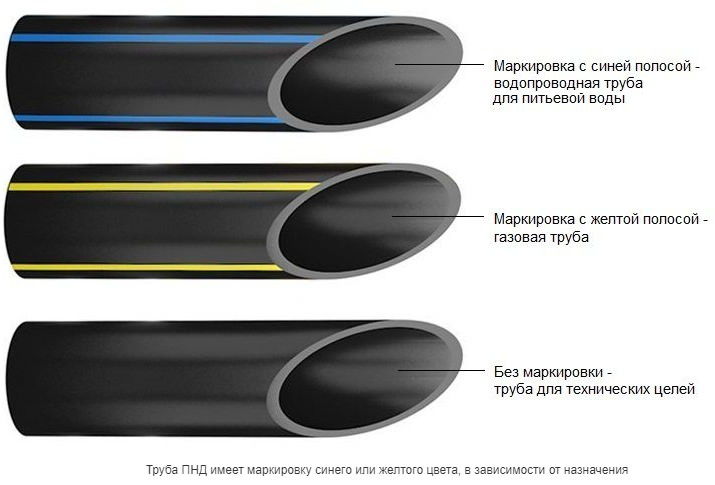
Advantages of using polyethylene pipes
Gas can be supplied in systems through steel or polyethylene lines. Steel pipes are used for all types of gas pipelines, polyethylene pipes are used only for underground laying. Polyethylene pipes are in great demand for gasification in the construction market, since they provide a lower budget for the costs necessary for the construction, maintenance and repair of a gas pipeline.
Polyethylene pipes have a number of advantages over other materials, namely:

- Not subject to aggressive environment, temperature changes, corrosion.
- Provide ease of installation (if necessary, pipe fitting, cutting).
- It is not required to create additional protection against the occurrence of a chemical reaction with any substances.
- The polymer is not a conductor of electric current, therefore, it protects against current “wandering” in the ground, which can cause an accident.
- The inner walls of polyethylene pipes are absolutely smooth, which increases the throughput of the gas pipeline, preventing clogging.
- They have an affordable cost, lower compared to analogues.
- The weight of polymer pipes is much less, which simplifies the process of transportation, storage and installation.
- They have a long service life, up to 50 years.
Laying underground gas pipelines
This type of installation includes laying a gas pipeline underground. As a rule, such installation requires pre-prepared dug trenches. In this case, one should take into account the depth of the dug channel and the wiring of communications according to the project, it should be at least 0.8 m. When choosing a location, it is necessary to take into account the distance to buildings, structures and other communications (sewerage, heating network). It is undesirable to lay an underground gas pipeline near trees, since their root system can make it difficult to repair and operate. When laying pipes and assembling a gas device in this way, the following points should be considered:
 Scheme of laying an underground gas pipeline
Scheme of laying an underground gas pipeline
- the gap between the gas pipeline and other underground utilities must be at least 0.2 m;
- at the intersection with communication collectors, gas pipes must be pulled in cases;
- the gas main is located above other engineering networks;
- cases should be removed from the intersection at a distance of at least 0.2 m;
- with the help of waterproofing materials, the ends of the cases are processed.
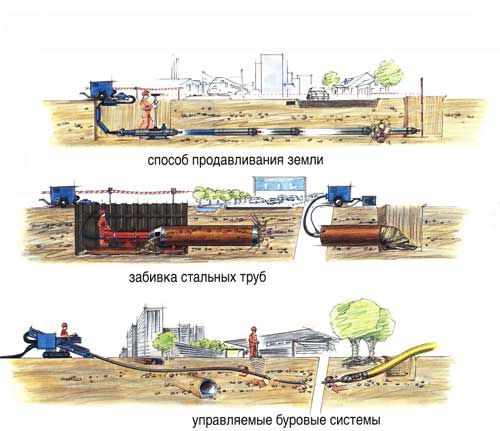
Another way of underground installation is trenchless laying. This option is the least expensive. The advantages of the trenchless method of laying a gas pipeline are as follows:
- yareduces financial costs for the installation of a gas pipeline;
- reduces installation time.
The underground method of laying a gas pipeline is the safest, however, the implementation of such installation is more expensive.
Types of fastening structures
Bearing fastening structures are divided into the following types:
- Fixed supports. When using this fastener, angular or linear movement of the fixed sections is not allowed.
- Guide supports. The use of this design allows displacement in only one direction. As a rule, only along the horizontal axis.
- Rigid pendants. Movements are allowed, but only in the horizontal plane.
- Spring hangers and supports. Both vertical and horizontal movements are possible.
Types of fastening pipelines to the wall
Requirements for supports and hangers
If fixation occurs between two fixed supports, movements that may occur as a result of temperature changes, mounting braces or displacement of supports must be self-compensating. But such a compensating ability, as calculations show, is sometimes not enough. In this case, special compensators must be installed.
Pipe clamp equipped with screw/bolt
They are made from pipes of the same type and diameter as the structure as a whole. Most often they are performed in the form of the letters "P" or "G".
If the structure is fixed fixedly, the fasteners must withstand the weight of the pipeline itself, the fluid that moves through it, as well as axial loads generated by thermal deformation, vibrations and hydraulic shocks. When mounting products made of polymers, movable supports are most often used.
If the installation is carried out in fixed supports, restrictive rings or segments 10-20 mm wide are welded to the pipes, which are made from pieces of pipes of the same plastic. These segments or rings should be located on both sides of the support.
Choice of fasteners
Suitable fasteners are selected taking into account many factors. The choice depends on the location of the installation site, on the purpose of a particular system, and so on.
Plastic pipe fixing
Sometimes the pipe must be insulated from the source of cold or heat. If you use a simple clamp that fixes the area, then it will not provide the gap from the adjacent surface necessary to solve the problem. But, for example, an annular support, which has a threaded extension and a plate for fixing to the supporting surface, will completely eliminate the problem.
If you have to fix heavy cast-iron pipes, then use special fasteners that can withstand heavy loads. For vertically located systems, it is installed on floors. Horizontally oriented systems are fixed not even one by one, but by groups of pipes laid on the console.
A competent approach to the selection and placement of fasteners allows for a long and efficient operation of the pipeline without fear of emergency situations. But do not forget about the economic component of this problem. After all, exceeding the required and sufficient number of elements can lead to an unjustified increase in the cost of the structure and complicate installation work.
What is an internal gas pipeline
The internal gas pipeline is the entire system of gas pipes located inside the building. The outer boundary of the internal gas pipelines is the outer surface of the walls or enclosing structural elements of the building, and their duration is taken into account to consumers - gas-using equipment. Simply put, these are all gas pipes that enter the wall of the building and lead to consumption devices. Consists of various elements:
- inputs.
- Risers.
- Apartment wiring.
All elements of the system, except for intra-apartment ones, should be located in non-residential premises (entrances) so that periodic inspection of pipes is possible. Also in the entrances should be located valves that require inspection.
Gas pipeline installation technique
Work begins with the introduction of pipes into the building. To do this, a case is placed in the outer wall and an input is made through it. Already inside, a riser is fixed, located 20 mm from the walls in a vertical position. Connections at this stage are made using a welding machine.
Cases should be located at all intersections of the pipe with interfloor ceilings, walls and stairwells.
Gas pipe fittings must be installed at a distance of at least 2 m from each other. These rules apply to pipes with a diameter of 25 mm.They should allow for the repair and diagnosis of possible damage during operation. The end of each of the fasteners is hammered into a special wooden plug located in the wall. After that, the attachment point is poured with cement mortar to give additional strength.
There are a number of rules for performing welding work:

- Welding can be performed on pipes with a diameter not exceeding 150 mm and with a wall thickness of up to 5 mm.
- Arc welding is used when the pipe thickness exceeds 150 mm or the wall thickness exceeds 5 mm.
- Before installation, it is necessary to prepare pipes for welding. To do this, they are cleaned of contaminants.
- Each welded joint must be easily accessible. Hiding seams in the wall or case is not allowed.
All connections are made by welding. Threaded connections are allowed only at the installation sites of shutoff valves, metering devices (gas meters), pipe connections with a hose leading directly to gas equipment.
Related video: Installation of a gas pipeline on the facade
A selection of questions
- Mikhail, Lipetsk — What discs for metal cutting should be used?
- Ivan, Moscow — What is the GOST of metal-rolled sheet steel?
- Maksim, Tver — What are the best racks for storing rolled metal products?
- Vladimir, Novosibirsk — What does ultrasonic processing of metals mean without the use of abrasive substances?
- Valery, Moscow — How to forge a knife from a bearing with your own hands?
- Stanislav, Voronezh — What equipment is used for the production of galvanized steel air ducts?
Requirements for domestic gas pipelines
The installation of internal gas pipelines must comply with certain requirements. Installation at your own discretion or on the basis of ease of installation is strictly prohibited. The most important issues include:
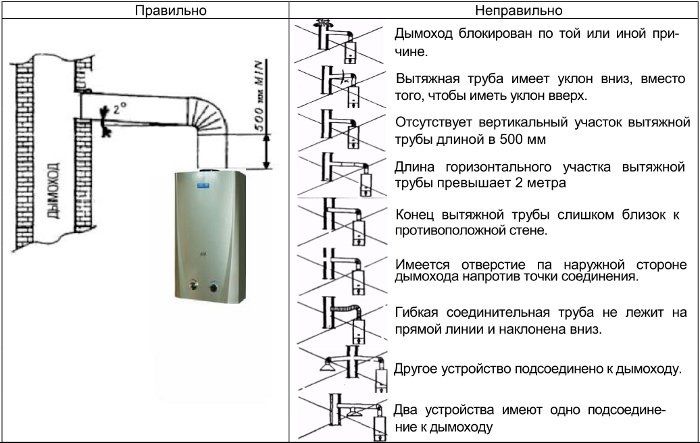
- Pipelines are introduced directly; laying a gas pipeline through other premises is prohibited.
- It is forbidden to cross air ducts that violate the mode of operation of the air-technical components of the building.
- The maximum permitted pressure is 3 kPa.
- In places where pipelines cross corridors, installation is carried out at a height of at least 2.2 m, but not less than 10 cm from the top of the pipe to the ceiling.
- Gas pipelines must be firmly attached to the walls with clamps, hooks or brackets.
- Free sagging of the pipeline due to its own elasticity is prohibited.
- It is not allowed to use one lowering for several devices, each of them must have its own.
The kitchen area should correspond to the number of stove burners:
- 2 burners will require 8 m2;
- for 3 burners - 12 m2;
- 4 burners will require at least 15 m2.
Requirements for the room in which the consumption device is located:
- well lit;
- it must have a ventilation duct. You can use special ventilation installations;
- the window unit must be equipped with a window (transom).
The device and use of internal gas pipelines must be carried out in compliance with all safety requirements provided for by SNiP and GOST. Any violations are fraught with criminal or administrative prosecution, depending on the severity of the detected violations.
Related video: Case in the wall for the gas pipeline, we carry gas to the house
A selection of questions
- Mikhail, Lipetsk — What discs for metal cutting should be used?
- Ivan, Moscow — What is the GOST of metal-rolled sheet steel?
- Maksim, Tver — What are the best racks for storing rolled metal products?
- Vladimir, Novosibirsk — What does ultrasonic processing of metals mean without the use of abrasive substances?
- Valery, Moscow — How to forge a knife from a bearing with your own hands?
- Stanislav, Voronezh — What equipment is used for the production of galvanized steel air ducts?
Specialty Installation and operation of equipment and gas supply systems Education66.ru
Specialties of secondary vocational educationInstallation and operation of equipment and gas supply systems
Graduate Qualification:
Technician
About the specialty: It's no secret to anyone what role gas plays in our lives. This includes heat in houses, hot water supply, and the ability to cook food. But gas is an explosive substance and working with it requires special permission, and most importantly, high-quality training of specialists, because people's lives depend on it. autonomous gas boilers, internal gas pipelines. And there are also industrial gas pipelines, which differ in other gas pressure parameters. Installation and operation of equipment and gas supply systems is a production area that deals with the operation, commissioning, design, construction, installation and repair of equipment and gas supply systems. All these subtleties can be learned in the specialty " Installation and operation of equipment and gas supply systems”. Full-time education in this specialty in Yekaterinburg is only available at an assembly college. Our graduates can work as a technician or foreman in organizations such as Ekaterinburggaz OJSC, Uraltransgaz LLC, etc. The main professional educational program is “Installation and operation of equipment and gas supply systems” provides for the study of the following academic disciplines and professional modules:
- Mathematics
- Informatics
- Ecological bases of nature management
- professional cycle
- Engineering graphics
- Technical mechanics
- electrical and Electronics
- Materials and products
- Basics of construction production
- Fundamentals of hydraulics, heat engineering and aerodynamics
- Fundamentals of geodesy
- Rationing of labor and estimates.
- Information technology in professional activities
- Legal support of professional activity
- Organization economics
- Management
- Occupational Safety and Health
Main activities: installation of equipment and gas supply systems in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documents, technical supervision of the construction and installation of gas supply systems; connection of newly constructed gas pipelines to the existing ones and launching gas into gas networks and equipment; performance of work to ensure reliable, safe operation of equipment and gas supply systems; acceptance into operation of equipment; localization and elimination of accidents in gas supply systems; shutdown of existing gas pipelines, their repair and replacement of damaged sections of the gas pipeline.
Entrance exams: (GIA, USE)
Without exams. Certificate competition.
Forms of study:
full-time part-time (evening) part-time.
Terms of study:
On the basis of 9th grade: 3 years 10 monthsOn the basis of 11th grade: 2 years 10 months
Professions:
WelderElectric and gas welderMechanic-repairman
Pipeline supports
- gas pipelines;
- oil pipelines;
- pipelines of thermal power plants and nuclear power plants;
- engineering communications of housing and communal services;
- industrial enterprises, etc.
Our production produces pipeline supports according to most existing standards, as well as according to individual drawings of the customer from ordinary steels or for the “northern version” from steel 09G2S.
Depending on the purpose and device, all supporting structures are either movable or fixed supports.
Movable pipeline supports
Movable supports of pipelines are focused on the perception of vertical loads, depending on the product flowing inside the pipeline and the weight of the pipeline itself. Structurally, movable supports consist of a rigid base, a semicircular metal holder, fasteners and gaskets.
Suspension supports are used to fasten horizontal pipelines.Hangers, which are attached to brackets, consoles, floors of structures using rods with bolts or welded springs, the dimensions of which are determined in each specific condition.
Fixed pipeline supports
Movable supports allow the pipeline to move, fixing any type of pipeline during deformations, in order to absorb linear elongations that occur when temperature changes, at the same time, fixed supports support the pipeline in certain places, experiencing vertical loads from its own weight and the weight of the galvanized or polyethylene shell of the employee. thermal insulation.
Horizontal loads are divided into horizontal axial and horizontal lateral. The force from horizontally lateral loads is transferred to those supports that are located in the places where the pipeline turns and near their attachment to the support. Horizontal axial forces are transferred to all available fixed supports. The production of all types of pipeline supports is carried out by albums and series in accordance with the requirements of OST and GOST for each specific support, taking into account the operating conditions and its scope.
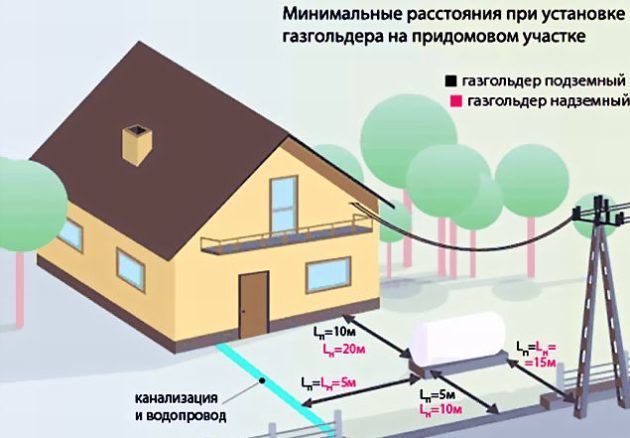
2 Underground gas pipelines
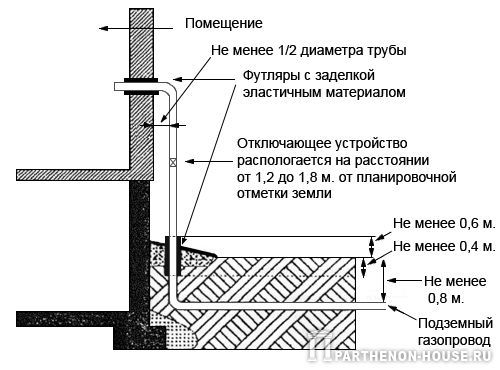
5.2.1 Laying of gas pipelines should be carried out at a depth of at least 0.8 m to the top of the gas pipeline, case or ballasting device, except as otherwise specified. In those places where the movement of vehicles and agricultural vehicles is not provided, the depth of laying steel gas pipelines should be at least 0.6 m. When laying gas pipelines on arable and irrigated lands, the laying depth should be at least 1.2 m to the top of the pipe.
In landslide and erosion-prone areas, gas pipelines should be laid to a depth of at least 0.5 m below the sliding mirror and below the boundary of the predicted destruction area.
(Changed edition. Rev. No. 2)
5.2.2 The vertical distance (in the light) between the gas pipeline (case) and underground utility networks and structures at their intersections is recommended to be taken in accordance with Appendix B*.
(Changed edition. Rev. No. 2)
5.2.3* At the intersection of gas pipelines with underground communication collectors and channels for various purposes, heating mains of channelless laying, as well as at places where gas pipelines pass through the walls of gas wells, it is recommended to lay the gas pipeline in a case. When crossing with heating networks, it is recommended to provide for the laying of gas pipelines in cases that are resistant to temperature effects of the medium transported through pipelines of heating networks, and in accordance with SP 124.13330.
The ends of the case are recommended to be led out at a distance of at least 2 m on both sides from the outer walls of the structures and communications being crossed, when crossing the walls of gas wells - at a distance of at least 2 cm. It is recommended to seal the ends of the case with waterproofing material.
At one end of the case at the top of the slope (except for the intersection of the walls of the wells), and at zero slopes at any end of the case, it is recommended to provide a control tube that goes under the protective device.
In the annular space of the case and the gas pipeline, it is allowed to lay an operational cable (communications, telemechanics and electrochemical protection) with a voltage of up to 60 V, intended for servicing gas distribution networks.
(Changed edition. Rev. No. 2)
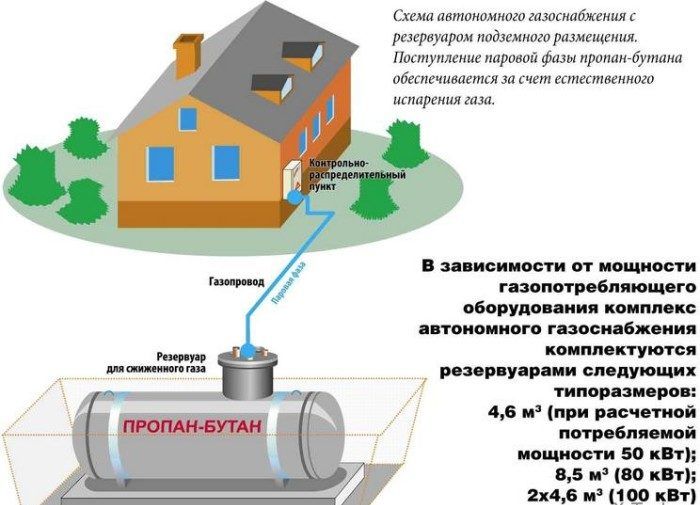
5.2.4* When using polyethylene pipes and fittings for the construction of gas pipelines, the following safety factors should be applied.
When laying polyethylene gas pipelines with a pressure of up to 0.3 MPa inclusive in the territories of cities and rural settlements, pipes and fittings with a safety factor of at least 2.7 must be used.
When laying polyethylene gas pipelines with a pressure of more than 0.3 to 0.6 MPa inclusive in the territories of cities and rural settlements, pipes and fittings made of polyethylene PE 100 with a safety factor of at least 3.2 should be used. On the territory of rural settlements, when using gas pipelines made of polyethylene PE 80, the safety factor should be taken at least 3.2 or from polyethylene PE 100 with a safety factor of at least 2.6 with a laying depth of at least 0.9 m to the top of the pipe.
For inter-settlement gas pipelines with a gas pressure of more than 0.3 to 0.6 MPa, pipes made of PE 80 with SDR no more than SDR 11 or made of PE 100 with SDR no more than SDR 13.6 should be used.
It is not allowed to lay gas pipelines from polyethylene pipes for transporting gases containing aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, as well as LPG gas pipelines, with the exception of the low-pressure vapor phase, and at a temperature of the gas pipeline wall under operating conditions below minus 20 ° C.
When laying gas pipelines with a pressure of more than 0.6 to 1.2 MPa, inclusive, for inter-settlement gas pipelines and in the industrial zone of settlements, as well as in their unbuilt part, if this does not contradict the layouts of capital construction objects provided for by the general plan of the settlement, pipes should be used PE 100 with a safety factor of at least 2.0.
The depth of laying gas pipelines must be at least 1.0 m.
(Changed edition. Rev. No. 2)
Gas pipeline installation
Gas pipeline installation
Gas pipeline installation
The installation of a gas pipeline is a very responsible process and access to it is carried out only by specially trained installers.
Inside the premises, gas pipelines are laid from steel pipes: seamless, longitudinally welded, spiral-seam, water and gas pipes, etc., the welds of which are equal in strength to the base metal of the pipe. Pipes are connected, as a rule, by welding. Threaded and flanged connections are provided only at the installation sites of shut-off valves, gas appliances, instrumentation, etc. Detachable connections of gas pipelines should be available for inspection and repair. Apply connecting parts and details of gas pipelines made of ductile iron or of calm steel (cast, forged, stamped, bent or welded).
In the manufacture of bent branches or bent sections of gas pipelines from water and gas pipes during the installation of a gas pipeline, the bending radius should be taken at least 2.5 DR - for pipes with a diameter of up to 40 mm inclusive and 3.5 DR - for pipes with a diameter of 40-50 mm inclusive. Pipes with a diameter of more than 50 mm are not used for these purposes.
To seal threaded joints, a linen strand coated with red lead or white lead, fluoroplastic material (FUM) in the form of a tape and a cord, as well as other seals that ensure the tightness of the joints, are used. Gaskets for flange connections are made of paronite. To connect gas pipes for welding, the type and brand of electrodes, welding wire and fluxes are selected depending on the grade of steel being welded. For manual arc welding of steel pipes and products, thickly coated electrodes E42, E46, E50A, E42A and E46A are used. For automatic and semi-automatic submerged arc welding, welding wire of the brand Sv-08-A is used, for pipes made of low-carbon steels and brand Sv-08-GA - for pipes made of low-alloy steels. When welding pipes in an environment of gaseous carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide), a welding wire of the Sv-08G2S brand is used, in gas welding - a welding wire of the Sv-08A and Sv-08GA brands.
On gas pipelines, valves, taps, valves designed for the gaseous medium are installed. Butterfly valves and gate valves must have 90° rotation stops, and gate valves with a non-rising stem must have opening degree indicators. Cranes with dat up to 80 mm must have a risk indicating the direction of gas passage in the plug. Valve seals are stuffed with asbestos cord impregnated with graphite mixed with mineral oil.
When installing internal gas pipelines, the pipes are connected by welding. Threaded and flanged connections are used in places where shut-off devices, compensators, pressure regulators, instrumentation and other fittings are installed, as well as in places where gas appliances and burners are connected to a gas pipeline. At the points of connection with fittings or fittings, gas pipelines should not have distortions.
Welded and threaded connections of gas pipelines and fittings are not allowed to be embedded in walls or ceilings. Sections of gas pipelines laid in cases should not have butt joints. They must be painted during installation. The distance from the weld to the case (when the gas pipeline passes through the wall or foundation) is assumed to be at least 100 mm.
You've viewed: Gas pipeline installation
Norms for the installation of a gas pipeline
The gas pipeline is one of the most important parts of the house. Thanks to him, heating appears in the room, with the help of gas appliances you can cook food and heat water for hot water supply. But if used incorrectly, gas can become a serious problem leading to tragedy. To avoid this, the standards used in the installation of the gas pipeline were invented. They ensure the safety and correct operation of the devices.
Fundamental rules:
- It is not allowed to cross the gas pipeline and window openings, doors and ventilation.
- The distance from the pipe to the electrical panel must be at least half a meter.
- There must be at least 25 cm between the gas system and electrical communications.
- The gas pipeline should be at a height of 220 mm from the floor, in rooms with a sloping ceiling this distance is 200 mm.
- A flexible hose with a diameter of 10 mm can be connected to the gas equipment.
- Water heaters cannot be installed in the bathroom.
- High humidity creates back draft, due to which the room is filled with carbon monoxide and can cause poisoning.
- The distance between the plate and the pipe must be maintained, it must exceed 80 cm.
- After metering devices, a pipe slope of 3% should begin.
- The metering device should be located at a height of 1600 mm from the floor.
- The meter should be located at a distance of 80 cm from the heating equipment or stove.
- To install the gas pipeline in the wall, it is necessary to make a hole in the wall separate from the ventilation.
- It is necessary to provide access to communications. You can put them in a box, but it must be equipped with a lid for access.
Types, designs and installation of gas pipeline supports
In industry, there are dozens of varieties of support structures designed for aboveground high and medium pressure gas networks. With low-pressure pipelines supplying blue fuel to private homes, the situation is much simpler. It does not use complex sliding supports and powerful flyovers. They are placed on pipelines of large diameter and length.
In private housing construction, rigid supports are used. They fix the pipe in the design position, preventing it from deviating from the horizontal and vertical. The rigid support structure consists of two elements:
- racks (pipe or profile);
- fastening platforms.
Steel pipes are most often used as racks. Its diameter is chosen depending on the size of the cross section of the gas pipeline. In practice, a simple rule is used: the diameter of the rack must be equal to the diameter of the gas pipeline, but not less than 57 mm.
It must be remembered that no matter how powerful the pipe you take as a stand, it will not hold the line without reliable grounding. Therefore, before starting the installation, concreting of the supporting structures is performed. To do this, holes are dug or drilled in the ground.The depth of embedding the posts in concrete depends on their height and the diameter of the gas pipe. It is determined by calculation and indicated in the documentation. Most often, the drawings of the standard series 5.905-18.05 are taken as a basis, which indicate the nodes and options for fixing aboveground gas pipelines.
In dense dry soil with a small content of large stones, concreting can be dispensed with. In this case, the pipes are simply driven into the ground to a predetermined depth or screw piles are placed. Having set the support posts in level, support platforms are welded to them.
Fixed supports are used to fix the pipe to the platform. The most widespread are two types of such structures:
- Fixing the support with a round clamp made of a metal rod;
- flat steel clamp.
Installation of pipes is carried out, leaving a gap of at least 1.5 mm between the clamp and the support platform. To protect against corrosion, an aluminum sheet gasket is placed between the pipe and the support.
What should be the distance between the supports
The answer to this question is given by the regulations. The distance between the support posts is chosen based on the diameter of the pipe used to lay the line. For low-pressure gas pipelines laid to private houses, the maximum allowable distances between supports should be as follows:
- gas pipe with a diameter of 25 mm - 2.5 m;
- 32mm - 3.2m;
- 40mm - 3.9m;
- 57mm - 4.9m;
- 76mm - 6.4m;
- 89mm - 6.9m;
- 108mm - 8.3m;
- 133mm - 9.6m;
- 159mm - 10.4m.
In addition to the diameter of the line, the location of the supports is chosen, taking into account the distance to the welding joints. According to the requirements of the OST 108 standard, for pipes with a diameter of up to 50 mm, the distance from the support to the nearest welding joint should not exceed 5 cm. For larger diameter pipelines, this value is taken to be no more than 20 cm.
The distance from the support to the point of installation on the pipe of a fitting or control valve is not clearly standardized. The standard contains only one requirement, which states that this distance should be as small as possible.
To eliminate the stresses caused by the thermal expansion of the metal of the gas main, lens and bellows compensators are used. The owner of a private house may not worry about installing them. These devices are necessary when the length of the pipe is hundreds of meters.
Requirements for the material of supports and the place of their installation
Since pipe support blocks can be purchased ready-made, there is no need to detail the strength characteristics of the metal from which they are made. Manufacturers use for them especially strong steel grades that are resistant to corrosion and deformation loads.
To eliminate bending stresses, these parts must be installed exactly in the middle of the support platform.
The main components of the gas pipeline
Blue fuel is supplied through gas pipelines through special distribution stations, where automatic regulator valves must reduce pressure and ensure its stable required level.
Gas pipeline networks consist of:
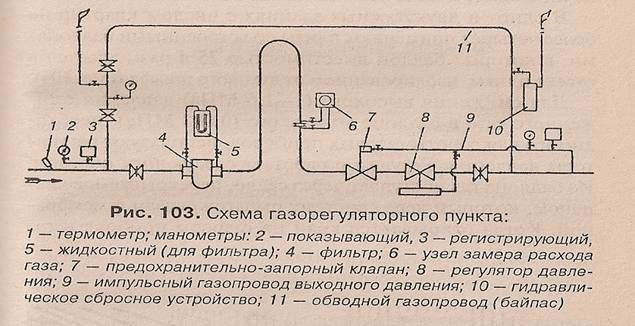
- internal highway;
- external highway of settlements;
- automated control systems;
- means of electrochemical protection;
- regulatory items.
There may be several options for installing a gas pipeline. The choice of installation method depends on many parameters and the specific case. Climatic conditions, site development and other parameters are taken into account.