Progressive heating systems
The device of modern heating systems for private houses is fundamentally different from traditional methods of heating. Heating technology is developing rapidly every year. Equipment is getting better and more efficient.
There are new sources of energy that meet the requirements of environmental protection and the overall comfort of equipment operation.
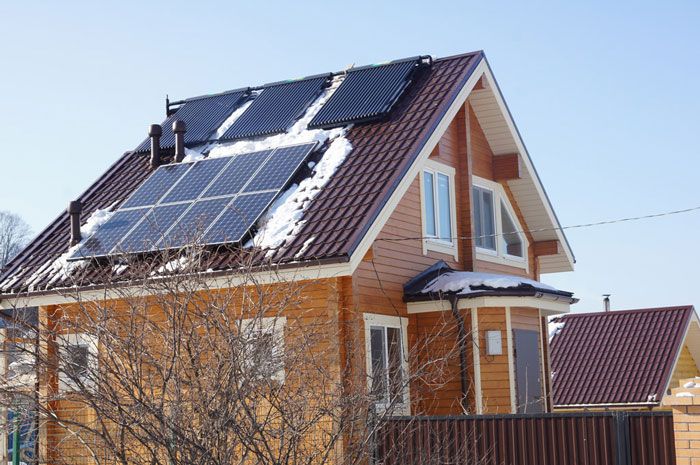
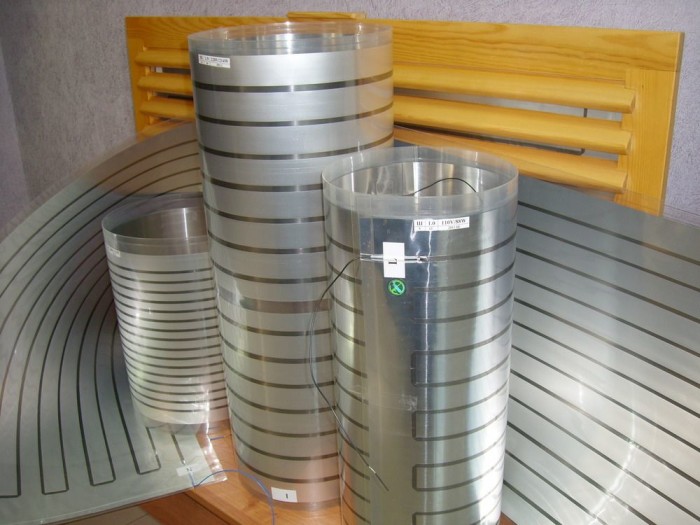
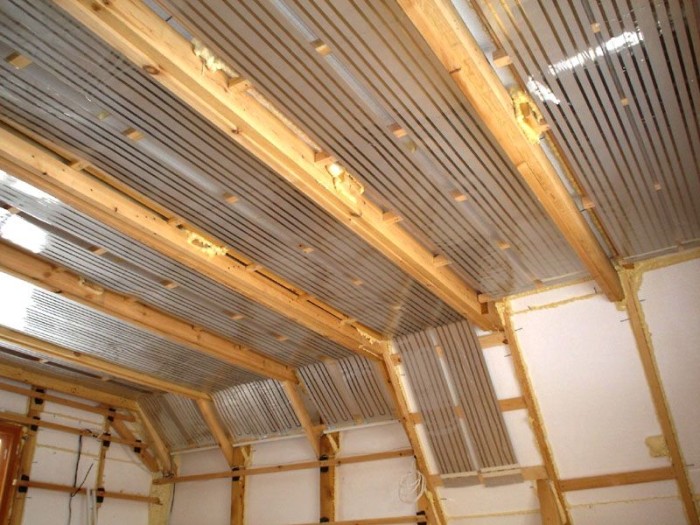
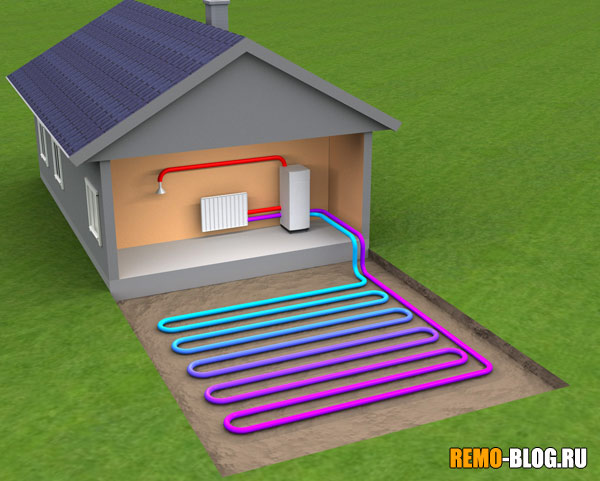
An innovative development of Russian scientists is the PLEN infrared heating system. It consists of the thinnest polymer film and a resistive-heating element made of carbon filaments.
PLEN emits the thermal component of sunlight, which is absorbed by the floor, ceiling, furniture and creates a comfortable room temperature.
Specifications
The maximum surface temperature of this structure is 60°C, but 30° - 40°C is enough to create the most comfortable conditions in the house.
PLEN can be laid over the entire surface of the base of the room, covered with laminate or any other type of coating on top. If you mount the system on the ceiling, you will get a feeling of warmth and comfort like from the sun. It is also possible to attach the structure to the walls, but its effectiveness will suffer from this.
One of the advantages of a film heater is the absence of a liquid heat carrier. This eliminates the installation of complex systems, leaks, freezing of the liquid. In addition, film heating systems have a number of other advantages:
- do not dry the air;
- there are no intense heat flows;
- do not create convective currents;
- fireproof;
- easy to install;
- completely safe for humans and the environment.
Another argument in favor of PLEN for a country house is the many years of research by scientists. They proved that long-wave infrared radiation at moderate power has a beneficial effect on the human body.
The main disadvantage of the infrared heating system is its high cost. For the device of the heating system of the whole house, you will have to make serious financial investments, which will not pay off quite soon.
2.Ventilation system
Target:
Familiarize yourself with ventilation systems
principles of their action.
Main
The purpose of ventilation is to maintain
the premises of the given meteorological
conditions and clean air.
ventilation
system is a collection of devices
for processing, transporting, feeding
and air removal.
Air,
supplied or entered into the premises,
calledinlet.
The air expelled from a room is called
exhaust.
By
the purpose of ventilation is: supply,
exhaust, supply—exhaust.
Depending on the mode of movement
air ventilation can be natural.
exhaust
ventilation
exhaust
ventilation does the opposite.
action in relation to the supply
ventilation. Exhaust ventilation removes
polluted and exhaust air from
premises
For efficient work
exhaust ventilation it is important that the volume
exhaust air compensated
the corresponding volume of inlet
air
Supply
ventilation
System
supply ventilation consists of supply
chambers and air vent systems for
air supply to the room. To types
supply ventilation include air
souls, air oases, air curtains.
Supply ventilation is used for
supply of clean fresh
air in the required amount.
Supply ventilation does not remove
exhaust air, it replaces it
with an influx of pure and fresh
air from outside. When replacing a used
air in the room with the help of the supply
ventilation occurs air outflow
through not tightly closed windows, doors,
openings or natural exhaust system.
Supply and exhaust
ventilation.
Principle
the operation of this ventilation system is based
on creation of 2 counter flows of air.
Such a system can be built on
basis of independent inflow systems and
air extractors, each with its own
fans, filters, automation
etc., or on the basis of the relevant
tasks of a complex installation, which
Works for both air supply and
to his draw.
V
depending on the type of organization
indoor air exchange, ventilation
may be local or general.
General exchange
ventilation is designed to create
and maintaining the necessary parameters
microclimate throughout the working
room zones. It is applied if
the room has a small amount
various harmful substances.
local
ventilation
called one in which the air
served at certain places (local
supply ventilation) and polluted
air is removed only from the places of formation
harmful emissions (local exhaust
ventilation). Local supply ventilation
can provide an influx of clean
air (previously purified and
heated) to certain places. AND
Conversely, local exhaust ventilation
removes air from certain places with
highest concentration of harmful
impurities in the air. An example of such
local exhaust ventilation can be
hood in the kitchen, which is installed
over a gas or electric stove.
The most commonly used systems
in industry.
By
way of creating pressure and moving
air
natural and artificial (mechanical)
prompting
At
natural ventilation
air exchange is carried out due to
pressure difference inside and outside
building. The pressure difference is due
primarily due to the thermal pressure arising
because the warmer air in
room has a lower density than
colder air outside.
Natural ventilation can be
unorganized and organized.
Key elements of the system
If in a city apartment the user is only interested in batteries, then in private households all the main elements of the heating system are important.
Boiler

This is a heat generator that converts the potential of energy resources into heat. Devices differ in the type of fuel used:
- Gas. The most economical devices. They are beneficial primarily because of the low cost of main gas. Liquefied or bottled fuel raises the cost of a kilowatt of thermal energy at times.
- Solid fuel. In terms of economy, they confidently occupy the second position. They can be used in almost any region of the country where there is a resource that can burn. Firewood, coal, briquettes, peat, solid organic waste, etc. are used as fuel. The main inconvenience is the need for frequent fuel loads.
- Liquid fuel. They can work fully automatically. They are used infrequently due to the relatively high cost of raw materials and the smell emitted during operation. It is also unsafe to store stocks of flammable liquids in a personal plot.
- Electrical. Use the most expensive resource. Very rarely mounted as the main source of heat. Much more common as an additional option. Combined with any other of the above heating methods.
Manufacturers even offer combined heating boilers for sale. When purchasing such equipment, it should be borne in mind that the efficiency of the device is inferior to specialized models.
Pipes
Trunks made of steel pipes are quite often installed in urban high-rise buildings to this day. But in private construction, mainly more modern materials are used:
- Galvanized steel.It is not inferior to traditional black steel in strength, and significantly exceeds it in corrosion resistance.
- Corrugated stainless steel. In addition to all the advantages characteristic of galvanized metals, it bends perfectly. Connections are made with special fittings and silicone seals. When assembling highways, threads are not used, which allows you to complete work quickly.
- Polyethylene. Lightweight and durable polymer is connected with an ordinary low-temperature soldering iron. For heating and hot water systems, manufacturers offer pipes reinforced with fiber or aluminum. They are very strong and have a low coefficient of linear expansion.
- Cross-linked polyethylene. An excellent material for arranging the popular "warm floors". High resistance to temperature fluctuations, mechanical strength and flexibility distinguish it from ordinary polyethylene.
Radiators

The retail network is saturated with a variety of offers. Like pipes, heating devices are usually distinguished by the material of manufacture:
- Cast iron. Good corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance. Do not withstand sharp impacts and frequent cycles of "heating-cooling".
- Steel. There are several versions of these devices - tubular, plate, registers and convectors. Vulnerable to rust, and lamellar models and to mechanical stress. Favorably low cost.
- Aluminum. Another relatively inexpensive type of device. They have excellent heat dissipation and resistance to oxidative processes. Cannot be used in systems containing copper. These two metals form a galvanic pair, which negatively affects the service life of aluminum radiators.
- Bimetallic. A successful design solution that allows you to combine the advantages of two different metals in one device.
Here is a brief summary of the main distinguishing features and structural elements of heating systems for a private house. There is no ready recipe for heating. For each building there is always an exception that is categorically not suitable for another.
It is important to involve qualified specialists with extensive practical experience in the drafting of the project. Their knowledge will help to avoid many mistakes.
Autonomous heating, what is it Apartments or houses, which is better
Now many apartments are tied to central heating, that is, there is a boiler room that supplies them with heat and hot water. It's not always cheap, or rather it's not always cheap! Because the systems (pipes) are often worn out, there is a huge loss of heat, and the management companies have a free hand, they can wind up as much as necessary. In general, we overpay for such heating mercilessly! However, now more and more developers are presenting apartments with the so-called autonomous heating, and this living space is a little more expensive, but later it quickly pays off. If you do not know what it is, then read our article ...
Let's start with a definition.
Autonomous heating is an autonomous heating system for an apartment or house that does not come into contact with external central systems. Usually you have either a gas boiler or an electric boiler in your apartment - you yourself already regulate the heat supply and water heating.
That is, no losses to the central system, just turn it on at home and enjoy, very reasonable and logical. Now let's go over the main systems that can be installed in apartments.
Requirements for heating industrial premises
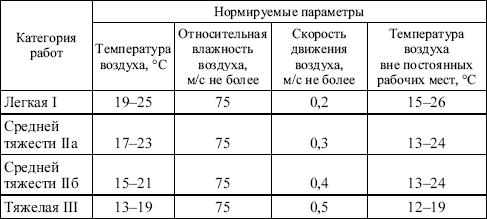
At low temperatures, heating of industrial premises, as required by labor protection, should be carried out in cases where the time spent by workers there exceeds 2 hours. The only exceptions are premises in which the permanent stay of people is not necessary (for example, rarely visited warehouses).Also, they do not heat structures, being inside of which is equated to carrying out work outside buildings. However, even here it is necessary to provide for the presence of special devices for heating workers.
Labor protection imposes a number of sanitary and hygienic requirements on the heating of industrial premises:
- heating indoor air to a comfortable temperature;
- the ability to regulate the temperature due to the amount of heat released;
- inadmissibility of air pollution with harmful gases and unpleasant odors (especially for furnace heating of industrial premises);
- the desirability of combining the heating process with ventilation;
- ensuring fire and explosion safety;
- reliability of the heating system during operation and ease of repair.
Other options
Of course, now there is also heating with solid fuel (coal, firewood), but it is difficult to use it in apartments! You will not store bundles of firewood for the winter, will you? And yes, it is a fire hazard.
Alternative sources, this is another matter, now there is geothermal, solar, wind, etc. heating. Of course, the efficiency is not always 100%, but if you combine all three at once, it can turn out not even bad - I would say almost for nothing.
Probably, now many people thought - damn it, how cool, I also want to heat up autonomously in the apartment, I’ll cut off these “central” radiators - I don’t need them! Yes, guys, I thought so too, but our government doesn’t think so, you can’t just cut off the batteries in the apartment! We are reading this article. Therefore, those who have central heating may not even dream of installing autonomous heating for themselves.
That's all, I think now you understand - what it is and why it is needed at all
If you are buying a new apartment, pay attention to this!. Read our construction blog
Read our construction blog.
natural ventilation
Natural
ventilation in the premises takes place under
the influence of thermal (arising in
as a result of density difference
indoor and outdoor air) and
wind (resulting from
wind action) pressure. Natural
seepage ventilation
air through loose external
fences - walls, windows, doors, etc., -
called infiltration.
Natural air exchange
volumes of supplied and
exhaust air and which depends
from random factors is called
unorganized natural ventilation
(ventilation).
Organized
natural ventilation, which
accurately, in accordance with external
meteorological conditions and in advance
given volumes regulate the supply and
removal of air is called aeration.
V
production area due to
heat gain from the equipment,
heated metal, people temperature
air, both in winter and in summer
the time of the year is higher than the temperature
outside air. Medium pressure
air in the room is almost equal
outside air pressure. but
equality of pressures is observed only in
some specific horizontal
plane lying approximately in the middle
the height of the room and the called plane
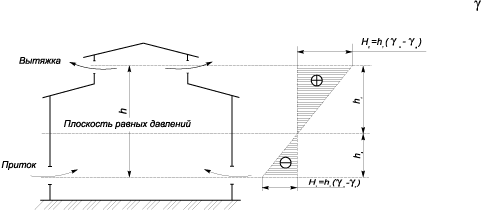
equal pressures (Figure 2). pressure on
level of this plane can be taken
equal to zero. Then the pressures created
columns of air from the center
lower open receptions up to the plane
equal pressures, will be inside
premises h1gV,
and outside
h1gH.
Therefore, at the level of the center of the lower
openings creates a vacuum H1,
through which air enters
through the lower opening into the room, and on
level of the center of openings located
above the plane of equal pressures, is created
pressure H2,
causing air to move out of the room
out.
V
as a result of the pressure difference
air exchange with air flow through
bottom openings and hood through the top.
Drawing
2. Pressure distribution in the building
Pressure
(Heat head) NT,
through which air is exchanged
indoors, same
|
(4) |
where
gn
— outside air density, kg/m3
gv
— density of internal air, kg/m3
h
- the height of the device for
air emission from the workshop, m (see Figure
2).
Lower
part of supply aeration openings
for the warm season should be
at a level not exceeding 1 m from the floor plane,
and for cold - at the level of 4-6 m.
Aeration
- the main type of ventilation of one-story
industrial buildings, especially
with heat surpluses.
At
natural ventilation device
multi-storey buildings are laid
exhaust ducts in the thickness of the walls or
arrange special exhaust shafts.
In order to use wind energy
to increase the natural (gravitational)
drafts over exhaust ducts or shafts
install special fittings
called deflectors. When flowing
cylindrical deflector blown on
5/7 of its circumference creates a reduced
pressure (vacuum), as a result of which
thrust increases in the air channel.
According to the type of heat carrier, systems of water, steam, and air heating are distinguished.
Comparative
the characteristic of heat carriers allows
choose the right type of coolant
(heating) taking into account economic,
technical and fire safety requirements.
The coolant must be non-flammable,
heat-intensive, mobile and cheap. Along
with this he must not degrade the sanitary
conditions in heated rooms.
As
coolants in heating systems
water, steam, flue
gases and air.
Water
easily exposed to heat in a wide
temperature range, has a large
heat capacity, which makes it possible to transfer
significant amounts of heat
its small consumption. In central and
local industrial heating systems,
residential, public and administrative
buildings are more likely to use water from
temperature 60-95 С,
so the mains temperature
pipelines is relatively low
and heat losses in water systems
heating is much less than in
steam heating systems. At
coolant "water" heat transfer from
heating appliances to air
rooms can be controlled from
substation by changing
water temperature. This allows for
climate change is easy
change the thermal regime in heated
premises.
Main disadvantages
water as a heat carrier is
that it has a high density,
therefore, when moving it, it is required
high energy costs, and
prolonged emergency shutdown of the system
possibly freezing.
Water
steam used in heating systems,
condenses in heaters,
releasing the latent heat of vaporization.
High heat content of steam and low
density allows you to transfer to
long distances
amount of heat at low cost
energy. In steam heating systems
water vapor is used at a temperature
105-130 С.
At the same temperature of water and steam
heat transfer from a steam heating system
higher than with water heating.
but
steam has significant disadvantages,
significantly limiting area
its application. In heating systems
steam heating heating
devices have a temperature of more than 100 С,
at which the organic dust settled
on the surface of devices, decompose
and products are released into the room air
decomposition (including oxide
carbon). With this coolant
central adjustment not possible
heat dissipation of heating devices.
Smoke
gases are the heat carrier in
heating installations operating
when burning solid, liquid or
gaseous fuel. Heat transfer
from combustion products to room air
carried out by heating structures
ovens or appliances. Flue gases in
heating installations have a temperature
from 1300 С
in the firebox up to 130 С
at the outlet of the chimney. red-hot
sooty particles contained in smoke
gases, in the absence of a spark arrester on
chimney can be a source
ignition of combustible roofs and
other combustible items.
Air
has low heat capacity and density,
its temperature in heating systems
does not exceed 70 С.
Supply air over long distances
with air heating is impractical.
The advantage of air as a heat carrier
is the ability to provide
heated rooms necessary
sanitary and hygienic conditions.
In terms of fire
water, steam and air, taking into account their physical
properties are not hazardous
(there are cases when the destruction
water or steam system piping
heating during a fire led to
fire suppression). However, in
industrial premises can
substances capable of
contact with water or steam to form
explosive mixtures, spontaneous combustion
or self-ignite, so for
of these premises, the use of water or
couple is not allowed.
fire department
the danger of heating systems is due
the presence of heated surfaces of the elements
heating equipment (heaters,
heating devices, pipelines
and etc.). So, in systems of steam and water
heating with pump recirculation
water temperature surface heating
appliances can exceed 100С.
At this temperature it is possible
self-ignition of substances such as
carbon disulfide, acetaldehyde, etc. Therefore
for rooms that use
given substances, coolant temperature
should be below temperature
self-ignition of the most dangerous
substances.
flammable
properties of heat transfer fluids should
take into account when developing activities
fire protection and selection
heating systems.
What are heating systems
Systems
with forced and natural
circulation. What is their difference? V
system with forced circulation
the movement of the coolant is carried out
using a circulation pump.
The advantages of such a system are: comfort
(it is possible to maintain a given
temperature in each room), more
high quality, small diameter
pipes, less temperature difference
hot water coming out of the boiler and
returning to the boiler cooled down
(increases the service life of the boiler). Basic
and, perhaps, the only disadvantage of such
systems - the pump requires
electricity. In system with natural
circulation there is no pump. The role of the pump
it performs the gravitational force,
arising due to the density difference
(specific gravity) of the coolant in the supply
and return pipes (density of hot
less water, i.e. it is lighter than
cold). Such a system requires
large diameter pipes (to reduce
resistance), it is practically not
amenable to regulation, and
use you get less
comfort with high fuel consumption.
WAYS
PIPING TO RADIATORS
Exists
two ways of piping to heating
devices - one-pipe and two-pipe.
With two-pipe for each radiator
two pipes are connected - "straight" and
"reverse". This wiring allows
have the same temperature
at the entrance to all devices. Two-pipe
wiring can be of two types: a) with
parallel connection of radiators
(see fig.2), b) radial (collector),
when from the collector "beams" to
each heating device is supplied
two pipes - direct and reverse. Minus
beam system - high pipe costs.
Plus - easy adjustment of heating
instrumentation and system balancing. At
single pipe wiring (see fig. 1)
the coolant passes in series
from one radiator to another
cooling down. Thus the last
the radiator in the chain can be significantly
colder than the first. If you care about
as a heating system - choose
two-pipe system that allows
regulate the temperature in each
room. The only plus of one-pipe
systems - lower price.
Rice. one
Single pipe wiring
Rice. 2
Two-pipe wiring with parallel
connecting radiators
OP -
heater
1 - straight
2
- reverse
on
relative position of the main
elements:
CENTRAL
LOCAL
Central
called heating systems
Designed for heating
several rooms from one thermal
point where the heat generator is located
(boiler room, CHP)
Local
heating systems are called this type
heating, in which all three main
elements are structurally combined in
one device installed in
heated room. (example oven,
gas and electrical appliances,
air heating units).
on
type of coolant:
steam
water
air
combined
on
coolant circulation method:
systems
with natural circulation
(gravity)
artificial
circulation
(pumping)
on
location of supply and return
highways:
top-mounted
supply lines (in the attic or
under the ceiling of the upper floor)
with the bottom
the location of both highways (according to
basement, above the floor of the first floor or in
underground channels)
on
location of supply and return
highways:
top-mounted
supply lines (in the attic or
under the ceiling of the upper floor)
with the bottom
the location of both highways (according to
basement, above the floor of the first floor or in
underground channels)
on
heating circuit diagram
appliances:
two-pipe (in which
hot water enters the appliances
one riser, and chilled water
assigned to others)
Single pipe (in
which hot water is supplied to appliances
and chilled water is discharged from them
one stand)
Heat carriers.
Wateris a liquid
practically incompressible medium
significant density and heat capacity.
Water changes density, volume and viscosity
depending on the temperature, and the temperature
boiling depending on pressure,
able to absorb or release
gases soluble in it when changing
temperature and pressure.
Steam
is an easily mobile medium with
relatively low density. Temperature
and vapor density depend on pressure.
Steam significantly changes the volume and
enthalpy during the phase transformation.
Air
is a highly mobile medium
relatively low viscosity, density
and heat capacity, which changes the density
and volume as a function of temperature.
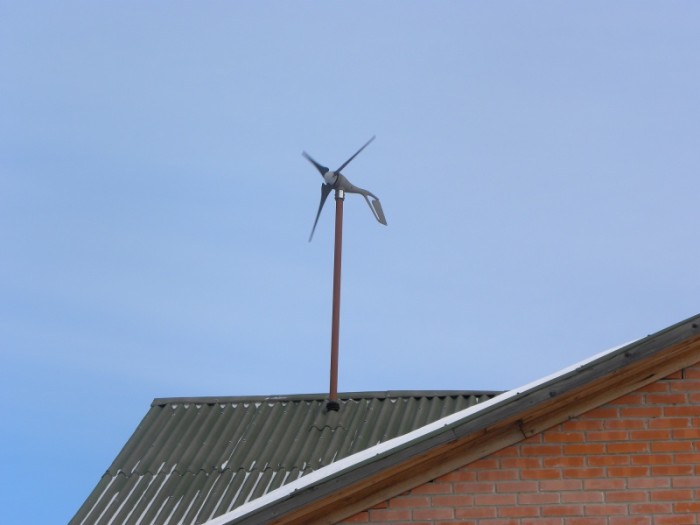
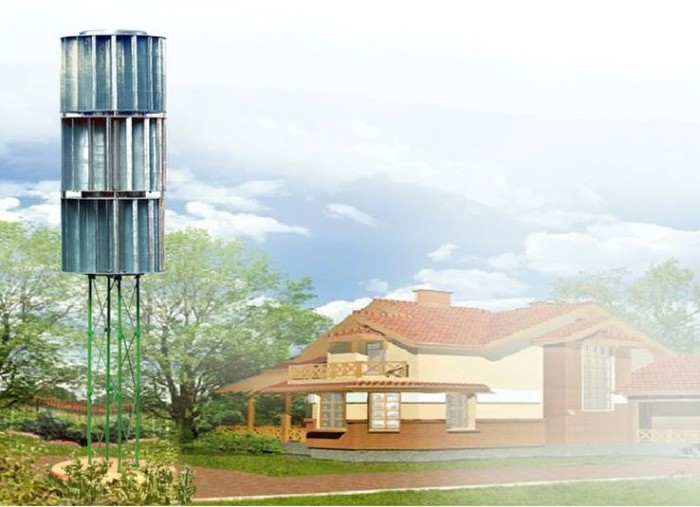
Wind power generator
Wind energy has long been used to generate electricity. But it can also be used to heat suburban housing. Scientists have created a gearless wind power generator, which is mounted on a vertical axis of rotation on the roof of a house. To reduce noise during operation of the structure, the axle must be equipped with a vibration isolator. An electric water heater and a heat accumulator are placed in the basement.
This device is quite difficult to manufacture, has a large size and weight. It is long and difficult to install. To obtain maximum wind energy, it is necessary to build a sufficiently high tower.
Pros and cons
The undoubted advantage of this type of heating is its environmental friendliness. Extracting energy from the wind does not cause any damage to the environment. In addition, this energy is absolutely free, and the cost of manufacturing and installing equipment is relatively low.
Despite the undoubted advantages, this method of heating country houses is not popular, due to the inconstancy of the strength and speed of the wind.
20 Placement of elements of the heating system in buildings
pad
pipes in the premises can be open
and hidden. Mainly used open
gasket as simpler and cheaper.
Hidden
gasket is provided only in
premises with high sanitary and hygienic
requirements.
Accommodation
eyeliners –
connecting pipe between riser or
branch and device - depends on the type
will heat the device and the position of the pipes in the system
heating. Supply and obr eyeliner
laid horizontally (with a length
up to 500 mm) or with a slope (5-10 mm for the entire length
eyeliners). Liners depending on
position of the longitudinal axis of the device along
in relation to the axis of the pipes can be straight
and with an indent called a "duck".
Accommodation
risers –
connecting pipes between lines
and eyeliners - depends on the position
highways and placement of connections to
heat appliances. The risers are laid
as a rule, at external walls it is open.
Distance from surface plaster up
pipes should be 3.5 cm.
risers are placed at a distance of 80 mm
between the axes of the pipes, and the supply risers
located on the right (when viewed from
premises). At the intersections
interfloor ceilings pipes enclose
in sleeves for providing free them
movement during thermal expansion.
Accommodation
highways
- connecting
pipes between local heating point
and risers - determined by the purpose
and the width of the building, the type of heating system.
In industrial buildings of the highway
laid on walls, columns under
ceiling, in the middle zone or near the floor, in
in some cases, highways are laid
on technical floors and underground channels.
V
civil buildings up to 9 m wide
highways can be laid along
their longitudinal axis. Also placed
highways at risers located at
interior walls of the building. In civil
buildings with a width of more than 9 m rationally
use two distribution lines
- along each facade wall
Highways
heating systems of civil buildings and
auxiliary buildings of industrial
enterprises are usually located in
attic and technical rooms on
a distance of 1÷1.5 m from the outer walls for
ease of installation and repair, as well as for
support for bending risers
natural compensation for their elongation.
In basements, in technical
floors and undergrounds, as well as in working
trunk lines to save
places are fixed on the walls. Highways
usually mounted with a slope that
in hot water heating systems
for withdrawal during operation
accumulation of air (in the upper part
systems), as well as for gravity descent
water from the pipes (in their lower part).
Highways
top wiring systems with artificial
circulation is recommended to mount
with a slope against the direction of travel
water in order to use
lifting force together with the force of the current
water to remove air. In gravitational
systems, laying is allowed
highways with a slope for the movement of water.
The lower highways are always laid
with a slope towards the heat point
buildings where, when emptying the system
water goes down the drain.
For
commissioning the system, and
to disable individual parts of the system
for repair on main heat pipelines
a shut-off and control valve is being installed
fittings: valves, gate valves or cocks
cork. On heating risers
hydraulic regulation,
disconnecting and emptying them are put
shut-off valves and cocks
cork. On connections to appliances
double adjustment valves are installed
or three-way valve. In auxiliary
rooms, stairwells and other
dangerous in relation to freezing water
taps are not installed.
Removal
air from heating appliances and from
of all sections of heat pipelines is
a necessary condition for normal operation
heating systems. In heating systems
with natural water circulation and
overhead serving position
lines for air removal
an expansion vessel is used
any additional devices.
In systems of water heating with lower
location of highways with natural
circulation to remove air
arrange a special air outlet
network by connecting it to the expansion
tank or air box. Of such
air systems can also be removed from
faucet faucet
Mayevsky.
V
water heating system with artificial
circulation speed of water
usually more than the ascent rate
air bubbles, and air bubbles
cannot move in the direction
opposite to the flow of water. So
in such systems, distributing main
heat pipelines are laid with a rise
to the extreme risers and at the highest points
systems install air collectors.