Calculation of the heating manifold and mounting sleeves
The above calculation technology can be applied to all types of heat supply - one-pipe, two-pipe and collector. However, for the latter, it is necessary to make a correct calculation of the diameter of the heating collector.
This heating element is necessary for the distribution of the coolant over several circuits. In this case, the calculation of the correct diameter of the heating manifold is inextricably linked with the calculation of the optimal section of the pipeline. This is the next stage in the design of the heating system.
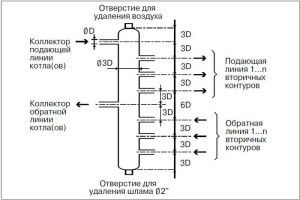
Collector calculation scheme
To calculate the diameter of the heating manifold, you must first calculate the cross section of the pipes according to the above scheme. Then you can use a fairly simple formula:
When determining the height and the optimal distance between the nozzles, the principle of "three diameters" is applied. According to him, the remoteness of the pipes on the structure should be 6 radii each. The total diameter of the heating manifold is also equal to this value.
Sleeve for mounting heating pipes
But in addition to this component of the system, it is often necessary to use additional ones. How to find out the diameter of the sleeve for heating pipes? Only by performing a preliminary calculation of the section of highways. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the thickness of the walls and the material of their manufacture. The design of the sleeve, the degree of its thermal insulation will depend on this.
The diameter of the sleeve for heating pipes is influenced by the material of the wall, as well as pipes
It is important to take into account the possible degree of expansion when the surface is heated. If the diameters of the plastic heat supply pipes are 20 mm, then the same parameter for the sleeve must be at least 24 mm
The sleeve must be mounted on cement mortar or a similar non-combustible material.
How to choose the right pipe diameter
In cases where heating is carried out in a private house or cottage, the pipes must be selected taking into account the fact that the diameter will not change only when there is a direct connection to the central heating system. In the case of an autonomous pipe system, any size (different diameter and length) can be used, depending on the preferences of the owner of the house.
When choosing the necessary blanks, it is necessary to take into account all the features, especially when it comes to a natural heating system, where the ratio of the cross section to the pump power will not be a primary feature. This fact is attributed to the advantages of this heating system.
Pipe installation scheme.
The disadvantage of such a system is the small radius of action and the high cost of the large-sized elements used in this case.
To ensure the efficiency of the system, it is necessary to maintain a certain level of pressure in it, allowing the water moving inside to overcome all obstacles in its path. Resistance (obstacles) can be in the form of friction of water against the walls, a tap or a tap and a heating device. The most interesting thing is that the resistance and speed at which water will flow depends on the length and diameter of the pipeline pipes. With a high water velocity, a small cross section and a long pipeline, the level of resistance in the path of water increases.
Capacity of the water pipe
Water pipes in the house are used most often. And since they are subjected to a large load, the calculation of the throughput of the water main becomes an important condition for reliable operation.
Passability of the pipe depending on the diameter
Diameter is not the most important parameter when calculating pipe patency, but it also affects its value. The larger the inner diameter of the pipe, the higher the permeability, as well as the lower the chance of blockages and plugs. However, in addition to the diameter, it is necessary to take into account the coefficient of friction of water on the pipe walls (table value for each material), the length of the line and the difference in fluid pressure at the inlet and outlet. In addition, the number of bends and fittings in the pipeline will greatly affect the patency.
Table of pipe capacity by coolant temperature
The higher the temperature in the pipe, the lower its capacity, as the water expands and thereby creates additional friction.
For plumbing, this is not important, but in heating systems it is a key parameter
There is a table for calculations of heat and coolant.
| Pipe diameter, mm | Bandwidth | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| By warmth | By coolant | |||
| Water | Steam | Water | Steam | |
| Gcal/h | t/h | |||
| 15 | 0,011 | 0,005 | 0,182 | 0,009 |
| 25 | 0,039 | 0,018 | 0,650 | 0,033 |
| 38 | 0,11 | 0,05 | 1,82 | 0,091 |
| 50 | 0,24 | 0,11 | 4,00 | 0,20 |
| 75 | 0,72 | 0,33 | 12,0 | 0,60 |
| 100 | 1,51 | 0,69 | 25,0 | 1,25 |
| 125 | 2,70 | 1,24 | 45,0 | 2,25 |
| 150 | 4,36 | 2,00 | 72,8 | 3,64 |
| 200 | 9,23 | 4,24 | 154 | 7,70 |
| 250 | 16,6 | 7,60 | 276 | 13,8 |
| 300 | 26,6 | 12,2 | 444 | 22,2 |
| 350 | 40,3 | 18,5 | 672 | 33,6 |
| 400 | 56,5 | 26,0 | 940 | 47,0 |
| 450 | 68,3 | 36,0 | 1310 | 65,5 |
| 500 | 103 | 47,4 | 1730 | 86,5 |
| 600 | 167 | 76,5 | 2780 | 139 |
| 700 | 250 | 115 | 4160 | 208 |
| 800 | 354 | 162 | 5900 | 295 |
| 900 | 633 | 291 | 10500 | 525 |
| 1000 | 1020 | 470 | 17100 | 855 |
Pipe capacity table depending on the coolant pressure
There is a table describing the throughput of pipes depending on the pressure.
| Consumption | Bandwidth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DN pipe | 15 mm | 20 mm | 25 mm | 32 mm | 40 mm | 50 mm | 65 mm | 80 mm | 100 mm |
| Pa/m — mbar/m | less than 0.15 m/s | 0.15 m/s | 0.3 m/s | ||||||
| 90,0 — 0,900 | 173 | 403 | 745 | 1627 | 2488 | 4716 | 9612 | 14940 | 30240 |
| 92,5 — 0,925 | 176 | 407 | 756 | 1652 | 2524 | 4788 | 9756 | 15156 | 30672 |
| 95,0 — 0,950 | 176 | 414 | 767 | 1678 | 2560 | 4860 | 9900 | 15372 | 31104 |
| 97,5 — 0,975 | 180 | 421 | 778 | 1699 | 2596 | 4932 | 10044 | 15552 | 31500 |
| 100,0 — 1,000 | 184 | 425 | 788 | 1724 | 2632 | 5004 | 10152 | 15768 | 31932 |
| 120,0 — 1,200 | 202 | 472 | 871 | 1897 | 2898 | 5508 | 11196 | 17352 | 35100 |
| 140,0 — 1,400 | 220 | 511 | 943 | 2059 | 3143 | 5976 | 12132 | 18792 | 38160 |
| 160,0 — 1,600 | 234 | 547 | 1015 | 2210 | 3373 | 6408 | 12996 | 20160 | 40680 |
| 180,0 — 1,800 | 252 | 583 | 1080 | 2354 | 3589 | 6804 | 13824 | 21420 | 43200 |
| 200,0 — 2,000 | 266 | 619 | 1151 | 2486 | 3780 | 7200 | 14580 | 22644 | 45720 |
| 220,0 — 2,200 | 281 | 652 | 1202 | 2617 | 3996 | 7560 | 15336 | 23760 | 47880 |
| 240,0 — 2,400 | 288 | 680 | 1256 | 2740 | 4176 | 7920 | 16056 | 24876 | 50400 |
| 260,0 — 2,600 | 306 | 713 | 1310 | 2855 | 4356 | 8244 | 16740 | 25920 | 52200 |
| 280,0 — 2,800 | 317 | 742 | 1364 | 2970 | 4356 | 8566 | 17338 | 26928 | 54360 |
| 300,0 — 3,000 | 331 | 767 | 1415 | 3076 | 4680 | 8892 | 18000 | 27900 | 56160 |
Pipe capacity table depending on diameter (according to Shevelev)
The tables of F.A. and A.F. Shevelev are one of the most accurate tabular methods for calculating the throughput of a water supply system. In addition, they contain all the necessary calculation formulas for each specific material. This is a voluminous informative material used by hydraulic engineers most often.
The tables take into account:
- pipe diameters - internal and external;
- wall thickness;
- service life of the pipeline;
- line length;
- pipe assignment.
Diameters of heating pipes and features of their choice
When starting to solve such a problem as calculating the diameter of the pipes of a heating system, it should be taken into account that there are several concepts united by the general term "pipe diameter". Each pipe can be characterized by the following parameters:
The inner diameter is the main characteristic of the pipe, indicating its throughput.
The outer diameter is an equally important characteristic that must be taken into account when designing a heating system.
Nominal diameter (nominal bore) - a certain rounded value, which is indicated when marking.
We should also not forget that pipes made of different materials have a number in their marking corresponding to one or another of its diameters:
- Steel and cast iron pipes are marked by the size of their inner diameter.
- Pipes made of copper or plastic - according to the size of the outer diameter.
That is why, when calculating the cross section of a heating pipe, it is imperative to take into account the material of the pipes. Especially if it is supposed to create a system that is a combination of different pipes.
One of the features that influence the choice of the size of any pipes is the unit of measurement adopted to assess the size of their diameter, and hence their marking. The basic unit for pipe size is an integer or fraction of an inch. To convert inches into the usual measurement system for us, you should remember that 1 inch = 25.4 mm.
Calculation of the diameter of heating pipes
To understand how to work with a table of diameters and how to choose a pipe diameter when laying a heating pipeline, consider a typical calculation for a room of 20 m2:
- First, we find out how much heat power is required to heat a particular room in the house.For every 10 m2 of area (provided that the walls are insulated and the ceiling height is no more than 3 m), 1 kW of thermal power is required.
- In our case, this is 20 m2, therefore, 2 kW.
- We add a 20% margin, we end up with 2.4 kW. This means that in order to create comfortable temperature conditions in such a room, it is necessary to provide heating with a power of 2.4 kW. You can carry out the described calculations using an online calculator.
Table of heating pipe diameters, according to which it is possible to determine the optimal pipe diameter in two-pipe heating
- If there are windows in the room, we purchase heating radiators. The number of radiators should be equal to the number of windows. That is, if there are two windows, we get two batteries of 1.2 kW each. We place them under the window sills or in any other place provided by the design.
You can increase the power value for radiators, but you can’t decrease it
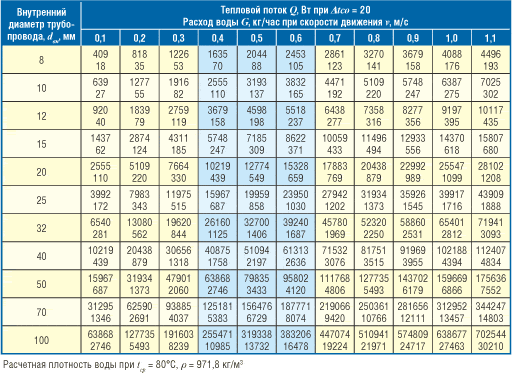
- According to the table of internal pipe diameters, we find the power value of 2.4 kW (2400 W), then we look at the upper value of the heat flux. The zone highlighted in blue represents the optimal fluid flow rate in the heating system, which was mentioned earlier in our article. It should be noted that the presented table shows the values of all parameters for a two-pipe heating system, taking into account the difference in fluid temperatures at the inlet to the pipeline and at the outlet.
So, let's summarize the work with the table. For heating a room of 20 m2, a pipe with a cross section of 8 mm is suitable. In this case, the speed of the coolant will be 0.6 m/s, its flow rate will be 105 kg/h, and the thermal power will be 2453 W. It is allowed to use 10 mm pipes, then the speed of movement will be equal to 0.4 m / s, the flow rate will be 110 kg / h, and the heat flux will be 2555 W.
The procedure for calculating the cross section of heat supply lines
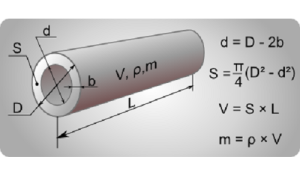
Before calculating the diameter of a heating pipe, it is necessary to determine their basic geometric parameters. To do this, you need to know the main characteristics of highways. These include not only performance, but also dimensions.
Each manufacturer indicates the value of the pipe section - diameter. But in fact, it depends on the wall thickness and the material of manufacture. Before purchasing a specific model of pipelines, you need to know the following features of the designation of geometric dimensions:
- The calculation of the diameter of polypropylene pipes for heating is done taking into account the fact that manufacturers indicate the outer dimensions. To calculate the useful section, it is necessary to subtract two wall thicknesses;
- For steel and copper pipes, internal dimensions are given.
Knowing these features, you can calculate the diameter of the heating manifold, pipes and other components for installation.
When choosing polymer heating pipes, it is necessary to clarify the presence of a reinforcing layer in the design. Without it, when exposed to hot water, the line will not have the proper rigidity.
Determination of the thermal power of the system
How to choose the right pipe diameter for heating and should it be done without calculated data? For a small heating system, complex calculations can be dispensed with
It is only important to know the following rules:
- The optimal diameter of pipes with natural circulation of heating should be from 30 to 40 mm;
- For a closed system with forced movement of the coolant, pipes of a smaller cross section should be used to create optimal pressure and water flow rate.
For an accurate calculation, it is recommended to use a program for calculating the diameter of heating pipes. If they are not, you can use approximate calculations. First you need to find the thermal power of the system. To do this, you need to use the following formula:
Where Q is the calculated heat output of heating, kW / h, V is the volume of the room (house), m³, Δt is the difference between the temperatures in the street and in the room, ° С, K is the calculated heat loss coefficient of the house, 860 is the value for converting the received values into an acceptable kWh format.
The greatest difficulty in the preliminary calculation of the diameter of plastic pipes for heating is caused by the correction factor K. It depends on the thermal insulation of the house. It is best taken from the table data.
The degree of thermal insulation of the building
High-quality insulation of the house, modern windows and doors installed
As an example of calculating the diameters of polypropylene pipes for heating, you can calculate the required heat output of a room with a total volume of 47 m³. In this case, the temperature outside will be -23°С, and indoors - +20°С. Accordingly, the difference Δt will be 43°C. We take the correction factor equal to 1.1. Then the required thermal power will be.
The next step in choosing the diameter of the pipe for heating is to determine the optimal speed of the coolant.
The presented calculations do not take into account the correction for the roughness of the inner surface of the highways.
Water velocity in pipes
Table for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe
The optimal pressure of the coolant in the mains is necessary for the uniform distribution of thermal energy over radiators and batteries. For the correct selection of the diameters of the heating pipes, the optimal values \u200b\u200bof the speed of water advancement in pipelines should be taken.
It is worth remembering that if the intensity of movement of the coolant in the system is exceeded, extraneous noise may occur. Therefore, this value should be between 0.36 and 0.7 m/s. If the parameter is less, additional heat losses will inevitably occur. If it is exceeded, noise will appear in pipelines and radiators.
For the final calculation of the diameter of the heating pipe, use the data from the table below.
Substituting into the formula for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe in the previously obtained values, it can be determined that the optimal pipe diameter for a particular room will be 12 mm. This is just an approximate calculation. In practice, experts recommend adding 10-15% to the obtained values. This is because the formula for calculating the diameter of the heating pipe may change due to the addition of new components to the system. For an accurate calculation, you will need a special program for calculating the diameter of heating pipes. Similar software systems can be downloaded in a demo version with limited calculation capabilities.