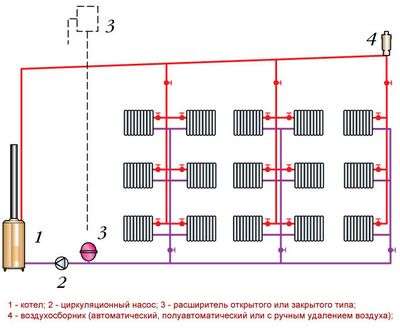
Heating systems for two wings
And yet, a system with a dead-end scheme is more often used. And all because the return line is longer and it is more difficult to assemble it. If your heating circuit is not very large, it is quite possible to adjust the heat transfer on each radiator and with a dead-end connection. If the circuit turns out to be large, but you don’t want to make a Tichelman loop, you can divide one large heating circuit into two smaller wings. There is a condition - for this there must be a technical possibility of such a network construction. In this case, after separation, valves must be installed in each circuit, which will regulate the intensity of the coolant flow in each of the circuits. Without such valves, it is either very difficult or impossible to balance the system.
Different types of coolant circulation are demonstrated in the video, it also provides useful tips on installation and selection of equipment for heating systems.
Self-installation of two-pipe heating of a private house
To successfully implement it, it is better to follow the order:
- Decide on a wiring diagram.
- Make a careful distribution of elements: valves, radiators, as well as pipe connections.
- Collect the network start with the boiler. If we are talking about solid or liquid fuel, then it is necessary to provide a separate room for it and without fail to build a concrete platform as a base. Electric and gas units can be equipped in a residential area, but you need to take care of a separate hood by installing a coaxial pipe, not forgetting about the expander.
- The pump for the operation of forced circulation is mounted in a line that is responsible for supplying water to the boiler. This action is necessary to protect against hot liquid.
Radiators are installed according to the standards:
- placement should be planned under the windows, this will help protect against the cold air flow that is directed through the window opening. The upper part should be at a distance of about 5 cm from the edge of the window sill and at least 6 cm from the bottom to the floor;
- the ribs must be placed in a horizontal plane at the same level.
For two-pipe heating of a two-story private house, the scheme is selected according to the individual structure and characteristics of the building, as well as the personal advantages of the owners. It can be with hidden installation of pipes and with wiring along the walls.
The arrangement of a two-pipe system should be carried out in compliance with certain principles:
- The presence of two pipelines: the upper one with the heat carrier and the lower one with the cold one.
- Pipes are installed at an angle.
- Highways are laid symmetrically and maintaining parallelism;
- For ease of maintenance and repair, technological units, radiators, as well as a bypass with a pump are equipped with taps.
- The distribution tank in a system with top wiring is located in an insulated attic.
- The pipeline is mounted without right angles where air pockets can form.
You should get a two-pipe closed network that maintains the temperature in the house. To be able to control the consumption of thermal energy, thermostats should be installed. Their new generation is able to control the operation of the boiler at an automatic level, turning on or off the additional heater if necessary, thereby saving fuel and energy.
Advantages and disadvantages
Despite the cheapness and simplicity, the single-pipe design is increasingly losing popularity over time due to the advantages of the two-pipe circuit:
- uniform temperature distribution around the perimeter;
- when carrying out repairs, the desired area is easily blocked;
- the ability to use in large areas and in multi-storey buildings;
The disadvantage of a two-pipe system is a large number of pipes and connections.
The nuances of installing heating systems
By choosing the right number of radiators, the boiler and the connection option, you can directly assemble all the elements into a single coherent system. First of all, you need to choose the right place for the boiler
For efficient operation, it is important to place the unit as low as possible.
Installation of radiators
At the next stage of the implementation of the heating scheme, radiators are installed with their own hands. As you can see in the photo above, it is more convenient to use batteries with valves at the inlet and return. First of all, they are installed under the windows. This is done for a reason, but because the warm air, blowing through the window, allows you to move the dew point.
The instructions for attaching the batteries are very simple:
- the installation site is determined based on the following dimensions - at least 5 cm from the wall, at least 5-10 cm from the floor and at least 5-10 cm to the edge of the window sill;
- brackets are selected and installed based on the weight and size of the radiator, brackets for cast-iron options are especially securely and deeply installed;
- the wall behind the radiator, if possible, gets off, since after installing the system, there will be no possibility to remove the batteries;
- air bleed valves are installed, if they are not included in the kit.
If you doubt your abilities, do not do the installation at random. There are tutorials and video tips. In extreme cases, you can always turn to professionals in their field.
After choosing a place for the boiler and installing it, marking and installing radiators, we install a circulation pump, if it is available in the scheme
Before the pump, it is important to put a coarse filter to prevent mechanical particles from entering the system. On both sides, you need to install two valves or taps, to be able to remove the pump without draining the water from the system
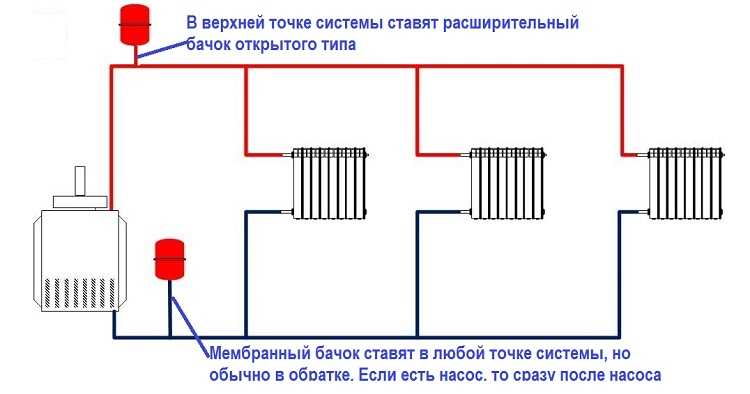
Expansion tank and its replacement
In the case of installing a heating system with natural circulation, an expansion tank is installed at the highest point. Most often it is placed in the attic and insulated in the winter season.
There are also schemes for installing heating without an expansion tank. Instead, a safety block and a hydroaccumulating tank are used. The tank is installed on the return heating main near the boiler. The safety block is placed where the expansion tank should be. Through the air valve of the block, air is bled at the right time.
Pipe installation
After installing all the elements of the system, they are connected into a common structure using pipes.
The tool used for installation will depend on the selected pipe material, and there are three main ones:
- metal;
- metal-plastic;
- PVC, polypropylene or XLPE.
Each material has its pros and cons, and, of course, the price-quality ratio.
Features of the scheme of primary-secondary rings
Such a scheme provides for the organization of the primary ring, through which the coolant must constantly circulate. Heating boilers and heating circuits are connected to this ring. Each circuit and each boiler is a secondary ring.
Another feature of this scheme is the presence of a circulation pump in each ring. The operation of a separate pump creates a certain pressure in the ring in which it is installed. The assembly also has a certain effect on the pressure in the primary ring. So, when it is turned on, water leaves the water supply pipe, entering the primary circle and changing the hydraulic resistance in it. As a result, a kind of barrier appears on the way of the coolant movement.
Since the return pipe is first connected to the circle, and after it the supply pipe, the coolant, having received considerable resistance from the supply pipe, begins to flow into the return pipe.If the pump is turned off, the hydraulic resistance in the primary ring becomes very small and the coolant cannot swim into the boiler heat exchanger. The binding continues to work as if the unit was not turned off at all.
For this reason, it is not necessary to use one complex automation to turn off the boiler. The only thing you need is to install a check valve between the pump and the water return pipe. The situation is similar with heating circuits. Only the supply and return lines are connected to the primary circuit in the opposite order: first the first, then the second.
Universal combined scheme
This system has the following binding:
- Two common collectors or hydrocollectors. The supply lines of the boilers are connected to the first one. To the second - the return line. All lines have shut-off valves. Circulation pumps are located on the coolant return pipes.
- The diaphragm tank is connected to a large return manifold.
- The indirect heating boiler is the link between the two collectors. On the pipe that connects the boiler to the supply manifold, there are a circulation pump and a shut-off valve. The pipe connecting the boiler to the return manifold also has a valve.
- The safety group is installed on the coolant supply manifold.
- The make-up pipe is connected to a collector, which is located on the hot water supply line. To prevent leakage of hot coolant through this pipe, a check valve is placed on it.
- A certain number of small hydrocollectors (there may be two, three or more). Each of them is connected to the aforementioned common collectors. These hydrocollectors and large reservoirs form primary rings. The number of such rings is equal to the number of small hydrocollectors.
- Heating circuits depart from small hydrocollectors. Each circuit has a miniature mixer and a circulation pump.
Dead-end and associated two-pipe systems
A dead-end system is such a system in which the movement of the coolant supply and return flow is multidirectional. There is a system with passing traffic. It is also called the Tichelman loop / scheme. The latter option is easier to balance and configure, especially with long networks. If radiators with the same number of sections are installed in a system with a passing movement of the coolant, it is automatically balanced, while with a dead-end circuit, a thermostatic valve or a needle valve will be required on each radiator.

Two schemes for the movement of the coolant in two-pipe systems: associated and dead-end
Even if radiators of different numbers of sections and valves / valves are installed with the Tichelman scheme, it is still necessary to install, then the chance to balance such a scheme is much higher than a dead-end one, especially if it is quite long.
To balance a two-pipe system with multidirectional movement of the coolant, the valve on the first radiator must be screwed very tightly. And a situation may arise in which it will need to be closed so much that the coolant will not flow there. It turns out that then you need to choose: the first battery in the network will not heat, or the last one, because in this case it will not be possible to equalize the heat transfer.
Two-pipe system for a two-story house
Two-pipe heating of a two-story house is perfect for a country house in which it is necessary to heat not one, but several floors. It is enough to supplement the system with several devices (circulation pump, expansion tank, heating control valves), so that it helps to create the most cozy, comfortable atmosphere in the house. In addition, the creation of this system is a fairly easy process that does not require the involvement of outside specialists. A do-it-yourself two-pipe heating system is a great way to save a fairly large amount.
The two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building has an important advantage - a large number of auxiliary elements can be connected to it. Most often, the "warm floor" system and heated towel rails are connected to it.
It is important that these elements can be connected both directly during the installation of the entire system, and later - after it has been functioning for a certain time.
Most often, the "warm floor" system and heated towel rails are connected to it.
It is important that these elements can be connected both directly during the installation of the entire system, and later - after it has been functioning for a certain time.
It should be understood that the most appropriate moment for the installation of the heating system is the period of construction of the house. That is, in the process of building a building, it is necessary to create a plan for the most efficient heating system and immediately implement the double-circuit heating of a private house.
A two-pipe heating system is a proven and effective way to heat a private house. Such a system allows you to regulate the heating of any room without changing the temperature in the rest of the house. A two-pipe heating system can be used in houses of any number of storeys. The main feature of a two-pipe system is the separation of the direct and return coolant circuits. Through the supply, the so-called pipe, heated water from the boiler enters the system, from which the coolant is disassembled into radiators, coils, and a floor heating system. After passing through them, the cooled liquid is discharged using another pipe - the return one.
Two-pipe heating system of a private house
The two-pipe system has several advantages:
- Ease of regulating the flow of coolant to any of the radiators;
- Possibility of application in the house of any number of storeys;
- Possibility of installation of systems of considerable extent.
Among the shortcomings, it is worth noting the doubled number of pipes compared to a single-pipe system. which increases the cost of installing the system and reduces its aesthetics - direct water pipes should be located above the level of radiators, they are usually laid under the ceiling or at the level of the window sill.
Two main schemes of the heating system
Heating schemes for buildings can be divided into:
In addition, each system is subdivided into components according to the physical layout. So, for example, a single-pipe heating system is star-shaped, radial and collector.
A single-pipe heating system (radiator connections) is a classic. Almost all multi-storey buildings, except those built in recent years, have just such a scheme. It can be found both in Khrushchev and in a new building.
The main advantages of this construction:
- easier installation than in other heating options;
- natural circulation of the coolant;
- saving material and pipes.
To increase the efficiency of such a system, a circulation pump is often installed. Due to the increase in the flow rate of the coolant, smaller pipes can be used.
Unfortunately, the previously popular single-pipe system has several disadvantages:
- use of large diameter pipes;
- the cost of a large amount of fuel;
- there is no possibility of adjusting the radiators;
- electricity costs, in the case of using forced circulation of the coolant.
A more efficient option can be implemented using a two-pipe scheme. In this case, the coolant passes in parallel through each battery and along a straight heating main. This increases the number of pipes used, but greatly increases the overall efficiency of the system.
Consider the main advantages of two-pipe schemes:
- versatility of application, both in single-storey and multi-storey buildings;
- uniform heating of all radiators in the system;
- small diameter pipes for heating lines;
- fine adjustment of the heat output of each radiator.
Connecting heating radiators with a two-pipe system
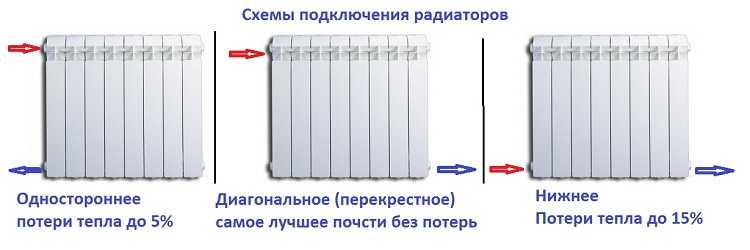
In a two-pipe system, any of the ways to connect radiators is implemented: diagonal (cross), one-sided and bottom. The best option is a diagonal connection. In this case, the heat transfer from the heater can be in the region of 95-98% of the rated heat output of the device.
Schemes for connecting radiators to a two-pipe system
Despite the different values of heat loss for each type of connection, they are all used, just in different situations. The bottom connection, although the most unproductive, is more common if the pipes are laid under the floor. In this case, it is the easiest to implement. It is possible to connect radiators with hidden laying according to other schemes, but then either large sections of pipes remain in sight, or they will need to be hidden in the wall.
Lateral connection is practiced, if necessary, with the number of sections not exceeding 15. In this case, there is almost no heat loss, but if the number of radiator sections is more than 15, a diagonal connection is already required, otherwise circulation and heat transfer will be insufficient.
Although more materials are used to organize two-pipe circuits, they are becoming more popular due to the more reliable circuit. In addition, such a system is easier to compensate.
Vertical and horizontal system diagrams
Two-pipe heat supply structures are of two types:
-
vertical
. It is usually used in multi-storey buildings. A two-pipe vertical heating system needs to use a large number of pipe products, but connecting radiators on each of the floors can be easily done. Its main advantage lies in the automatic removal of air - it rushes to the top and there it comes out through the drain valve or expansion tank. -
Horizontal
. Such a system has found application in one-story, maximum two-story buildings. To bleed air from it, so-called Mayevsky cranes are mounted on batteries.
A variety of residential heating schemes
All typical heating schemes imply time-tested options. These include familiar to us single-pipe and two-pipe structures, collector or beam, as well as the well-known "Leningrad".
The beam system is characterized by the installation of a pair of pipes for each radiator. Very easy to install and maintain. For efficient heat dissipation, it needs to be pre-balanced.
"Leningradka" is known for its solution for independent adjustment of each radiator in a single-pipe scheme. This is achieved by shunting each battery with a bypass pipe, as well as using valves on radiators.
An interesting heating scheme for two wings. It is convenient for use in a multi-storey building. Can be used with one or two circulation pumps. As in the case of the beam scheme, it requires adjustment and balancing of the “wings”.
Symbols in heating schemes are not particularly difficult. Most often, these are rectangles - a boiler and radiators connected by straight lines - heating pipes. Gates are designated in the form of an hourglass. Modern schemes are more like pictures, where each element is represented by its own pattern. Therefore, the designations on the heating diagrams are drawn in simple language.
Classification of 2 pipe systems
Heating systems of any type are divided into open and closed. In the closed ones, a membrane-type expansion tank is installed, which makes it possible for the system to function at elevated pressure. Such a system makes it possible to use not only water as a coolant, but also ethylene glycol-based compounds, which have a lower freezing point (up to -40 ° C) and are also called antifreezes.For the normal operation of equipment in heating systems, special compositions designed for these purposes should be used, and not for general purposes, and even more so, not for automobiles. The same applies to the additives and additives used: only specialized ones. It is especially tough to adhere to this rule when using expensive modern boilers with automatic control - repairs in case of malfunctions will not be guaranteed, even if the breakdown is not directly related to the coolant.
The installation location of the expansion tank depends on its type.
In an open system, an open-type expansion tank is built in at the top point. A pipe is usually connected to it to remove air from the system, and a pipeline is also organized to drain excess water in the system. Sometimes warm water can be taken from the expansion tank for household needs, but in this case it is necessary to make the system recharge automatically, and also not to use additives and additives.
From a safety point of view, closed systems are more promising and most modern boilers are designed for them. Read more about closed heating systems here.
One highway pros and cons
The single-pipe heating system of a two-story house - the Leningradka scheme - consists of one line laid horizontally along the perimeter of the building, above the floor of each floor. Heating devices are connected to the line with 2 ends, alternately. This type of heating network is well suited for houses where two floors occupy a small area (up to 80 m² each). There are reasons for this:
- The coolant entering each subsequent radiator has an increasingly lower temperature due to the admixture of chilled water from previous batteries. Therefore, the length of the ring is limited to 4-5 heaters.
- In order to heat the second floor and the rooms where the last batteries stand, their heat transfer should be increased by adding sections.
- The horizontal network of a two-story house with natural circulation should be carried out with a large slope (up to 1 cm per 1 m running pipe). The boiler is placed in a recess, and in the attic there is an expansion tank that communicates with the atmosphere.
The Leningrad heating distribution of a two-story house with a forced supply of a coolant works much more stable and more efficiently than by gravity. For natural circulation in a private house, it is better to make vertical risers that penetrate the floors and distribute heat to radiators near the windows. The water supply to the risers is carried out from a horizontal collector laid in the attic, the return to the boiler is via the same line running above the floor of the 1st floor.

As in the first case, an open expansion tank is placed in the attic of a 2-storey cottage, and the lines are laid with a slope. If the heating system is closed, then the minimum slopes are required (3 mm per linear meter of pipe), and the membrane tank is placed in the boiler room.
Single-pipe wiring for heating a two-story house, although inexpensive to install, is difficult to calculate and execute.
And not every owner will like it when large-diameter pipelines pass through part of the premises, they have to be hidden under the boxes.
The main elements of the heating system
Having determined the heat loss of the dwelling, we select the indicators of the main element of the heating system - the boiler. To understand the power of this device, you should consider:
- maximum heating of the boiler in winter frosts;
- the material of the walls of the building in which the heating system is being designed;
- the number of heating batteries;
- heating structure.
The next step is the choice of fuel, and hence the boiler itself. Not many options:
- firewood;
- peat, briquettes, sawdust or coal;
- gas.
Very rare, but there are options for liquid fuel.
The second important element or elements of the thermal structure of the house are radiators.The market for modern radiators is quite full.
According to the type of material, there are:
You can also conditionally subdivide water radiators by price range. These are budget cast-iron heating batteries, and individual devices, up to batteries with artistic casting. The average price range is represented by aluminum and bimetallic options.
Cast iron batteries are the cheapest, but also the most inert in terms of heat transfer. They take a long time to warm up, but then they cool down slowly. They have a relatively short service life. In general, heating radiators are selected based on heat transfer, service life, price and appearance.
Which fuel is more convenient
If gas is used as fuel, then natural circulation heating is based on the principle of taking air from the room into an open burner and removing the combustion product into the ventilation ducts. In this case, the boiler will need a room of 4m2 with good ventilation (windows and a door).
Therefore, such a scheme is not very convenient. Much more often, a closed or open water heating system with natural circulation is used, which can be done by hand.
In multi-storey buildings, a single-pipe system is often used. Basically, a circuit with closing sections is used, when part of the water goes up from the riser, and some goes down, thanks to the closing section, which ensures a balance of temperatures between the lower and upper floors. The system works thanks to the difference in the diameter of the connection pipes and the pipe of the closing section (one size smaller). A two-pipe system, in comparison with a single-pipe system, is less compact and easy to install.
Distinctive features of the heating system
The biggest plus is electrical independence, and the minus is the pipes, which have a large diameter and the wiring is sloped.
Compared to the two-pipe option, there are quite a few advantages:
- pipes can be diverted to the “warm floor” system or heating radiators can be connected;
- it can be carried out regardless of the layout of the room;
- it covers the entire perimeter with a closed ring;
- it is less material-intensive and has a lower cost.
In use, it may sometimes be difficult to circulate through the pipes, but this is easily solved by installing pump equipment. It produces competent circulation of the coolant through the pipes.
The vertical single pipe scheme is a popular example of wiring in apartment buildings.
Single pipe heating system with pump.
And the horizontal one is used mainly for heating huge rooms and is very rarely used in private buildings (mainly in small one-story houses). Here the supply pipe bypasses the heaters, which are on the same level. The water in each radiator cools down and, approaching the last heating devices, it becomes already significantly cooled. This scheme will help reduce installation and piping costs, but has two drawbacks.
Firstly, this is a problem with heat regulation in any heating device. You can not increase heat transfer, reduce it, turn off the radiator. In installation practice, there is a jumper - a bypass, which allows you to turn off the radiator without shutting down the system. Heating of the room is carried out indirectly by means of a riser or supply pipes. Another drawback is that you need to use radiators of various sizes. In order for the heat transfer to be the same, the first heater must be very small, and the last one must be large. A horizontal single-pipe heating scheme is also used.
Conclusion
We examined the main elements and components, analyzed the heating circuit of a typical variant, found out the differences in connecting boilers and radiators. We determined that there is nothing complicated in building a heating system with your own hands. Having the time, money and desire, you can perform the most difficult work at first glance.
Heating, water supply and sewerage are three pillars on which the comfort of a home stands. The right choice of wiring the heating system in the house will create a cost-effective and efficient heat supply. The design of the heat supply scheme and the construction of the building are carried out simultaneously, since in this case possible nuances are taken into account.