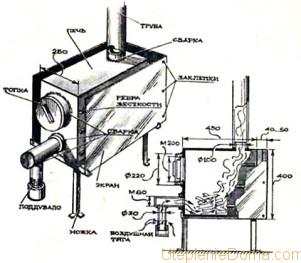
Afterburner for unburned fuel in a heating fireplace.
- Afterburner in a heating fireplace
- Heating fireplace in Suojärvi.
An important advantage of a counterflow heating fireplace is the possibility of afterburning unburned fuel.
Afterburning provides a more complete combustion, which significantly increases the temperature of the gases inside the furnace and saves firewood.
Also, afterburning, reduces the planting of channels inside the furnace.
During combustion, the fuel is split and part of the fuel that has not yet been split flies into the furnace channels and the chimney.
Here, under certain conditions, its secondary ignition, afterburning is possible.
To carry out effective afterburning, it is necessary to create a number of conditions inside the furnace.
- Oxygen is required for the secondary ignition of the fuel (afterburning).
- To ignite unburned fuel, it is necessary to mix it with oxygen.
- A high temperature is required to ignite unburned fuel.
- The temperature in the afterburning area is very high, so here it is necessary to reinforce the furnace with a refractory lining.
1. To start the afterburning process, it is necessary to supply secondary air.
Innings secondary air through door.
In the process of heating the furnace, oxygen, which is supplied to the grate, or under the furnace, is already used for the main combustion of the fuel, and in order for air to reappear inside the furnace, it must be specially organized for its supply.
Read more about this material “Secondary air in the furnace”.
Afterburner in a heating fireplace. View from the furnace.
In a heating fireplace, the mixing of oxygen and unburned fuel is carried out by passing through a slit passage at the top of the furnace tooth.
The stepped tooth of the fireplace is also a good improvement in mixing.
3. High temperature is required for secondary ignition.
Heating fireplace with large glass door.
In fireplaces with large glass doors, secondary ignition is worse than with small doors without glass.
The reason for this is that most of the energy goes through the glass, from the firebox.
And with a large door, you need to make a large firebox.
In a furnace with a lot of emptiness, the temperature is much lower than in a furnace densely filled with fire.
But, attention, if your fireplace has a large firebox, this does not mean that it can be loaded with firewood to the top. If, put, more firewood than required, overheating will occur and possibly the destruction of the furnace
If, put, more firewood than required, overheating will occur and possibly the destruction of the furnace.
4. High temperature in the afterburning area can destroy the furnace lining.
Furnace overheating
To strengthen the furnace, in the afterburning area, in the heating counterflow fireplace, a special afterburner is provided.
The afterburner is made of refractory materials and serves as a continuation of the firebox.
1 GENERAL DATA
|
Ambient conditions |
|||
|
Country / city of installation: |
Russia / Yaroslavl Oil Refinery |
||
|
Location: |
Outside, under a canopy (provided by the customer) |
||
|
Height: |
~100 m above sea level |
||
|
Barometric pressure: |
760 mmHg / 1.013 mbar |
||
|
Relative Humidity: |
min. - % |
nom. 83% |
Max. - % |
|
Ambient temperature: |
min. - 46°C |
nom. — °C |
Max. + 37 °C |
|
Wind load: |
— |
230kgf/m² |
— |
|
Snow load: |
— |
2400kgf/m² |
— |
|
Seismic zone: MSK-64 |
— |
6 |
— |
|
Installation safety |
|
|
Type of protection / for outdoor equipment: |
IP65 |
|
Type of protection / control system: |
IP55 |
|
Protection class: |
Standard protection or SIL 2 |
|
Explosion protection: |
Zone 2, IIC T3 |
|
Ignition burner: |
EEx-d |
|
Flame Scanner: |
EEx-d |
|
Solenoid valve: |
EEx-m |
|
KIP: |
EEx-i |
|
Junction box or local control panel: |
EEx-e |
|
Electrical data |
|
|
Supply voltage: |
230 V AC, 50 Hz |
|
Control voltage: |
24 V DC |
|
Supply voltage (blower): |
3 x 400 V AC, 50 Hz |
|
Limit switches: |
inductive, mechanical |
|
Control valves: |
4-20 mA supply signal, 4-20 mA feedback signal |
|
Mechanical characteristics |
|
|
Area for scope of delivery: |
Subject to verification |
|
Coating / burner: |
CS - standard - corrosion category C4 |
|
Coating / valve stand: |
CS - standard - corrosion category C4 |
|
Coating / piping: |
CS - standard - corrosion category C4 |
|
Coating / valves: |
Supplier standard |
|
Coating / combustion chamber: |
CS - standard |
|
Fitting standard: |
ANSI - flange, welded, screwed, pipeline according to ASME |
|
Instrument air piping: |
Stainless steel |
|
Marking: |
CS standard (TAG no. on SS board) |
|
Insulation, burner: |
not applicable |
|
Insulation, valve trains: |
Customer |
|
Insulation, combustion chamber: |
CS |
|
Accompanying heating: |
Electrical frost protection CS |
|
Process shut-off valves: |
NO |
Modern potbelly stoves with a water circuit
The traditional potbelly stove is designed to heat one room due to the convection of thermal air and, in part, as a result of the generation of infrared radiation. It is also based on the pyrolysis of wood. But, unlike a solid fuel boiler, the firebox of a potbelly stove is not divided into two parts. As a result, if the furnace-chimney system is improperly organized, the pyrolysis gases quickly leave the combustion zone and go outside without giving up their heat.
That is why, doing all the work with your own hands, you need to pay due attention to:
- combustion chamber volume;
- chimney pipe diameter;
- temperature control in the furnace.
So, for example, the volume of the firebox is 40 liters. In this case, the chimney is made with a diameter of up to 106 mm. Such a ratio will allow the pyrolysis gases to be retained in the upper part of the stove and the gas will have time to burn out. On the other hand, a chimney of this diameter will quickly bring out the products of combustion and prevent smoke in the room.
The second nuance in the manufacture of the furnace is the grate. In order for pyrolysis to take place in the heating element, the grate is removed. Thus, artificial inflation of oxygen into the furnace is excluded. The smoldering mass will independently draw in the right amount of air through the blower. It is made in a round shape.
The third nuance: for the hasty operation of the heating equipment, it is necessary to monitor the temperature inside its furnace. The easiest way to do this is by observing the temperature of the flue gases. If it drops to +100°C, this indicates a violation of the pyrolysis process. In this case, condensation will fall in the chimney. It turns into a solid mass, which makes the cleaning process difficult.
How is a long-burning stove with a water circuit like a potbelly stove arranged? It is distinguished from the traditional model by the L-shaped pipe, which is welded to the blower. It performs the function of an air duct. To do this, small (up to 8 mm in diameter) radial holes are made in its lower part. They are covered with a screw cap. By screwing or unscrewing the latter, it is easy to regulate the gas supply to the furnace, therefore, the intensity of combustion is also regulated.
A drawing of a long-burning stove with a water circuit provides for a water jacket for the house heating system. It is mounted instead of a heat shield and is a rectangular container with water.
The water jacket must not be placed close to the body of the stove. This will lead to a rapid cooling of the furnace, which will adversely affect the pyrolysis process inside.
How the long-burning furnace shown in the figure works:
- to begin with, firewood is laid;
- The L-shaped air duct opens completely, the fuel is ignited;
- as soon as the temperature of the potbelly stove body reaches the desired limit, this is judged by its red color, the duct openings are closed.
Thus, the air supply is limited. The pyrolysis process begins in the furnace. Heat from the walls of the potbelly stove is transferred to the water jacket and then to the heating system of the house.Good to know: "The heating system of a one-story private house".
Experts point out the disadvantages of long-burning furnaces of this type - this is low power. Here it is impractical to increase the volume of the combustion chamber, since the square-cube law will be violated. The device in the above diagram is suitable for heating a room up to 25 sq.m. It is also forbidden to take water from the circuit for household needs.