Installing a thermostat
Another reason for the frequent switching on and off of a gas heating boiler is that the operation of the equipment is regulated only by the temperature of the coolant. The water heated up to the desired temperature, the device turned off, the water cooled, the boiler turned on. But the coolant cools down much faster than the air in the room. Such management is not rational, as this increases fuel costs, it can be hot in the rooms, which, of course, will affect the comfort of residents.
The best way out of this situation is to install a room thermostat. The device is designed for automatic control of a gas boiler. The functioning of the heating unit becomes more efficient, it is possible to save on fuel. The system will only start when the room temperature drops, which can remain at a level due to sunlight entering the room or crowds in the room.
The range of thermostats allows you to choose a model in accordance with your wishes and financial capabilities. The cheapest are mechanical products. They do not require special treatment, they are durable and reliable. Much more difficult with modern programmers. These are devices that can be programmed, set certain options for them, set different temperatures depending on your needs.
For the efficient and economical functioning of the heating system, care must be taken to properly perform installation work. You will not need to worry about how often the heating boiler should turn on if its operation is controlled by a thermostat. This will not only save on fuel, but also extend the life of the heating equipment.
Ways to reduce heat loss
But it is important to remember that the temperature in the room is affected not only by the temperature of the coolant, outdoor air and wind strength. The degree of insulation of the facade, doors and windows in the house should also be taken into account.
To reduce the heat loss of housing, you need to worry about its maximum thermal insulation. Insulated walls, sealed doors, metal-plastic windows will help reduce heat leakage. It will also reduce heating costs.
The efficiency of the heating system depends on many factors. These include the rated power, the degree of heat transfer of radiators and the temperature regime of operation.
For the latter indicator, it is important to choose the right degree of heating of the coolant. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the optimal temperature in the heating system for water, radiators and the boiler.
Removal of air from the heating system of a solid fuel boiler.
Air in the heating system can cause a number of problems: poor circulation of the coolant or its absence, noise during pump operation, corrosion of radiators or elements of the heating system. To avoid this, it is necessary to bleed air from the system. There are two ways for this - the first one manually - we think over the installation of cranes at the highest point of the system and on the lifting sections and periodically pass these cranes, releasing air. The second way is to install an automatic air release valve. The principle of its operation is simple - when there is no air in the system, the valve is filled with water and the float is located at the top of the valve, and, through a hinged lever, seals the air outlet valve.
When air enters the valve chamber, the water level in the valve drops, the float moves down and through the articulated arm opens the air outlet on the outlet valve.As air escapes from the chamber, the water level rises and the valve returns to its upper position.
We have already described the device of the boiler safety group above when we talked about protection against high coolant pressure. Ideally, if you have installed a safety group, it has an automatic air release valve. Just make sure that the safety group is installed at the top of your heating system. If not, we recommend installing a separate automatic air release valve and permanently solve the problem of finding air pockets in your heating system.
 Solid fuel boiler piping - Automatic air release valve
Solid fuel boiler piping - Automatic air release valve
Optimal values in an individual heating system
Autonomous heating helps to avoid many problems that arise with a centralized network, and the optimal temperature of the coolant can be adjusted according to the season. In the case of individual heating, the concept of norms includes the heat transfer of a heating device per unit area of the room where this device is located. The thermal regime in this situation is provided by the design features of the heating devices.
It is important to ensure that the heat carrier in the network does not cool below 70 ° C. 80 °C is considered optimal
It is easier to control heating with a gas boiler, because manufacturers limit the possibility of heating the coolant to 90 ° C. Using sensors to adjust the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be controlled.
A little more difficult with solid fuel devices, they do not regulate the heating of the liquid, and can easily turn it into steam. And it is impossible to reduce the heat from coal or wood by turning the knob in such a situation. At the same time, the control of heating of the coolant is rather conditional with high errors and is performed by rotary thermostats and mechanical dampers.
Electric boilers allow you to smoothly adjust the heating of the coolant from 30 to 90 ° C. They are equipped with an excellent overheating protection system.
What temperature to set in the heating boiler low and high values
Let's share our experience regarding different temperature regimes.
- 40 degrees. Such a regime is often uneconomical. At this temperature, the gas boiler may well be underheated to half a degree. Because of this, the circulation pump and heating are not switched off. Accordingly, the gas consumption only increases. In some boiler models, the flow rate may even be higher than at the set temperature of 70°C. In addition, it is better to refuse such a temperature regime even in cases of unstable operation of the power grid. The coolant will cool down in a short time, the room will become cold after a few hours.
- 50 degrees. Most tests show that at this temperature setting, gas flow is the lowest. However, the circulation pump runs for a long time, which increases the cost of electricity. Plus, in the event of a power outage, the batteries retain heat a little longer. In general calculations, this mode of operation of the system is less economical than the following.
- 60 degrees. This is by far the most economical mode. More gas is required than with a 50-degree mode, but electricity costs are noticeably reduced. The total costs are lower. Yes, and the room heats up better.
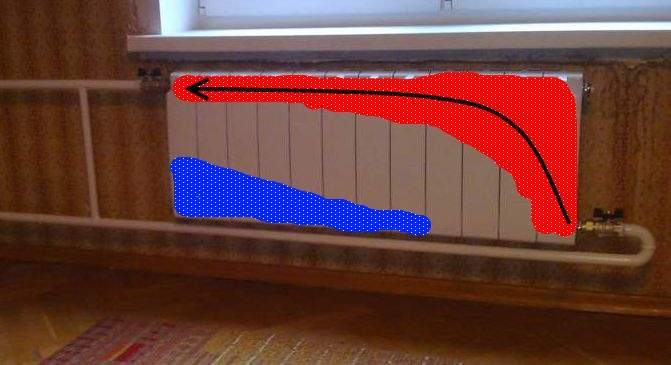
- 70 degrees. In this mode, electricity is spent less, but gas consumption increases. But a more important problem is that with some models of boilers in this mode of operation, jumps in air temperature in the room are possible. They can be both almost imperceptible and quite tangible. The fact is that the radiators continue to heat the premises strongly even after turning off the heating in the boiler, then they cool down, then they heat up again.
Setting an even higher temperature is not worth it, unless you live in cold northern regions. And there are several reasons for this.The main thing is that such high temperatures are simply not needed in the house. And even if you need to heat the rooms as much as possible, it is better to set the temperature lower. If the values are too high, an unpleasant smell of burning dust from the batteries appears, polypropylene pipes wear out faster.
So what temperature should be on the heating boiler? We recommend about 60-65 degrees if the outside temperature is not lower than -10°C. If lower, you can increase the power. If the street is near zero, more than 50-55 degrees will not be needed.

What temperature on the boiler is optimal for heating without a temperature difference in the rooms?
Often, the homeowner is more important than saving, but uniform heating of all rooms in the house. The boiler works constantly, preventing the temperature from dropping below the selected value. Of course, more electricity is needed for this mode, but you can save on gas.
40 degrees for comfortable and uniform heating is not always enough. In this mode, the house will warm up by an average of 20-20.5 degrees at an outdoor temperature of at least -9 ° C. If twenty degrees in the room is not enough for you, you can set 45-50 degrees on the boiler.

Temperature norms
 The requirements for the temperature of the coolant are set out in the regulatory documents that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems of residential and public buildings. They are described in the State building codes and regulations:
The requirements for the temperature of the coolant are set out in the regulatory documents that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems of residential and public buildings. They are described in the State building codes and regulations:
- DBN (B. 2.5-39 Heat networks);
- SNiP 2.04.05 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning".
For the calculated temperature of the water in the supply, the figure is taken that is equal to the temperature of the water at the outlet of the boiler, according to its passport data.
For individual heating, it is necessary to decide what the temperature of the coolant should be, taking into account such factors:
- The beginning and end of the heating season according to the average daily temperature outside +8 ° C for 3 days;
- The average temperature inside heated premises of housing and communal and public importance should be 20 ° C, and for industrial buildings 16 ° C;
- The average design temperature must comply with the requirements of DBN V.2.2-10, DBN V.2.2.-4, DSanPiN 5.5.2.008, SP No. 3231-85.
According to SNiP 2.04.05 "Heating, ventilation and air conditioning" (clause 3.20), the limiting indicators of the coolant are as follows:
- For a hospital - 85 ° C (excluding psychiatric and drug departments, as well as administrative or domestic premises);
- For residential, public, as well as domestic buildings (not counting the halls for sports, trade, spectators and passengers) - 90 ° C;
- For auditoriums, restaurants and premises for production of category A and B - 105 ° C;
- For catering establishments (excluding restaurants) it is 115 °С;
- For production premises (categories C, D and D), where combustible dust and aerosols are released - 130 ° C;
- For stairwells, lobbies, pedestrian crossings, technical rooms, residential buildings, industrial premises without the presence of flammable dust and aerosols - 150 ° C.
Depending on external factors, the water temperature in the heating system can be from 30 to 90 °C. When heated above 90 ° C, dust and paintwork begin to decompose. For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit more heating.
To calculate the optimal indicators, special graphs and tables can be used, in which the norms are determined depending on the season:
- With an average value outside the window of 0 °С, the supply for radiators with different wiring is set at a level of 40 to 45 °С, and the return temperature is from 35 to 38 °С;
- At -20 °С, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °С, while the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °С;
- At -40 ° C outside the window for all heating devices set the maximum allowable values. At the supply it is from 95 to 105 ° C, and at the return - 70 ° C.
Model examples
- Baksi.
The optimal mode of operation of this wall-mounted gas boiler is achieved as follows: in small apartments, the indicators are set to F08 and F10. The modulation spectrum starts at 40% of the highest power. And the minimum possible operating mode is 9 kW.
Many models of this company are very economical and can work at low gas pressure. Pressure limits: 9 - 17 mbar. Suitable voltage range: 165 - 240 V.
- Vaillant.
Many devices of this brand work optimally under such conditions: power - 15 kW. Submission is placed at 50-60. The device works for 35 minutes, rests for 20 minutes.
- Ferroli.
Best conditions: 13 kW for heating, 24 kW for water heating.
- Mercury.
The water pressure in the network is a maximum of 0.1 MPa. The highest temperature indicator at the outlet section is 90 C, the nominal value of flue gases is at least 110 C. The vacuum downstream of the apparatus is a maximum of 40 Pa.
- Navien.
Basically, these are two-circuit units. Automation works here. The mode is self-configuring. Sets the room heating setting. There is a pump that can reduce the parameters by 4-5 degrees.
- Ariston.
The automatic mode setting also works. Often people choose models with the "Comfort-Plus" mode.
- Buderus.
Values are usually set on the feed: 40 - 82 C. The current parameter is usually reflected on the monitor. The most convenient summer mode is at 75 C.
Protection against low temperature of the coolant in the return of a solid fuel boiler.
What will happen to a solid fuel boiler if its “return” temperature is below 50 °C? The answer is simple - a resinous coating will appear on the entire surface of the heat exchanger. This phenomenon will reduce the performance of your boiler, make it much more difficult to clean and, most importantly, can lead to chemical damage to the walls of the boiler heat exchanger. To prevent such a problem, it is necessary to provide appropriate equipment when installing a heating system with a solid fuel boiler.
The task is to ensure the temperature of the coolant that returns to the boiler from the heating system at a level not lower than 50 °C. It is at this temperature that the water vapor contained in the flue gases of a solid fuel boiler begins to condense on the walls of the heat exchanger (transition from a gaseous state to a liquid one). The transition temperature is called the "dew point". The condensation temperature directly depends on the moisture content of the fuel and the amount of hydrogen and sulfur formations in the combustion products. As a result of a chemical reaction, ferrous sulfate is obtained - a substance useful in many industries, but not in a solid fuel boiler. Therefore, it is quite natural that manufacturers of many solid fuel boilers remove the boiler from the guarantee in the absence of a return water heating system. After all, here we are not dealing with the burning of metal at high temperatures, but with chemical reactions that no boiler steel can withstand.
The simplest solution to the low return temperature problem is to use a thermal three-way valve (anti-condensation thermostatic mixing valve) . The thermal anti-condensation valve is a thermomechanical three-way valve that ensures the admixture of the coolant between the primary (boiler) circuit and the coolant from the heating system in order to achieve a fixed temperature of the boiler water. In fact, the valve lets the unheated coolant through a small circle and the boiler heats itself. After reaching the set temperature, the valve automatically opens the access of the coolant to the heating system and works until the return temperature drops below the set values again.
 Piping of a solid fuel boiler - Anti-condensation valve
Piping of a solid fuel boiler - Anti-condensation valve
Ways to reduce heat loss

But it is important to remember that the temperature in the room is affected not only by the temperature of the coolant, outdoor air and wind strength. The degree of insulation of the facade, doors and windows in the house should also be taken into account.
To reduce the heat loss of housing, you need to worry about its maximum thermal insulation. Insulated walls, sealed doors, metal-plastic windows will help reduce heat leakage. It will also reduce heating costs.
Maintenance of a gas boiler with low productivity is expensive. Therefore, anyone who uses such a device wants to find optimal operation of the gas boiler
, at which it will have the highest possible efficiency (coefficient of performance) with minimal fuel consumption. This problem becomes especially urgent on the eve of the next heating season.
The performance of a gas boiler is influenced by various factors. If you have not yet bought this device, but only plan to purchase it, please note that the main condition for its installation is the presence of a centralized gas supply. Some believe that they can get by with bottled gas, but this will significantly increase costs. In this case, it is better to install electric heating.
Optimum performance
depends on the following criteria:
- Boiler designs - they can be single-circuit, double-circuit, mounted, floor, etc.
- Efficiency - nominal and real.
- Proper organization of heating in the house: the power of the boiler must correspond to the area of \u200b\u200bthe heated premises.
- The technical condition of the equipment.
- Gas quality.
Now let's take a closer look at how each of the criteria can be optimized to maximize device performance.
Boiler design
Boilers are single-circuit and double-circuit. The first one will have to buy an indirect heating boiler so that it can heat water. The double-circuit option is preferable, as it is equipped with everything necessary for the production of hot water and home heating. For ease of use, the priority mode in such a boiler is the supply of hot water. This means that when the water supply is turned on, the heating stops.
There are wall and floor gas boilers. The former have less power and can only heat a room up to 300 m². If your house is larger, you will need to purchase another wall-hung or floor-standing boiler.
Nominal and real efficiency
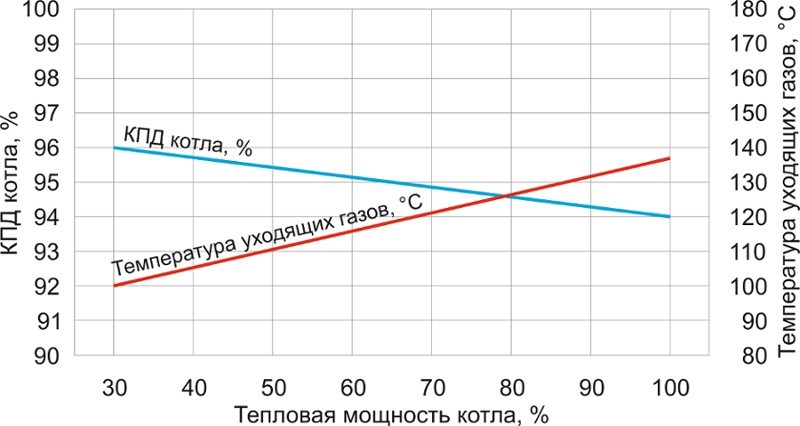
The instructions for any gas boiler indicate the nominal efficiency, usually it is 92-95%, for condensing models - about 108%. However, the real figure is usually 9-10% lower. It is further reduced by the presence of various types of heat loss:
- Physical underburning - this indicator depends on the amount of excess air in the unit during the combustion process. It is also affected by the temperature of the flue gases: the higher it is, the lower the efficiency of the boiler.
- Chemical underburning - this indicator fluctuates depending on the amount of carbon monoxide that appears from the combustion of carbon.
- Heat loss that escapes through the walls of the boiler.
You can increase the actual efficiency of the device in the following ways:
- Reducing the physical underburning rate by regularly cleaning soot on the pipeline and removing scale from the water circuit.
- Reducing the amount of excess air by installing a draft limiter on the chimney.
- By adjusting the position of the blower damper in such a way that the maximum temperature of the coolant is reached.
- Regular cleaning of soot on the combustion chamber, which increases gas consumption.
To increase the efficiency of a gas boiler will allow replacing the chimney with a more innovative one. Most of the traditional branch pipes are too dependent on weather conditions. They were replaced by a coaxial chimney, which is resistant to temperature changes and is able to increase efficiency, as well as save fuel.
Matching the temperature of the heat carrier and the boiler
 Regulators help to coordinate the temperature of the coolant and the boiler. These are devices that create automatic control and correction of the return and supply temperatures.
Regulators help to coordinate the temperature of the coolant and the boiler. These are devices that create automatic control and correction of the return and supply temperatures.
The return temperature depends on the amount of liquid passing through it.The regulators cover the liquid supply and increase the difference between the return and supply to the level that is needed, and the necessary pointers are installed on the sensor.
If you need to increase the flow, then a boost pump can be added to the network, which is controlled by a regulator. To reduce the heating of the supply, a “cold start” is used: that part of the liquid that has passed through the network is again transferred from the return to the inlet.
The regulator redistributes the supply and return flows according to the data taken by the sensor, and ensures strict temperature standards for the heating network.
Conclusion
Thanks to the gas boiler, you can conveniently adjust the climate in the house. Especially if you use innovative technology with automatic modes and many useful options.
A heating boiler is a device that, by means of the combustion of fuel (or electricity), heats the coolant.
The device (design) of the heating boiler
: heat exchanger, thermally insulated housing, hydraulic unit, as well as safety elements and automation for control and monitoring. For gas and diesel boilers, a burner is provided in the design, for solid fuel boilers - a firebox for firewood or coal. Such boilers require a chimney connection to remove combustion products. Electric boilers are equipped with heating elements, do not have burners and a chimney. Many modern boilers are equipped with built-in pumps for forced circulation of water.
The principle of operation of the heating boiler
- the coolant, passing through the heat exchanger, heats up and then circulates through the heating system, giving off the received thermal energy through radiators, underfloor heating, heated towel rails, and also providing water heating in the indirect heating boiler (if it is connected to the boiler).
Heat exchanger - a metal container in which the coolant (water or antifreeze) is heated - can be made of steel, cast iron, copper, etc. Cast iron heat exchangers are resistant to corrosion and quite durable, but are sensitive to sudden temperature changes and are heavy. Steel can suffer from rust, so their internal surfaces are protected by various anti-corrosion coatings to increase their service life. Such heat exchangers are the most common in the production of boilers.
Corrosion is not terrible for copper heat exchangers, and due to the high heat transfer coefficient, low weight and dimensions, such heat exchangers are popular, often used in wall-mounted boilers, but usually more expensive than steel ones.
In addition to the heat exchanger, an important part of gas or liquid fuel boilers is a burner, which can be of various types: atmospheric or fan, single-stage or two-stage, with smooth modulation, double. (A detailed description of the burners is presented in the articles about gas and liquid fuel boilers)
To control the boiler, automation is used with various settings and functions (for example, a weather-dependent control system), as well as devices for remote control of the boiler - a GSM module (controlling the operation of the device via SMS messages).
The main technical characteristics of heating boilers are: boiler power, type of energy carrier, number of heating circuits, type of combustion chamber, type of burner, type of installation, presence of a pump, expansion tank, boiler automation, etc.
To determine required power
heating boiler for a house or apartment, a simple formula is used - 1 kW of boiler power for heating 10 m 2 of a well-insulated room with a ceiling height of up to 3 m. Accordingly, if heating of a basement, glazed winter garden, rooms with non-standard ceilings, etc. is required. boiler power must be increased. It is also necessary to increase the power (about 20-50%) when providing a boiler and hot water supply (especially if heating of water in the pool is necessary).
We note the feature of calculating the power of gas boilers: the nominal gas pressure at which the boiler operates at 100% of the power declared by the manufacturer for most boilers is from 13 to 20 mbar, and the actual pressure in gas networks in Russia can be 10 mbar, and sometimes below. Accordingly, a gas boiler often only works at 2/3 of its capacity, and this must be taken into account when calculating. When choosing the power of the boiler, be sure to note all the features of the thermal insulation of the house and premises. In more detail with a table for calculating the power of a heating boiler, you can
So which boiler is better to choose
? Consider the types of boilers:
"Middle class"
- average price, not so prestigious, but quite reliable, standard standard solutions are presented. These are Italian boilers Ariston, Hermann and Baxi, Swedish Electrolux, German Unitherm and boilers from Slovakia Protherm.
"Economy class"
- budget options, simple models, the service life is less than that of boilers of a higher category. Some manufacturers have budget models of boilers, for example,