Rules for setting tariffs for maintaining a house
The tariff for the maintenance of the house is understood as the cost of a unit of a utility service or resource spent on the maintenance of common house property. Such resources include thermal energy spent on heating entrances, electricity for lighting landings, etc. A resource unit can be kWh of electricity, the volume of one cubic meter of water, or one Gcal of heat.
This article talks about typical ways to resolve the issue, but each case is unique. If you want to know how to solve your particular problem, please call:
- Moscow: +7 (499) 350-8059 .
- St. Petersburg: +7 (812) 309-9401 .
Or ask a lawyer on the site. It's fast and free!
The service consumption standard is a standard for the volume of its costs, determined depending on the number of residents of the house, the number of square meters of common premises and the features of architecture and engineering communications.
The list of utilities and resources aimed at maintaining and repairing the house includes the following items:
- repair of elevators and garbage chutes;
- maintenance of the local area and buildings;
- heating of common premises (entrances, basements, etc.);
- power supply of common premises (including lighting of entrances);
- water supply;
- services of repair organizations;
- services of janitors and cleaners.
The tariff for the services of workers is determined depending on the volume of work performed, time standards for each type of work and the amount of hourly wages of workers.
Legislative regulation of determining the cost of maintaining a house is carried out:
According to paragraph 31 of Sec. 3 of Resolution No. 491, the determination of tariffs for paying for the maintenance of an apartment building takes place in the following order:
- The managing organization forms a proposal for the tariff scale.
- The General Meeting of Owners considers and approves the proposal of the Criminal Code by a majority vote.
- The management of the Criminal Code sends an application for the approval of tariffs to the municipal housing committee.
- The application is considered within 30 days and a decision is made.
The proposal of the management company for tariffs is formed based on the actual costs of maintaining the house in the past period, as well as the climate and the state of engineering communications.
In the application, the employees of the Criminal Code substantiate the necessity and legality of the established tariffs, citing preliminary calculations of the consumption of services and resources. Attached to the application:
- copies of constituent documents of the Criminal Code;
- draft tariff scale;
- income and expenditure estimate, justifying the tariffs;
- a copy of the minutes of the tenants' meeting at which the proposed tariffs were approved.
If the house is managed with the help of an HOA, then the proposal for tariffs is prepared by members of the board, and approval takes place at a meeting of members of the partnership.
Ways to calculate the cost of maintaining a house
The calculation of the amount of the cost of maintaining a house for each of the responsible payers can be carried out in the following ways:
- through an online calculator;
- by sending a request to the Criminal Code;
- by formula calculation.
Submitting a request to the CC
A request to the Criminal Code for the provision of a detailed calculation is submitted in the following order:
- The payer collects documents and sends an application to the Criminal Code.
- Employees of the Criminal Code make an extract from accounting documents.
- The extract is sent to the applicant in a completed form within 5 working days from the date of application.
- If the amount on the statement does not match the amount on the receipt, the applicant is recalculated for the maintenance of the house.
The following documents are attached to the application:
- copy of the passport;
- extract from the USRN confirming the right to housing;
- home maintenance bill.
If at the time of filing the application the composition of the applicant living in the apartment has changed, he must also provide a certificate of registered persons from the Federal Migration Service.
Calculation by formulas
The total amount of payment for the repair and maintenance of the house is determined by the formula:
P = T*S(kv) + N*S(o)*S(kv)/S(d), where T is the tariff approved by the general meeting of tenants and the city housing committee, S(kv) is the area of the payer's apartment, N is the rate of payment for the service, S(o) is the area of common premises, and S(d) is the total area of all premises of the apartment building.
The standard is calculated depending on the type of service provided. In particular, the standard for heat consumption for heating entrances and adjoining buildings is calculated as follows:
N \u003d Q / (S * n), where Q is the norm of the amount of heat determined by the decree of the subject of the federation, S is the area of \u200b\u200bheated common premises, and n is the number of months of the heating period. The calculated value of N is substituted into the formula for calculating the total payment amount P.
Data for self-calculation of standards can be viewed in the receipt, on the website of the Criminal Code and the local department of housing supervision. If the calculated amounts do not correspond to those indicated in the receipt, a request for recalculation should be sent to the Criminal Code.
The amount of payment for the maintenance of an apartment building depends on the tariff approved by the meeting of owners, the resource consumption standard, as well as the ratio of the size of the owner's living space and the area of all rooms in the house. To avoid overpayments for services, you need to check the amounts in the receipt in several ways and, if necessary, require recalculation.
Dear readers, each case is individual. If you want to know how to solve your particular problem, call:
- Moscow: +7 (499) 110-49-03 .
- St. Petersburg: +7 (812) 425-34-28 .
Or ask a lawyer on the site. It's fast and free!
Approval of the tariff for the maintenance and repair of housing ZhK rf
E.V. Nabatova, I.K. Shevtsova The collection was prepared by specialists from SRO NP "Association of Management Companies" with the assistance of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation. The publication is aimed at specialists from management companies and homeowners associations, authorized representatives of owners, initiative groups, representatives of territorial public self-government bodies 3 Regulatory framework for tariff calculation 4 Stages of tariff adoption 5 Chapter 2 Tariff calculation 7 Stages and procedure for forming a tariff for MKD 7 Form for calculating the tariff for economic cost items 9 Form for calculating the tariff for functional cost items 10 Chapter 3 How to calculate the tariff for maintenance and current repair? (based on the Guidelines for the financial justification of tariffs for the maintenance and repair of the housing stock of the Gosstroy of the Russian Federation of December 28, 2000) 14 APPENDICES 29 Chapter 1.
What is included in the maintenance of housing in an apartment building and what is it
What seasonal work included in the payment for maintenance of housing in an apartment building should be carried out by management organizations? It is simply impossible to ignore the issue of seasonal work. Let's look at the entire list so that every citizen can know what he pays taxes for.
- Roof repair.
- Repair of gutters, ventilation and the like.
This can also include repair of the garbage chute.
Repair, installation, strengthening of railings. This includes the repair of steps, as well as visors at the exit from the entrance.
Repair of doors and windows.
Replacement of glass, doors, as well as the replacement of components.
Care of the territory adjacent to the house. Painting fences, gates, removal of branches, leaves, snow removal and the like.
Landscaping.
Maintenance of playgrounds.
How will the payment for the maintenance and repair of housing be calculated in 2018
Due to contributions under the line "maintenance and repair":
- salaries are paid to employees involved in the management of apartment buildings
- maintenance and current repairs of common property, in particular, in-house engineering systems, are carried out
- expenses for the maintenance and operation of administrative premises used to manage an apartment building are paid
- collection, processing and storage of data on payments for residential premises and utilities is provided, payment documents for payment of residential premises and utilities are issued
- financing activities to collect debts for payment of utility bills
The procedure for calculating payment for heat according to the rules of 2006
According to the rules, every year a recalculation must be carried out.
If payment for heat is charged according to the old rules, and a common house meter is installed in the house, then the final figures in consumer receipts will depend on how much heat the apartment building consumed during the past year.
This value is divided by the total area of the building, taking into account both residential apartments and non-residential premises such as offices and shops. The result is the amount of heat per 1 sq. square meter, it is divided into 12 months.
After that, the resulting average monthly energy consumption is multiplied by the tariff approved by the local government. The resulting value must be multiplied by the area of \u200b\u200bthe apartment. Calculation example based on 2011 tariffs for Izhevsk. According to the general house meter, the total amount of thermal energy consumed in one year amounted to 990 gigacalories.
The total area of all apartments in the house and common areas is 5500 meters. After the calculation, it turns out that during the year per 1 sq. meter spent 0.015 gigacalories per month. The resulting average monthly volume is multiplied by the cost of 1 gigacalorie of heat at the established rate. 943.60 (tariff) * 0.015 * 1.18 (VAT) = 16.70 rubles per 1 sq. meter of heated area.
The resulting value must be multiplied by the area of \u200b\u200beach particular apartment. If, for example, it is 45 sq. meters, then the total monthly cost of heating will be 751.5 rubles per month. It is this figure that residents will see in their bills throughout the year, since it is not the amount of heat spent per month that is taken into account, but the average monthly consumption received at the end of the last year.
How is the payment for heating calculated according to these rules if a common house meter is not installed in the house? In this case, the standard is used - the amount of thermal energy required for heating. For each house it is determined separately, this information should be in the public domain for consumers. When contacting the management company, a tenant of an apartment building must receive all the information on how the payment for heat is calculated.
According to the rules of Decree No. 307, a recalculation must be carried out in the house every year. It takes into account the amount of heat consumed in the past year, and a new payment is calculated based on it.
If the numbers in the payment cause the owner to doubt and seem overpriced, he has the right to demand a recalculation. To do this, an application is written and sent to the management company, it must indicate the time for which it is necessary to recalculate. Public utilities do not have the right to refuse to apply, the answer is provided within 4 days. If, after re-calculation, an overpayment is detected, it must be deducted from the amount of the debt for the next month.
Knowing the laws allows you to fight for your rights and seek justice. Regular tariff increases create a serious burden on the family budget. therefore, it is necessary to achieve a fair calculation of heat losses.
You can find out how the payment for heating is calculated from the video:
Noticed an error? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter. to let us know.
How to calculate heating in an apartment
Sometimes a bill with figures for paying for heating causes amazement among the owners of houses or apartments with its amounts.In order to figure out where which figure “grows from”, you need to know how the heating in the apartment is calculated.
Moreover, the norms for the consumption and payment of various energy resources are constantly growing in price, and we must have time to navigate this flow. it is also worth noting that an additional column called ODN heating has recently grown in bills (stands for general house needs).
This material will help you understand how the heating in the apartment is calculated. According to the latest rules introduced not so long ago, now each service will be divided into two parts and also calculated separately. These are fees for the maintenance of residential premises (that is, corny speaking, for warming the apartment) and monetary compensation for services provided to the entire house. That is why one more "extra" column materialized in the bills.
Calculation formula
According to the rules, if heat is metered using a common house appliance, it will be possible to calculate the fee based on the established parameters. The standard for the consumption of thermal energy for heating can vary in each specific region of the country. It determines the number of gigacalories that are needed to heat the area within 30 calendar days.

The heating tariff is approved individually for each region by local authorities. We are talking about the cost of 1 Gcal for heating. An important parameter is the area of \u200b\u200bliving premises
Please note that the heated area of the room does not include a balcony or loggia.
The formula with which you can calculate the fee in the absence of an individual or common house meter involves multiplying the following values:
- heating standard.
- The total area of a residential or non-residential type of premises.
- A certain cost of consumed energy (thermal).
If you understand the calculation formula in more detail, then you need to multiply the number of gigacalories for heating a room by the price of 1 hl, and then multiply by the area of \u200b\u200bthe apartment.
How to calculate the payment for water on the meter
Paying for water by the meter and electricity by the meter is convenient because you can calculate in advance how much you will need to pay this month. This is easy to do with the formula:
X=N×Y,
where N is the number of consumed resources, and Y is the tariff.
The amount of consumed resources must be calculated independently. To do this, take a receipt for payment for the last month and take readings in the current one. Then subtract today's numbers from last month's. The resulting figure is the number of consumed resources. For example, if last month there were 26 kilowatts on the receipt, and this time there are already 31 on the meter, you used 5 kilowatts in a month.
The resulting number must be multiplied by the tariff. Tariffs change every year, and sometimes several times a year. Current rates can be viewed on the website of the local administration or on the website of the management company. If you take into account the rates indicated on the receipt for the previous month, the calculations may not be correct if the rates have changed.
For example, in Moscow, the tariff for houses and apartments with gas stoves is 5.38 ₽. This means that for a month for 5 kilowatts you will need to pay 26.9 ₽. And in Stavropol, the tariff is 4.48 ₽. For the same 5 kilowatts, Stavropol residents will have to pay less - 22.4 ₽.
Amounts payable for hot, cold water, sewerage and electricity must be considered separately, because each type of resource has its own tariffs. The amounts received can simply be added up to find out how much you will have to pay for a communal apartment in general. Just do not forget to add to this amount the payment for general house needs, major repairs, housing maintenance and other lines in the receipt.
System SUCCESS
The system allows you to make payments according to Price List 10-01 (both within Russia and for export/import), the Tariff Policy of the CIS and Baltic countries, domestic transportation according to the Tariff Guide of Belarus, domestic transportation according to the price list N1 of Ukraine, domestic and export/import transportation according to Temporary price list of Kazakhstan, transportation according to the Tariff policy of Lithuania, Ukraine, Uzbekistan. The system automatically determines the type of calculation of the railway tariff along the route of the cargo and automatically takes into account discounts valid on the date of calculation, increasing and decreasing coefficients and special rates, as well as changes in the calculation rules for individual cargoes.
- The program has a rich range of features, which include the following:
- when choosing a station of departure and a station of destination, the issuance of additional information on them;
- when choosing a cargo, the issuance of such characteristics as the need for mandatory protection, whether it refers to bulk cargo or not, etc.;
- Simultaneous calculation of the railway tariff for groups of wagons from one to a route shipment when calculating transportation in one wagon (that is, without making additional calculations);
- automatic accounting of the formation plan;
- calculation of the distance (tariff or transit) for each country participating in the transportation;
- determines the goods subject to mandatory protection for each country, and calculates its cost;
- determines the degree of danger of the cargo, affecting both the delivery time and the railway tariff;
- calculate the cost of cargo escort by conductors;
- change the distances that affect the calculation of the railway tariff for each country;
- change the route of the cargo in several ways;
- calculate the amount of fees for escort and protection of transported goods;
- Calculation of the standard delivery time of goods;
- Data transfer to MS WORD and EXEL;
- Automatic calculation of mandatory additional fees;
- Selective job accounting add. fees;
In the program for calculating the railway tariff Success there is an archive of calculations. The user can, at his own discretion, set the number of calculations to be saved in the archive and delete individual calculations.
In addition, the program implements the ability to calculate on a given date, taking into account all existing discounts and coefficients related to it.

The system also has such a unique opportunity as group calculations for individual parameters, so, for example, in one calculation you can get a tariff between one group of stations to another group of stations (from each to each).
In our market niche of the highest quality railway fare calculation programs, we have a fairly low price policy. This is due to two factors: firstly, we do not break the product into separate modules, designed by the program, in order to set a price for each (for the settlement module, for the "DOCUMENTS" module, for the "ADDITIONAL FEES" module, etc. And, secondly, the fact that fundamentally different products for calculating the railway tariff are implemented on the core of the Success system, such as pages for websites, modules for trading floors, various modules for integrating them into corporate systems.
In addition, we conclude a license agreement for the use of products of intellectual activity, in which, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT is not charged on the basis of subparagraph 26 of paragraph 2 of article 149.
Factors affecting the accuracy of railway fare calculation
- the correct ratio of GNG and ETSNG codes and the name of the cargo;
- correspondence of station names and their codes;
- ownership of the rolling stock;
- border crossing stations;
- entering the necessary data into the shipping documents;>
- gross weight of the cargo (loading into the wagon) and many others.
Carriage charges are calculated separately for each state participating in the transportation for the transportation distances and in the currency determined in accordance with the applicable tariffs for this transportation in international traffic.

- Agreement on International Rail Freight Traffic (SMGS) - establishes uniform legal norms for the contract for the carriage of goods in direct international rail traffic and in direct international rail-ferry traffic.
- Price list 10-01 "Tariffs for the carriage of goods and infrastructure services performed by Russian railways".
- MTT – International Rail Transit Tariff, applies to shipments transported by rail: Belarusian Railways, Bulgarian State Railways, Georgian Railways, Railways of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Latvian Railways State Joint Stock Company, Lithuanian Railways Special Purpose Joint Stock Company, SE Moldovan Railways, Mongolian Railways, Polish State Railways Joint Stock Company, Russian Railways, Railway Joint Stock Company (Slovak Republic), Uzbek Railways, Ukrainian Railways, Czech Railways, Estonian Railways.
- CTT - Uniform Transit Tariff. The participants of this Tariff are: Closed Joint Stock Company "Azerbaijan Railways", Belarusian Railways, Holding "Bulgarian State Railways", Vietnamese Railways, Joint Stock Company "Georgian Railways", Railway of the Republic of Kazakhstan - Joint Stock Company "National Company "Kazakhstan Temir Zholy, Chinese Railways, Railways of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Kyrgyz Railway - State Enterprise National Company Kyrgyz Temir Zholy, State Joint Stock Company Latvijas Dzelzzelsh, State Enterprise Railway of Moldova, Joint Stock Company Ulaanbaatar Railway", Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation, Tajik Railway - State Unitary Enterprise "Rokhi Ohani Tochikiston", State Joint-Stock Railway Company "Uzbekiston Temir Yullari", Railways of Ukraine - Ministry of Infrastructure Tours of Ukraine, Joint Stock Company "Estonian Railway".
- TP - tariff policy, applicable for the carriage of goods in international traffic between the participants of the tariff agreement: the Republic of Azerbaijan, the Republic of Armenia, the Republic of Belarus, Georgia, the Republic of Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Moldova, the Russian Federation, the Republic of Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, the Republic of Uzbekistan , Ukraine, Republic of Estonia. Tariffs are set on the basis of MTT and ETT.
- other local acts and documents.
How prices, tariffs, fees for housing and communal services are formed
At the same time, if any employees do not participate in the provision of works and services, then it is not necessary to take them into account. For example:
- The house is new and the management company does not provide repairs, so workers such as a concrete worker, bricklayer, painter, etc. not to be taken into account
- Public areas are not cleaned at the entrances, therefore, the cleaner of common areas does not need to be taken into account.
It is not so easy with management personnel. The fact is that the costs of management personnel are indirect costs that are distributed to the entire serviced housing stock. For example, 4.76 managers are needed to service our house, and 9.75 managers are needed to service 7 similar houses. That is, 7 similar houses need twice as many managers, and so on.
Easy and simple to work
- Installation on a computer is not required - the service works on any device with Internet access.
- The Internet service is simple and accessible, so you do not have to spend time learning.
- When registering on the site, the program itself recognizes which region you are from and substitutes the cost of materials and wages for workers in your region.
- Saving ready-made calculations to your computer in Excel format. Estimates also remain in the program for further work.
- Automatic updating of prices for the next period, expansion of the list of works.
- Collaboration for employees of one organization - exchange of estimates and publication of templates.
How to reduce current heating costs
Scheme of central heating of an apartment building
Given the ever-increasing tariffs for housing and communal services for heat supply, the issue of reducing these costs becomes only more relevant every year. The problem of reducing costs lies in the specifics of the operation of a centralized system.
How to reduce the payment for heating and at the same time ensure the proper level of heating of the premises? First of all, you need to learn that the usual effective ways to reduce heat losses do not work for district heating. Those. if the facade of the house was insulated, the window structures were replaced with new ones - the amount of payment will remain the same.
The only way to reduce heating costs is to install individual heat meters. However, you may encounter the following problems:
- A large number of thermal risers in the apartment. Currently, the average cost of installing a heating meter ranges from 18 to 25 thousand rubles. In order to calculate the cost of heating for an individual device, they must be installed on each riser;
- Difficulty in obtaining permission to install a meter. To do this, it is necessary to obtain technical conditions and, on their basis, select the optimal model of the device;
- In order to make timely payment for heat supply according to an individual meter, it is necessary to periodically send them for verification. To do this, dismantling and subsequent installation of the device that has passed verification is carried out. This also entails additional costs.
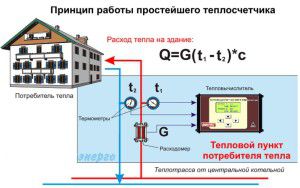
The principle of operation of a common house meter
But despite these factors, the installation of a heat meter will ultimately lead to a significant reduction in payment for heat supply services. If the house has a scheme with several heat risers passing through each apartment, you can install a common house meter. In this case, the cost reduction will not be so significant.
When calculating payment for heating according to a common house meter, it is not the amount of heat received that is taken into account, but the difference between it and in the return pipe of the system. This is the most acceptable and open way to form the final cost of the service. In addition, by choosing the optimal model of the device, you can further improve the heating system of the house according to the following indicators:
- The ability to control the amount of heat energy consumed in the building depending on external factors - the temperature in the street;
- A transparent way to calculate payment for heating. However, in this case, the total amount is distributed among all apartments in the house depending on their area, and not on the amount of thermal energy that came to each room.
In addition, only representatives of the management company can deal with the maintenance and configuration of the common house meter. However, residents have the right to demand all the necessary reporting for reconciliation of completed and accrued utility bills for heat supply.
In addition to installing a heat meter, it is necessary to install a modern mixing unit to control the degree of heating of the coolant included in the heating system of the house.
Calculation of the fee with the installed common house meter
A more common situation today is that a common house meter has been installed in an apartment building. at the same time, there are no individual heat consumption meters in the apartments. The engineering communications in many houses are such that it is simply impossible to include individual meters in the heating system, and each consumer does not have the opportunity to independently increase or decrease heating. In this case, the calculation is based on four main parameters:
- The total amount of heat energy consumed by the house is determined by the readings of the common house meter. Its installation allows you not to pay for the heat lost along the road due to uninsulated heating mains and other problems of heating networks.
- The heated area of the consumer's apartment or non-residential premises.
- The total heated area of the building. All residential premises are taken into account, as well as entrances, attached shops connected to a common heating system, etc.
- The statutory tariff for thermal energy. Tariffs are determined by local authorities.
The calculation formula is as follows: Payment for heat = total volume * area of the apartment / area of the house * established tariff. Thus, the distribution of fees becomes more equitable, since each house actually pays only for itself.
However, even in this case, the calculation system is not ideal: since consumers do not have the ability to control heat consumption, it is often necessary to simply “heat the street”, releasing heat outside due to its excess. However, you still have to pay for it in full. Because of this, a more modern version of the calculation with individual meters is becoming more and more popular.