What types of heating schemes are
There are only two types of systems with natural circulation:
- Single pipe system. The pipe from the radiator enters directly into the boiler.
- Two-pipe heating system. The water that has cooled down does not immediately go through the pipe to the boiler, but first it goes into another line, and then goes back to the boiler.
If there is a vertical riser in the wiring diagram, then such a heating system is more convenient, since the heating device can be installed on each floor. But still, in a two-story house, gravitational heating, which has a horizontal wiring, is considered more profitable.
Rice. 2
The most important thing to know when installing gravity heating in a house is that radiators have little hydraulic resistance.
The best options for installation are:
- Cast iron radiators. They have the lowest hydraulic resistance.
- aluminum radiators.
- Bimetal radiators. They are also well suited for heating, but you need to consider before buying that the inner diameter must be at least ¾.
It is better to connect the batteries in the house to each other with different types of connections - this way the system will work better.
Pipes also need to be chosen wisely, since not all are suitable for a gravity system. All parameters must be observed. You must first look at what material the pipes are made of, and then at the diameter of the pipe itself. The cheapest option is simple metal pipes. But since they are rough inside, and after some time they will become even rougher (from corrosion, etc.), they need to be bought with the largest diameter.
The best options for the gravitational heating system of a two-story house are:
- Metal pipes.
- Reinforced polypropylene pipes.
In the first option, there are so-called fittings in the pipes that narrow the clearance, and this is unacceptable for gravity heating. Therefore, the most ideal option is the installation of reinforced polypropylene pipes. But even here there is a “but”. Reinforced pipes cannot withstand temperatures above 100˚C, but metal-plastic pipes can. Whatever option you choose, be sure to make sure that this is a quality product.
Rice. 3
Types of pumps
The choice of the injection unit can be approached from different angles. You will have to take into account the design of the unit when used as a supercharger specifically for a system that heats floors, and product labeling.
Determining the pump label

When choosing a circulation pump for a water-based underfloor heating system, the marking on the unit is of great importance. This two-digit numerical value, written with a dash, comes immediately after the model name. For example: 20–40.
The first number indicates the size of the connecting tube - 20 mm. As a rule, all mounting nuts are included with the unit. This number indicates their size.
The second number indicates the height of the water supply and injection in decimeters. That is, the number 40 will mean a feed of 4 meters. Thus, the pump will pump water with a pressure of 0.4 atmospheres.
The unit for circulating the coolant in the underfloor heating system can have three switching modes, which differ in the degree of performance. That is, each mode of operation will pump liquid with different effort. For example, the third mode is the most intense. Depending on the intensity of the pump, a different amount of electricity will be consumed.
Types of pump designs
By design, all units for circulating water in the underfloor heating system have common features.The differences mainly lie in the appearance and control method. The German-made units from Grundpos and Wilo can be considered the most reliable. The unit of the second company has a more affordable price. The above companies produce pumps for domestic use.

There are also circulation units for use in industrial premises. A distinctive feature is the fastening: for this, special flanges over 50 mm are used, and not nuts. This is due to the dual structure.
If the pump is planned to be used for a floor heating water system, then you need to purchase a unit with a three-way valve. It should be borne in mind that the valves have different performance. For example, some valves may have a rate of less than 2.5 m3/h. This indicator will be ineffective when using the heating system on an area of more than 50 m2.
Therefore, if you plan to use a pump with water floors on large areas up to 150 m2, then you need to buy a unit with the ability to control the operation of the valves, thereby allowing you to increase the intensity to 4 m3 / h.
How to choose a pump for underfloor heating according to the design parameters
The unit creates sufficient pressure so that the coolant can move at the desired speed. At the same time, the speed of movement of heated water should depend on the amount of heat required for a comfortable temperature condition of the room, depending on external weather conditions. For such purposes, you need to choose pumps with the ability to control and three speeds.
The selection of a pump for underfloor heating for heating will be made according to the following parameters:
- consumption;
- head.
But in each individual case, these parameters must be calculated. The following formula is used to calculate performance:
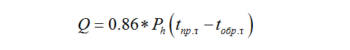
- Ph- heating circuit power, kW;
- t pr.t- the temperature at which the coolant is supplied to the circuit, gr .;
- t arr.t - temperature at the return pipe, gr.
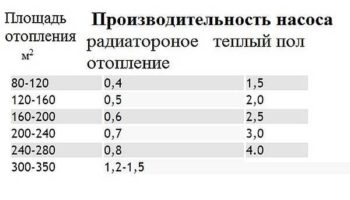
Usually the difference between the temperature at the outlet and at the return pipe is no more than 5 degrees. The power of the heating circuit is most often determined by the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated surface. In order to select the pump according to the required power, you can use a special table. All data in it are indicated for central Russia. Therefore, with more severe weather conditions or in the absence of good thermal insulation of the house, about 20% must be added to the pump performance obtained. In any case, the performance should be taken with a margin for the calculation of abnormal cold and so that the system does not operate at the highest degree of performance.
The second parameter that needs to be calculated for the pump is the head pumped by the pump blades. The pressure is needed to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the coolant conductors, fittings, as well as other elements of the system. Pipe resistance is determined by:
- pipe material;
- diameter.
The value of the resistance of the pipe should be in the documents, or you can use the average indicators. You will also need to take into account the resistance of fittings, mixers and valves. To calculate the pump head, you can use the following formula:
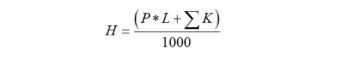
- P is the hydraulic resistance of pipes per linear meter, Pa/m;
- L is the length of the pipe contour;
- K is the power factor.
To calculate the required pressure in the water floor heating system, you need to multiply the resistance per meter of pipe by the length of the circuit. The resulting value in kilopascals will need to be converted to atmospheres. To do this, divide the value with the added safety factor by 1000.The adjusted result, called the pump duty point, can be compared with the marking on the unit.
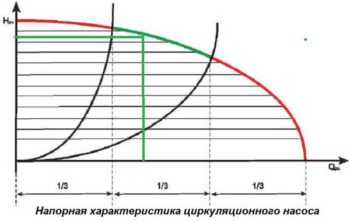
In order to select the desired model, you need to compare the result obtained with the data of a special graph. When choosing a model, you need to act in such a way that the operating point is in the middle third. If you plan to use a three-speed unit, then it is better to choose a model for the second speed. This ensures optimal operation of the unit in an acceptable mode with partial load.
Using a circulation pump is not a luxury, but a necessity. Even with small areas of the circuit, the natural circulation of the coolant will be weak. This will cause the discomfort of staying in the apartment, and will also require more electricity for heating.
Foreword
The methodological guide summarizes
fundamentals of the theory of natural circulation
in boilers and steam generators, is given
hydraulic
calculation of boilers with natural circulation
and evaluation of reliability indicators
natural circulation. In the application
manuals are graphs, tables and
nomograms required to perform
course work. For calculations
theoretical
drawing of the boiler body, so the composition
application included hull drawing
high-pressure boiler type KVN-98/64
(KVG-3).
The need to issue this
methodological manual due to the fact
that in the literature describing the principles
and methods for calculating steam boilers,
only general principles are stated
carrying out EC calculations, without description
the method of calculation itself.
When writing the manual, the basis was
adopted a method for calculating the natural
circulation set out in the textbook
Indeikina A.I., Aleksandrovsky Yu.V. and
etc. “Ship steam boilers. Basics
theory and calculations”, publishing houses
Leningrad Higher Naval
engineering school. IN AND. Lenin (now
Naval Engineering Institute) and
based on the calculation method,
developed by the Central Boiler Turbine
institute, St. Petersburg. In the manual
the calculation method is given in
tabular form, more convenient for
work of the student audience.
Completion of course work on
hydraulic calculation of the steam boiler
will allow you to better understand the essence
physical processes that take place
operation of the steam boiler, and their dependence
from various factors.
Causes of poor coolant circulation
There may be no circulation of the coolant in the heating system for the following reasons:
- insufficient power of the circulation pump (or pumps, if there are more than one). For this reason, the coolant simply does not reach the radiators farthest from the boiler, so they are cold (or slightly warm, which is why it’s not easier anyway). On how to choose the power of the circulation pump, there are several articles and videos in the section on heating calculations;
- non-return valves are not installed. Usually their absence is "painful" for complex systems with several circuits. Check valves are used to ensure that the coolant moves along the desired circuit and in the desired direction (read more below);
- system contamination. It happens that the pipes are clogged all over the diameter - what kind of circulation is there! It is treated only in one way: by replacing the pipes. This is exactly the case when the best treatment is prevention. And "prevention" should be carried out at the stage of installation of the pipeline and radiators. First, make sure that debris does not get inside the pipes. To do this, first making sure that there is nothing inside, we close the ends of the pipes with something before installation. For example, it is convenient with simple plastic bags. Secondly, there may be debris in the radiators. Even new ones! So we check and get rid of;
- pipe diameter is too small.Small pipe diameter - high hydraulic resistance - the pump is not able to “push” the coolant through the entire pipeline - there is no circulation in the heating system (well, or it is so bad that it doesn’t matter that it doesn’t exist). Again, at the design stage, you need to calculate the hydraulic resistance;
- accumulation of air in the system (airing). Air, of course, is not garbage, but air congestion in the same way will not allow the coolant to circulate freely. Air locks may appear due to violations of the rules for installing the heating system. Getting rid of air is easy - install an automatic air vent at the highest point of the system and Mayevsky taps on radiators.
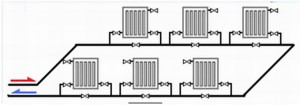
Coolant circulation in a combined branched heating system
Let's start the analysis of the circulation of the coolant with a complex system - then you will deal with simple circuits without problems.
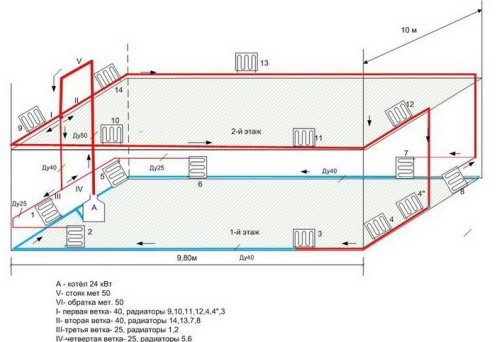
Here is a diagram of such a heating system:
It has three circuits:
1) boiler - radiators - boiler;
2) boiler - collector - water heated floor - boiler;
3) boiler - indirect heating boiler - boiler.
Firstly, the presence of circulation pumps (H) for each circuit is mandatory. But this is not enough.
In order for the system to work as we want it: the boiler is separate, the radiators are separate, check valves (K) are needed:
Without non-return valves, let's say we turned on the boiler, however, the radiators "for no reason" began to warm up (and it's summer in the yard, we just needed hot water in the plumbing). Cause? The coolant went not only to the boiler circuit, which we now need, but also to the radiator circuits. And all because we saved on check valves that would not let the coolant through where it is not needed, but would allow each circuit to work independently of the others.
Even if we have a system without boilers and not combined (radiators + water heated floor), but “only” branched with several pumps, then we put check valves on each branch, the price of which is definitely less than reworking the system.
general information
Basic moments
The absence of a circulation pump and generally moving elements and a closed circuit, in which the amount of suspensions and mineral salts is finite, makes the service life of this type of heating system very long. When using galvanized or polymer pipes and bimetallic radiators - at least half a century.
Natural heating circulation means a fairly small pressure drop. Pipes and heating appliances inevitably provide a certain resistance to the movement of the coolant. That is why the recommended radius of the heating system we are interested in is estimated at about 30 meters. Clearly, this does not mean that with a radius of 32 meters the water will freeze - the border is rather arbitrary.
The inertia of the system will be quite large. Several hours may elapse between the ignition or start-up of the boiler and the stabilization of the temperature in all heated rooms. The reasons are clear: the boiler will have to warm up the heat exchanger, and only then will the water begin to circulate, and rather slowly.
All horizontal sections of pipelines are made with a mandatory slope in the direction of water movement. It will ensure the free movement of cooling water by gravity with minimal resistance.
What is no less important - in this case, all air plugs will be forced out to the upper point of the heating system, where the expansion tank is mounted - sealed, with an air vent, or open.
All air will collect at the top.
Self-regulation
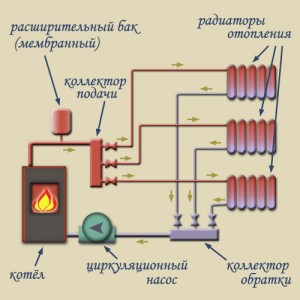
Home heating with natural circulation is a self-regulating system. The colder it is in the house, the faster the coolant circulates. How it works?
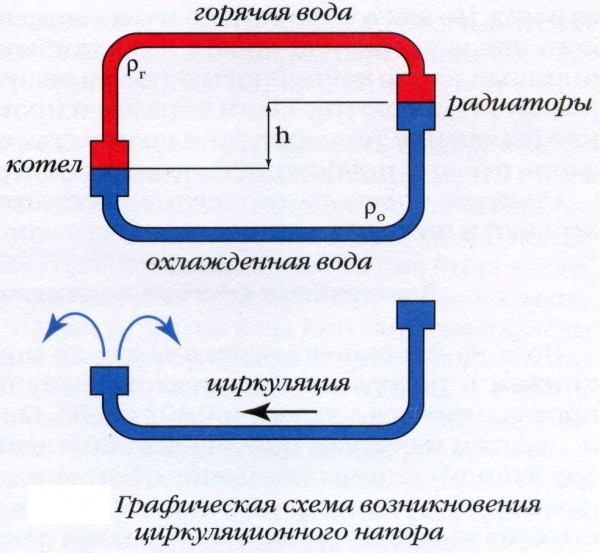
The fact is that the circulation pressure depends on:
Differences in height between the boiler and the bottom heater. The lower the boiler is relative to the lower radiator, the faster the water will overflow into it by gravity.The principle of communicating vessels, remember? This parameter is stable and unchanged during the operation of the heating system.
The diagram demonstrates the principle of operation of heating clearly.
Curious: that is why the heating boiler is recommended to be installed in the basement or just as low as possible indoors. However, the author has seen a perfectly functioning heating system in which the heat exchanger in the furnace furnace was noticeably higher than the radiators. The system was fully operational.
Differences in the density of water at the outlet of the boiler and in the return pipeline. Which, of course, is determined by the temperature of the water. And it is precisely thanks to this feature that natural heating becomes self-regulating: as soon as the temperature in the room drops, the heaters cool down.
With a drop in the temperature of the coolant, its density increases, and it begins to quickly displace the heated water from the lower part of the circuit.
Circulation rate
In addition to pressure, the circulation rate of the coolant will be determined by a number of other factors.
- Wiring pipe diameter. The smaller the internal section of the pipe, the greater the resistance it will provide to the movement of fluid in it. That is why for wiring in the case of natural circulation, pipes with a deliberately oversized diameter are taken - DN32 - DN40.
- Pipe material. Steel (especially corroded and covered with deposits) resists the flow several times more than, for example, a polypropylene pipe with the same cross section.
- The number and radius of turns. Therefore, the main wiring is best done as straight as possible.
- The presence, quantity and type of valves. a variety of retaining washers and pipe diameter transitions.
Each valve, each bend causes a pressure drop.
It is precisely because of the abundance of variables that an accurate calculation of a heating system with natural circulation is extremely rare and gives very approximate results. In practice, it is enough to use the recommendations already given.
Heating schemes for wooden residential buildings
It should be noted that the heating scheme in a wooden house is not easy. Of course, you can use electric, air and oven options. But most users opt for water heating systems.
A house made of wood has a high heat capacity, so more heat energy is needed to warm it up.
Heating scheme for a two-story residential building
A two-pipe system differs from a single-pipe system only in the order in which the heating elements are connected. Before each battery, it is recommended to put an adjusting tank. To ensure normal water circulation in a two-story house, there is always enough distance between the center of the boiler and the upper point of the supply pipeline. Therefore, the storage tank for heating can be equipped not in the attic of the room, but on the second floor.
Heating scheme of a one-story residential building
The scheme of such a system is simple.
In the private sector, a horizontal heating system is widely used, which is classified into dead-end and associated water movement systems. With a dead-end system, each of the batteries is located further from the boiler. Such a system can be easily unbalanced. Therefore, they set it up for a very long time. It should be noted that the associated heating system, the scheme of which involves a greater consumption of pipes compared to a dead-end one, is used mainly in simple heat supply systems.
When choosing a passing system, it must be taken into account that the circulation rings must be the same.
All radiators in the system work as one. Today, flexible hoses are very often used for home heating. They are used to connect heaters to the heating system.
Features and varieties of heating schemes with natural circulation
Heating with natural heat carrier current has been used for as long as pipe heating itself has long been invented.And the first time. And for a long time, only one scheme worked in the houses - with one pipeline, a single-pipe scheme with piping along the top. In modern heating schemes, this variety is practically not used, since the two-circuit scheme is recognized as more efficient. In addition, heating through two pipes can be arranged according to a scheme with a lower or upper wiring.
The list of advantages of natural heating over heating with forced circulation:
- Installation and operation of "physics" is much faster, easier and more economical;
- The "gravity" system has absolute independence from external factors - electricity, gas, etc. In forced systems, the heat in the house depends on whether the electric pump will work or not. In addition, when the pump is turned off, air jams will necessarily appear in the system, and all radiators will have to be checked for their presence or absence by opening the Mayevsky taps;
- The duration of guaranteed uninterrupted operation reaches 35-40 years with metal pipes. With PVC pipes or metal-plastic pipes, the system will last even longer, but due to its novelty, there are no such statistics yet;
- Stable heat transfer, provided by self-regulation of the system.
With proper wiring, observing at least a slight slope, even heating of the “warm floor” type can be organized, and this will not require large investments or labor costs. Self-regulation in a system with gravitational movement of the coolant helps to increase the speed of movement of hot water and, accordingly, increase the air temperature in the room, and in a forced circuit, on the contrary, automatic pressure control will reduce heat transfer.
- Small total length of pipes - with an increase in the length of the pipeline, it is necessary to increase the pressure, and this cannot always be done by means of the system, without turning on the pump. Therefore, natural water circulation is not suitable for multi-storey buildings;
- The system heats up for a long time - much longer than radiators in a circuit with a circulation pump. This happens due to the fact that all pipes and the air itself in the room must warm up well before the accelerated movement of the coolant begins;
- A clear disadvantage of a system with gravitational movement of the coolant is that for some short time the boiler burns fuel almost empty, and the heating efficiency is lower than that of a system with forced circulation.
The heating system of a two-story house with natural circulation updated: March 18, 2017 by: kranch0
Read on topic
Pipes, expansion tank and accessories of the heating system
In addition to boilers, other mandatory components must be present in any water heating scheme for a one-story house. These include pipes, radiators, safety groups, expansion tanks.
The choice of elements directly depends on the piping layout, the method of movement of the coolant (gravitational or forced), as well as the budget of the heat supply organization. Consider the minimum configuration of the system for heating circuits of a one-story private house with a pump and two-pipe piping:
- Pipes. For forced circulation, polypropylene models with diameters from 16 to 24 mm can be used. In a gravity system, this indicator should be at least 369 mm. Therefore, steel pipelines would be the best option for her;
- Expansion tank. For water heating of a one-story house with natural circulation, this is an ordinary container with two connection pipes. It is installed in the highest part of the circuit. In closed systems, membrane expansion tanks are used, mounted on the return pipe in front of the circulation pump;
- Safety group - selection and installation of an air vent and a bleed valve. Mandatory components for closed heating, in which the pressure is not equal to atmospheric.
In addition to these elements, the scheme may include others. Particularly the shut-off valve.It is necessary to limit the flow of coolant in certain parts of the system. To optimize the heating of radiators, thermostats are mounted. Without fail, Mayevsky cranes should be installed in the piping of the batteries. They are designed to timely remove air from the heating system.
If all the above options are unacceptable, you can consider installing film electric heating or convectors. They are relevant for one-story houses with non-permanent residence. Despite the high maintenance costs (cost of electricity), electric heating is characterized by low inertia and independence from the initial temperature in the room.
The video shows a scheme for organizing single-pipe heating of a one-story house:
Functional purpose of the pump
The operation of the entire heating system with a water coolant is based on the circulation of the latter. In order to achieve efficient heat supply, water flow must be carried out throughout the circuit. For example, if the house has an area of more than 100 square meters. m, it is necessary to use forced injection of water through pipes.

The circulation pump for a warm water floor pumps the coolant through the heating circuit and radiators at a uniform speed. Therefore, it is necessary to select a pump that is suitable for hydraulic parameters.
The coolant can circulate in two ways:
- naturally under the influence of the density difference between hot and chilled water;
- forcibly with a circulation pump.
If the heating system works on the circulation of the coolant in a natural way, then more fuel will be needed to maintain a high temperature in the supply line. After all, the circulation rate will depend on the density difference, and this difference will be greater with strong heating. A similar effect is reflected not only in the bill for electricity or gas, but also in the absence of a comfortable temperature in the apartment. For example, the rooms that are the first from the outlet of the boiler heat up strongly, while the remote rooms remain cold.
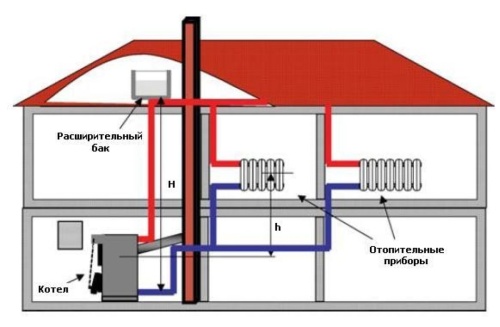
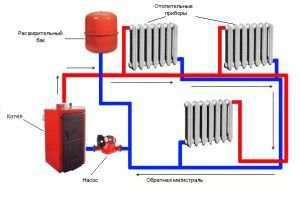
Heating systems with top water supply
The coolant - in this case water - is subject to heating and supply to the upper part of the heating system through a pipeline. The pipe used to supply water must have a larger diameter compared to the pipes that are responsible for supplying water to the radiator. This is necessary to achieve the greatest resistance to heat exchange. Horizontal pipes should be installed with a minimum slope of one centimeter per linear meter.
Tip: if you are going to use a heating system with natural water circulation, remember that the radiators must be connected using a diagonal method
After direct heating of the room, the water passes into the boiler through a specialized pipe - the return pipe. Here it is heated again and the cycle of water movement is repeated. The heating boiler is located in the lowest section of the system, under the radiators. Usually, these elements are installed in boiler rooms, for which basements are allocated.
Pipe diameter
To calculate the diameter of the pipes, you need:
- Perform a thermal calculation of the premises and add about 20% to the result.
- Calculate the cross section of the pipeline based on the ratio of the thermal power and the internal section of the pipe (the values \u200b\u200bare indicated in the tables of SNiP).
- Select the pipe diameter based on the heat engineering calculations performed and taking into account the pipe material. For steel pipes, the minimum internal section size is 50 mm.
In order for gravity to be more intense, the following principle is applied: the diameter of the supply pipe after each branch must be 1 size smaller than the previous one. The return must be collected with an extension.
Thus, the calculation allows you to determine the minimum diameter of the supply and return pipes, with respect to this value, the parameters of the pipes in different parts of the system are determined according to the prepared scheme for a one-story or two-story house.
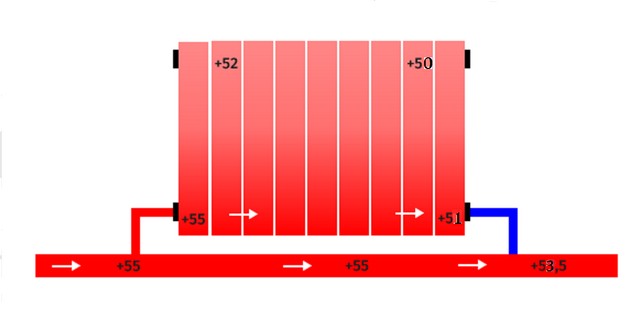
How does a properly assembled circuit work?
When performing the classic one-pipe scheme (“Leningrad”), when a main pipe is laid under the radiators, the situation is different. The moving coolant, meeting the first tee on its way, is distributed into two flows in accordance with the values of the hydraulic resistance of the straight path and the lateral branch of the tee. Due to the greater hydraulic resistance of the side outlet, a small part of the total coolant flow flows into the radiator (the usual "leakage factor" is 0.2-0.3). This small part cools down a few degrees inside the battery, as shown in the figure below, mixing at the outlet with the main uncooled stream. Its resulting temperature is higher than when the entire volume of liquid is passed through the heater.
The distribution of the coolant in the piping of the radiator of the "Leningrad" scheme.
When moving along the contour, the temperature of the liquid still decreases, but to a lesser extent, to a temperature of not 35 ° C, but approximately 45 ° C, i.e. the batteries in the chain are more evenly heated. Experts are of the opinion that the single-pipe circuit ("Leningradka") allows you to achieve uniform heating of up to 10-11 radiators in the circuit (ten sections in each device).