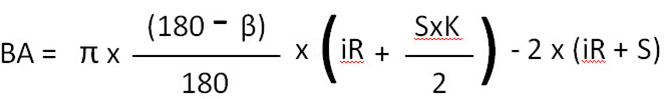Pipe bending methods without factory fixtures
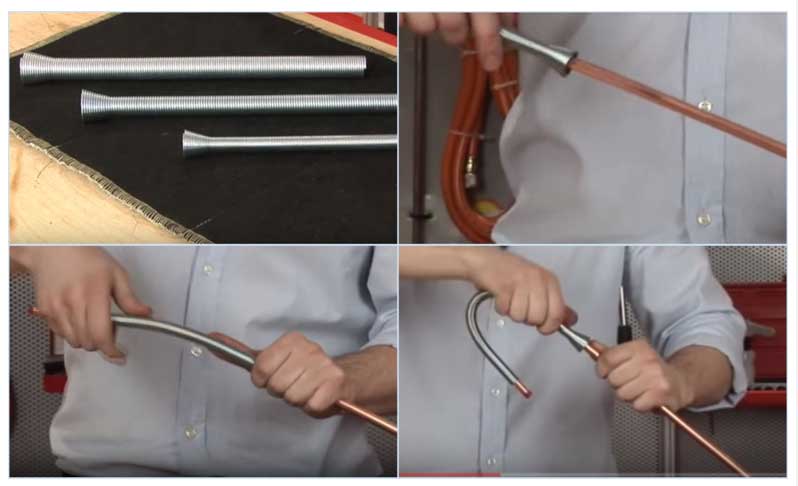
In domestic conditions, it often becomes necessary to bend pipe blanks during construction work or the installation of gas pipelines. At the same time, it is not economically feasible to spend financial resources on the purchase of factory pipe benders for one-time operations; many use simple home-made devices for these purposes.
Steel pipes
Steel belongs to rather rigid and durable materials, which are very difficult to deform, the main method of changing its configuration is bending in a heated state with a filler with simultaneous physical impact. For pipes made of thin-walled stainless steel, the following technology is used to obtain a long section with a small bending radius:
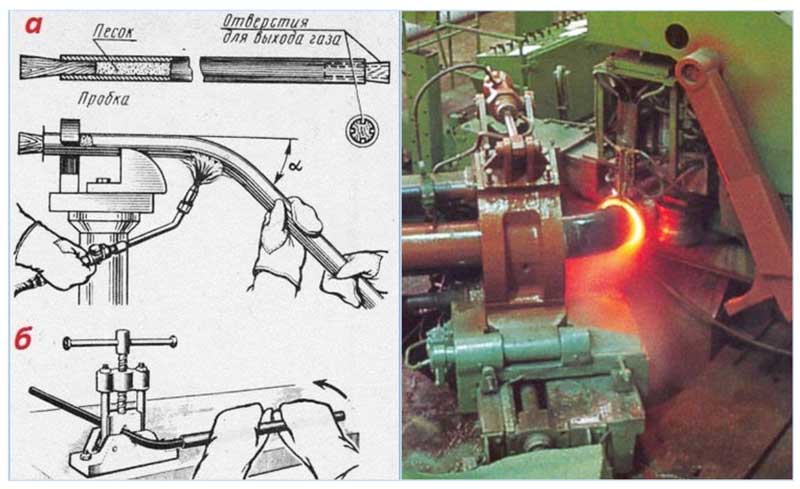
- Set the workpiece vertically, close it at one end with a cork, and very fine dry sand is poured inside, after complete filling, the cork is inserted from the other side.
- Find a pipe or a low vertical column of the required diameter and rigidly fix the pipe end on its surface.
- The part is wrapped around the pipe axis, turning the template or bypassing it around.
- After winding, the end is released and the curved part is removed from the template, the plugs are removed and sand is poured out.
Rice. 11 How to get the right bending radius of a copper pipe
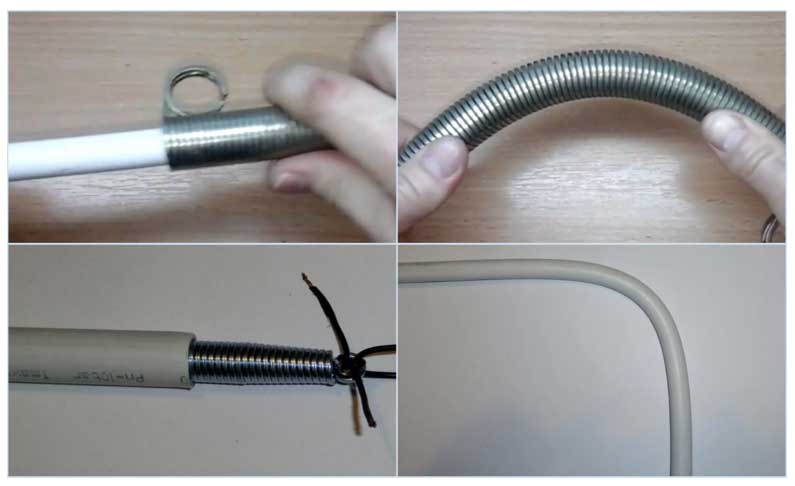
Copper pipes
Copper is a softer material than steel, it is also convenient to bend it when heated or with the help of sand poured inside. You can also use a household mandrel substitute for bending - a steel spring with dense thick coils and a cross section slightly smaller than the workpiece. During the work, the element is inserted inside and is located at the point where the deformation is performed, and after the necessary operations, it is easily removed outside. But it is much easier to bend copper pipes with a special spring pipe bender (these products can be purchased from the distribution network), which are effective on short routes and work by evenly distributing the applied force to the surface. The spring device works as follows:
- The spring is put on top of the pipe in the right place, after which it is manually bent along with the pipe.
- With further bending, the spring is moved and a bend is made at another point.
- Upon completion of the operation, the spring segment is easily removed from the outside without the use of auxiliary tools.
Another popular material is aluminum, which is easier to bend with torch heat.

Rice. 12 How to bend pipes without an aluminum machine
Metal-plastic pipes
Yes, for bending metal-plastic pipes in the household, an internal or external spring (conductor) is used. The technology of work is similar to operations with a copper pipe; when bending, allowable limits on the radius should be observed in order to avoid damage to the product.
plastic pipes
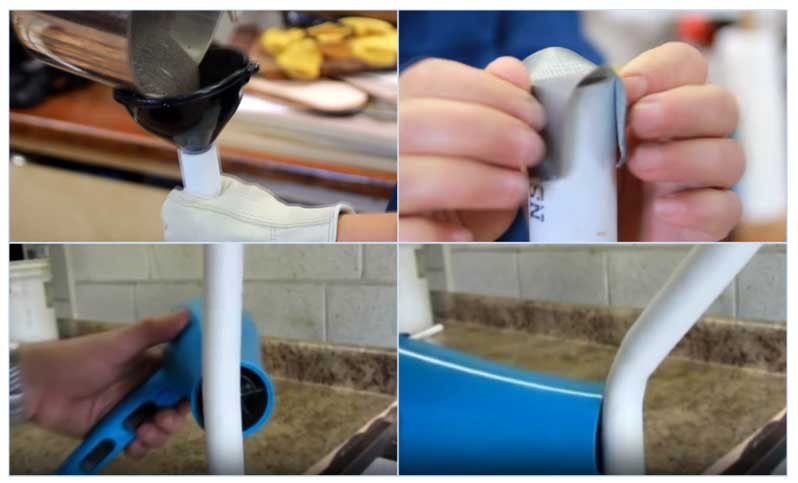
The main element for changing the configuration of plastic pipes is a building or household hair dryer; sand can be used to facilitate the work. Products of complex shape are bent as follows:
- Self-tapping screws are screwed onto a wooden plate using a screwdriver according to the desired configuration of the workpiece.
- The pipe end is inserted between two screws and the pipe wall is heated with a hair dryer, ensuring the direction of the product with turns and flexible along a given route.
- At the end of the work, the screws are unscrewed and the workpiece is removed.
Rice. 13 Methods for bending pipes made of metal-plastic with an external and internal conductor
You can use another simple technology:
- Pour sand into the plastic pipe and tightly close its ends.
- The product is placed for some time in boiling water and then removed to the surface.
- Give the workpiece the desired shape, fixing it in the desired position and waiting for cooling.
Rice. 14 How plastic elements are bent
Existing industrial and household methods for obtaining the required bending radius allow these operations to be carried out with any materials of various diameters. To carry out the work, special devices of a manual or electromechanical principle of operation are used, in which hydraulic units are often used. In the household, effective methods of bending are the use of special springs and heating of products with gas burners or a household hair dryer (when bending plastic).
GOST 17365-71 Handbook of cold stamping

The minimum pipe bending radii R should be:
- for pipes with outer diameter up to 20 mm, not less than…2.5D
- for pipes with an outer diameter of more than 20 mm, not less than ... 3.5D (where D is the outer diameter of the pipe).
The thinning of the walls in places of pipe bends and transitions of curved sections into straight ones should not exceed:
- for steel pipes - 20% of the original wall thickness
- for pipes of aluminum alloys - 25% of the original wall thickness.
The thinning of the walls of pipes stamped from sheets should not exceed 15% of the original thickness of the sheet.
Smallest bend radius
Bending radii along the pipe axis. Bending without filling or melting. For smaller bending radii, bending should be done with melting or filling.
Designations: D - pipe diameter; S - pipe wall thickness
To the table of contents
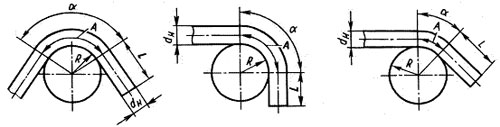
The smallest radii and the smallest lengths of straight sections of bent pipes are shown in fig. one.
The length of the bent pipe section A is determined by the formula:
Where R is the smallest bending radius, mm; dn is the outer diameter of the pipes, mm.
When choosing a bending radius, cold bending should be preferred whenever possible.
The shortest length of the straight section of the pipe Lmin is required to clamp the end of the pipe when bending
Bending radii of copper and brass pipes manufactured according to GOST 617-90 and GOST 494-90, respectively (see Fig. 1)
Outer diameter dn
Smallest bend radius R
The smallest length of the straight section Lmin
Bending radii of steel water and gas pipes manufactured in accordance with GOST 3262-75 (see Fig. 1)
Conditional passage Dy
Outer diameter dn
Smallest bend radius R
The smallest length of the straight section Lmin
Hot
Cold
Bending radii of steel pipes depending on their diameter and wall thickness Dimensions, mm
Pipe diameter, d
Smallest bending radius at wall thickness
IN AND. Anuryev, Handbook of the designer-machine builder, volume 3, pp. 368-369., Moscow 2001
How to Calculate the Minimum Allowable Radius
The minimum bending radius of the pipe, at which a critical degree of deformation appears, determines the ratio:
- Rmin means the minimum possible bending radius of the product;
- S denotes the thickness that the pipeline has (in mm).
Therefore, the radius along the median pipe axis is: R=Rmin+0.5∙Dn. Here Dn means the nominal diameter of the round rod.
A prerequisite for correctly calculating the minimum bending radius is the need to take into account the ratio:
- Kt means the coefficient of thin-walled products;
- D indicates the outer diameter of the pipes.
Therefore, the universal formula for calculating the minimum allowable bending radius is:
When the specified radius is greater than the value obtained by the above formula, then the cold pipe bending method
. If it is less than the calculated value, the material should be preheated. Otherwise, its walls are deformed during bending.
- Then the minimum allowable bending radius of a hollow rod, without using a special tool, should be: R ≥9.25∙((0.2-Kt)∙0.5).
- When the minimum bending radius is less than the calculated value, then the use of a mandrel is mandatory.
Correction of the bending radius of pipes after unloading, taking into account springback (straightening inertia), is calculated by the formula:
- Do means the section of the mandrel;
- Ki is the coefficient of elastic deformation for a particular material (according to the reference book).
- For an approximate calculation of elastic deformation for a steel, copper pipe with a passage of up to 4 cm, a coefficient value of 1.02 is assumed.
- For analogues with an internal diameter greater than 4 cm, this figure will be equal to 1.014.
To know exactly the angle to which the material should be bent, taking into account the radius of gyration of the pipe, the formula is applied:
- ∆c is the angle of rotation of the median axis;
- Ki is the coefficient of springback according to the reference book.
When the desired radius is 2-3 times greater than the cross section of the hollow rod, a springback coefficient of 40-60 is taken.
Watch the video
Bending radius of a pipe of a device for receiving in life and the industry
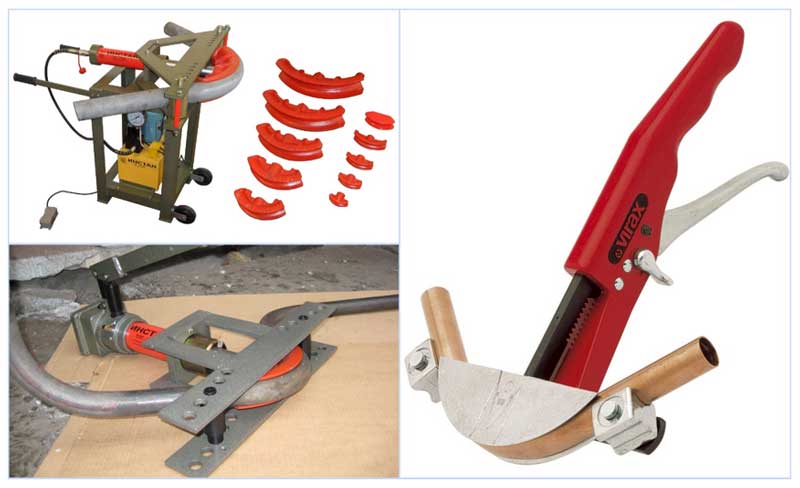
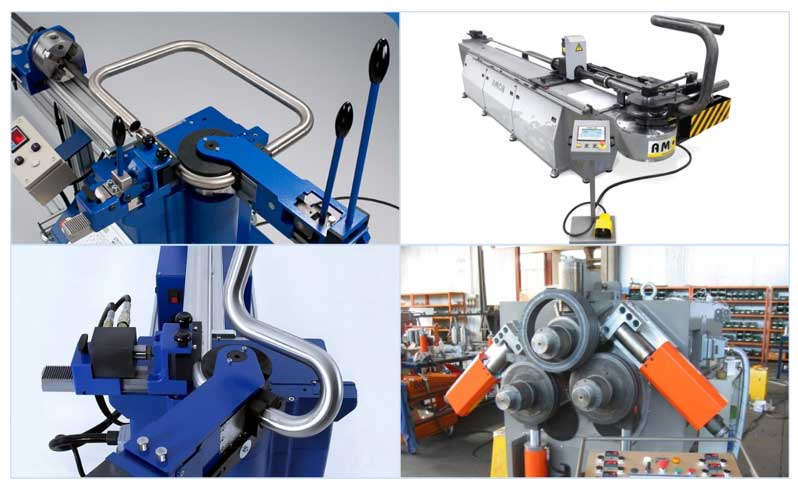
On the construction market, you can find a large number of devices for individual use for bending pipes, from the simplest springs to complex electromechanical machines with hydraulic feed.
Manual pipe benders
Pipe benders of this class are of low cost, have a simple design, low weight and dimensions, the process of bending the workpiece occurs due to the physical effort of the worker. According to the principle of operation, hand-held units manufactured by the industry can be divided into the following categories.
Lever. Bending is produced by a large lever, which reduces the applied muscle effort. In such devices, the workpiece is inserted into a mandrel of a given shape and size (punch) and, with the help of a lever, the product wraps around the template surface - as a result, an element of a given profile is obtained. Lever devices allow you to get a radius of curvature of 180 degrees and are suitable for small diameter soft metal pipes (up to 1 inch). To obtain roundings of various sizes, replaceable punches are used; to facilitate work, many models are equipped with a hydraulic drive.
Rice. 7 Hand type crossbow attachments
Crossbow. During operation, the workpiece is placed on two rollers or stops, and bending occurs by pressure on its surface between the stops of the punch of a given shape and section. The units have replaceable punch nozzles and movable stops that allow you to set the bending radius of a steel pipe or non-ferrous metal blanks.
The bending shoe is mounted on a rod that can be moved by screw gear, hydraulic fluid pressure with manual injection or by electrically actuated hydraulics. Such devices allow bending pipes made of soft materials with a diameter of up to 100 mm.
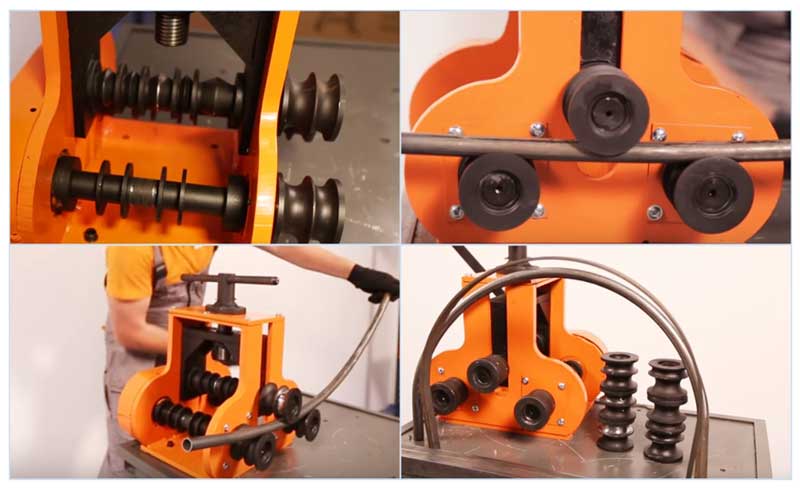
Three-roller units (pipe bending rolls). They are the most common type of pipe bending units in everyday life and industry, they work on the principle of cold rolling. Structurally, they are made in the form of two rollers, in the streams of which the workpiece is installed, the third roller is gradually brought to the surface, simultaneously rolling the product in different directions. As a result, the workpiece is deformed without wrinkling of a larger section than in other manual pipe benders.
A distinctive feature of the unit is the impossibility of obtaining a small radius of curvature (the usual value is 3 - 4 of the inner diameter).
All of the above devices are mandrelless units, therefore they are ineffective when bending thin-walled products, it is also undesirable to use them when working with workpieces with a welded joint of the walls - during plastic deformation, it is possible to open individual sections of the seam.
Rice. 8 Tube bending rolls
Electromechanical pipe benders
Electromechanical units are mainly used in industry and provide the following technological processes.
Bare bending. The machines are used when working with workpieces, for bending radii of 3 - 4 D., capable of bending thick-walled pipes for the furniture and construction industries, main pipelines. The machines have the simplest design and control compared to other types, they are distinguished by small overall dimensions and weight.
Booster processing.Units operating on a special technology for advancing the carriage with an additional unit are designed to obtain complex bends without thinning the walls. They are used for the manufacture of coils of various shapes in thermal power engineering, boiler and water heating industries.
Dorn bending. Units of this type allow high-quality bending of thin-walled elements with an outer diameter of up to 120 mm. Industrial machines can be automatic or semi-automatic with numerical control.
Three roll bending. The design is widely used for bending any metals and alloys, it is versatile: it does an excellent job with a round or rectangular profile, corners and flat plates. The versatility of the unit is achieved by changing rolls with different types of working surfaces and sizes.
With the help of this unit, it is convenient to bend elements of great length with the same large radius of curvature throughout.
Rice. 9 Industrial pipe benders
Metal-plastic pipes
As metal-plastic pipes spread, many began to use them in all possible communications. They are reliable, practical, inexpensive and easy to install. But how to bend metal-plastic pipes? To do this, either simple manual labor is used (if the metal in the pipe is soft), or the bending method using a spring (it was discussed above). It is mandatory to fulfill the condition that it is impossible to bend a metal-plastic pipe more than 15 degrees for every 2 centimeters. If this parameter is neglected, the pipe may simply become unusable due to a large amount of damage.
Behavior of round, square and rectangular sections, types of destruction

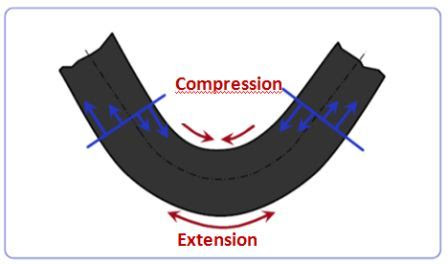
- The outer wall, which has become thin, gravitates towards a bulge directed towards the median axis of the pipe. This leads to the fact that its cross section is deformed.
- When the tensile strength of the product is exceeded, it breaks along the outer bending plane.
How do square and rectangular profiles behave:
- Their tube walls are subjected to compressive and tensile stress, both on the outer and inner plane of the bend, to the maximum.
- The material has an increased tendency to deformation, it is difficult for the master to control them.
- The profile material on the inside of the bend tends to expand vertically. At the same time, it flows horizontally along the end of the product. These stresses indent vertically arranged pipe walls. In this case, the square of the cross section is deformed. It acquires a trapezoid configuration.
- The cross-section of rectangular and square shape does not transmit clamping forces between the bending and clamping jaws well.
- The profile tends to slip along the block at the beginning of the bend. At the same time, he can rub it, which leads to wear of the equipment.
The behavior of a material with a circular cross section when it is bent:
- The material is less deformed in areas of the highest stress. Places of maximum compression/stretching are located along the tangent of the center line to the cross section.
- The round shape allows the metal to spread evenly in all directions during bending. Thanks to this wizard, it is easier to control the processes of material deformation.
- Thanks to its rounded cross-section, the pipe transfers forces well between the bending and clamping jaws.
- When bending round pipes along the radius, they practically do not slip in the tool.
Pipe bending methods and their benefits
Pipe bending is a technology where the desired turn in the direction of the pipeline line is created by physical impact on the workpiece, the method has the following advantages:
- Reduced metal consumption, there are no adapter flanges, couplings and branch pipes in the line.
- Reduced labor costs during the installation of pipelines compared to welded joints.
- Low hydraulic losses due to unchanged profile section.
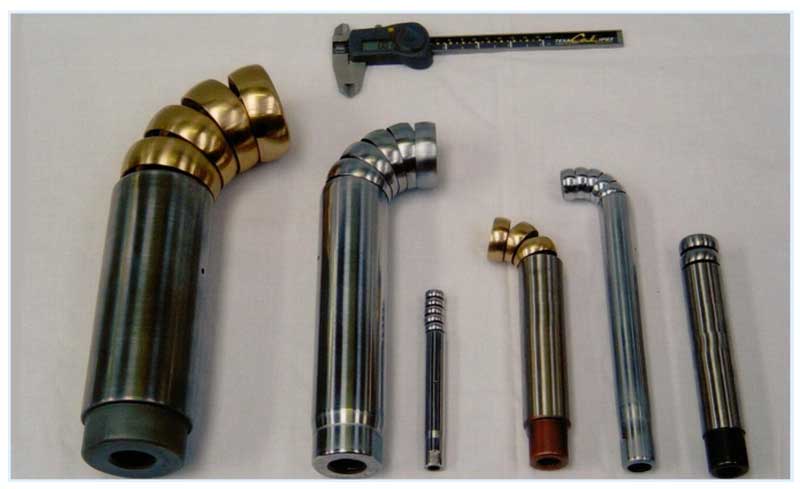
Rice. 3 Mandrels for pipe benders
- Unchanged metal structure, its physical and chemical parameters in comparison with welding.
- High quality sealing, the line has a uniform structure without breaks and joints.
- Aesthetic appearance of the highway
There are two main bending technologies - hot and cold bending, fixtures and methods can be divided into the following categories:
- According to the type of physical impact, the pipe bending unit can be manual and electric with a mechanical or hydraulic drive.
- According to the bending technology - mandrel (bending with the help of special internal protectors), mandrelless, and rolling machines with rollers.
- By profile - installations for metal-profile rectangular or round products.
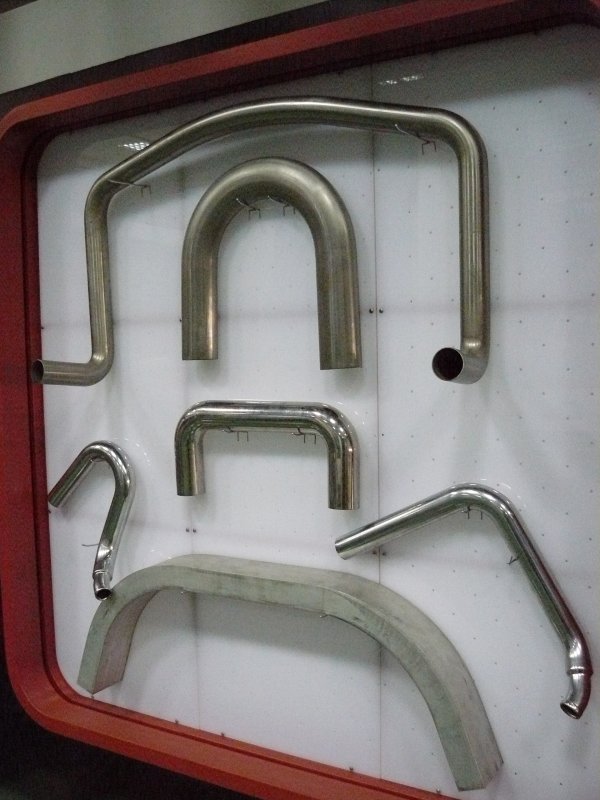
Rice. 4 Hot pipe bending methods
hot bending
The technology popular in everyday life is used in cases where there is no pipe bender or it is not possible to work in a cold way, the process consists of several operations:
- The workpiece is filled with river fine-grained seeded sand without foreign inclusions in a dry form. To do this, a plug is inserted from one end, sand is poured in and the hole is closed on the other side.
- The place of bending is heated to a temperature of no more than 900 degrees in order to avoid overburning, and a gradual smooth mechanical winding of the part around the rounded template is performed.
- At the end of the process, the plugs are removed and sand is poured out of the workpiece.
Cold bending methods for round pipes
Cold methods have undeniable advantages over hot technologies: they do not disturb the structure of the metal, are more productive and require less cost. When cold bending, the following defects occur:
- reduction of the pipe section from the outside of the profile;
- curvature in the bend in the form of a corrugation on the inside;
- changing the profile shape at the bends of pipes from round to oval.
Rice. 5 Bending blanks from a metal profile in everyday life
Most often, such defects occur during the deformation of thin-walled pipes, therefore, during operations with them, an internal protector is used - a mandrel inserted into the internal cavity.
The mandrel is a device consisting of a rigid rod with movable segments on the edge of a spherical or hemispherical shape. Before operation, the device is placed in the internal cavity of the workpiece so that its movable elements are located at the bending point, at the end of the procedure, the mandrel is removed from the finished element and the process is repeated.
Pipe bending radii
Pipe bending radii
Pipe bending is a technological process, as a result of which, under the influence of external loads, the slope of the geometric axis of the pipe changes. In this case, elastic and elastic-plastic deformations occur in the metal of the pipe walls. Tensile stresses occur on the outer part of the camber, and compressive stresses occur on the inner part. As a result of these stresses, the outer wall of the pipe with respect to the bending axis is stretched, and the inner wall is compressed. In the process of bending the pipe, a change in the shape of the cross section occurs - the initial annular profile of the pipe turns into an oval one. The greatest ovality of the section is observed in the central part of the camber and decreases towards the beginning and end of the camber. This is explained by the fact that the greatest tensile and compressive stresses during bending occur in the central part of the bend. The ovality of the section at the bend should not exceed: for pipes with a diameter of up to 19 mm - 15%, for pipes with a diameter of 20 mm or more - 12.5%. The ovality of the section Q in percent is determined by the formula:
where Dmax, Dmin, Dnom are the maximum, minimum and nominal outer diameters of the pipes at the bend.
In addition to the formation of ovality during bending, especially for thin-walled pipes, folds (corrugations) sometimes appear on the concave part of the bend. Ovality and wrinkling adversely affect the operation of the pipeline, as they reduce the flow area, increase the hydraulic resistance and are usually the site of clogging and increased corrosion of the pipeline.
In accordance with the requirements of Gosgortekhnadzor, the bending radii of steel pipes, bends, compensators and other bent elements of pipelines must be at least the following values:
when bending with pre-stuffing with sand and with heating - at least 3.5 DH.
when bending on pipe bending machines in a cold state without sanding - at least 4DH,
when bending with semi-corrugated folds (on one side) without sand stuffing, heated by gas burners or in special furnaces - at least 2.5 DH,
for curved bends made by hot drawing or stamping, at least one DH.
It is allowed to bend pipes with a bending radius less than those indicated in the first three paragraphs, if the bending method guarantees thinning of the wall by no more than 15% of the thickness required by the calculation.
The following main methods of pipe bending are used at pipe procurement depots and plants, as well as installation sites: cold bending on pipe bending machines and fixtures, hot bending on pipe bending machines with heating in furnaces or high-frequency currents, bending with folds, bending in hot sand-filled condition.
The length of the pipe L, necessary to obtain a bent element, is determined by the formula:
L = 0.0175 Rα + l,
where R is the pipe bend radius, mm;
α—pipe bending angle, deg;
l - a straight section 100-300 mm long, necessary to grip the pipe during bending (depending on the design of the equipment).
1. Name the tolerances for the ovality of the pipe section.
2. How is ovality calculated as a percentage?
3. What bending radii are allowed by the requirements of Gosgortekhnadzor when bending pipes in various ways?
4. How to determine the length of the pipe to obtain a bent element?
All materials of the section "Pipe processing" :
● Pipe cleaning and straightening
● Flanging of pipe ends, fittings and holes
● Threading and thread rolling on pipes
● Pipe bending radii
● Cold pipe bending
● Hot pipe bending
● Cutting and processing of pipe ends
● Processing of non-ferrous pipes
● Plastic and glass pipe processing
● Preparation and revision of fittings
● Production of gaskets in pipe shops and workshops
● Safety regulations for pipe processing
On our website you will find a lot more information about sheet metal bending Read the article Digitizing the work of a bending machine
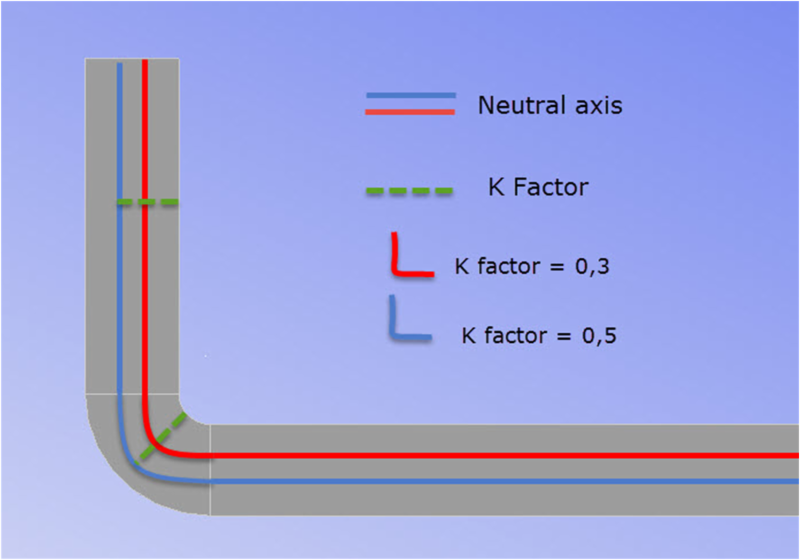
K-factor (neutral line factor)
When bending on a sheet bending machine, the inner side of the metal sheet is compressed, while the outer side, on the contrary, is stretched. This means that there is a place on the sheet where the fibers are neither compressed nor stretched. This place is called the "neutral line". The distance from the inside of the fold to the neutral line is called the K-factor, the position factor of the neutral line.
It is not possible to change this factor as it is constant for each type of material. It is expressed as a fraction, and the smaller the K-factor, the closer the neutral line will be located to the inner radius of the sheet.
K-factor = fine tuning
The K-factor value affects slab stock, perhaps not as much as part radius, but should be taken into account when fine-tuning stock calculations. The smaller the K-factor, the more the material is stretched and "pushed out", causing the workpiece to be "bigger".
K-factor prediction
In most cases, we can predict and adjust the K-factor when performing slab stock calculations.
It is necessary to carry out several tests on the selected V-notch and measure the radius of the part. If you need to calculate the K-factor more accurately, you can use the bending K-factor formula below:
Example solution:
B = 150 + 100 + 60 + BA1 + BA2
K-factor prediction
B1: R/S=2 => K=0.8
B2: R/S=1.5 => K=0.8
Both folds are less than or equal to 90°:
which means:
B1 = 3.14 x 0.66 x (6 + ((4×0.8)/2) – 2 x 10
B1 = -4.25
B2 = 3.14 x 0.5 x (8 + ((4×0.8)/2) – 2 x 12
B2 = -8.93
Total:
B = 150 + 100 + 60 + (-4.25) + (-8.93)
B= 296.8mm
Author of the method: Julio Alcacer, International Sales Manager Rolleri Press Brake Tools
Dreambird's comment
Sheet metal working in modern manufacturing is often used to produce parts where precise dimensional accuracy is critical. Moreover, in an environment where speed of production is paramount and determines whether a subcontractor receives an order to manufacture parts, manufacturers try to avoid wasting time doing manual costing, performing various tests and correcting mistakes. The method used in the article can undoubtedly be considered accurate and the formulas presented in it are useful, but their constant use in calculations leads to additional time costs in production.
Today's press brakes are often equipped with CNC stands and the bending sequence for a particular product can be set on the computer immediately after the design of the product. If there is a ready-made flat-reamed geometry file, the bending sequence required to perform it is also calculated on the computer after directly importing this file into a specialized bending CAD/CAM solution.
Radbend's state-of-the-art stand-alone software solution, part of Radan's sheet metal CAD/CAM suite, is the world's leading application of this nature. All the calculations presented in the article are incorporated in Radbend in the form of algorithms and do not require manual calculations. The part is bent in the Radbend environment as it would actually be, then the "too long" sides are trimmed for absolute precision. Next, the already bent product is sent to the Radan3D module, where a blank is created on its basis, the length of which is calculated taking into account the fit previously performed in Radbend. Thus, during the production of the product, all the required parameters will be observed and the processing will be performed correctly from the first approach.
Radbend allows you to pre-determine the manufacturability of a part by generating and showing graphically a complete machining simulation and bending sequence, helping you to select the tool and place the stops. With this module, you can avoid problems that often arise in production - to prevent collisions between the tool, workpiece and machine parts.