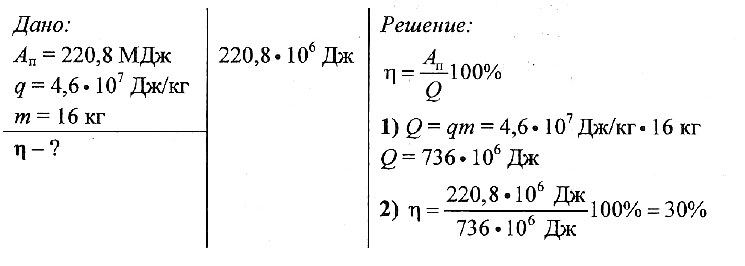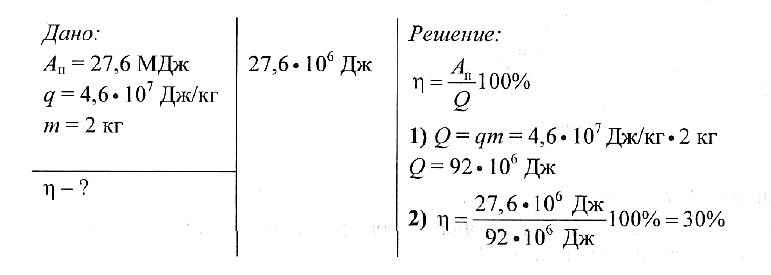We analyze the effectiveness of the work of personnel
For effective personnel management and increase in production volumes, daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly and annual reports on their performance and work efficiency are constantly carried out.
Not only the performance of one employee, but also of entire departments is taken into account and comparisons are made in one direction or another of the enterprise's activities, which directly affect the annual output indicators and, accordingly, the receipt of the planned profit depends on this. All of the above factors and indicators that are used to calculate the productivity of personnel are closely related to each other and characterize the overall performance of the company.
When analyzing the productivity of personnel, the share of individual types of products in the overall productivity is taken into account. Here, calculations are made for products with high labor costs and lower, if necessary, calculate the average value.
They analyze not only performance indicators and carry out their comparison and optimization, but also indicate the corresponding reserves of the company to reduce the overall labor intensity for the manufacture of products both for specific types and for the enterprise as a whole.
The simplest way to control and manage the productivity of personnel is to fulfill planned targets (or, accordingly, their underfulfillment or overfulfillment).
The main objectives of the analysis are the following:
- tension plan for staff performance, determining the degree;
- identification of factors that affect the performance of employees;
- comparison of relevant indicators;
- implementation and optimization of enterprises aimed at increasing the productivity of employees of organizations.
Performance plans are mainly analyzed in terms of such indicators as planned and actual indicators, and already based on the results of deviations (up or down), appropriate methods and measures are implemented.
Efficiency drop and total losses in the electric motor
There are many negative factors that influence the amount of total losses in electric motors. There are special techniques that allow you to determine them in advance. For example, you can determine the presence of a gap through which power is partially supplied from the network to the stator, and then to the rotor.
The power losses that occur in the starter itself consist of several terms. First of all, these are the losses associated with and partial remagnetization of the stator core. Steel elements have little effect and are practically not taken into account. This is due to the speed of rotation of the stator, which is much higher than the speed of the magnetic flux. In this case, the rotor must rotate in strict accordance with the declared technical characteristics.
The value of the mechanical power of the rotor shaft is lower than the electromagnetic power. The difference is the amount of losses that occur in the winding. Mechanical losses include friction in bearings and brushes, as well as the effect of an air barrier on rotating parts.
Asynchronous electric motors are characterized by the presence of additional losses due to the presence of teeth in the stator and rotor. In addition, vortex flows may occur in individual engine components. All these factors together reduce the efficiency by about 0.5% of the rated power of the unit.
When calculating possible losses, the engine efficiency formula is also used, which allows calculating the decrease in this parameter. First of all, the total power losses are taken into account, which are directly related to the engine load.As the load increases, the losses increase proportionally and the efficiency decreases.
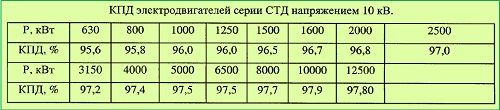
In the designs of asynchronous electric motors, all possible losses are taken into account in the presence of maximum loads. Therefore, the range of efficiency of these devices is quite wide and ranges from 80 to 90%. In high power engines, this figure can reach up to 90-96%.
Efficiency is a characteristic of the efficiency of a device or machine. Efficiency is defined as the ratio of useful energy at the output of the system to the total amount of energy supplied to the system. Efficiency is dimensionless and is often expressed as a percentage.
Formula 1 - efficiency
Where-A
useful work
—Q
the total work that was spent
Any system that performs any work must receive energy from the outside, with the help of which the work will be done. Take, for example, a voltage transformer. A mains voltage of 220 volts is applied to the input, 12 volts is removed from the output to power, for example, an incandescent lamp. So the transformer converts the energy at the input to the required value at which the lamp will work.
But not all the energy taken from the network will go to the lamp, since there are losses in the transformer. For example, the loss of magnetic energy in the core of a transformer. Or losses in the active resistance of the windings. Where electrical energy will be converted into heat without reaching the consumer. This thermal energy in this system is useless.
Since power losses cannot be avoided in any system, the efficiency is always below unity.
Efficiency can be considered as for the whole system, consisting of many separate parts. So to determine the efficiency for each part separately, then the total efficiency will be equal to the product of the efficiency of all its elements.
In conclusion, we can say that the efficiency determines the level of perfection of any device in the sense of transferring or converting energy. It also indicates how much energy supplied to the system is spent on useful work.
Tasks on the efficiency of heat engines with solutions
Formulas used in the lessons "Tasks for the efficiency of heat engines."
Does the gun belong to heat engines? Yes, because when fired, the internal energy of the fuel is converted into mechanical energy.
EXAMPLES OF SOLVING PROBLEMS
Task number 1.
Determine the efficiency of the car engine, which required 8 kg of gasoline to perform work of 110.4 MJ.

Task number 2.
Determine the efficiency of the engine of a car that needed 16 kg of gasoline to perform work of 220.8 MJ.
Task number 3.
Determine the efficiency of the car engine, which required 2 kg of gasoline to perform the work of 27.6 MJ.
Task number 4.
The ship is equipped with a 80 kW diesel engine with an efficiency of 30%. For how many kilometers will he need 1 ton of diesel fuel at a speed of 20 km/h? The specific heat of combustion of diesel fuel is 43 MJ/kg.
Task number 5.
The cartridge of the traumatic pistol "Osa" 18 × 45 mm, contains a rubber bullet weighing 8.4 g. Determine the efficiency of the cartridge if the bullet acquired a speed of 140 m/s when fired. The mass of the powder charge of the cartridge is 0.18 g, the specific heat of combustion of the powder is 3.8 x 106 J/kg.
Task number 6.
The first caterpillar tractor designed by A.F. Blinov, 1888, had two steam engines. For 1 hour, he spent 5 kg of fuel, in which the specific heat of combustion is 30 • 106 J / kg. Calculate the efficiency of the tractor if its engine power was about 1.5 kW.

Task number 7.
The internal combustion engine has done useful work equal to 2.3 x 104 kJ, and at the same time it has consumed gasoline weighing 2 kg. Calculate the efficiency of this engine.
Task number 8.
For a 3-hour run, a car with an efficiency of 25% consumed 24 kg of gasoline.What is the average power developed by the car engine during this run?
Task number 9.
An internal combustion engine with a power of 36 kW consumed 14 kg of gasoline in 1 hour of operation. Determine the efficiency of the engine.
Task number 10.
OGE
An ideal heat engine operating according to the Carnot cycle transfers 80% of the heat received from heating to the cooler. The amount of heat received by the working fluid in one cycle from the heater, Q1 \u003d 6.3 J. Find the cycle efficiency ɳ and the work A done in one cycle.

Task number 11.
USE
A heat engine operating according to the Carnot cycle performs work A \u003d 2.94 kJ in one cycle and gives the amount of heat Q to the cooler in one cycle2 = 13.4 kJ. Find the cycle efficiency ɳ.

This is a summary on the topic "TASKS for the efficiency of heat engines." Choose next steps:
- Jump to the topic: CHALLENGES on Ohm's Law.
- View abstract “Heat engines. ICE. Specific calorific value”.
- Return to the list of abstracts in Physics.
- Test your knowledge of Physics.
Why labor productivity is so important in the activities of every organization
Labor productivity is the efficiency of the work of personnel in a particular industry and service market, which is displayed by the quantitative number of manufactured products or services sold by a specific employee for a certain period of time. Basically, this indicator is calculated for a month of work and compared with the results of the work of other employees who work in similar positions and have the same labor duties in quantitative terms.
The inverse indicator of the value of labor productivity of personnel is labor intensity. Labor intensity is the period of time (its amount) for the manufacture of one unit of product or service (depending on the scope of the employee in the organization).
If the efficiency of the work of the organization's personnel increases, then the amount of working time costs decreases accordingly, the cost of manufactured products is significantly reduced, and the overall economic efficiency of production increases.
The efficiency of the personnel directly affects the production cycle and its turnover. The faster the turnover of funds (working capital), the sooner these working capital are "released" from the turnover process.
The following indicators influence the rate of increase in the turnover of working capital:
- increasing the number and volume of sales;
- work on reducing the cost of human resources for the manufacture of products or services;
- continuous improvement of the quality and competitiveness of goods and services;
- general reduction and acceleration of the pace of the production cycle;
- improvement of supply and marketing systems, etc.
All companies are constantly trying to increase the number of manufactured products or services offered for a specific period of time, and this in turn reduces the cost of manufacturing one unit of it.
At the end of each month, personnel departments (or other recruiting departments) conduct statistics on the productivity of personnel in a particular area. These may be different production departments in the same company. They practice “weak link” methods: with employees with the lowest indicators of labor productivity, additional training is conducted, systems of fines are applied, etc.
It is not profitable for companies to pay for the work of personnel with low work efficiency, as this directly affects the overall profit. At the same time, employees with good performance indicators are constantly encouraged in the form of bonuses, bonuses, additional vacations and other types of bonus programs.