | 4 | 4 830 — 4 930 | |
| TOP-RL model 25/7.5 | 115 / 165 / 205 | 7 | 6 | 9 230 — 9 740 | |
| Grundfos | UPS 32-40 | 45 | 4 | 12 | 4 700 — 7 000 |
| ALPHA2 type L 25-40 | 22 | 4 | 3,1 | 6 390 — 9 270 | |
| Dab | VA 25/130 | 57 | 2,71 | 3 | 3 750 — 5 060 |
| EVOTRON 60/180 | 43 | 6 | 3,5 | 7 740 — 8 420 | |
| Unipump | UPC 25-40 | 62 | 4 | 3,5 | 2 200 — 4 300 |
| UPF 40-120 | 700 | 12 | 12 | 29 360 — 29 770 | |
| UPA 15-90 | 120 | 9 | 1,5 | 7 380 — 7 480 |
The main parameters of pumps for heating
There are not so many parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing a device. In fact, there are only two of them - pressure and performance (flow)
Head is the hydraulic resistance of the system, which the pump is able to overcome. This value is measured in meters of water column. As a rule, the hydraulic resistance of the entire system is set by the highest point of the pipeline through which water circulates.
The performance of the pump, measured in m³ / h, shows how much liquid it can drive through the pipeline per unit of time. Therefore, before choosing the required model, you need to know the exact volume of coolant in the system.
Important! Pressure and productivity are inversely proportional to each other. That is, the maximum pressure is achieved at zero flow
Conversely, the maximum flow rate is possible at zero pipeline height.
It is the pressure-flow characteristic of the device that makes it possible to determine the model with optimal parameters for a particular system. At the same time, the standard formula - the more powerful, the better - is not entirely suitable for this case. Because this means buying a more expensive unit and increasing energy consumption.
Commissioning the pump
Before connection, the device is filled with water and air is pumped out. To release air, the bolt located on the back of the motor is rotated. Air bleeding will start. If water starts to flow out, then the air is deflated. The bolt returns to its original position. The valves on the suction and discharge sides open.
To switch the speed, use the speed switch located on the capacitor box.
Installation rules
- Installation is carried out in a ventilated warm room.
- Installation is carried out after welding and cleaning of the system.
- Shut-off valves are mounted at the inlet and outlet to the pump, this will prevent leaks and draining of water from the system during the repair of the unit.
- To prevent damage, the device is installed above or near pipes.
- The device is connected to the pipeline in such a way that the axis of the incoming and outgoing pipes coincides.
- To ensure quiet operation and lack of vibration, the unit is not installed close to the knee.
- The diameter of the pipe must match the diameter of the unit;
- Installation is carried out so that the direction of the arrow on the device coincides with the direction of the working fluid;
- The unit is mounted taking into account accessibility to it if necessary.
Safety
Before dismantling or installing the unit, it is disconnected from the network. Before dismantling the device, wait for it to cool.
Protect the electrical parts during bleeding. To avoid damage, the pump is installed in a dry place.
Characteristics and installation diagram of the pump Gileks Compasses
The temperature range of the room is from minus ten to plus fifty degrees Celsius.
Gilex problems and how to fix them
Circulators are reliable, but there are minor problems. To eliminate them, you need to know the cause.
List of problems:
- when starting, the unit stops immediately. The reason is plaque between the impeller and the housing. You can fix the problem by removing plaque and unlocking the shaft;
- high noise level. The reason is air in the system or high water pressure. Troubleshoot by bleeding the system and reducing fluid velocity;
- the unit does not start. The reason is that there is no voltage in the network, the capacitor has broken, the plaque on the bearings has blocked the shaft. It is necessary to check the integrity of the cable, unlock the shaft;
Subject to the rules of operation, the Compass serves for many years and does not require repair work.
Gileks Compasses are distinguished by reliability and quality. Positive reviews confirm the quality of the devices.
Tips for choosing a device for a floor heating system in a house
How to choose a pump for underfloor heating? Today, the market is mainly represented by pumps for CO, with a standard flow of about 40 l / min (about 2.5 m3 / h) and a head of up to six meters. The flow rate is directly proportional to the head pressure.
When buying, it should be understood that the flow rate of 40 l / min indicated on the pump will not always correspond to the actual flow rate. Because the latter depends on the throughput of the floor node or the system itself. A large number of long circuits reduces consumption.
It is easy to deal with this using two graphs: theoretical (for all such pumps) - No. 1, and real for the 2.5 cubic meter pump considered in the example. with a pressure of six meters - No. 2.
The higher the throughput of your system, the weaker the pressure on all connected circuits. Those. the more circuits are closed to one mixing unit, the greater the flow.
CENTRIFUGAL MULTISTAGE SECTIONAL PUMPS
TYPES AND MAIN PARAMETERS
GOST 10407-88
Official edition
USSR STATE COMMITTEE ON STANDARDS
Moscow
UDC 621.671:006.354 Group G82
STATE STANDARD OF THE UNION OF THE SSR
CENTRIFUGAL MULTISTAGE SECTIONAL PUMPS Types and main parameters
Centrifugal multistage segmental pumps. Types and basic parameters
OKP 36 3113, 36 3152
GOST
10407—88
Date of introduction 01.01.90
Non-compliance with the standard is punishable by law
This standard applies to centrifugal multistage sectional pumps designed for pumping water, and establishes the types of pumps depending on the properties of the pumped water and their main parameters.
1. Pumps must be manufactured in the following types:
CNS - pumps for pumping water with a pH of 7-8.5, with a mass fraction of mechanical impurities not more than 0.1%, a solid particle size of not more than 0.1 mm, a microhardness of not more than 1.47 GPa, a temperature of not more than 318 K (45 °С);
CNSg - the same, with a temperature not exceeding 378 K (105 ° C);
TsNSs - pumps in a single-casing design for pumping aggressive oilfield waters, including hydrogen sulfide-containing ones with a mass fraction of mechanical impurities not more than 0.1%, a solid particle size of not more than 0.1 mm, a microhardness of not more than 1.47 GPa, a temperature of not more than 333 K (60 ° С;;
CNS - the same, in a two-case version.
2. Pumps must be manufactured in UHL climatic version, placement category during operation 4 according to GOST 15150-69.
3. The main parameters of the pumps for the nominal mode must correspond to those indicated in the table.
4. The designation of pumps must comply with the block diagram given in Appendix I.
5. The working parts of the characteristics of Q-H pumps are given in Appendix 2.
Official Edition ★
No reprint (B) Standards Publishing, 1988
|
Submission, Q |
|||
|
Size |
OKP CODE |
m8/s |
m*/h |
|
CNS J 8 44 (CNSg 38-44) |
3G 3113 0800 (36 3113 2500) |
||
|
CNS 36-66 (CNSg 38-66) |
36 3113 0810 (36 3113 2510) |
||
|
CNS 38 -88 (CNSg 38-88) |
36 3113 0820 (36 3113 2520) |
||
|
DNS 38-110 (TsNSg 38-110) |
36 3113 0830 (36 3113 2530) |
||
|
CNS 38-132 (CNSg 38-132) |
36 3113 0840 (36 3113 2540) |
0,0106 |
38 |
|
CNS 38-154 (CNSg 38-154) |
36 3113 0850 (36 3113- 2550) |
||
|
CNS 38-176 (CNSg 38-176) |
36 3113 0860 (36 3113 2560) |
||
|
CNS 38-198 (CNSg 38-198) |
36 3113 C870 (36 3113 2570) |
||
|
CNS 38-220 (CNSg 38-220) |
36 3113 0880 (36 3113 2580) |
||
|
CNS 6S-66 (TsNSg 60-66) |
36 3113 5610 (36 3113 2590) |
0,0167 |
60 |
Head R, m (limit deviation
44
66
88
110
132
154
176
198
220
66
Speed (sync)
With
rpm
Permissible cavitation
reserve, m, no more
efficiency, x. at least
Weight, kg, no more
178
67
198
50
3000
3,6
219
239
259
280
69
300
321
341
60
3000
4,5
69
209
GOST 10407-88 C.
|
Size |
OKP code |
Shdeta, Q |
|
|
m/s |
M*/H |
||
|
CNS 60-99 (CNSg 60-99) |
36 3113 5620 (36 3113 2600) |
0,0167 |
60 |
|
CNS 60-132 (CNSg 60-132) |
36 3113 5630 (36 3113 2610) |
||
|
CNS 60-165 (CNSg 60-165) |
3 6 3113 5 640 (36 3113 2 620) |
||
|
CNS 60-198 (CNSg 60-198) |
36 3113 5650 (36 3113 2630) |
||
|
CNS 60-231 (CNSg 60-231) |
36 3113 5660 (36 3113 2640) |
||
|
CNS 60-264 (CNSg 60-264) |
36 3113 5 680 (36 3113 2650) |
||
|
CNS 60-297 (CNSg 60-297) |
36 3113 5690 (36 3113 2660) |
||
|
CNS 60-330 (CNSg 60-330) |
36 3113 5700 (36 3113 2670) |
||
|
CNS 63-10000 |
0,0175 |
63 |
|
|
CNS 63-1500 |
0,0175 |
63 |
|
|
CNS 63-2000 |
0,0175 |
63 |
|
|
CNS 63 -zos 0 |
0,0175 |
63 |
Continuation
|
Head R, m (limit deviation |
Frequency rotation (synchronous) |
Permissible cavitation reserve, m, no more |
efficiency, %, at least |
Weight, kg, ns more |
|
—c/o) |
-1 With |
rpm |
99>
233
69
132
165
258
232
O
198
231
264
297
339
1000
1500
2000
3000
50
73