Why do we need annealing of metals
The exact nature of the annealing process to which the metal is subjected depends largely on the purpose of the annealed metal.
There is a significant difference in annealing methods between annealing in factories where a huge amount of sheet steel is produced, and annealing in a small car workshop, when only one part requires such treatment.
In short, cold working is plastic deformation by destroying or distorting the grain structure of the metal.
During annealing, the metal or alloy is heated to a temperature at which recrystallization occurs - the formation of new grains instead of old - deformed and elongated - grains - non-deformable and round. Then the metal is cooled at a given rate. In other words, crystals or grains within the metal that have been displaced or deformed during cold plastic working are allowed to rebuild and recover to their natural state, but at an elevated annealing temperature.
Copper plating of parts in solution with electrolyte
For metal parts, copper plating can be done at home. Consider copper plating, with lowering the part into a solution with an electrolyte. For this you need to have:
- small copper plates
- several meters of conductive wire;
- current source, with voltage up to 6 V;
- it is also recommended to use a rheostat to regulate the current and an ammeter.
Operating procedure
- As a liquid that dissolves copper well, a conventional electrolyte is used. You can buy it or make it at home. This will require 3 ml sulfuric acid, for every 100 ml of distilled water. The required solution can be obtained by adding up to 20 g to the resulting electrolyte. copper sulfate.
- Before starting the copper plating process, the part must be cleaned with sandpaper to remove the oxide film from the surface.
- Then, the part is degreased with hot soda solution, and washed with clean water.
- The prepared electrolyte solution is poured into a glass container of the required volume.
- Then, two copper plates are lowered there, on conductive wires. Between two copper plates, a part intended for copper plating at home is suspended on a similar wire. It is necessary to ensure that the copper plates and the part are completely flooded with an electrolyte solution.
- At the next stage, the ends of the wires from the copper plates are connected to the positive, and the workpiece to the negative terminals of the current source. In series, a rheostat and an ammeter must be connected to the created electrical circuit. After turning on the current in the circuit, is it set by a rheostat within 15 mA per 1 cm? surface area of the part.
- Having kept the workpiece in the solution for 15-20 minutes, you need to turn off the power supply and remove the product from the solution. During this short period of time, the surface of the part will be covered with a thin layer of copper. The thickness of the coating will depend on the duration of the copper plating process. Thus, it is possible to achieve copper plating of the surface of any product with a layer of 300 microns or more.
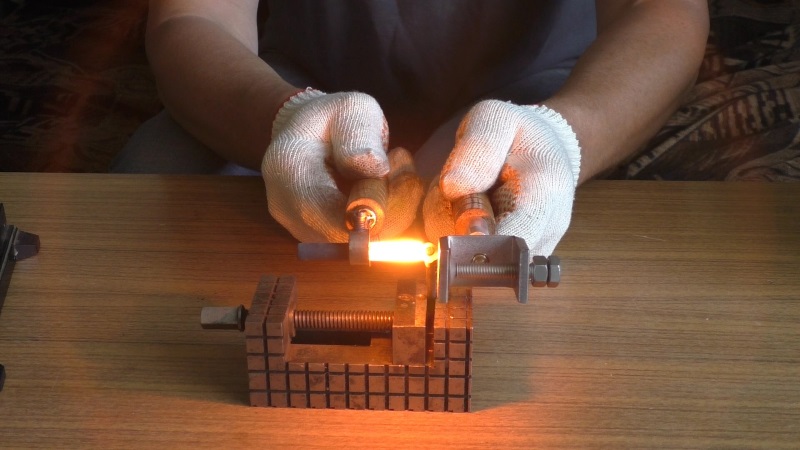
Welding of copper and its alloys with steel. How to weld copper and steel
In practice, welding of copper and steel is most often carried out in butt joints. Depending on the nature of the structure, the seams in such a joint can be external and internal.
For welding brass to steel, gas welding is best, and for welding red copper to steel, metal arc welding is best.
Good results are also obtained when welding with carbon electrodes under a layer of flux and gas welding under a flux BM-1.Often in practice, gas welding of brass to steel is performed using copper as a filler material.
The preparation of welded edges with the same thickness of non-ferrous metal and steel is carried out in the same way as when welding ferrous metals.
Sheets with a thickness of less than 3 mm are welded without cutting, and sheets, starting from 3 mm, with beveled edges.
If the bevel of the edges is insufficient, or if there is dirt on the ends of the parts to be welded, it is impossible to achieve good penetration. Based on this, when welding parts of large thicknesses in which an X-shaped groove is made, blunting should not be done.
Welding copper with steel is a difficult task, but quite feasible for surfacing and welding, for example, parts of chemical equipment, copper wire with a steel block.
The quality of welding of such joints satisfies the requirements for them. The strength of copper can be increased by introducing up to 2% iron into its composition. With more iron, the strength begins to fall.
When welding with a carbon electrode, direct current of direct polarity must be used.
The voltage of the electric arc is 40-55V, and its length is approximately 14-20mm. Welding current is selected in accordance with the diameter and quality of the electrode (carbon or graphite) and is in the range of 300-550A. The flux used is the same as for welding copper, the composition of these fluxes is given on this page.
The flux is introduced into the welding zone, pouring it into the groove.
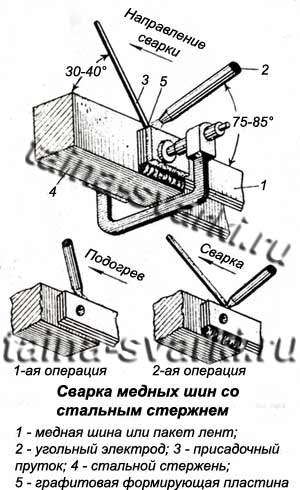
The best results when welding copper busbars to steel busbars are obtained by boat welding. The scheme of such welding is shown in the figure. First, the copper edges are heated with a carbon electrode, and then welding with a certain position of the electrode and filler rod (see figure). Welding speed is 0.25m/h. Welding of copper with cast iron is carried out using the same technological methods.
Welding of low-alloyed bronze of small thickness (up to 1.5 mm) to steel up to 2.5 mm thick can be carried out with an overlap with a non-consumable tungsten electrode in an argon environment on an automatic machine with a filler wire with a diameter of 1.8 mm fed from the side.
In this case, it is very important to direct the arc to the overlap from the copper side. Such welding modes: current strength 190A, arc voltage 11.5V, welding speed 28.5m/h, wire feed speed 70m/h
Copper and brass weld well to steel by flash butt welding.
With this method of welding, the steel edges are melted quite strongly, and the edges of non-ferrous metal are slightly melted. Taking into account this circumstance, and taking into account the difference in the specific resistances of these metals, take the overhang for steel equal to 3.5d, for brass 1.5d, for copper 1.0d, where d are the diameters of the rods to be welded.
For resistance butt welding of such rods, a stick out of 2.5d for steel, 1.0d for brass and 1.5d for copper is recommended. The specific resistance of precipitation is taken in the range of 1.0-1.5 kg/mm2.
In practice, it often becomes necessary to weld studs with a diameter of 8-12 mm from copper and its alloys to steel, or steel studs to copper products.
Such welding is carried out on a direct current of reverse polarity under a fine flux grade OSC-45 without preheating.
Copper studs up to 12 mm in diameter or L62 brass studs up to 10 mm in diameter at a current of 400A are well welded to steel or cast iron.
And studs made of brass brand LS 59-1 are not used for welding.
Steel studs are poorly welded to copper and brass products.
Electrodes for copper welding
To join copper without filler wire, consumable electrodes with a special coating are used. When melted, it creates a layer of slag that protects the welding site from contact with air. The additives that make up the coating, when combined with the metal, improve the quality of the seam. The slag layer slows down the cooling of the joint, which helps to remove more gases.
Non-consumable carbon and graphite electrodes are used in conjunction with the filler wire required to create a seam. When choosing, keep in mind that:
- for manual welding of copper, the color of the coating is red;
- grades with a gray coating are intended for non-ferrous metals;
- refractory metals are cooked with blue electrodes;
- with yellow coating heat-resistant alloy steel.
Features of the process of copper plating steel at home
To produce copper plating at home, it is necessary to fulfill a number of requirements arising from the technological process itself, since the immersion method involves the use of an electrolyte. This solution is caustic, subject to evaporation, and since during operation it will also heat up, the evaporation will be intense. For electroplating at home, you should take care of protective equipment and good ventilation.
Electroplating with copper at home, despite the rather primitive equipment, nevertheless gives excellent results. Of all metals, steel provides the strongest connection with a copper film, therefore it is during copper plating of steel that excellent, durable current conductors are obtained. Coating a steel product with a copper film will give the item a more attractive look.

Copper plating of steel with immersion in electrolyte
Before starting the copper plating process, you should prepare your home, workplace, necessary materials and personal protective equipment for these works. After that, you should prepare the workpiece. The oxide film should be removed from its surface with a thin emery and a fine metal brush. After removing the film, the part is washed, degreased in warm soapy water and washed again with clean water under strong pressure.
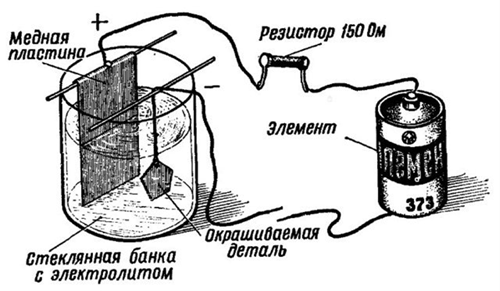
Two copper plates are placed in a container (preferably glass), electrically connected to each other. These plates are anodes, and are connected by a conductor to the plus of the current source. A conductor is connected to the minus of the source, connected to the workpiece being processed, which is the cathode in this circuit. A rheostat is included in the anode circuit to adjust the current strength and an ammeter for control.
The prepared electrolyte solution is poured into the container, which includes copper sulfate, distilled water and acid. The solution is poured in an amount sufficient to completely cover the electrodes and the workpiece. Voltage is applied to the circuit, a current is set by the rheostat at the rate of 15 mA per square centimeter of the part area.
After half an hour, the voltage is removed, the copper-plated part is removed from the solution, freed from the conductor, thoroughly washed, and dried. Process completed. Necessary note: all operations should be carried out in a respirator, rubber gloves and with ventilation turned on.
Welding machine for copper
The main units are defined as semi-automatic, automatic, argon, inverter units. Each of the devices performs work in a different way of production, is equipped with distinctive characteristics.
- The connection of copper plates can be carried out by tungsten-type organs in an argon environment. Modern type inverters are powered by a household network, equipped with an independent cooling system, and are lightweight.
- With wire, semi-automatic installations are used. There are various nodes, including domestic ones, which are not inferior to imported analogues in terms of performance.
- Copper wires are also connected by inverter, the main feature is cost-effective, low power consumption. Protection against sticking, hot start will allow a novice master to operate without prior training.
Homemade welding machine for welding with carbon electrodes
For home use, the best choice is a unit with a power of up to 3.5 kW. The output power is sufficient for connecting copper with a thickness of 5 mm. Low resource mechanisms will not harm the household electrical network, prevent the failure of appliances.
Preparation for patination
As with any work with chemicals, safety must be the first priority. Most of the compounds used in blackening are very toxic. The vapors emitted can be hazardous to health if released into the atmosphere. There are certain standard rules that should not be neglected:
- it is necessary to store substances in special test tubes, tightly closed with stoppers for sealing;
- keep solutions out of the reach of children;
- the process must take place in a specialized cabinet with built-in ventilation (the cabinet doors should be slightly open).
Before processing, the material should be thoroughly washed, cleaned and degreased to achieve the best effect.
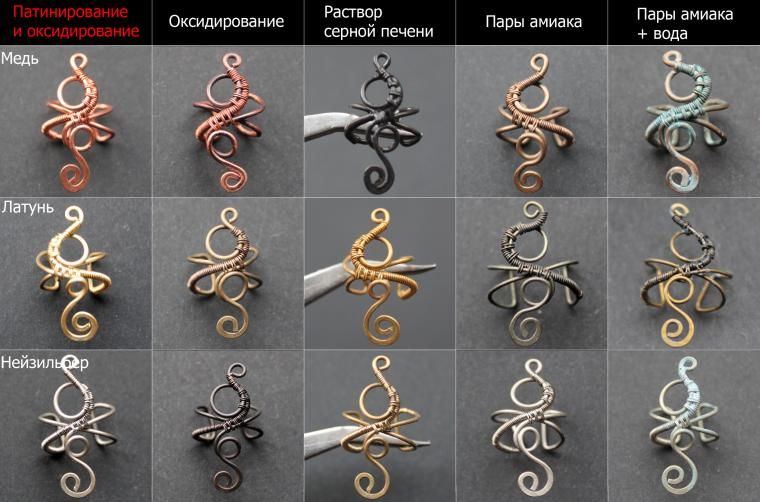

Oxidation and patination - these concepts are not synonymous, the consequences of each of these processes differ in order from each other.
Oxidation of copper - the formation of oxides and oxides on the surface of the metal due to its interaction with oxygen-containing elements and other certain chemical reagents.
Patination - the formation of a thin layer of chlorine and sulfur compounds by exposing the metal to the appropriate compounds. Both processes lead to a change in the color of the material, for which, under natural conditions, considerable periods of time would be required.
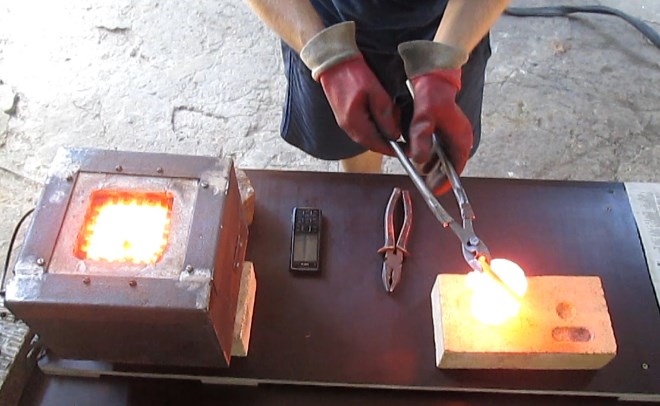
Step-by-step instructions for melting copper
Copper smelting, if you prepare everything necessary for the implementation of such a technological process and approach its implementation correctly, allows you to make copper products for both decorative and purely practical purposes even at home.
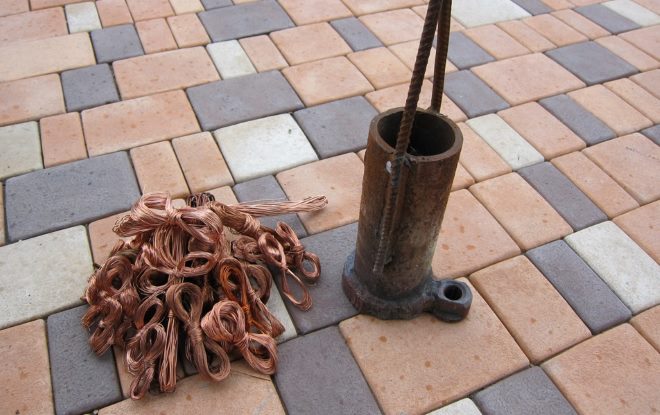
In order to melt copper, you will need the following tools, equipment and supplies:
- muffle furnace (preferably with adjustable heating temperature);
- a crucible in which you will melt copper (crucibles made of ceramic or refractory clay are used to melt copper);
- tongs with which the hot crucible will be removed from the furnace;
- hook (it can be made from ordinary steel wire);
- household vacuum cleaner;
- charcoal;
- the form in which the casting will be performed;
- gas burner and horn.
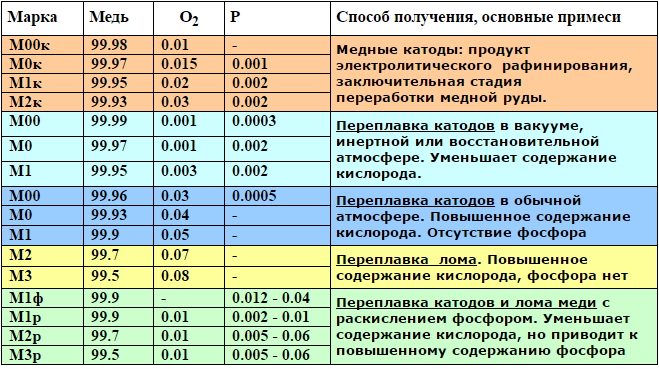
The smallest amount of impurities is found in electrical copper
Step one
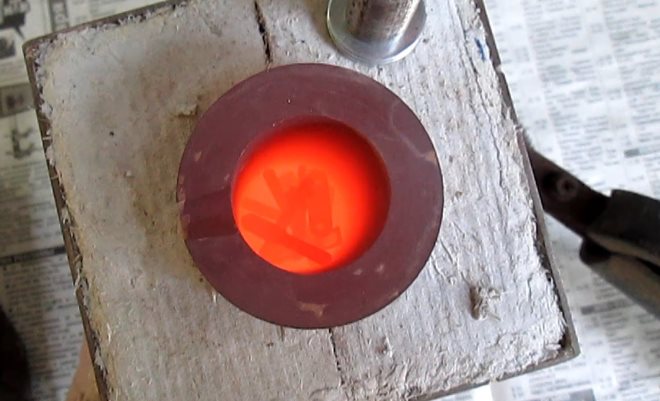
Copper in a crushed state is placed in a crucible. It should be borne in mind: the smaller the pieces of metal, the faster it will melt. The crucible, after being filled with copper, is placed in a furnace, which, using a temperature controller, must be heated to the required state. In the doors of serial muffle furnaces, a window is necessarily provided through which you can observe the melting process.
The viewing window will allow you to control the process without opening the door once again, thereby not lowering the temperature in the oven
step two
After all the copper in the crucible has melted, it must be removed from the furnace using special tongs. An oxide film is necessarily present on the surface, which must be moved to one of the walls of the crucible with a steel hook. The molten metal, after the release of its surface from the oxide film, should be poured as quickly and accurately as possible into a previously prepared mold. The details and rules for performing this procedure are well demonstrated by a video that is easy to find on the Internet.
It will be necessary to pour the metal into molds very quickly if the heating method you have chosen could not provide the desired temperature.
Step Three
In the event that you do not have a muffle furnace at your disposal, then you can heat up the crucible with copper using a gas burner, placing it vertically under the bottom of the tank
At the same time, it is important to ensure that the flame of the gas burner is evenly distributed over the entire area of the bottom of the crucible.
Step Four
If at home it is necessary to melt low-melting copper-based alloys (brass and some), then an ordinary blowtorch can be used as a heating device, also placing it vertically under the bottom of the crucible. During melting performed by this and previous methods, the surface of the molten metal will actively interact with oxygen, which will lead to intense oxidation. To reduce the intensity of oxidation, molten copper can be sprinkled with crushed charcoal.
Melting copper with a blowtorch in a homemade stove
Step Five
If your home workshop has a forge, it can also be used to melt copper, brass, or bronze. In this case, the crucible with crushed metal is placed on a layer of red-hot charcoal. In order for the process of heating and melting to take place more intensively, air can be supplied to the combustion zone of coal, for which a conventional vacuum cleaner is suitable, which works not for retraction, but for blowing. In the event that you will use a vacuum cleaner, a metal tip with a small diameter blowing hole must be made on its hose.
The melting process will be even more efficient in a gas furnace
When choosing a muffle furnace for casting operations with copper and its alloys, one should pay attention to the temperature regime that such a device can provide. Depending on the type of melted metal, such a furnace should provide the following heating temperatures:
- copper - 1083°;
- various grades of bronze - 930–1140°;
- brass - 880–950°.
It is possible that you decide to make a melting furnace yourself by watching the video.
Ordinary copper, which does not contain any alloying additives in its chemical composition, does not have good fluidity in the molten state, therefore, it is not suitable for casting products of complex configuration and small sizes. For these purposes, it is best to use brass, and choose an alloy whose surface color is lighter (this indicates that brass of this brand has a lower melting point).
Purpose of patination

Nowadays, copper patination is done artificially, but they pursue a single goal - to give things a rare look, to attract attention, to arouse a desire to purchase it.
Characteristics of copper
Copper is one of the first metals that man learned to extract and process. Products from copper and its alloys were used as early as the 3rd century BC, as evidenced by historical data and the results of archaeological excavations. The widespread use of copper was largely facilitated by the fact that it is quite easy to process by various mechanical methods. In addition, it can be easily melted.
Copper, the surface of which is distinguished by a pronounced yellowish-red color, due to its softness, can be easily processed by plastic deformation. The surface of copper, when it interacts with the surrounding air, is covered with an oxide film, which paints it in such a beautiful color.
Technical copper grades and their chemical composition
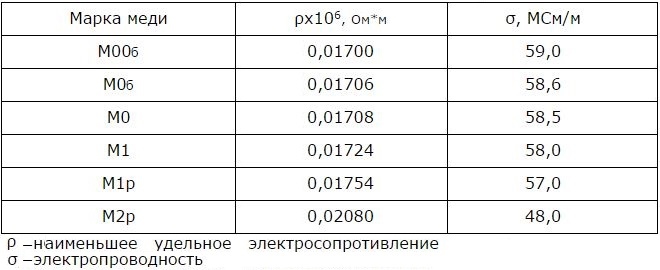
Of great importance are such characteristics of copper as electrical and thermal conductivity, in which it ranks second among all metals, second only to silver. Due to these properties, products made from it are actively used in the electrical industry, as well as in cases where it is necessary to ensure rapid heat removal from a heated object.
Another important parameter of copper, which directly affects the amount of energy and labor consumed in the production of products from it, is the melting point. For pure copper, the temperature at which the metal changes from solid to liquid is 1083°. If you mix copper with tin and get bronze, then the melting point of such an alloy will be already 930–1140 °, depending on the content of the main alloying additive in it. Such as brass, which is obtained by adding zinc to the base metal, has an even lower melting point, which is in the range of 900–1050 °.
Electrical properties of copper at 20°
If you decide to implement at home such a technological process as, it is important to know one more parameter - its boiling point. At 2560 ° copper begins to literally boil, which is clearly visible in the video of this process.
The appearance of bubbles on the surface of the liquid metal and active gas formation in it is facilitated by carbon released from copper as a result of its oxidation, which occurs during strong heating.
Subject to the melting technology, shallow pores may remain on the surface of the copper ingot, which can be easily removed by grinding.
How to melt copper at home
Items made of copper, as well as various products in which it is included, are widely used in everyday life. Therefore, many ask quite a standard question: “How to melt copper yourself?”
Having an idea about this technology, people learned how to make various objects from pure metal, as well as alloys obtained from it - bronze and brass.
- 1 Melting point
- 2 Copper melting
Melting temperature
Melting is a process that characterizes the gradual transition of a metal from a standard solid state to a liquid consistency. Each metal compound or metal in its pure form has its own temperature, under the influence of which it begins to melt.
An important factor in this case is what impurities are included in the composition of the melted compound.
So, copper begins to melt at a temperature of 1083 degrees Celsius. If tin is added to it, then the melting point will decrease and will be approximately 930-1140 degrees Celsius.
In this case, such a fluctuation is due to the amount of tin included in the alloy. A compound of copper and zinc melts at an even lower temperature - 900-1050 degrees. The heating of any metals is associated with the gradual destruction of the lattice formed from many crystals.
With heating, the melting temperature rises to the maximum required level, then its growth stops and remains at the reached level until the entire metal is melted, after which it begins to decrease.
Cooling is the reverse process of temperature change. As it cools, it falls and "freezes" at a certain level until the metal is completely solidified.
Thus, carbon comes out of copper during the boiling process, formed as a result of oxidation and its close contact with air.
Melting copper
The technology of melting copper has been widely used since ancient times, when people used a fire to melt metal to make arrows, arrowheads and other weapons, and household items.
Melting copper at home is also possible. For this you will need:
- The crucible where the copper will be melted, and the tongs needed to remove the crucible from the furnace or remove it from the fire.
- Charcoal.
- Muffle furnace (it is better if the heating temperature is regulated in it).
- Horn.
- Ordinary vacuum cleaner.
- A mold into which molten liquid is poured.
- Hook made of steel wire.
- Gas burner, if there is no muffle furnace.
The melting algorithm includes several step-by-step steps:
Grind the metal and pour into the crucible. Moreover, the smaller the fragments, the sooner it reaches the molten state. Put the crucible in a furnace heated to the highest possible temperature necessary to start the melting process (here, by the way, you will need a temperature controller). Many muffle furnaces have a window cut into the door. Through it, you can safely monitor the process.
Upon reaching the liquid, finally molten state of the copper, the crucible with tongs should be tried as carefully as possible and removed from the furnace as soon as possible. A film will form on the surface of the liquid substance, move it to the edge of the crucible using a wire hook. Pour the metal cleaned from the film as quickly as possible into a pre-prepared form.
If there is no muffle furnace, copper can be melted using a conventional gas burner. But then copper will be in close contact with air, and the oxidation process itself will be much faster. Therefore, to prevent the formation of a thick film on the surface of the metal, copper, when it reaches a liquid state, is sprinkled with crushed charcoal.
You can also melt copper and its alloys with a forge. To do this, charcoal needs to be heated well and a crucible with metal should be placed on it (pre-grind copper). To speed up the heating process, direct a vacuum cleaner on the coal, switched on in the blowing mode
Particular attention should be paid to the tip of the pipe. It must be metal, because the plastic will melt under the influence of high temperature.